詳細介紹JavaScript二元樹及各種遍歷演算法
本篇文章為大家帶來了關於javascript的相關知識,主要介紹了JavaScript二元樹及各種遍歷演算法詳情,文章圍繞主題展開詳細的內容介紹,具有一定的參考價值,需要的小夥伴可以參考一下,希望對大家有幫助。

【相關推薦:javascript影片教學、web前端】
什麼是二元樹
二元樹是每個節點最多只能有兩個子節點的樹,如下圖所示:
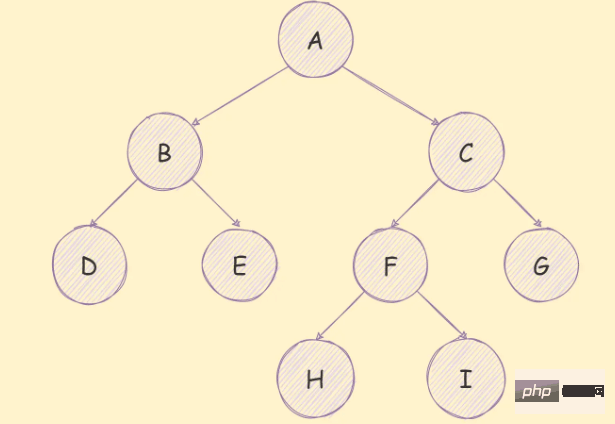
一個二元樹具有以下幾個特質:
- 第
i層的節點最有隻有2^(i-1)個; - 如果這顆二元樹的深度為
k,那二元樹最多有2^k-1節點; - 在一個非空的二元樹中,若使用
n0表示葉子節點的個數,n2是度為2的非葉子節點的個數,那麼兩者滿足關係n0 = n2 1。
滿二叉樹
如果在一個二元樹中,除了葉子節點,其餘的節點的每個度數都是2,則說明該二元樹是一個滿二叉樹,
如下圖所示:
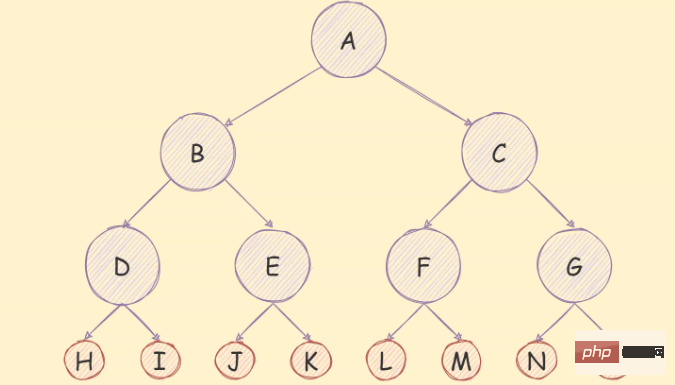
#滿叉樹除了滿足普通二元樹特質,還具有如下幾個特質:
- 滿二元樹的第
