在寫Go 的過程中經常對比這兩種語言的特性,踩了不少坑,也發現了不少有意思的地方,下面本篇就來聊聊Go 自帶的HttpClient 的超時機制,希望對大家有幫助。

在介紹Go 的HttpClient 逾時機制之前,我們先來看看Java 是如何實現超時的。 【相關推薦:Go影片教學】
寫一個Java 原生的HttpClient,設定連線逾時、讀取逾時時間分別對應到底層的方法分別是:
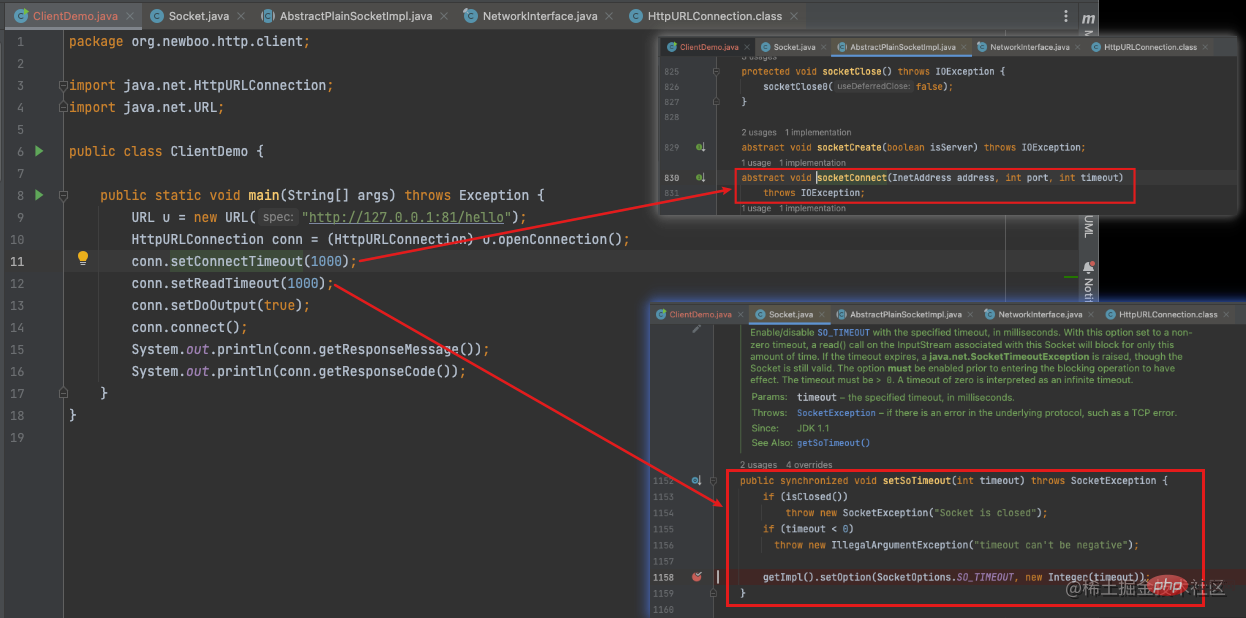
#再追溯到JVM 原始碼,發現是系統呼叫的封裝,其實不光是Java,大部分的程式語言都藉助了作業系統提供的逾時能力。
然而 Go 的 HttpClient 卻提供了另一個超時機制,挺有意思,我們來盤一盤。但在開始之前,我們先來了解 Go 的 Context。
Context 是什麼?
根據 Go 原始碼的註解:
// A Context carries a deadline, a cancellation signal, and other values across // API boundaries. // Context's methods may be called by multiple goroutines simultaneously.
