python解析之namedtuple函數的用法
【相關推薦:Python3影片教學】
原始碼解釋:##
def namedtuple(typename, field_names, *, rename=False, defaults=None, module=None):
"""Returns a new subclass of tuple with named fields.
>>> Point = namedtuple('Point', ['x', 'y'])
>>> Point.__doc__ # docstring for the new class
'Point(x, y)'
>>> p = Point(11, y=22) # instantiate with positional args or keywords
>>> p[0] + p[1] # indexable like a plain tuple
33
>>> x, y = p # unpack like a regular tuple
>>> x, y
(11, 22)
>>> p.x + p.y # fields also accessible by name
33
>>> d = p._asdict() # convert to a dictionary
>>> d['x']
11
>>> Point(**d) # convert from a dictionary
Point(x=11, y=22)
>>> p._replace(x=100) # _replace() is like str.replace() but targets named fields
Point(x=100, y=22)
"""語法結構:
namedtuple(typename, field_names, *, rename=False, defaults=None, module=None)
- typename: 代表新建的一個元組的名字。
- field_names: 是元組的內容,是一個類似list的['x','y']
範例程式碼1:
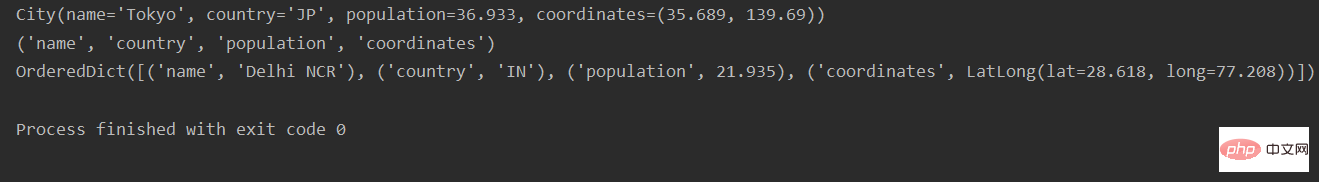
from collections import namedtuple # 定义一个命名元祖city,City类,有name/country/population/coordinates四个字段 city = namedtuple('City', 'name country population coordinates') tokyo = city('Tokyo', 'JP', 36.933, (35.689, 139.69)) print(tokyo) # _fields 类属性,返回一个包含这个类所有字段名称的元组 print(city._fields) # 定义一个命名元祖latLong,LatLong类,有lat/long两个字段 latLong = namedtuple('LatLong', 'lat long') delhi_data = ('Delhi NCR', 'IN', 21.935, latLong(28.618, 77.208)) # 用 _make() 通过接受一个可迭代对象来生成这个类的一个实例,作用跟City(*delhi_data)相同 delhi = city._make(delhi_data) # _asdict() 把具名元组以 collections.OrderedDict 的形式返回,可以利用它来把元组里的信息友好地呈现出来。 print(delhi._asdict())
運行結果:
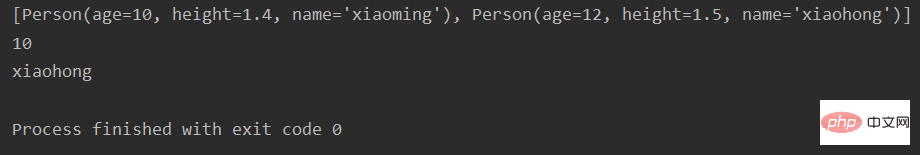
from collections import namedtuple
Person = namedtuple('Person', ['age', 'height', 'name'])
data2 = [Person(10, 1.4, 'xiaoming'), Person(12, 1.5, 'xiaohong')]
print(data2)
res = data2[0].age
print(res)
res2 = data2[1].name
print(res2)
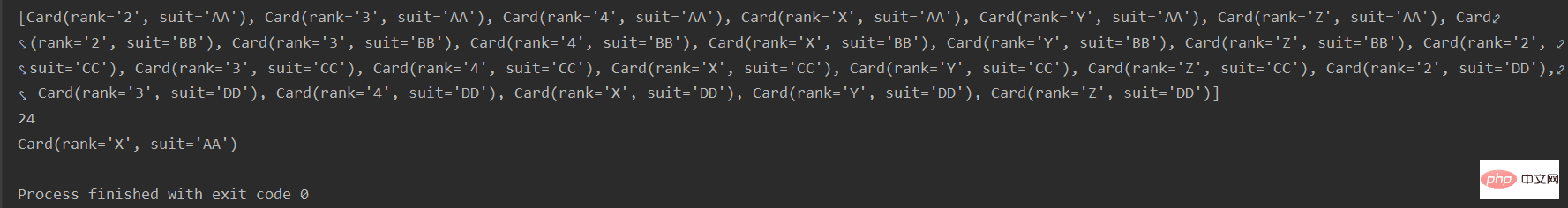
from collections import namedtuple
card = namedtuple('Card', ['rank', 'suit']) # 定义一个命名元祖card,Card类,有rank和suit两个字段
