Vue3 發布已經有一段時間了,它採用了新的響應式系統,而且建構了一套全新的Composition API。 Vue 的周邊生態都在加緊適配這套新的系統,官方的狀態管理庫 Vuex 也在適配中,為此官方提出了一個 Vuex 5 的全新提案。 【相關推薦:《vue.js教學》】

- #支援兩種文法建立Store:
Options Api和Composition Api; - 刪除
mutations,只支援state、getters、actions# ; - 模組化的設計,能很好地支援程式碼分割;
- 沒有巢狀的模組,只有Store 的概念;
- 完整的
TypeScript支持;
在這個提案下方,有個評論很有意思。簡單翻譯一下:

好巧不巧,Vuex5 的提案,與Pinia 實現的功能不能說毫無關係,只能說一模一樣,今天的文章就來給大家介紹一下這個鳳梨。
安裝
在現有專案中,使用下列指令進行 Pinia 模組的安裝。
# yarn yarn add pinia@next # npm npm i pinia@next
安裝完成後,需要在 Vue3 專案的入口檔案中,進行匯入安裝。
// main.js
import { createApp } from 'vue'
import { createPinia } from 'pinia'
import App from './App.vue'
// 实例化 Vue
const app = createApp(App)
// 安装 Pinia
app.use(createPinia())
// 挂载在真实 DOM
app.mount('#app')上手
要使用 Pinia 的話,只需要定義一個 store,然後在用到該資料的地方進行匯入。
定義Store
import { defineStore } from "pinia"
// 对外部暴露一个 use 方法,该方法会导出我们定义的 state
const useCounterStore = defineStore({
// 每个 store 的 id 必须唯一
id: 'counter',
// state 表示数据源
state: () => ({
count: 0
}),
// getters 类似于 computed,可对 state 的值进行二次计算
getters: {
double () {
// getter 中的 this 指向 state
return this.count * 2
},
// 如果使用箭头函数会导致 this 指向有问题
// 可以在函数的第一个参数中拿到 state
double: (state) => {
return state.count * 2
}
},
// actions 用来修改 state
actions: {
increment() {
// action 中的 this 指向 state
this.count++
},
}
})
export default useCounterStore除了使用上述類似vuex 的方式來建立state,還可以使用function 的形式來建立store,有點類似於Vue3 中的setup()。
import { ref, computed } from "vue"
import { defineStore } from "pinia"
// 对外部暴露一个 use 方法,该方法会导出我们定义的 state
const useCounterStore = defineStore('counter', function () {
const count = ref(0)
const double = computed(() => count.value * 2)
function increment() {
count.value++
}
return {
count, double, increment
}
})
export default useCounterStore使用Store
前面也介紹過,Pinia 提供了兩種方式來使用store,Options Api 和Composition Api 中都完美支援。
Options Api
在Options Api 中,可直接使用官方提供的mapActions 和mapState 方法,匯出store 的state、getter、action,其用法與Vuex 基本一致,很容易上手。
import { mapActions, mapState } from 'pinia'
import { useCounterStore } from '../model/counter'
export default {
name: 'HelloWorld',
computed: {
...mapState(useCounterStore, ['count', 'double'])
},
methods: {
...mapActions(useCounterStore, ['increment'])
}
}Composition Api
Composition Api 中,不管是state 或getter 都需要透過computed 方法來監聽變化,這和Options Api 中,需要放到computed 物件中的道理一樣。另外, Options Api 中拿到的 state 值是可以直接進行修改操作的,當然還是建議寫一個 action 來操作 state 值,方便後製。
// Composition Api
import { computed } from 'vue'
import { useCounterStore } from '../stores/counter'
export default {
name: 'HelloWorld',
setup() {
const counter = useCounterStore()
return {
// state 和 getter 都需要在使用 computed,这和 Options Api 一样
count: computed(() => counter.count),
double: computed(() => counter.double),
increment: () => { counter.count++ }, // 可以直接修改 state 的值
increment: counter.increment, // 可以引用 store 中定义的 action
}
}
}類型提示
在 Vuex 中,TypeScript 的類型提示做得不是很好,在進行類型推導時,只能找到它的 state。特別是在寫程式碼的過程中,程式碼提示就很不聰明。

而 pinia,就能推導出所有定義的 state、getter、action,這樣在寫程式碼的時候,就會方便很多。


主要是pinia 透過TypeScript 進行了十分友善的類型定義,感興趣的可以看看pinia 的類型定義檔(pinia.d.ts):
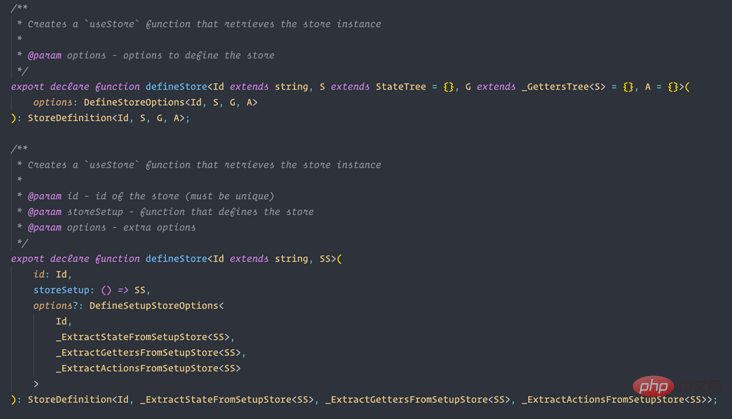
程式碼分割
由於使用了模組化設計,所有的store 都能夠單獨引入,而不是像vuex 一樣,透過modules 的方式,將所有的module 掛載到一個store 上。
假設,我們目前透過 Vuex 建立了一個 Store,這個 Store 下有兩個 module,分別是使用者模組(User)和商品模組(Goods)。即使目前首頁只使用到了使用者訊息,但是整個 Store 都會被打包到首頁的 js chunk 中。


如果我們使用 pinia,我們會使用 defineStore 定義兩個 完全是分離狀態的 store,兩個頁面在引入時,也互不影響。最後打包的時候,首頁的 js chunk 和商品頁的 js chunk 會分別打包對應的 store。

Pinia 的介紹到這裡就告一段落了,如果現在有新專案要使用 Vue3 進行開發,推薦無腦使用 Pinia,更加簡潔,而且大小僅 1KB。
更多程式相關知識,請造訪:程式設計入門! !



























