MySQL進階學習:深入了解explain指令
這篇文章是MySQL的進階學習,帶大家深入了解explain各字段的意義,希望對大家有幫助!

explain有何用:為了知道最佳化SQL語句的執行,需要查看SQL語句的特定執行過程,以加快SQL語句的執行效率。
可以使用explain SQL語句來模擬最佳化器執行SQL查詢語句,從而知道mysql是如何處理sql語句的。透過查看執行計劃以了解執行器是否按照我們想要的那樣處理SQL。
explain執行計畫中包含的資訊如下:
測試使用mysql版本5.7, 使用的3個表格結構如下id: 查詢序號
select_type: 查詢類型
# 別名 partitions: 相符的分區 type: 存取類型possible_keys: 可能使用的索引## 實際到
# key_len: 索引長度 ref: 與索引比較的列 rows: 估算的行數# rows: 估計的行數
## rows: 估計的行數##
# Extra: 額外資訊下方說下具體每一列的表示的意義和對應sql。
CREATE TABLE `demo`.`emp` ( `emp_id` bigint(20) NOT NULL, `name` varchar(20) CHARACTER SET utf8mb4 COLLATE utf8mb4_bin NULL DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '姓名', `empno` int(20) NOT NULL COMMENT '工号', `deptno` int(20) NOT NULL COMMENT '部门编号', `sal` int(11) NOT NULL DEFAULT 0 COMMENT '销售量', PRIMARY KEY (`emp_id`) USING BTREE, INDEX `u1`(`deptno`) USING BTREE, UNIQUE INDEX `u2`(`empno`) USING BTREE) ENGINE = InnoDB CHARACTER SET = utf8 COLLATE = utf8_bin ROW_FORMAT = Dynamic;
CREATE TABLE `demo`.`dept` ( `id` bigint(20) NOT NULL, `deptno` int(20) NOT NULL COMMENT '部门编码', `dname` varchar(20) CHARACTER SET utf8 COLLATE utf8_bin NULL DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '部门名称', PRIMARY KEY (`id`) USING BTREE, UNIQUE INDEX `dept_u1`(`deptno`) USING BTREE) ENGINE = InnoDB CHARACTER SET = utf8 COLLATE = utf8_bin ROW_FORMAT = Dynamic;
CREATE TABLE `demo`.`salgrade` ( `id` bigint(20) NOT NULL, `losal` int(20) NULL DEFAULT NULL, `hisal` int(20) NULL DEFAULT NULL, `emp_id` bigint(20) NULL DEFAULT NULL, PRIMARY KEY (`id`) USING BTREE) ENGINE = InnoDB CHARACTER SET = utf8 COLLATE = utf8_bin ROW_FORMAT = Dynamic;
select查詢的序列號(一組數字),表示查詢中執行select子句或操作表的順序。
id欄位有三種情況: 1、如果id相同,那麼執行順序由上到下mysql> explain select * from emp e join dept d on e.deptno = d.deptno join salgrade sg on e.sal between sg.losal and sg.hisal;
2 、如果id不同,如果是子查詢,id的序號會遞增,id值越大優先級越高,越先被執行
mysql> explain select * from emp e where e.deptno = (select d.deptno from dept d where d.dname = 'SALES');
3、 id相同和不同的,同時存在:相同的可以認為是一組,從上往下順序執行,在所有組中,id值越大,優先級越高,越先執行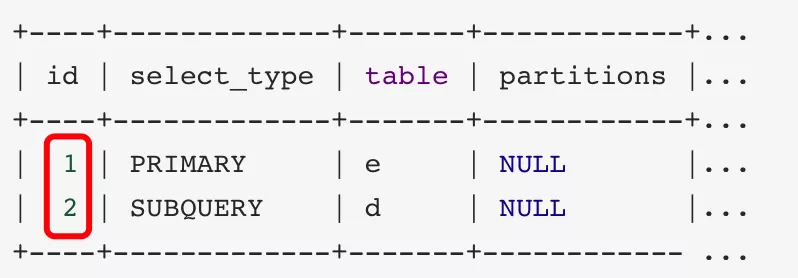
mysql> explain select * from emp e join dept d on e.deptno = d.deptno join salgrade sg on e.sal between sg.losal and sg.hisal wheree.deptno = (select d.deptno from dept d where d.dname = 'SALES');