Context 簡單來說是一個可以攜帶超時時間、取消信號和其他數據的接口,Context 的方法會被多個協程同時調用。
Context 有點類似Java 的ThreadLocal,可以在線程中傳遞數據,但又不完全相同,它是顯示傳遞,ThreadLocal 是隱式傳遞,除了傳遞數據之外,Context 還能攜帶超時時間、取消信號。
Context 只是定義了接口,具體的實現在Go 中提供了幾個:
#針對Context 的三個特性,可以透過Go 提供的Context 實作以及原始碼中的範例來進一步了解下。
Context 三個特性範例
這部分的範例來自Go 的源碼,位於src/context/example_test.go
使用context.WithValue 來攜帶,使用 Value 來取值,原始碼中的例子如下:
// 来自 src/context/example_test.go
func ExampleWithValue() {
type favContextKey string
f := func(ctx context.Context, k favContextKey) {
if v := ctx.Value(k); v != nil {
fmt.Println("found value:", v)
return
}
fmt.Println("key not found:", k)
}
k := favContextKey("language")
ctx := context.WithValue(context.Background(), k, "Go")
f(ctx, k)
f(ctx, favContextKey("color"))
// Output:
// found value: Go
// key not found: color
}先起一個協程執行一個死循環,不停地往channel 中寫數據,同時監聽ctx. Done() 的事件
// 来自 src/context/example_test.go
gen := func(ctx context.Context) <-chan int {
dst := make(chan int)
n := 1
go func() {
for {
select {
case <-ctx.Done():
return // returning not to leak the goroutine
case dst <- n:
n++
}
}
}()
return dst
}然後透過context.WithCancel 產生一個可取消的Context,傳入gen 方法,直到gen 傳回5 時,呼叫cancel 取消gen 方法的執行。
// 来自 src/context/example_test.go
ctx, cancel := context.WithCancel(context.Background())
defer cancel() // cancel when we are finished consuming integers
for n := range gen(ctx) {
fmt.Println(n)
if n == 5 {
break
}
}
// Output:
// 1
// 2
// 3
// 4
// 5這麼看起來,可以簡單理解為在一個協程的循環中埋入結束標誌,另一個協程去設置這個結束標誌。
有了cancel 的鋪墊,超時就好理解了,cancel 是手動取消,超時是自動取消,只要起一個定時的協程,到時間後執行cancel 即可。
設定逾時時間有2種方式:context.WithTimeout 與context.WithDeadline,WithTimeout 是設定一段時間後,WithDeadline 是設定一個截止時間點,WithTimeout最後也會轉換為WithDeadline。
// 来自 src/context/example_test.go
func ExampleWithTimeout() {
// Pass a context with a timeout to tell a blocking function that it
// should abandon its work after the timeout elapses.
ctx, cancel := context.WithTimeout(context.Background(), shortDuration)
defer cancel()
select {
case <-time.After(1 * time.Second):
fmt.Println("overslept")
case <-ctx.Done():
fmt.Println(ctx.Err()) // prints "context deadline exceeded"
}
// Output:
// context deadline exceeded
}基於Context 可以設定任意程式碼段執行的逾時機制,就可以設計一個脫離作業系統能力的請求超時能力。
逾時機制簡介
看一下Go 的HttpClient 逾時設定說明:
client := http.Client{
Timeout: 10 * time.Second,
}
// 来自 src/net/http/client.go
type Client struct {
// ... 省略其他字段
// Timeout specifies a time limit for requests made by this
// Client. The timeout includes connection time, any
// redirects, and reading the response body. The timer remains
// running after Get, Head, Post, or Do return and will
// interrupt reading of the Response.Body.
//
// A Timeout of zero means no timeout.
//
// The Client cancels requests to the underlying Transport
// as if the Request's Context ended.
//
// For compatibility, the Client will also use the deprecated
// CancelRequest method on Transport if found. New
// RoundTripper implementations should use the Request's Context
// for cancellation instead of implementing CancelRequest.
