Java8中Stream詳細用法歸納
本篇文章為大家帶來了關於java的相關知識,其中主要介紹了關於Stream詳細用法的相關問題,版本新增的Stream,配合約版本出現的Lambda ,給我們操作集合(Collection)提供了極大的便利,下面一起來看看,希望對大家有幫助。

推薦學習:《java影片教學》
一、概述
Java 8 是一個非常成功的版本,這個版本新增的Stream,配合約版本出現的Lambda ,給我們操作集合(Collection)提供了極大的便利。 Stream流是JDK8新增的成員,允許以聲明性方式處理資料集合,可以把Stream流看作是遍歷資料集合的一個進階迭代器。 Stream 是 Java8 中處理集合的關鍵抽象概念,它可以指定你希望對集合進行的操作,可以執行非常複雜的查找/篩選/過濾、排序、聚合和映射資料等操作。使用Stream API 對集合資料進行操作,就類似於使用 SQL 執行的資料庫查詢。也可以使用 Stream API 來並行執行操作。簡而言之,Stream API 提供了一種高效且易於使用的處理資料的方式。
1、使用流的好處
程式碼以宣告性方式書寫,說明想要完成什麼,而不是說明如何完成一個動作。
可以把幾個基礎操作連接起來,來表達複雜的資料處理的管線,同時保持程式碼清晰可讀。
2、流是什麼?
從支援資料處理操作的來源產生元素序列.資料來源可以是集合,陣列或IO資源。
從操作角度來看,流與集合是不同的. 流不儲存資料值; 流的目的是處理資料,它是關於演算法與計算的。
如果把集合當作流的資料來源,建立流時不會導致資料流動; 如果流的終止運算需要值時,流會從集合中取得值; 流只使用一次。
流中心思想是延遲計算,流直到需要時才計算值。 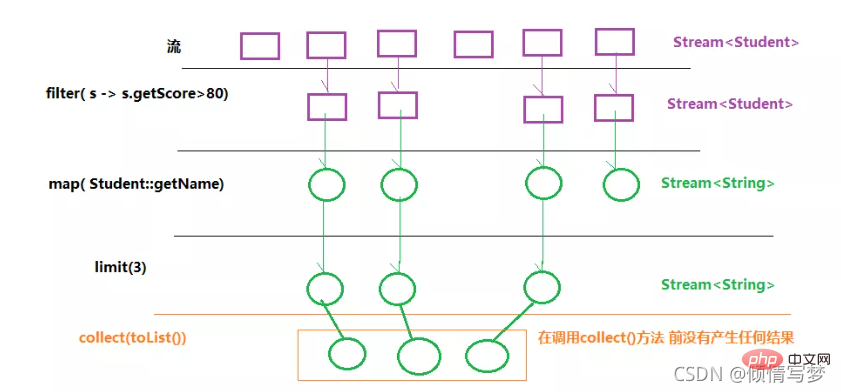
Stream可以由陣列或集合創建,對流的操作分為兩種:
#中間操作,每次傳回一個新的流,可以有多個。
終端機操作,每個流只能進行一次終端操作,終端操作結束後流無法再次使用。終端操作會產生一個新的集合或值。
特性:
不是資料結構,不會儲存資料。
不會修改原來的資料來源,它會將操作後的資料儲存到另一個物件中。 (保留意見:畢竟peek方法可以修改流中元素)
惰性求值,流在中間處理過程中,只是對操作進行了記錄,並不會立即執行,需要等到執行終止操作的時候才會進行實際的計算。
二、分類
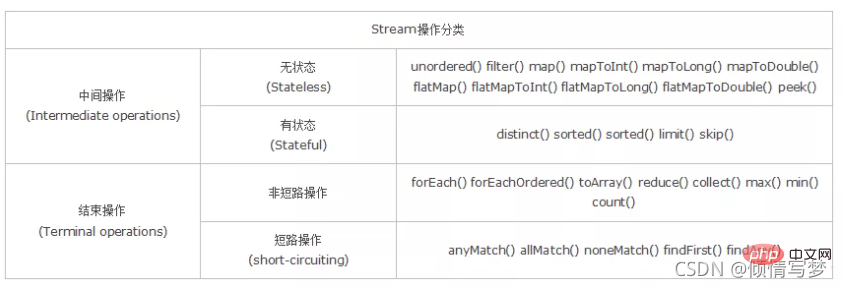
無狀態:指元素的處理不受先前元素的影響;
有狀態:指該運算只有拿到所有元素之後才能繼續下去。
非短路運算:指必須處理所有元素才能得到最終結果;
短路運算:指遇到某些符合條件的元素就可以得到最終結果,如A || B,只要A為true,則無需判斷B的結果。
三、Stream的創建
Stream可以透過集合陣列來建立。
1、透過java.util.Collection.stream() 方法用集合建立流
List<string> list = Arrays.asList("a", "b", "c");// 创建一个顺序流
Stream<string> stream = list.stream();// 创建一个并行流
Stream<string> parallelStream = list.parallelStream();</string></string></string>2、使用java.util.Arrays.stream(T[]array)方法用陣列建立流
int[] array={1,3,5,6,8};IntStream stream = Arrays.stream(array);3、使用Stream的靜態方法:of()、iterate()、generate()
Stream<integer> stream = Stream.of(1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6); Stream<integer> stream2 = Stream.iterate(0, (x) -> x + 3).limit(4);stream2.forEach(System.out::println); Stream<double> stream3 = Stream.generate(Math::random).limit(3);stream3.forEach(System.out::println);</double></integer></integer>