#select_type列 #主要用來分辨查詢的類型,是普通查詢還是聯合查詢還是子查詢
#主要用來分辨查詢的類型,是普通查詢還是聯合查詢還是子查詢
sample
: 簡單的查詢,不包含子查詢和unionmysql> explain select * from emp;
2. primary: 查詢中若包含任何複雜的子查詢,最外層查詢則標示為Primary
mysql> explain select * from emp e where e.deptno = (select d.deptno from dept d where d.dname = 'SALES');
3. union: 在union,union all和子查詢中的第二個和隨後的select被標記為union
mysql> explain select * from emp where deptno = 10 union select * from emp where sal >2000;
4. dependent union: 在包含UNION或UNION ALL的大查詢中,如果各個小查詢都依賴外層查詢的話,那除了最左邊的小查詢之外,其餘的小查詢的select_type的值就是DEPENDENT UNION。 
mysql> explain select * from emp e where e.empno in ( select empno from emp where deptno = 10 union select empno from emp where sal >2000)
5. union result: 從union表中取得結果的select。 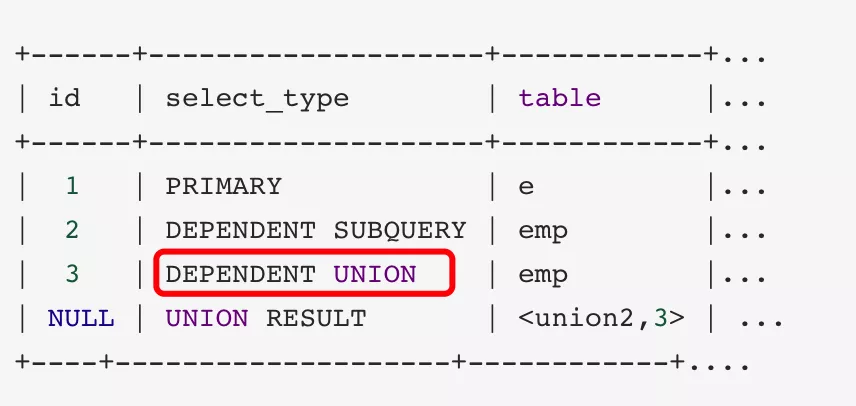
mysql> explain select * from emp where deptno = 10 union select * from emp where sal >2000;
6. subquery: 在select或where清單中包含子查詢(不在from子句中)
mysql> explain select * from emp where sal > (select avg(sal) from emp) ;
7. dependent subquery: 子查詢中的第一個select(不在from子句中),而且取決於外面的詢問。 
mysql> explain select e1.* from emp e1 WHERE e1.deptno = (SELECT deptno FROM emp e2 WHERE e1.empno = e2.empno);
8. derived: 在FROM清單中包含的子查詢被標記為DERIVED,也稱為衍生類別
mysql> explain select * from ( select emp_id,count(*) from emp group by emp_id ) e;

9. UNCACHEABLE SUBQUERY:一个子查询的结果不能被缓存,必须重新评估外链接的第一行对于外层的主表,子查询不可被物化,每次都需要计算(耗时操作)
mysql> explain select * from emp where empno = (select empno from emp where deptno=@@sort_buffer_size);

10. uncacheable union: 表示union的查询结果不能被缓存:没找到具体的sql语句验证.
table列
对应行正在访问哪一个表,表名或者别名,可能是临时表或者union合并结果集.
1、如果是具体的表名,则表明从实际的物理表中获取数据,当然也可以是表的别名.
2、表名是derivedN的形式,表示使用了id为N的查询产生的衍生表.
3、当有union result的时候,表名是union n1,n2等的形式,n1,n2表示参与union的id.
type列
type显示的是访问类型,访问类型表示我是以何种方式去访问我们的数据,最容易想的是全表扫描,直接暴力的遍历一张表去寻找需要的数据,效率非常低下。
访问的类型有很多,效率从最好到最坏依次是:
system > const > eq_ref > ref > fulltext > ref_or_null > index_merge > unique_subquery > index_subquery > range > index > ALL
一般情况下,要保证查询至少达到range级别,最好能达到ref
1. all: 全表扫描,需要扫描整张表,从头到尾找到需要的数据行。一般情况下出现这样的sql语句而且数据量比较大的话那么就需要进行优化。
mysql> explain select * from emp;

2. index:全索引扫描这个比all的效率要好,主要有两种情况,一种是当前的查询时覆盖索引,即我们需要的数据在索引中就可以索取,或者是使用了索引进行排序,这样就避免数据的重排序
mysql> explain select empno from emp;

3. range:表示利用索引查询的时候限制了范围,在指定范围内进行查询,这样避免了index的全索引扫描,适用的操作符:=, <>, >, >=, <, <=, IS NULL, BETWEEN, LIKE, or IN()
mysql> explain select * from emp where empno between 100 and 200;

4. index_subquery:利用索引来关联子查询,不再扫描全表
mysql> explain select * from emp where deptno not in (select deptno from emp)
但是大多数情况下使用SELECT子查询时,MySQL查询优化器会自动将子查询优化为联表查询,因此 type 不会显示为 index_subquery,而是ref