n層具有2^(n-1)個節點; - 深度為
k的滿二叉樹一定存在2^k-1個節點,葉子節點的個數為2^(k-1); - 具有
n個節點的滿二元樹的深度為log_2^(n 1)。
完全二元樹
如果一個二元樹去掉最後一次層是滿二叉樹,且最後一次的節點是依序從左到右分佈的,則這個二元樹是一個完全二元樹,
如下圖所示:
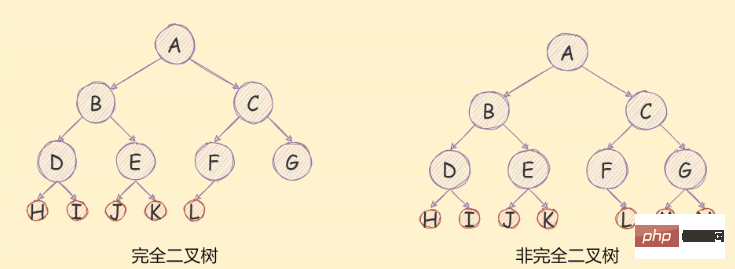
#二元樹的儲存
儲存二元樹的常見方式分為兩種,一種是使用陣列儲存,另一種使用鍊錶儲存。
陣列儲存
使用陣列儲存二元樹,如果遇到完全二元樹,儲存順序從上到下,從左到右,如下圖所示:
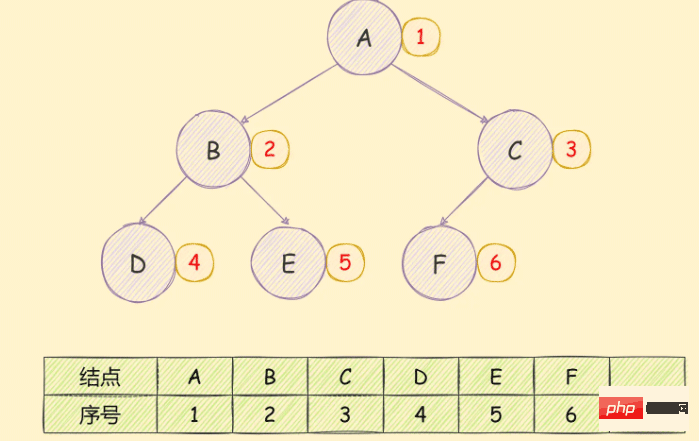
如果是非完全二元樹,如下圖所示:
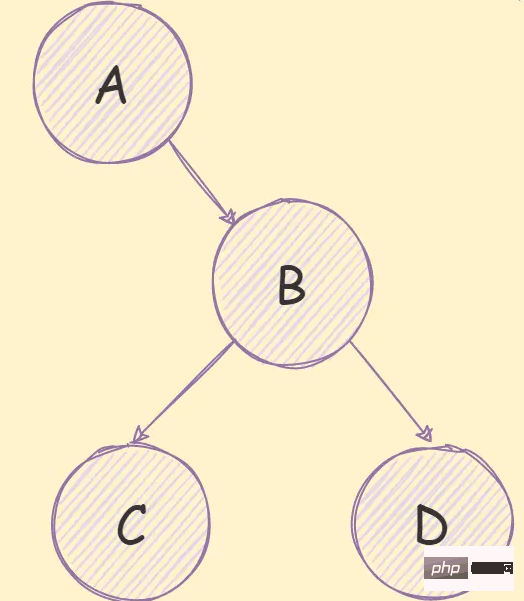
需要先將其轉換為完全二元樹,然後在進行存儲,如下圖所示:
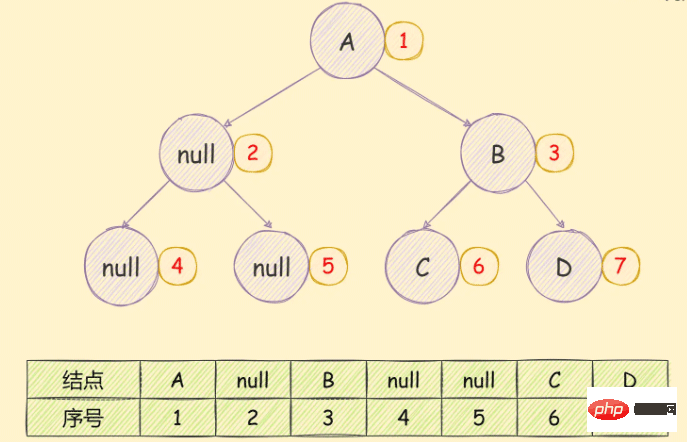
#可以很明顯的看到存儲空間的浪費。
鍊錶儲存
使用鍊錶儲存通常將二元樹中的分為3個部分,如下圖:

##這三個部分依序是左子樹的引用,該節點包含的數據,右子樹的引用,儲存方式如下圖所示:
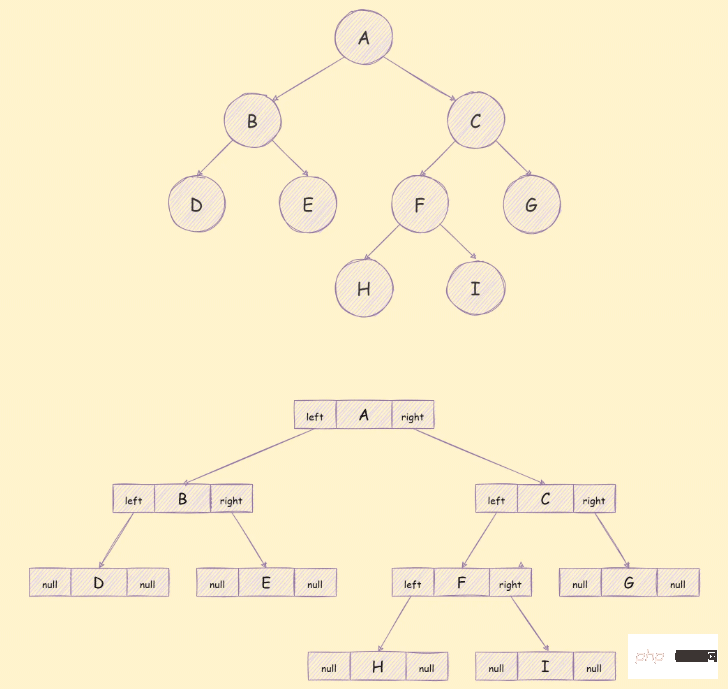
以下演算法中遍歷用到的樹如下:
// tree.js
const bt = {
val: 'A',
left: {
val: 'B',
left: { val: 'D', left: null, right: null },
right: { val: 'E', left: null, right: null },
},
right: {
val: 'C',
left: {
val: 'F',
left: { val: 'H', left: null, right: null },
right: { val: 'I', left: null, right: null },
},
right: { val: 'G', left: null, right: null },
},
}
module.exports = bt二元樹的深度優先遍歷與樹的深度優先遍歷思路一致,思路如下:
- #訪問根節點;訪問根節點的
- left
- right
實作程式碼如下: #
const bt = {
val: 'A',
left: {
val: 'B',
left: { val: 'D', left: null, right: null },
right: { val: 'E', left: null, right: null },
},
right: {
val: 'C',
left: {
val: 'F',
left: { val: 'H', left: null, right: null },
right: { val: 'I', left: null, right: null },
},
right: { val: 'G', left: null, right: null },
},
}
function dfs(root) {
if (!root) return
console.log(root.val)
root.left && dfs(root.left)
root.right && dfs(root.right)
}
dfs(bt)
/** 结果
A B D E C F H I G
*/實作想法如下:
- #建立佇列,把根節點入隊把對頭出隊並訪問把隊頭的
- left
和right依序入隊#重複執行2、3步,直到隊列為空
實作程式碼如下:
function bfs(root) {
if (!root) return
const queue = [root]
while (queue.length) {
const node = queue.shift()
console.log(node.val)
node.left && queue.push(node.left)
node.right && queue.push(node.right)
}
}
bfs(bt)
/** 结果
A B C D E F G H I
*/二元樹的先序遍歷實作想法如下: #
- 访问根节点;
- 对当前节点的左子树进行先序遍历;
- 对当前节点的右子树进行先序遍历;
如下图所示:
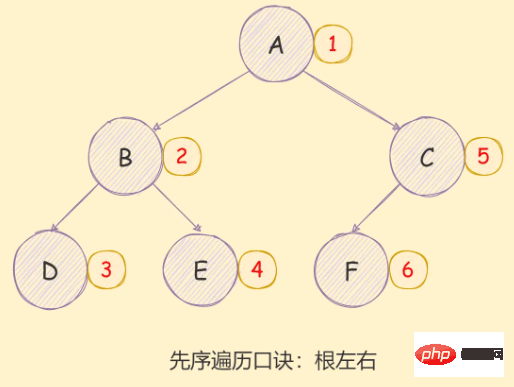
递归方式实现如下:
const bt = require('./tree')
function preorder(root) {
if (!root) return
console.log(root.val)
preorder(root.left)
preorder(root.right)
}
preorder(bt)
/** 结果
A B D E C F H I G
*/迭代方式实现如下:
// 非递归版
function preorder(root) {
if (!root) return
// 定义一个栈,用于存储数据
const stack = [root]