class FrenchDeck(object):
ranks = [str(n) for n in range(2, 5)] + list('XYZ')
suits = 'AA BB CC DD'.split() # 生成一个列表,用空格将字符串分隔成列表
def __init__(self):
# 生成一个命名元组组成的列表,将suits、ranks两个列表的元素分别作为命名元组rank、suit的值。
self._cards = [card(rank, suit) for suit in self.suits for rank in self.ranks]
print(self._cards)
# 获取列表的长度
def __len__(self):
return len(self._cards)
# 根据索引取值
def __getitem__(self, item):
return self._cards[item]
f = FrenchDeck()
print(f.__len__())
print(f.__getitem__(3))
##
from collections import namedtuple person = namedtuple('Person', ['first_name', 'last_name']) p1 = person('san', 'zhang') print(p1) print('first item is:', (p1.first_name, p1[0])) print('second item is', (p1.last_name, p1[1]))
範例程式碼5: 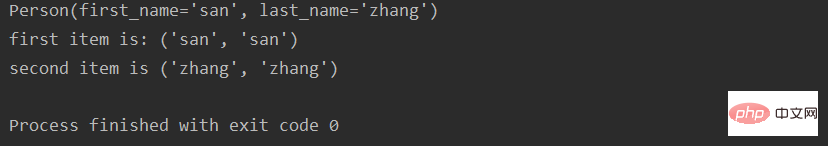 【_make 從存在的序列或迭代建立實例】
【_make 從存在的序列或迭代建立實例】
from collections import namedtuple
course = namedtuple('Course', ['course_name', 'classroom', 'teacher', 'course_data'])
math = course('math', 'ERB001', 'Xiaoming', '09-Feb')
print(math)
print(math.course_name, math.course_data)
course_list = [
('computer_science', 'CS001', 'Jack_ma', 'Monday'),
('EE', 'EE001', 'Dr.han', 'Friday'),
('Pyhsics', 'EE001', 'Prof.Chen', 'None')
]
for k in course_list:
course_i = course._make(k)
print(course_i)#執行結果:
範例程式碼6: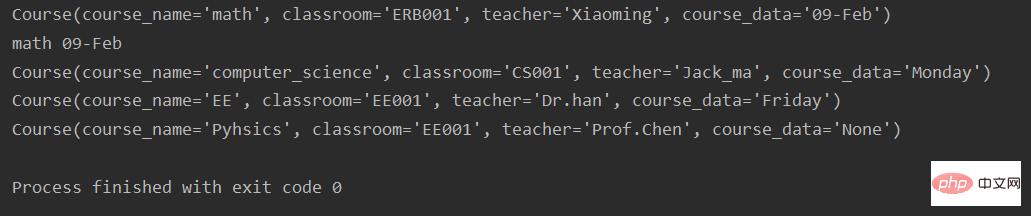 【_asdict 傳回一個新的ordereddict,將欄位名稱對應到對應的值】
【_asdict 傳回一個新的ordereddict,將欄位名稱對應到對應的值】
from collections import namedtuple person = namedtuple('Person', ['first_name', 'last_name']) zhang_san = ('Zhang', 'San') p = person._make(zhang_san) print(p) # 返回的类型不是dict,而是orderedDict print(p._asdict())
執行結果:
範例程式碼7: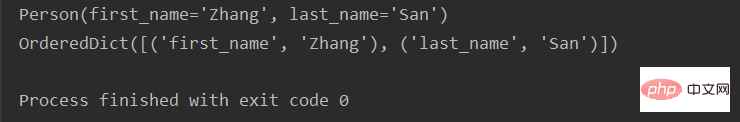 【_replace 傳回一個新的實例,並將指定域替換為新的值】
【_replace 傳回一個新的實例,並將指定域替換為新的值】
from collections import namedtuple person = namedtuple('Person', ['first_name', 'last_name']) zhang_san = ('Zhang', 'San') p = person._make(zhang_san) print(p) p_replace = p._replace(first_name='Wang') print(p_replace) print(p) p_replace2 = p_replace._replace(first_name='Dong') print(p_replace2)