Timeout time.Duration
}翻譯一下註解: Timeout 包含了連線、redirect、讀取資料的時間,計時器會在Timeout 時間後打斷資料的讀取,設為0則沒有逾時限制。
也就是說這個超時是一個請求的總體超時時間,而不必再分別去設定連線超時、讀取超時等等。
這對使用者來說可能是一個更好的選擇,大部分場景,使用者不必關心到底是哪部分導致的超時,而只是想這個 HTTP 請求整體什麼時候能返回。
超時機制底層原理
以一個最簡單的例子來闡述超時機制的底層原理。
这里我起了一个本地服务,用 Go HttpClient 去请求,超时时间设置为 10 分钟,建议使 Debug 时设置长一点,否则可能超时导致无法走完全流程。
client := http.Client{
Timeout: 10 * time.Minute,
}
resp, err := client.Get("http://127.0.0.1:81/hello")// 来自 src/net/http/client.go deadline = c.deadline()
// 来自 src/net/http/client.go stopTimer, didTimeout := setRequestCancel(req, rt, deadline)
这里返回的 stopTimer 就是可以手动 cancel 的方法,didTimeout 是判断是否超时的方法。这两个可以理解为回调方法,调用 stopTimer() 可以手动 cancel,调用 didTimeout() 可以返回是否超时。
设置的主要代码其实就是将请求的 Context 替换为 cancelCtx,后续所有的操作都将携带这个 cancelCtx:
// 来自 src/net/http/client.go
var cancelCtx func()
if oldCtx := req.Context(); timeBeforeContextDeadline(deadline, oldCtx) {
req.ctx, cancelCtx = context.WithDeadline(oldCtx, deadline)
}同时,再起一个定时器,当超时时间到了之后,将 timedOut 设置为 true,再调用 doCancel(),doCancel() 是调用真正 RoundTripper (代表一个 HTTP 请求事务)的 CancelRequest,也就是取消请求,这个跟实现有关。
// 来自 src/net/http/client.go
timer := time.NewTimer(time.Until(deadline))
var timedOut atomicBool
go func() {
select {
case <-initialReqCancel:
doCancel()
timer.Stop()
case <-timer.C:
timedOut.setTrue()
doCancel()
case <-stopTimerCh:
timer.Stop()
}
}()Go 默认 RoundTripper CancelRequest 实现是关闭这个连接
// 位于 src/net/http/transport.go
// CancelRequest cancels an in-flight request by closing its connection.
// CancelRequest should only be called after RoundTrip has returned.
func (t *Transport) CancelRequest(req *Request) {
t.cancelRequest(cancelKey{req}, errRequestCanceled)
}// 位于 src/net/http/transport.go
for {
select {
case <-ctx.Done():
req.closeBody()
return nil, ctx.Err()
default:
}
// ...
pconn, err := t.getConn(treq, cm)
// ...
}代码的开头监听 ctx.Done,如果超时则直接返回,使用 for 循环主要是为了请求的重试。
后续的 getConn 是阻塞的,代码比较长,挑重点说,先看看有没有空闲连接,如果有则直接返回
// 位于 src/net/http/transport.go
// Queue for idle connection.
if delivered := t.queueForIdleConn(w); delivered {
// ...
return pc, nil
}如果没有空闲连接,起个协程去异步建立,建立成功再通知主协程
// 位于 src/net/http/transport.go // Queue for permission to dial. t.queueForDial(w)
再接着是一个 select 等待连接建立成功、超时或者主动取消,这就实现了在连接过程中的超时
// 位于 src/net/http/transport.go
// Wait for completion or cancellation.
select {
case <-w.ready:
// ...
return w.pc, w.err
case <-req.Cancel:
return nil, errRequestCanceledConn
case <-req.Context().Done():
return nil, req.Context().Err()
case err := <-cancelc:
if err == errRequestCanceled {
err = errRequestCanceledConn
}
return nil, err
}在上一条连接建立的时候,每个链接还偷偷起了两个协程,一个负责往连接中写入数据,另一个负责读数据,他们都监听了相应的 channel。
// 位于 src/net/http/transport.go go pconn.readLoop() go pconn.writeLoop()
其中 wirteLoop 监听来自主协程的数据,并往连接中写入
// 位于 src/net/http/transport.go
func (pc *persistConn) writeLoop() {
defer close(pc.writeLoopDone)
for {
select {
case wr := <-pc.writech:
startBytesWritten := pc.nwrite
err := wr.req.Request.write(pc.bw, pc.isProxy, wr.req.extra, pc.waitForContinue(wr.continueCh))
// ...