5. unique_subquery: 该连接类型类似于index_subquery,使用的是唯一索引
mysql> explain SELECT * from emp where emp_id not in (select emp.emp_id from emp );
大多数情况下使用SELECT子查询时,MySQL查询优化器会自动将子查询优化为联表查询,因此 type 不会显示为 index_subquery,而是eq_ref

6. index_merge:在查询过程中需要多个索引组合使用.
mysql> 没有模拟出来
7. ref_or_null:对于某个字段即需要关联条件,也需要null值的情况下,查询优化器会选择这种访问方式.
mysql> 没模拟出来
8. ref:使用了非唯一性索引进行数据的查找
mysql> explain select * from emp where deptno=10;

9. eq_ref :当进行等值联表查询使用主键索引或者唯一性非空索引进行数据查找(实际上唯一索引等值查询type不是eq_ref而是const)
mysql> explain select * from salgrade s LEFT JOIN emp e on s.emp_id = e.emp_id;

10. const:最多只能匹配到一条数据,通常使用主键或唯一索引进行等值条件查询
mysql> explain select * from emp where empno = 10;

11. system:表只有一行记录(等于系统表),这是const类型的特例,平时不会出现,不需要进行磁盘io
mysql> explain SELECT * FROM `mysql`.`proxies_priv`;

possible_keys列
显示可能应用在这张表中的索引,一个或多个,查询涉及到的字段上若存在索引,则该索引将被列出,但不一定被查询实际使用。
key列
实际使用的索引,如果为null,则没有使用索引,查询中若使用了覆盖索引,则该索引和查询的select字段重叠。
key_len列
表示索引中使用的字节数,可以通过key_len计算查询中使用的索引长度,在不损失精度的情况下长度越短越好。
索引越大占用存储空间越大,这样io的次数和量就会增加,影响执行效率
ref列
显示之前的表在key列记录的索引中查找值所用的列或者常量
rows列
根据表的统计信息及索引使用情况,大致估算出找出所需记录需要读取的行数,此参数很重要,直接反应的sql找了多少数据,在完成目的的情况下越少越好。
filtered列
针对表中符合某个条件(where子句或者联接条件)的记录数的百分比所做的一个悲观估算。
extra列
包含额外的信息。
1. using filesort: 说明mysql无法利用索引进行排序,只能利用排序算法进行排序,会消耗额外的位置
mysql> explain select * from emp order by sal;

2. using temporary: 建立临时表来保存中间结果,查询完成之后把临时表删除
mysql> explain select name,count(*) from emp where deptno = 10 group by name;

3. using index: 这个表示当前的查询是覆盖索引的,直接从索引中读取数据,而不用访问数据表。如果同时出现using where 表名索引被用来执行索引键值的查找,如果没有,表面索引被用来读取数据,而不是真的查找
mysql> explain select deptno,count(*) from emp group by deptno limit 10;
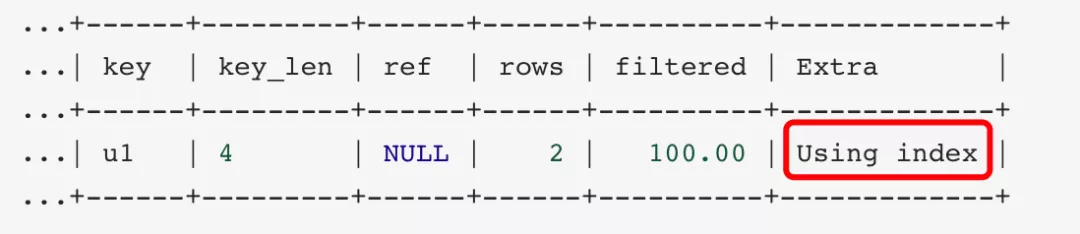
4. using where: 使用where进行条件过滤
mysql> explain select * from emp where name = 1;
5. using join buffer: 使用连接缓存
mysql> explain select * from emp e left join dept d on e.deptno = d.deptno;

6. impossible where:where语句的结果总是false
mysql> explain select * from emp where 1=0;

更多编程相关知识,请访问:编程视频!!
以上是MySQL進階學習:深入了解explain指令的詳細內容。更多資訊請關注PHP中文網其他相關文章!