輸出結果:
0 3 6 90.67961569092719940.19143142088542830.8116932592396652
stream和parallelStream的簡單區分:stream是順序流,由主執行緒依序對流執行操作,而parallelStream是並行流,內部以多執行緒並行執行的方式對流進行操作,但前提是流中的資料處理沒有順序要求。例如篩選集合中的奇數,兩者的處理不同之處: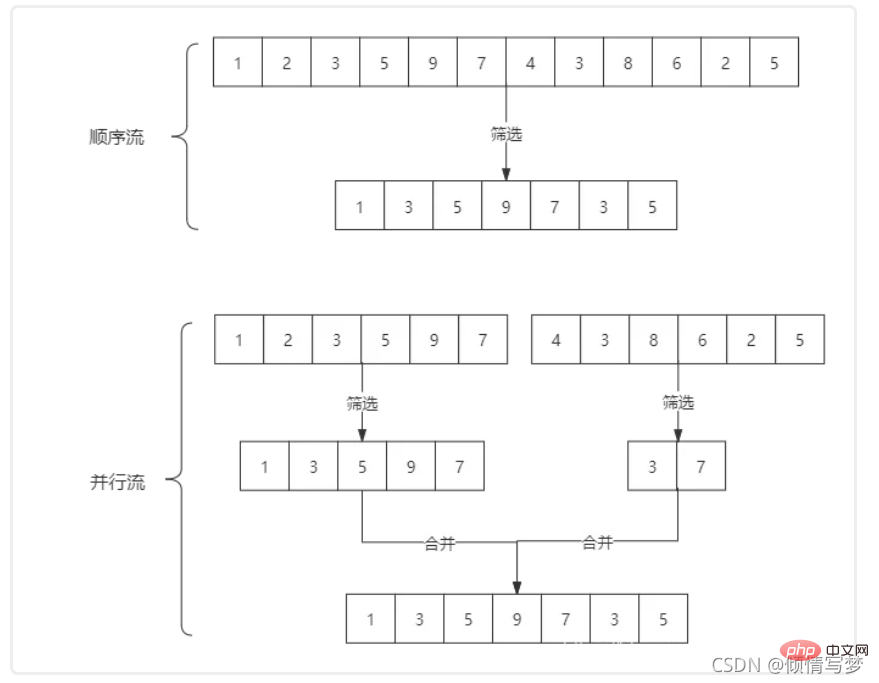
如果流中的資料量夠大,並行流可以加快處速度。
除了直接建立並行流,還可以透過parallel()把順序流轉換成並行流:
Optional<integer> findFirst = list.stream().parallel().filter(x->x>6).findFirst();</integer>
四、Stream API簡介
先贴上几个案例,水平高超的同学可以挑战一下:从员工集合中筛选出salary大于8000的员工,并放置到新的集合里。统计员工的最高薪资、平均薪资、薪资之和。将员工按薪资从高到低排序,同样薪资者年龄小者在前。将员工按性别分类,将员工按性别和地区分类,将员工按薪资是否高于8000分为两部分。用传统的迭代处理也不是很难,但代码就显得冗余了,跟Stream相比高下立判。
前提:員工類別
static List<person> personList = new ArrayList<person>();private static void initPerson() {
personList.add(new Person("张三", 8, 3000));
personList.add(new Person("李四", 18, 5000));
personList.add(new Person("王五", 28, 7000));
personList.add(new Person("孙六", 38, 9000));}</person></person>1、遍歷/匹配(foreach/find/match)
Stream也是支援類似集合的遍歷和匹配元素的,只是Stream中的元素是以Optional類型存在的。 Stream的遍歷、配對非常簡單。
// import已省略,请自行添加,后面代码亦是
public class StreamTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<integer> list = Arrays.asList(7, 6, 9, 3, 8, 2, 1);
// 遍历输出符合条件的元素
list.stream().filter(x -> x > 6).forEach(System.out::println);
// 匹配第一个
Optional<integer> findFirst = list.stream().filter(x -> x > 6).findFirst();
// 匹配任意(适用于并行流)
Optional<integer> findAny = list.parallelStream().filter(x -> x > 6).findAny();
// 是否包含符合特定条件的元素
boolean anyMatch = list.stream().anyMatch(x -> x <h3 id="按条件匹配filter">2、按条件匹配filter</h3>
<p><img src="/static/imghw/default1.png" data-src="https://img.php.cn/upload/article/000/000/067/c32799257ddfee7ae65dfaf7bce4b27c-5.png" class="lazy" alt="在这里插入Java8中Stream詳細用法歸納描述"></p>
<p><strong>(1)筛选员工中已满18周岁的人,并形成新的集合</strong></p>
<pre class="brush:php;toolbar:false">/**
* 筛选员工中已满18周岁的人,并形成新的集合
* @思路
