淺談React+Storeon進行狀態管理的方法
本篇文章為大家介紹React中使用事件驅動程式進行狀態管理的方法。有一定的參考價值,有需要的朋友可以參考一下,希望對大家有幫助。

自 Hook 被引入 React 以來,Context API 與 Hook 函式庫在應用程式狀態管理中被一起使用。但把 Context API 和 Hooks(許多基於 Hooks 的狀態管理函式庫建立在其基礎上)組合的用法對於大規模應用來說可能效率不高。
由於必須建立一個自訂的 Hook 才能啟用對狀態及其方法的訪問,然後才能在元件中使用它,所以在實際開發中很繁瑣。這違反了 Hook 的真正目的:簡單。但對於較小的應用,Redux 可能會顯得太重了。
今天我們將討論 Context API 的替代方法:Storeon。 Storeon 是一個微型的、事件驅動的 React 狀態管理函式庫,其原理類似於 Redux。用 Redux DevTools 可以查看並視覺化狀態操作。 Storeon 內部使用 Context API 來管理狀態,並採用事件驅動的方法進行狀態操作。
【相關教學推薦:React影片教學】
#Store
store 是在應用程式狀態下儲存的數據的集合。它是透過從 Storeon 庫導入的 createStoreon() 函數建立的。
createStoreon() 函數接受模組列表,其中每個模組都是接受 store 參數並綁定其事件監聽器的函數。這是一個store 的例子:
import { createStoreon } from 'storeon/react'
// todos module
const todos = store => {
store.on(event, callback)
}
export default const store = createStoreon([todos])模組化
Storeon 中的store 是模組化的,也就是說,它們是獨立定義的,並且沒有被綁定到Hook 或元件。每個狀態及其操作方法均在稱為模組的函數中定義。這些模組會傳遞到 createStoreon() 函數中,然後將其註冊為全域 store。
store 有三種方法:
store.get()– 用於擷取狀態中的目前資料。store.on(event, callback)– 用來把事件偵聽器註冊到指定的事件名稱。store.dispatch(event, data)– 用於發出事件,並根據定義的事件要求將可選資料傳遞進來。
Events
Storeon 是基於事件的狀態管理庫,狀態變更由狀態模組中定義的事件發出。 Storeon 中有三個內建事件,它們以 @ 開頭。其他事件不帶 @ 前綴定義。三個內建事件是:
@init– 在套用載入時觸發此事件。它用於設定應用程式的初始狀態,並執行傳遞給它的回呼中的所有內容。@dispatch– 此事件在每個新動作上觸發。這對於調試很有用。@changed– 當應用程式狀態發生變更時,將觸發此事件。
注意:store.on(event,callback) 用於在我們的模組中新增事件監聽器。 示範程式
為了示範在 Storeon 中如何執行應用程式狀態操作,我們將建立一個簡單的 notes 程式。也會用 Storeon 的另一個軟體套件把狀態資料保存在 localStorage 中。
假設你有 JavaScript 和 React 的基本知識。你可以在 https://github.com/Youngestde... 上找到本文中使用的程式碼。
設定
在深入探討之前,讓我們先勾勒出 Notes 程式所需的專案結構和相依性的安裝。從建立專案資料夾開始。
mkdir storeon-app && cd storeon-app
mkdir {src,public,src/Components}
touch public/{index.html, style.css} && touch src/{index,store,Components/Notes}.js接下來,初始化目錄並安裝所需的依賴項。
npm init -y npm i react react-dom react-scripts storeon @storeon/localstorage uuidv4
接下來就是在 index.js檔案中寫父元件了。
index.js
這個檔案負責渲染我們的筆記元件。首先導入所需的包。
import React from 'react'
import { render } from 'react-dom';
function App() {
return (
<>
Hello!
</>
);
}
const root = document.getElementById('root');
render(<App />, root);接下來透過在 store.js 中編寫用於狀態的初始化和操作的程式碼來建立 store。
store.js
此檔案負責處理應用程式中的狀態和後續狀態管理作業。我們必須建立一個模組來儲存狀態以及支援事件,以處理操作變更。
首先,從 Storeon 匯入 createStoreon 方法和唯一隨機ID產生器 UUID。
createStoreon 方法負責將我們的 狀態 註冊到全域 store 。
import { createStoreon } from 'storeon';
import { v4 as uuidv4 } from 'uuid'
import { persistState } from '@storeon/localstorage';
let note = store => {}我們將狀態儲存在陣列變數 notes 中,該變數包含以下格式的註解:
{
id: 'note id',
item: 'note item'
},接下来,我们将用两个注释(在首次启动程序时会显示)来初始化状态,从而首先填充注释模块。然后,定义状态事件。
let note = store => {
store.on('@init', () => ({
notes: [
{ id: uuidv4(), item: 'Storeon is a React state management library and unlike other state management libraries that use Context, it utilizes an event-driven approach like Redux.' },
{ id: uuidv4(), item: 'This is a really short note. I have begun to study the basic concepts of technical writing and I'\'m optimistic about becoming one of the best technical writers.' },
]
});
store.on('addNote', ({ notes }, note) => {
return {
notes: [...notes, { id: uuidv4(), item: note }],
}
});
store.on('deleteNote', ({ notes }, id) => ({
notes: notes.filter(note => note.id !== id),
});
}在上面的代码中,我们定义了状态,并用两个简短的注释填充了状态,并定义了两个事件和一个从 dispatch(event, data) 函数发出事件后将会执行的回调函数。
在 addNote 事件中,我们返回添加了新 note 的更新后的状态对象,在 deleteNote 事件中把 ID 传递给调度方法的 note 过滤掉。