while (stack.length) {
const node = stack.pop()
console.log(node.val)
/* 由于栈存在先入后出的特性,所以需要先入右子树才能保证先出左子树 */
node.right && stack.push(node.right)
node.left && stack.push(node.left)
}
}
preorder(bt)
/** 结果
A B D E C F H I G
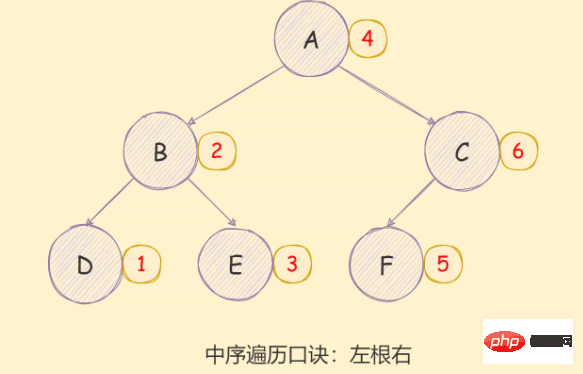
*/中序遍历
二叉树的中序遍历实现思想如下:
- 对当前节点的左子树进行中序遍历;
- 访问根节点;
- 对当前节点的右子树进行中序遍历;
如下图所示:
递归方式实现如下:
const bt = require('./tree')
// 递归版
function inorder(root) {
if (!root) return
inorder(root.left)
console.log(root.val)
inorder(root.right)
}
inorder(bt)
/** 结果
D B E A H F I C G
*/迭代方式实现如下:
// 非递归版
function inorder(root) {
if (!root) return
const stack = []
// 定义一个指针
let p = root
// 如果栈中有数据或者p不是null,则继续遍历
while (stack.length || p) {
// 如果p存在则一致将p入栈并移动指针
while (p) {
// 将 p 入栈,并以移动指针
stack.push(p)
p = p.left
}
const node = stack.pop()
console.log(node.val)
p = node.right
}
}
inorder(bt)
/** 结果
D B E A H F I C G
*/后序遍历
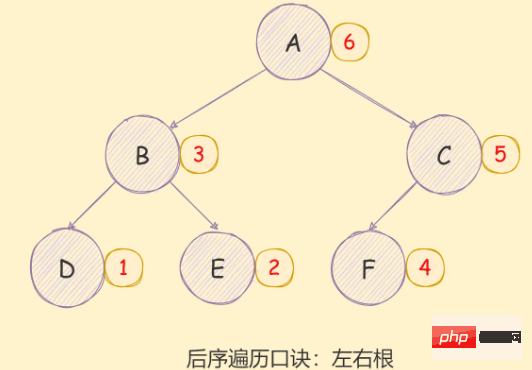
二叉树的后序遍历实现思想如下:
- 对当前节点的左子树进行后序遍历;
- 对当前节点的右子树进行后序遍历;
- 访问根节点;
如下图所示:
递归方式实现如下:
const bt = require('./tree')
// 递归版
function postorder(root) {
if (!root) return
postorder(root.left)
postorder(root.right)
console.log(root.val)
}
postorder(bt)
/** 结果
D E B H I F G C A
*/迭代方式实现如下:
// 非递归版
function postorder(root) {
if (!root) return
const outputStack = []
const stack = [root]
while (stack.length) {
const node = stack.pop()
outputStack.push(node)
// 这里先入left需要保证left后出,在stack中后出,就是在outputStack栈中先出
node.left && stack.push(node.left)
node.right && stack.push(node.right)
}
while (outputStack.length) {
const node = outputStack.pop()
console.log(node.val)
}
}
postorder(bt)
/** 结果
D E B H I F G C A
*/【相关推荐:javascript视频教程、web前端】
以上是詳細介紹JavaScript二元樹及各種遍歷演算法的詳細內容。更多資訊請關注PHP中文網其他相關文章!