* List<person> list = new ArrayList<person>();
* for(Person person : personList) {
* if(person.getAge() >= 18) {
* list.add(person);
* }
* }
*/
private static void filter01() {
initPerson();
List<person> collect = personList.stream().filter(x -> x.getAge()>=18).collect(Collectors.toList());
System.out.println(collect);}</person></person></person>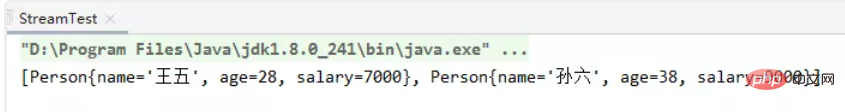
(2)自定义条件匹配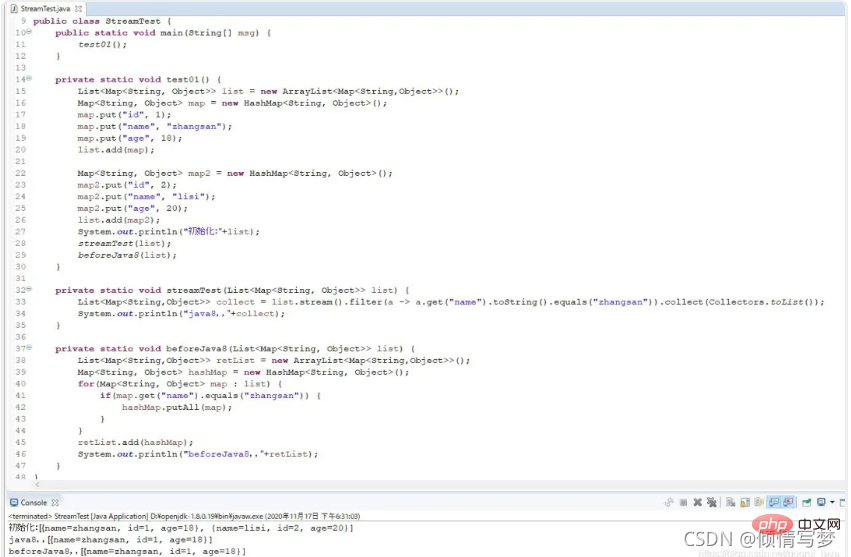
3、聚合max、min、count
(1)获取String集合中最长的元素
/**
* 获取String集合中最长的元素
* @思路
* List<string> list = Arrays.asList("zhangsan", "lisi", "wangwu", "sunliu");
* String max = "";
* int length = 0;
* int tempLength = 0;
* for(String str : list) {
* tempLength = str.length();
* if(tempLength > length) {
* length = str.length();
* max = str;
* }
* }
* @return zhangsan
*/
private static void test02() {
List<string> list = Arrays.asList("zhangsan", "lisi", "wangwu", "sunliu");
Comparator super String> comparator = Comparator.comparing(String::length);
Optional<string> max = list.stream().max(comparator);
System.out.println(max);}</string></string></string>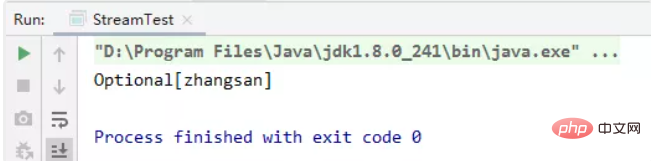
(2)获取Integer集合中的最大值
//获取Integer集合中的最大值
private static void test05() {
List<integer> list = Arrays.asList(1, 17, 27, 7);
Optional<integer> max = list.stream().max(Integer::compareTo);
// 自定义排序
Optional<integer> max2 = list.stream().max(new Comparator<integer>() {
@Override
public int compare(Integer o1, Integer o2) {
return o1.compareTo(o2);
}
});
System.out.println(max2);}</integer></integer></integer></integer>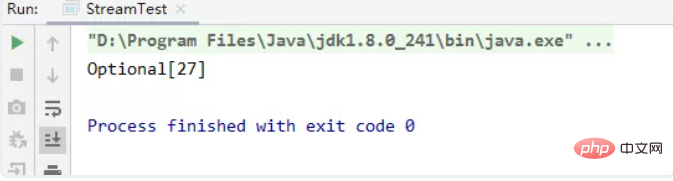
//获取员工中年龄最大的人
private static void test06() {
initPerson();
Comparator super Person> comparator = Comparator.comparingInt(Person::getAge);
Optional<person> max = personList.stream().max(comparator);
System.out.println(max);}</person>(3)获取员工中年龄最大的人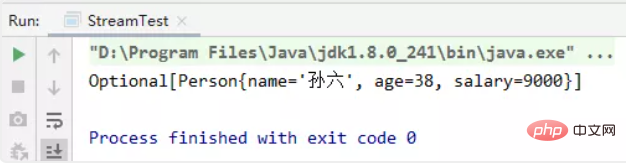
(4)计算integer集合中大于10的元素的个数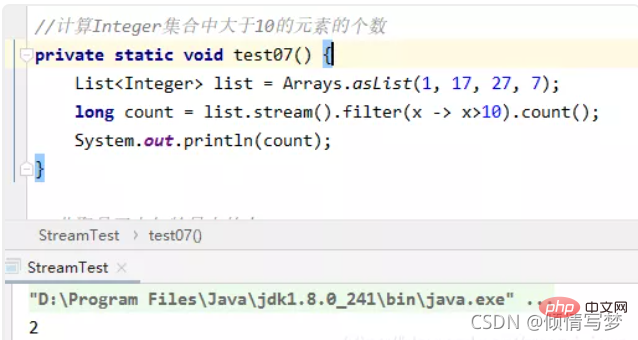