最后,把模块分配给可导出变量 store ,将其注册为全局 store,以便稍后将其导入到上下文 provider 中,并将状态存储在 localStorage 中。
const store = createStoreon([ notes, // Store state in localStorage persistState(['notes']), ]); export default store;
接下来,在 Notes.js 中编写 Notes 应用组件。
Notes.js
此文件包含 Notes 程序的组件。我们将从导入依赖项开始。
import React from 'react';
import { useStoreon } from 'storeon/react';接下来,编写组件。
const Notes = () => {
const { dispatch, notes } = useStoreon('notes');
const [ value, setValue ] = React.useState('');
}在上面的代码的第二行中,useStoreon() hook 的返回值设置为可破坏的对象。 useStoreon() hook 使用模块名称作为其参数,并返回状态和调度方法以发出事件。
接下来定义在组件中发出状态定义事件的方法 。
const Notes = () => {
...
const deleteNote = id => {
dispatch('deleteNote', id)
};
const submit = () => {
dispatch('addNote', value);
setValue('');
};
const handleInput = e => {
setValue(e.target.value);
};
}Let’s review the three methods we defined the above:
让我们回顾一下上面定义的三种方法:
deleteNote(id)– 此方法在触发时调度deleteNote事件。submit()– 该方法通过传递输入状态的值来调度addNote事件,该状态在Notes组件中本地定义。handleInput()– 此方法将本地状态的值设置为用户输入。
Next, we’ll build the main interface of our app and export it.
接下来,我们将构建应用程序的主界面并将其导出。
const Notes = () => {
...
return (
<section>
<header>Quick Notes</header>
<div className='addNote'>
<textarea onChange={handleInput} value={value} />
<button onClick={() => submit()}> Add A Note </button>
</div>
<ul>
{notes.map(note => (
<li key={note.id}>
<div className='todo'>
<p>{note.item}</p>
<button onClick={() => deleteNote(note.id)}>Delete note</button>
</div>
</li>
))}
</ul>
</section>
);
}这样就构成了我们的 Notes 组件。接下来为我们的应用和 index.html 文件编写样式表。
index.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge">
<link rel="stylesheet" href="style.css">
<title>Storeon Todo App</title>
</head>
<body>
<div id="root"></div>
</body>
</html>接下来,填充我们的 style.css 文件。
style.css
* {
box-sizing: border-box;
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
}
section {
display: flex;
justify-content: center;
align-items: center;
flex-direction: column;
width: 300px;
margin: auto;
}
header {
text-align: center;
font-size: 24px;
line-height: 40px;
}
ul {
display: block;
}
.todo {
display: block;
margin: 12px 0;
width: 300px;
padding: 16px;
box-shadow: 0 8px 12px 0 rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.3);
transition: 0.2s;
word-break: break-word;
}
li {
list-style-type: none;
display: block;
}
textarea {
border: 1px double;
box-shadow: 1px 1px 1px #999;
height: 100px;
margin: 12px 0;
width: 100%;
padding: 5px 10px;
}
button {
margin: 8px 0;
border-radius: 5px;
padding: 10px 25px;
}
.box:hover {
box-shadow: 0 8px 16px 0 rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.2);
}运行
现在我们已经成功编写了组件和样式表,但是还没有更新 index.js 中的父组件来渲染 Notes 组件。接下来让我们渲染 Notes 组件。
index.js
要访问我们的全局 store,必须导入 store 和 Storeon store 上下文组件。我们还将导入 notes 组件来进行渲染。
用以下代码替换组件的内容:
import React from 'react';
import { render } from 'react-dom';
import { StoreContext } from 'storeon/react';
import Notes from './Components/Notes';
import store from '../src/store';
function App() {
return (
<>
<StoreContext.Provider value={store}>
<Notes />
</StoreContext.Provider>
</>
);
}
const root = document.getElementById('root');
render(<App />, root);在第 8-10 行,调用 store 上下文提供程序组件,并将 notes 组件作为使用者传递。store 上下文提供程序组件将全局 store 作为其上下文值。
接下来把 package.json 文件中的脚本部分编辑为以下内容:
"scripts": {
"start": "react-scripts start",
}然后运行我们的程序:
npm run start
让我们继续添加和删除注释:

Storeon devtools
Storeon 与 Redux 有着相似的属性,可以在 Redux DevTools 中可视化和监视状态的更改。为了可视化 Storeon 程序中的状态,我们将导入 devtools 包,并将其作为参数添加到我们 store.js 文件的 createStoreon() 方法中。
...
import { storeonDevtools } from 'storeon/devtools';
...
const store = createStoreon([
...,
process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production' && storeonDevtools,
]);这是用 Redux DevTools 可视化状态变化的演示:
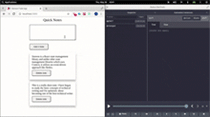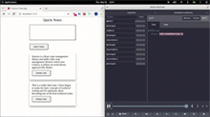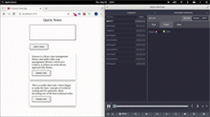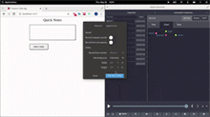
结论
Storeon 是一个非常有用的状态管理库,它用事件驱动和 Redux 改编的模块化样式来管理状态。你可以在https://github.com/Youngestdev/storeon-app上找到本文中的代码。
原文地址:https://blog.logrocket.com/event-driven-state-management-in-react-using-storeon/
作者:Abdulazeez Abdulazeez Adeshina
更多编程相关知识,请访问:编程视频!!
以上是淺談React+Storeon進行狀態管理的方法的詳細內容。更多資訊請關注PHP中文網其他相關文章!

熱AI工具

Undresser.AI Undress
人工智慧驅動的應用程序,用於創建逼真的裸體照片

AI Clothes Remover
用於從照片中去除衣服的線上人工智慧工具。

Undress AI Tool
免費脫衣圖片

Clothoff.io
AI脫衣器

Video Face Swap
使用我們完全免費的人工智慧換臉工具,輕鬆在任何影片中換臉!