運行結果:
範例程式碼8: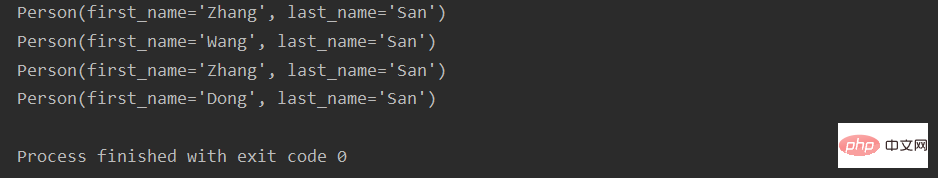 【 _fields 回傳欄位名稱】
【 _fields 回傳欄位名稱】
from collections import namedtuple person = namedtuple('Person', ['first_name', 'last_name']) zhang_san = ('Zhang', 'San') p = person._make(zhang_san) print(p) print(p._fields)
運行結果:
範例程式碼9: 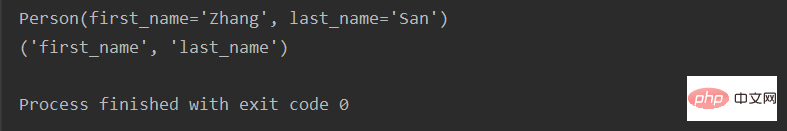 #【利用fields可以將兩個namedtuple組合在一起】
#【利用fields可以將兩個namedtuple組合在一起】
from collections import namedtuple person = namedtuple('Person', ['first_name', 'last_name']) print(person._fields) degree = namedtuple('Degree', 'major degree_class') print(degree._fields) person_with_degree = namedtuple('person_with_degree', person._fields + degree._fields) print(person_with_degree._fields) zhang_san = person_with_degree('san', 'zhang', 'cs', 'master') print(zhang_san)
運行結果:
範例程式碼10:  #【 field_defaults】
#【 field_defaults】
from collections import namedtuple person = namedtuple('Person', ['first_name', 'last_name'], defaults=['san']) print(person._fields) print(person._field_defaults) print(person('zhang')) print(person('Li', 'si'))
運行結果:
##範例程式碼11:
【namedtuple是一個類,所以可以透過子類別更改功能】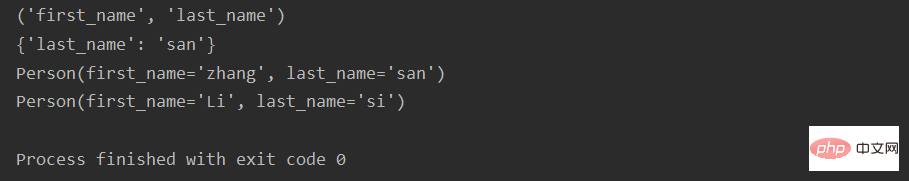
from collections import namedtuple
Point = namedtuple('Point', ['x', 'y'])
p = Point(4, 5)
print(p)
class Point(namedtuple('Point', ['x', 'y'])):
__slots__ = ()
@property
def hypot(self):
return self.x + self.y
def hypot2(self):
return self.x + self.y
def __str__(self):
return 'result is %.3f' % (self.x + self.y)
aa = Point(4, 5)
print(aa)
print(aa.hypot)
print(aa.hypot2)運行結果:
範例程式碼12:
【注意觀察兩種寫法的差異】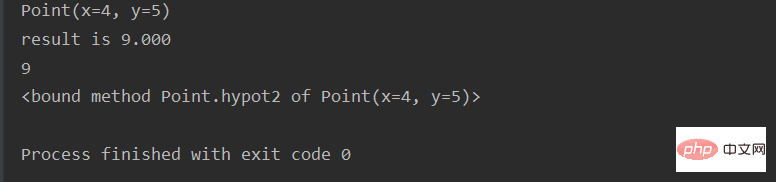
from collections import namedtuple
Point = namedtuple("Point", ["x", "y"])
p = Point(11, 22)
print(p)
print(p.x, p.y)
# namedtuple本质上等于下面写法
class Point2(object):
def __init__(self, x, y):
self.x = x
self.y = y
o = Point2(33, 44)
print(o)
print(o.x, o.y)運行結果:
#【相關推薦:
Python3影片教學 】
以上是python解析之namedtuple函數的用法的詳細內容。更多資訊請關注PHP中文網其他相關文章!