4、map与flatMap
map:接收一个函数作为参数,该函数会被应用到每个元素上,并将其映射成一个新的元素。
flatMap:接收一个函数作为参数,将流中的每个值都换成另一个流,然后把所有流连接成一个流。
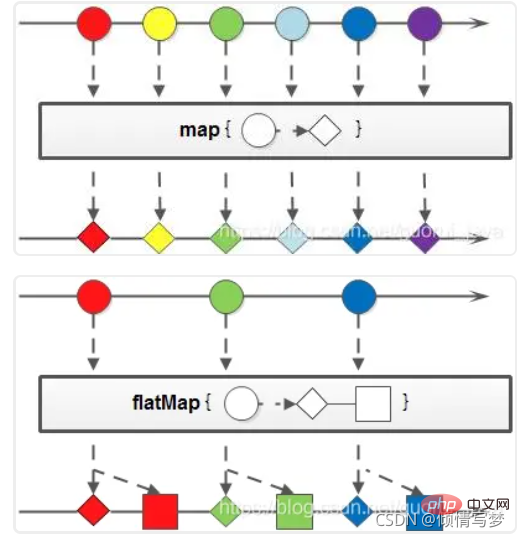
(1)字符串大写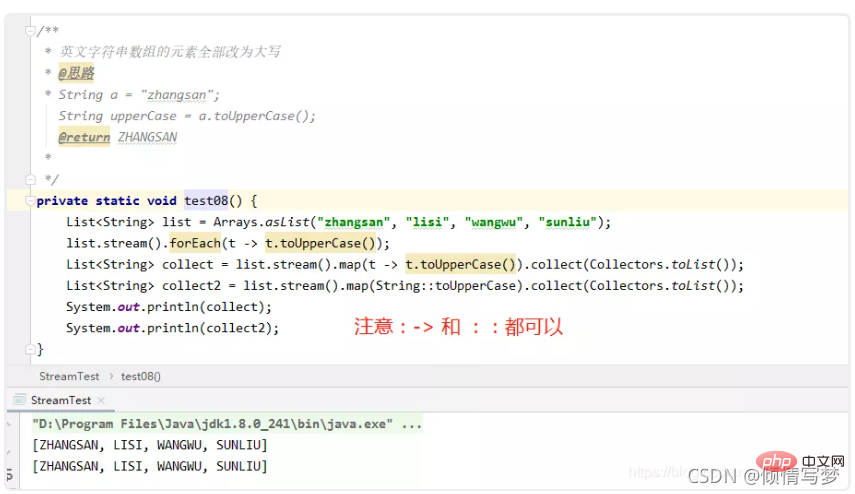
(2)整数数组每个元素+3
/**
* 整数数组每个元素+3
* @思路
* List<integer> list = Arrays.asList(1, 17, 27, 7);
List<integer> list2 = new ArrayList<integer>();
for(Integer num : list) {
list2.add(num + 3);
}
@return [4, 20, 30, 10]
*/
private static void test09() {
List<integer> list = Arrays.asList(1, 17, 27, 7);
List<integer> collect = list.stream().map(x -> x + 3).collect(Collectors.toList());
System.out.println(collect);}</integer></integer></integer></integer></integer>(3)公司效益好,每人涨2000
/**
* 公司效益好,每人涨2000
*
*/
private static void test10() {
initPerson();
List<person> collect = personList.stream().map(x -> {
x.setAge(x.getSalary()+2000);
return x;
}).collect(Collectors.toList());
System.out.println(collect);}</person>(4)将两个字符数组合并成一个新的字符数组
/**
* 将两个字符数组合并成一个新的字符数组
*
*/
private static void test11() {
String[] arr = {"z, h, a, n, g", "s, a, n"};
List<string> list = Arrays.asList(arr);
System.out.println(list);
List<string> collect = list.stream().flatMap(x -> {
String[] array = x.split(",");
Stream<string> stream = Arrays.stream(array);
return stream;
}).collect(Collectors.toList());
System.out.println(collect);}</string></string></string>(5)将两个字符数组合并成一个新的字符数组
/**
* 将两个字符数组合并成一个新的字符数组
* @return [z, h, a, n, g, s, a, n]
*/
private static void test11() {
String[] arr = {"z, h, a, n, g", "s, a, n"};
List<string> list = Arrays.asList(arr);
List<string> collect = list.stream().flatMap(x -> {
String[] array = x.split(",");
Stream<string> stream = Arrays.stream(array);
return stream;
}).collect(Collectors.toList());
System.out.println(collect);}</string></string></string>5、规约reduce
归约,也称缩减,顾名思义,是把一个流缩减成一个值,能实现对集合求和、求乘积和求最值操作。
(1)求Integer集合的元素之和、乘积和最大值
/**