熱門文章

熱工具

記事本++7.3.1
好用且免費的程式碼編輯器

SublimeText3漢化版
中文版,非常好用

禪工作室 13.0.1
強大的PHP整合開發環境

Dreamweaver CS6
視覺化網頁開發工具

SublimeText3 Mac版
神級程式碼編輯軟體(SublimeText3)
 C++ 函式在並發程式設計中的事件驅動機制?
Apr 26, 2024 pm 02:15 PM
C++ 函式在並發程式設計中的事件驅動機制?
Apr 26, 2024 pm 02:15 PM
並發程式設計中的事件驅動機制透過在事件發生時執行回呼函數來回應外部事件。在C++中,事件驅動機制可用函數指標實作:函數指標可以註冊回呼函數,在事件發生時執行。 lambda表達式也可以實現事件回調,允許建立匿名函數物件。實戰案例使用函數指標實作GUI按鈕點擊事件,在事件發生時呼叫回呼函數並列印訊息。
 PHP、Vue和React:如何選擇最適合的前端框架?
Mar 15, 2024 pm 05:48 PM
PHP、Vue和React:如何選擇最適合的前端框架?
Mar 15, 2024 pm 05:48 PM
PHP、Vue和React:如何選擇最適合的前端框架?隨著互聯網技術的不斷發展,前端框架在Web開發中起著至關重要的作用。 PHP、Vue和React作為三種代表性的前端框架,每一種都具有其獨特的特徵和優勢。在選擇使用哪種前端框架時,開發人員需要根據專案需求、團隊技能和個人偏好做出明智的決策。本文將透過比較PHP、Vue和React這三種前端框架的特徵和使
 Java框架與前端React框架的整合
Jun 01, 2024 pm 03:16 PM
Java框架與前端React框架的整合
Jun 01, 2024 pm 03:16 PM
Java框架與React框架的整合:步驟:設定後端Java框架。建立專案結構。配置建置工具。建立React應用程式。編寫RESTAPI端點。配置通訊機制。實戰案例(SpringBoot+React):Java程式碼:定義RESTfulAPI控制器。 React程式碼:取得並顯示API回傳的資料。
 vue.js vs.反應:特定於項目的考慮因素
Apr 09, 2025 am 12:01 AM
vue.js vs.反應:特定於項目的考慮因素
Apr 09, 2025 am 12:01 AM
Vue.js適合中小型項目和快速迭代,React適用於大型複雜應用。 1)Vue.js易於上手,適用於團隊經驗不足或項目規模較小的情況。 2)React的生態系統更豐富,適合有高性能需求和復雜功能需求的項目。
 C++ 中的事件驅動程式設計如何最佳化記憶體管理?
Jun 01, 2024 pm 12:57 PM
C++ 中的事件驅動程式設計如何最佳化記憶體管理?
Jun 01, 2024 pm 12:57 PM
在C++事件驅動程式設計中,有效管理記憶體至關重要,涉及以下最佳化技術:使用智慧指標(如std::unique_ptr、std::shared_ptr)自動釋放物件內存,避免記憶體洩漏。建立物件池,預先分配特定類型的物件並重複使用,優化記憶體分配和取消分配開銷。
 React在HTML中的作用:增強用戶體驗
Apr 09, 2025 am 12:11 AM
React在HTML中的作用:增強用戶體驗
Apr 09, 2025 am 12:11 AM
React通過JSX與HTML結合,提升用戶體驗。 1)JSX嵌入HTML,使開發更直觀。 2)虛擬DOM機制優化性能,減少DOM操作。 3)組件化管理UI,提高可維護性。 4)狀態管理和事件處理增強交互性。
 React與Vue:Netflix使用哪個框架?
Apr 14, 2025 am 12:19 AM
React與Vue:Netflix使用哪個框架?
Apr 14, 2025 am 12:19 AM
NetflixusesAcustomFrameworkcalled“ Gibbon” BuiltonReact,notReactorVuedIrectly.1)TeamSperience:selectBasedonFamiliarity.2)ProjectComplexity:vueforsimplerprojects:reactforforforproproject,reactforforforcompleplexones.3)cocatizationneedneeds:reactoffipicatizationneedneedneedneedneedneeds:reactoffersizationneedneedneedneedneeds:reactoffersizatization needefersmoreflexibleise.4)
 React的前端開發:優勢和技術
Apr 17, 2025 am 12:25 AM
React的前端開發:優勢和技術
Apr 17, 2025 am 12:25 AM
React的優勢在於其靈活性和高效性,具體表現在:1)組件化設計提高了代碼重用性;2)虛擬DOM技術優化了性能,特別是在處理大量數據更新時;3)豐富的生態系統提供了大量第三方庫和工具。通過理解React的工作原理和使用示例,可以掌握其核心概念和最佳實踐,從而構建高效、可維護的用戶界面。