熱AI工具

Undresser.AI Undress
人工智慧驅動的應用程序,用於創建逼真的裸體照片

AI Clothes Remover
用於從照片中去除衣服的線上人工智慧工具。

Undress AI Tool
免費脫衣圖片

Clothoff.io
AI脫衣器

Video Face Swap
使用我們完全免費的人工智慧換臉工具,輕鬆在任何影片中換臉!

熱門文章

熱工具

記事本++7.3.1
好用且免費的程式碼編輯器

SublimeText3漢化版
中文版,非常好用

禪工作室 13.0.1
強大的PHP整合開發環境

Dreamweaver CS6
視覺化網頁開發工具

SublimeText3 Mac版
神級程式碼編輯軟體(SublimeText3)
 如何使用WebSocket和JavaScript實現線上語音辨識系統
Dec 17, 2023 pm 02:54 PM
如何使用WebSocket和JavaScript實現線上語音辨識系統
Dec 17, 2023 pm 02:54 PM
如何使用WebSocket和JavaScript實現線上語音辨識系統引言:隨著科技的不斷發展,語音辨識技術已成為了人工智慧領域的重要組成部分。而基於WebSocket和JavaScript實現的線上語音辨識系統,具備了低延遲、即時性和跨平台的特點,成為了廣泛應用的解決方案。本文將介紹如何使用WebSocket和JavaScript來實現線上語音辨識系
 WebSocket與JavaScript:實現即時監控系統的關鍵技術
Dec 17, 2023 pm 05:30 PM
WebSocket與JavaScript:實現即時監控系統的關鍵技術
Dec 17, 2023 pm 05:30 PM
WebSocket與JavaScript:實現即時監控系統的關鍵技術引言:隨著互聯網技術的快速發展,即時監控系統在各個領域中得到了廣泛的應用。而實現即時監控的關鍵技術之一就是WebSocket與JavaScript的結合使用。本文將介紹WebSocket與JavaScript在即時監控系統中的應用,並給出程式碼範例,詳細解釋其實作原理。一、WebSocket技
 如何利用JavaScript和WebSocket實現即時線上點餐系統
Dec 17, 2023 pm 12:09 PM
如何利用JavaScript和WebSocket實現即時線上點餐系統
Dec 17, 2023 pm 12:09 PM
如何利用JavaScript和WebSocket實現即時線上點餐系統介紹:隨著網路的普及和技術的進步,越來越多的餐廳開始提供線上點餐服務。為了實現即時線上點餐系統,我們可以利用JavaScript和WebSocket技術。 WebSocket是一種基於TCP協定的全雙工通訊協議,可實現客戶端與伺服器的即時雙向通訊。在即時線上點餐系統中,當使用者選擇菜餚並下訂單
 如何使用WebSocket和JavaScript實現線上預約系統
Dec 17, 2023 am 09:39 AM
如何使用WebSocket和JavaScript實現線上預約系統
Dec 17, 2023 am 09:39 AM
如何使用WebSocket和JavaScript實現線上預約系統在當今數位化的時代,越來越多的業務和服務都需要提供線上預約功能。而實現一個高效、即時的線上預約系統是至關重要的。本文將介紹如何使用WebSocket和JavaScript來實作一個線上預約系統,並提供具體的程式碼範例。一、什麼是WebSocketWebSocket是一種在單一TCP連線上進行全雙工
 JavaScript與WebSocket:打造高效率的即時天氣預報系統
Dec 17, 2023 pm 05:13 PM
JavaScript與WebSocket:打造高效率的即時天氣預報系統
Dec 17, 2023 pm 05:13 PM
JavaScript和WebSocket:打造高效的即時天氣預報系統引言:如今,天氣預報的準確性對於日常生活以及決策制定具有重要意義。隨著技術的發展,我們可以透過即時獲取天氣數據來提供更準確可靠的天氣預報。在本文中,我們將學習如何使用JavaScript和WebSocket技術,來建立一個高效的即時天氣預報系統。本文將透過具體的程式碼範例來展示實現的過程。 We
 簡易JavaScript教學:取得HTTP狀態碼的方法
Jan 05, 2024 pm 06:08 PM
簡易JavaScript教學:取得HTTP狀態碼的方法
Jan 05, 2024 pm 06:08 PM
JavaScript教學:如何取得HTTP狀態碼,需要具體程式碼範例前言:在Web開發中,經常會涉及到與伺服器進行資料互動的場景。在與伺服器進行通訊時,我們經常需要取得傳回的HTTP狀態碼來判斷操作是否成功,並根據不同的狀態碼來進行對應的處理。本篇文章將教你如何使用JavaScript來取得HTTP狀態碼,並提供一些實用的程式碼範例。使用XMLHttpRequest
 javascript如何使用insertBefore
Nov 24, 2023 am 11:56 AM
javascript如何使用insertBefore
Nov 24, 2023 am 11:56 AM
用法:在JavaScript中,insertBefore()方法用於在DOM樹中插入一個新的節點。這個方法需要兩個參數:要插入的新節點和參考節點(即新節點將要插入的位置的節點)。
 如何在JavaScript中取得HTTP狀態碼的簡單方法
Jan 05, 2024 pm 01:37 PM
如何在JavaScript中取得HTTP狀態碼的簡單方法
Jan 05, 2024 pm 01:37 PM
JavaScript中的HTTP狀態碼取得方法簡介:在進行前端開發中,我們常常需要處理與後端介面的交互,而HTTP狀態碼就是其中非常重要的一部分。了解並取得HTTP狀態碼有助於我們更好地處理介面傳回的資料。本文將介紹使用JavaScript取得HTTP狀態碼的方法,並提供具體程式碼範例。一、什麼是HTTP狀態碼HTTP狀態碼是指當瀏覽器向伺服器發起請求時,服務