* 求Integer集合的元素之和、乘积和最大值
*
*/
private static void test13() {
List<integer> list = Arrays.asList(1, 2, 3, 4);
//求和
Optional<integer> reduce = list.stream().reduce((x,y) -> x+ y);
System.out.println("求和:"+reduce);
//求积
Optional<integer> reduce2 = list.stream().reduce((x,y) -> x * y);
System.out.println("求积:"+reduce2);
//求最大值
Optional<integer> reduce3 = list.stream().reduce((x,y) -> x>y?x:y);
System.out.println("求最大值:"+reduce3);}</integer></integer></integer></integer>(2)求所有员工的工资之和和最高工资
/*
* 求所有员工的工资之和和最高工资
*/
private static void test14() {
initPerson();
Optional<integer> reduce = personList.stream().map(Person :: getSalary).reduce(Integer::sum);
Optional<integer> reduce2 = personList.stream().map(Person :: getSalary).reduce(Integer::max);
System.out.println("工资之和:"+reduce);
System.out.println("最高工资:"+reduce2);}</integer></integer>6、收集(toList、toSet、toMap)
取出大于18岁的员工转为map
/**
* 取出大于18岁的员工转为map
*
*/
private static void test15() {
initPerson();
Map<string> collect = personList.stream().filter(x -> x.getAge() > 18).collect(Collectors.toMap(Person::getName, y -> y));
System.out.println(collect);}</string>7、collect
Collectors提供了一系列用于数据统计的静态方法:
计数: count
平均值: averagingInt、 averagingLong、 averagingDouble
最值: maxBy、 minBy
求和: summingInt、 summingLong、 summingDouble
统计以上所有: summarizingInt、 summarizingLong、 summarizingDouble
/**
* 统计员工人数、平均工资、工资总额、最高工资
*/
private static void test01(){
//统计员工人数
Long count = personList.stream().collect(Collectors.counting());
//求平均工资
Double average = personList.stream().collect(Collectors.averagingDouble(Person::getSalary));
//求最高工资
Optional<integer> max = personList.stream().map(Person::getSalary).collect(Collectors.maxBy(Integer::compare));
//求工资之和
Integer sum = personList.stream().collect(Collectors.summingInt(Person::getSalary));
//一次性统计所有信息
DoubleSummaryStatistics collect = personList.stream().collect(Collectors.summarizingDouble(Person::getSalary));