熱AI工具

Undresser.AI Undress
人工智慧驅動的應用程序,用於創建逼真的裸體照片

AI Clothes Remover
用於從照片中去除衣服的線上人工智慧工具。

Undress AI Tool
免費脫衣圖片

Clothoff.io
AI脫衣器

AI Hentai Generator
免費產生 AI 無盡。

熱門文章

熱工具

記事本++7.3.1
好用且免費的程式碼編輯器

SublimeText3漢化版
中文版,非常好用

禪工作室 13.0.1
強大的PHP整合開發環境

Dreamweaver CS6
視覺化網頁開發工具

SublimeText3 Mac版
神級程式碼編輯軟體(SublimeText3)

熱門話題
 mysql:簡單的概念,用於輕鬆學習
Apr 10, 2025 am 09:29 AM
mysql:簡單的概念,用於輕鬆學習
Apr 10, 2025 am 09:29 AM
MySQL是一個開源的關係型數據庫管理系統。 1)創建數據庫和表:使用CREATEDATABASE和CREATETABLE命令。 2)基本操作:INSERT、UPDATE、DELETE和SELECT。 3)高級操作:JOIN、子查詢和事務處理。 4)調試技巧:檢查語法、數據類型和權限。 5)優化建議:使用索引、避免SELECT*和使用事務。
 phpmyadmin怎麼打開
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:51 PM
phpmyadmin怎麼打開
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:51 PM
可以通過以下步驟打開 phpMyAdmin:1. 登錄網站控制面板;2. 找到並點擊 phpMyAdmin 圖標;3. 輸入 MySQL 憑據;4. 點擊 "登錄"。
 navicat premium怎麼創建
Apr 09, 2025 am 07:09 AM
navicat premium怎麼創建
Apr 09, 2025 am 07:09 AM
使用 Navicat Premium 創建數據庫:連接到數據庫服務器並輸入連接參數。右鍵單擊服務器並選擇“創建數據庫”。輸入新數據庫的名稱和指定字符集和排序規則。連接到新數據庫並在“對象瀏覽器”中創建表。右鍵單擊表並選擇“插入數據”來插入數據。
 MySQL:世界上最受歡迎的數據庫的簡介
Apr 12, 2025 am 12:18 AM
MySQL:世界上最受歡迎的數據庫的簡介
Apr 12, 2025 am 12:18 AM
MySQL是一種開源的關係型數據庫管理系統,主要用於快速、可靠地存儲和檢索數據。其工作原理包括客戶端請求、查詢解析、執行查詢和返回結果。使用示例包括創建表、插入和查詢數據,以及高級功能如JOIN操作。常見錯誤涉及SQL語法、數據類型和權限問題,優化建議包括使用索引、優化查詢和分錶分區。
 為什麼要使用mysql?利益和優勢
Apr 12, 2025 am 12:17 AM
為什麼要使用mysql?利益和優勢
Apr 12, 2025 am 12:17 AM
選擇MySQL的原因是其性能、可靠性、易用性和社區支持。 1.MySQL提供高效的數據存儲和檢索功能,支持多種數據類型和高級查詢操作。 2.採用客戶端-服務器架構和多種存儲引擎,支持事務和查詢優化。 3.易於使用,支持多種操作系統和編程語言。 4.擁有強大的社區支持,提供豐富的資源和解決方案。
 navicat怎麼新建連接mysql
Apr 09, 2025 am 07:21 AM
navicat怎麼新建連接mysql
Apr 09, 2025 am 07:21 AM
可在 Navicat 中通過以下步驟新建 MySQL 連接:打開應用程序並選擇“新建連接”(Ctrl N)。選擇“MySQL”作為連接類型。輸入主機名/IP 地址、端口、用戶名和密碼。 (可選)配置高級選項。保存連接並輸入連接名稱。
 redis怎麼使用單線程
Apr 10, 2025 pm 07:12 PM
redis怎麼使用單線程
Apr 10, 2025 pm 07:12 PM
Redis 使用單線程架構,以提供高性能、簡單性和一致性。它利用 I/O 多路復用、事件循環、非阻塞 I/O 和共享內存來提高並發性,但同時存在並發性受限、單點故障和不適合寫密集型工作負載的局限性。
 MySQL和SQL:開發人員的基本技能
Apr 10, 2025 am 09:30 AM
MySQL和SQL:開發人員的基本技能
Apr 10, 2025 am 09:30 AM
MySQL和SQL是開發者必備技能。 1.MySQL是開源的關係型數據庫管理系統,SQL是用於管理和操作數據庫的標準語言。 2.MySQL通過高效的數據存儲和檢索功能支持多種存儲引擎,SQL通過簡單語句完成複雜數據操作。 3.使用示例包括基本查詢和高級查詢,如按條件過濾和排序。 4.常見錯誤包括語法錯誤和性能問題,可通過檢查SQL語句和使用EXPLAIN命令優化。 5.性能優化技巧包括使用索引、避免全表掃描、優化JOIN操作和提升代碼可讀性。