if err != nil {
pc.close(err)
return
}
case <-pc.closech:
return
}
}
}同理,readLoop 读取响应数据,并写回主协程。读与写的过程中如果超时了,连接将被关闭,报错退出。
超时机制小结
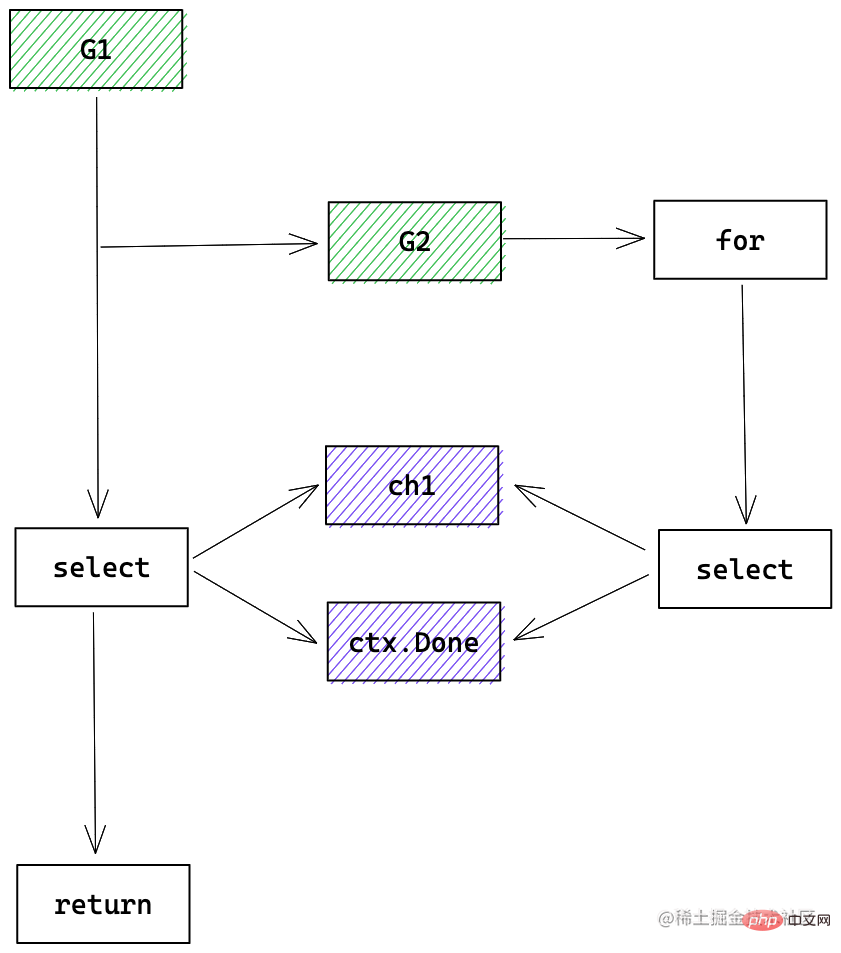
Go 的这种请求超时机制,可随时终止请求,可设置整个请求的超时时间。其实现主要依赖协程、channel、select 机制的配合。总结出套路是:
以循环任务为例
Java 能实现这种超时机制吗
直接说结论:暂时不行。
首先 Java 的线程太重,像 Go 这样一次请求开了这么多协程,换成线程性能会大打折扣。
其次 Go 的 channel 虽然和 Java 的阻塞队列类似,但 Go 的 select 是多路复用机制,Java 暂时无法实现,即无法监听多个队列是否有数据到达。所以综合来看 Java 暂时无法实现类似机制。
本文介绍了 Go 另类且有趣的 HTTP 超时机制,并且分析了底层实现原理,归纳出了这种机制的套路,如果我们写 Go 代码,也可以如此模仿,让代码更 Go。
原文地址:https://juejin.cn/post/7166201276198289445
更多编程相关知识,请访问:编程视频!!
以上是聊聊Golang自帶的HttpClient超時機制的詳細內容。更多資訊請關注PHP中文網其他相關文章!