System.out.println("统计员工人数:"+count);
System.out.println("求平均工资:"+average);
System.out.println("求最高工资:"+max);
System.out.println("求工资之和:"+sum);
System.out.println("一次性统计所有信息:"+collect);}</integer>8、分组(partitioningBy/groupingBy)
分区:将stream按条件分为两个 Map,比如员工按薪资是否高于8000分为两部分。
分组:将集合分为多个Map,比如员工按性别分组。有单级分组和多级分组。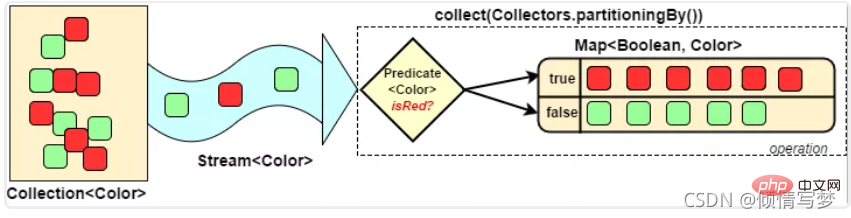
将员工按薪资是否高于8000分为两部分;将员工按性别和地区分组
public class StreamTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
personList.add(new Person("zhangsan",25, 3000, "male", "tieling"));
personList.add(new Person("lisi",27, 5000, "male", "tieling"));
personList.add(new Person("wangwu",29, 7000, "female", "tieling"));
personList.add(new Person("sunliu",26, 3000, "female", "dalian"));
personList.add(new Person("yinqi",27, 5000, "male", "dalian"));
personList.add(new Person("guba",21, 7000, "female", "dalian"));
// 将员工按薪资是否高于8000分组
Map<boolean>> part = personList.stream().collect(Collectors.partitioningBy(x -> x.getSalary() > 8000));
// 将员工按性别分组
Map<string>> group = personList.stream().collect(Collectors.groupingBy(Person::getSex));
// 将员工先按性别分组,再按地区分组
Map<string>>> group2 = personList.stream().collect(Collectors.groupingBy(Person::getSex, Collectors.groupingBy(Person::getArea)));
System.out.println("员工按薪资是否大于8000分组情况:" + part);
System.out.println("员工按性别分组情况:" + group);
System.out.println("员工按性别、地区:" + group2);
}}</string></string></boolean>9、连接joining
joining可以将stream中的元素用特定的连接符(没有的话,则直接连接)连接成一个字符串。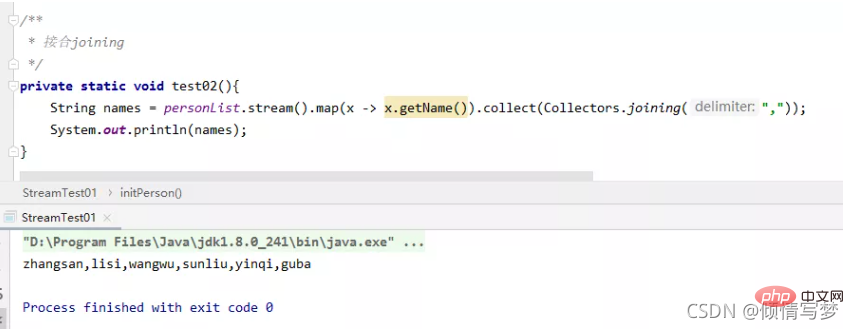
10、排序sorted
将员工按工资由高到低(工资一样则按年龄由大到小)排序
private static void test04(){
// 按工资升序排序(自然排序)
List<string> newList = personList.stream().sorted(Comparator.comparing(Person::getSalary)).map(Person::getName)
.collect(Collectors.toList());
// 按工资倒序排序
List<string> newList2 = personList.stream().sorted(Comparator.comparing(Person::getSalary).reversed())
.map(Person::getName).collect(Collectors.toList());