熱AI工具

Undresser.AI Undress
人工智慧驅動的應用程序,用於創建逼真的裸體照片

AI Clothes Remover
用於從照片中去除衣服的線上人工智慧工具。

Undress AI Tool
免費脫衣圖片

Clothoff.io
AI脫衣器

Video Face Swap
使用我們完全免費的人工智慧換臉工具,輕鬆在任何影片中換臉!

熱門文章

熱工具

記事本++7.3.1
好用且免費的程式碼編輯器

SublimeText3漢化版
中文版,非常好用

禪工作室 13.0.1
強大的PHP整合開發環境

Dreamweaver CS6
視覺化網頁開發工具

SublimeText3 Mac版
神級程式碼編輯軟體(SublimeText3)
 PHP和Python:解釋了不同的範例
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:26 AM
PHP和Python:解釋了不同的範例
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:26 AM
PHP主要是過程式編程,但也支持面向對象編程(OOP);Python支持多種範式,包括OOP、函數式和過程式編程。 PHP適合web開發,Python適用於多種應用,如數據分析和機器學習。
 在PHP和Python之間進行選擇:指南
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:24 AM
在PHP和Python之間進行選擇:指南
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:24 AM
PHP適合網頁開發和快速原型開發,Python適用於數據科學和機器學習。 1.PHP用於動態網頁開發,語法簡單,適合快速開發。 2.Python語法簡潔,適用於多領域,庫生態系統強大。
 sublime怎麼運行代碼python
Apr 16, 2025 am 08:48 AM
sublime怎麼運行代碼python
Apr 16, 2025 am 08:48 AM
在 Sublime Text 中運行 Python 代碼,需先安裝 Python 插件,再創建 .py 文件並編寫代碼,最後按 Ctrl B 運行代碼,輸出會在控制台中顯示。
 PHP和Python:深入了解他們的歷史
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:25 AM
PHP和Python:深入了解他們的歷史
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:25 AM
PHP起源於1994年,由RasmusLerdorf開發,最初用於跟踪網站訪問者,逐漸演變為服務器端腳本語言,廣泛應用於網頁開發。 Python由GuidovanRossum於1980年代末開發,1991年首次發布,強調代碼可讀性和簡潔性,適用於科學計算、數據分析等領域。
 Python vs. JavaScript:學習曲線和易用性
Apr 16, 2025 am 12:12 AM
Python vs. JavaScript:學習曲線和易用性
Apr 16, 2025 am 12:12 AM
Python更適合初學者,學習曲線平緩,語法簡潔;JavaScript適合前端開發,學習曲線較陡,語法靈活。 1.Python語法直觀,適用於數據科學和後端開發。 2.JavaScript靈活,廣泛用於前端和服務器端編程。
 Golang vs. Python:性能和可伸縮性
Apr 19, 2025 am 12:18 AM
Golang vs. Python:性能和可伸縮性
Apr 19, 2025 am 12:18 AM
Golang在性能和可擴展性方面優於Python。 1)Golang的編譯型特性和高效並發模型使其在高並發場景下表現出色。 2)Python作為解釋型語言,執行速度較慢,但通過工具如Cython可優化性能。
 vscode在哪寫代碼
Apr 15, 2025 pm 09:54 PM
vscode在哪寫代碼
Apr 15, 2025 pm 09:54 PM
在 Visual Studio Code(VSCode)中編寫代碼簡單易行,只需安裝 VSCode、創建項目、選擇語言、創建文件、編寫代碼、保存並運行即可。 VSCode 的優點包括跨平台、免費開源、強大功能、擴展豐富,以及輕量快速。
 notepad 怎麼運行python
Apr 16, 2025 pm 07:33 PM
notepad 怎麼運行python
Apr 16, 2025 pm 07:33 PM
在 Notepad 中運行 Python 代碼需要安裝 Python 可執行文件和 NppExec 插件。安裝 Python 並為其添加 PATH 後,在 NppExec 插件中配置命令為“python”、參數為“{CURRENT_DIRECTORY}{FILE_NAME}”,即可在 Notepad 中通過快捷鍵“F6”運行 Python 代碼。