// 先按工资再按年龄升序排序
List<string> newList3 = personList.stream()
.sorted(Comparator.comparing(Person::getSalary).thenComparing(Person::getAge)).map(Person::getName)
.collect(Collectors.toList());
// 先按工资再按年龄自定义排序(降序)
List<string> newList4 = personList.stream().sorted((p1, p2) -> {
if (p1.getSalary() == p2.getSalary()) {
return p2.getAge() - p1.getAge();
} else {
return p2.getSalary() - p1.getSalary();
}
}).map(Person::getName).collect(Collectors.toList());
System.out.println("按工资升序排序:" + newList);
System.out.println("按工资降序排序:" + newList2);
System.out.println("先按工资再按年龄升序排序:" + newList3);
System.out.println("先按工资再按年龄自定义降序排序:" + newList4);}</string></string></string></string>11、提取/组合
流也可以进行合并、去重、限制、跳过等操作。
private static void test05(){
String[] arr1 = { "a", "b", "c", "d" };
String[] arr2 = { "d", "e", "f", "g" };
Stream<string> stream1 = Stream.of(arr1);
Stream<string> stream2 = Stream.of(arr2);
// concat:合并两个流 distinct:去重
List<string> newList = Stream.concat(stream1, stream2).distinct().collect(Collectors.toList());
// limit:限制从流中获得前n个数据
List<integer> collect = Stream.iterate(1, x -> x + 2).limit(10).collect(Collectors.toList());
// skip:跳过前n个数据
List<integer> collect2 = Stream.iterate(1, x -> x + 2).skip(1).limit(5).collect(Collectors.toList());
System.out.println("流合并:" + newList);
System.out.println("limit:" + collect);
System.out.println("skip:" + collect2);}</integer></integer></string></string></string>12、读取文件的流操作
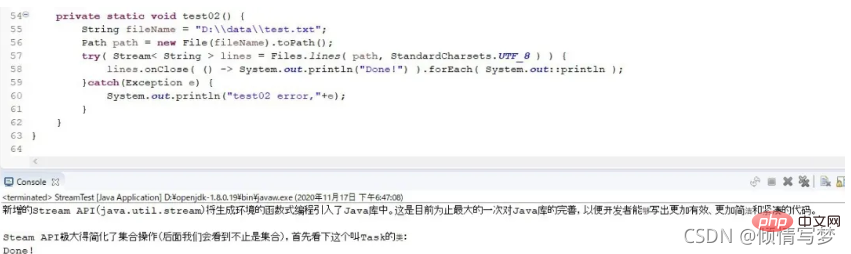
13、计算两个list中的差集
//计算两个list中的差集 List<string> reduce1 = allList.stream().filter(item -> !wList.contains(item)).collect(Collectors.toList());</string>
推荐学习:《java视频教程》
以上是Java8中Stream詳細用法歸納的詳細內容。更多資訊請關注PHP中文網其他相關文章!

熱AI工具

Undresser.AI Undress
人工智慧驅動的應用程序,用於創建逼真的裸體照片

AI Clothes Remover
用於從照片中去除衣服的線上人工智慧工具。

Undress AI Tool
免費脫衣圖片

Clothoff.io
AI脫衣器

Video Face Swap
使用我們完全免費的人工智慧換臉工具,輕鬆在任何影片中換臉!

熱門文章

熱工具

記事本++7.3.1
好用且免費的程式碼編輯器

SublimeText3漢化版
中文版,非常好用

禪工作室 13.0.1
強大的PHP整合開發環境

Dreamweaver CS6
視覺化網頁開發工具

SublimeText3 Mac版
神級程式碼編輯軟體(SublimeText3)
 突破或從Java 8流返回?
Feb 07, 2025 pm 12:09 PM
突破或從Java 8流返回?
Feb 07, 2025 pm 12:09 PM
Java 8引入了Stream API,提供了一種強大且表達力豐富的處理數據集合的方式。然而,使用Stream時,一個常見問題是:如何從forEach操作中中斷或返回? 傳統循環允許提前中斷或返回,但Stream的forEach方法並不直接支持這種方式。本文將解釋原因,並探討在Stream處理系統中實現提前終止的替代方法。 延伸閱讀: Java Stream API改進 理解Stream forEach forEach方法是一個終端操作,它對Stream中的每個元素執行一個操作。它的設計意圖是處
 PHP:網絡開發的關鍵語言
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:08 AM
PHP:網絡開發的關鍵語言
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:08 AM
PHP是一種廣泛應用於服務器端的腳本語言,特別適合web開發。 1.PHP可以嵌入HTML,處理HTTP請求和響應,支持多種數據庫。 2.PHP用於生成動態網頁內容,處理表單數據,訪問數據庫等,具有強大的社區支持和開源資源。 3.PHP是解釋型語言,執行過程包括詞法分析、語法分析、編譯和執行。 4.PHP可以與MySQL結合用於用戶註冊系統等高級應用。 5.調試PHP時,可使用error_reporting()和var_dump()等函數。 6.優化PHP代碼可通過緩存機制、優化數據庫查詢和使用內置函數。 7
 PHP與Python:了解差異
Apr 11, 2025 am 12:15 AM
PHP與Python:了解差異
Apr 11, 2025 am 12:15 AM
PHP和Python各有優勢,選擇應基於項目需求。 1.PHP適合web開發,語法簡單,執行效率高。 2.Python適用於數據科學和機器學習,語法簡潔,庫豐富。
 PHP與其他語言:比較
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:19 AM
PHP與其他語言:比較
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:19 AM
PHP適合web開發,特別是在快速開發和處理動態內容方面表現出色,但不擅長數據科學和企業級應用。與Python相比,PHP在web開發中更具優勢,但在數據科學領域不如Python;與Java相比,PHP在企業級應用中表現較差,但在web開發中更靈活;與JavaScript相比,PHP在後端開發中更簡潔,但在前端開發中不如JavaScript。
 PHP與Python:核心功能
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:16 AM
PHP與Python:核心功能
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:16 AM
PHP和Python各有優勢,適合不同場景。 1.PHP適用於web開發,提供內置web服務器和豐富函數庫。 2.Python適合數據科學和機器學習,語法簡潔且有強大標準庫。選擇時應根據項目需求決定。
 PHP的影響:網絡開發及以後
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:10 AM
PHP的影響:網絡開發及以後
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:10 AM
PHPhassignificantlyimpactedwebdevelopmentandextendsbeyondit.1)ItpowersmajorplatformslikeWordPressandexcelsindatabaseinteractions.2)PHP'sadaptabilityallowsittoscaleforlargeapplicationsusingframeworkslikeLaravel.3)Beyondweb,PHPisusedincommand-linescrip
 PHP:許多網站的基礎
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:07 AM
PHP:許多網站的基礎
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:07 AM
PHP成為許多網站首選技術棧的原因包括其易用性、強大社區支持和廣泛應用。 1)易於學習和使用,適合初學者。 2)擁有龐大的開發者社區,資源豐富。 3)廣泛應用於WordPress、Drupal等平台。 4)與Web服務器緊密集成,簡化開發部署。
 PHP與Python:用例和應用程序
Apr 17, 2025 am 12:23 AM
PHP與Python:用例和應用程序
Apr 17, 2025 am 12:23 AM
PHP適用於Web開發和內容管理系統,Python適合數據科學、機器學習和自動化腳本。 1.PHP在構建快速、可擴展的網站和應用程序方面表現出色,常用於WordPress等CMS。 2.Python在數據科學和機器學習領域表現卓越,擁有豐富的庫如NumPy和TensorFlow。






