Java Spring Bean生命週期管理的範例分析
Spring Bean的生命週期管理
一、Spring Bean的生命週期
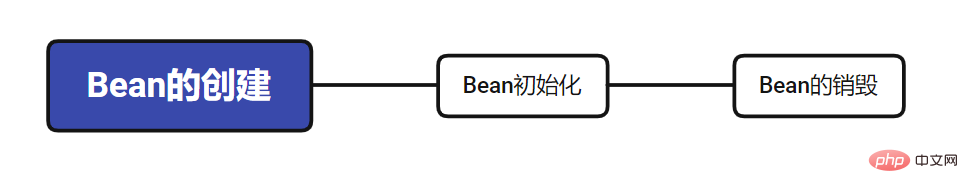
通过以下方式来指定Bean的初始化和销毁方法, 当Bean为单例时,Bean归Spring容器管理,Spring容器关闭,就会调用Bean的销毁方法 当Bean为多例时,Bean不归Spring容器管理,Spring容器关闭,不会调用Bean的销毁方法
二、透過@Bean的參數(initMethod ,destroyMethod)指定Bean的初始化和銷毀方法
1、專案結構
public class Person {
public Person(){
System.out.println("Person 创建了...");
}
public void init(){
System.out.println("Person 初始化了...");
}
public void destroy(){
System.out.println("Person 被销毁了...");
}
}登入後複製
3、Bean註冊配置類別(單一實例)public class Person {
public Person(){
System.out.println("Person 创建了...");
}
public void init(){
System.out.println("Person 初始化了...");
}
public void destroy(){
System.out.println("Person 被销毁了...");
}
}import com.dashu.bean.Person;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.*;
@Configuration
public class BeanConfig {
@Bean(initMethod = "init",destroyMethod = "destroy")
public Person person(){
return new Person();
}
}登入後複製
4、測試類別import com.dashu.bean.Person;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.*;
@Configuration
public class BeanConfig {
@Bean(initMethod = "init",destroyMethod = "destroy")
public Person person(){
return new Person();
}
}import com.dashu.bean.Person;
import com.dashu.config.BeanConfig;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//加载配置类获取容器
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext annotationConfigApplicationContext = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(BeanConfig.class);
//获取Bean
Person bean = annotationConfigApplicationContext.getBean(Person.class);
//关闭容器
annotationConfigApplicationContext.close();
}
}登入後複製
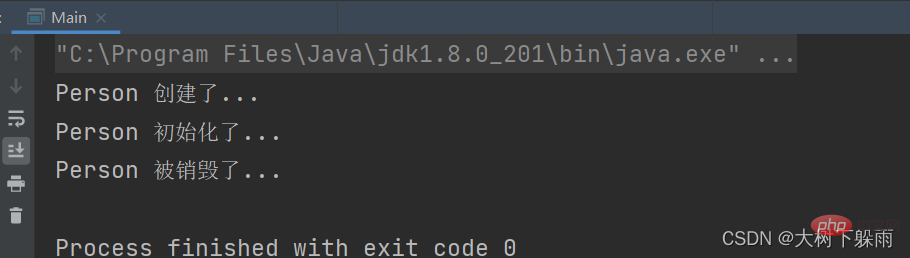
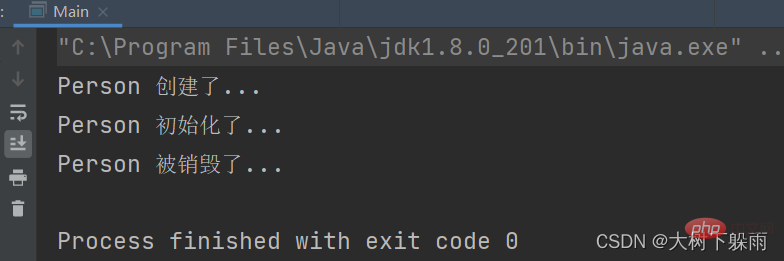
5、測試結果import com.dashu.bean.Person;
import com.dashu.config.BeanConfig;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//加载配置类获取容器
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext annotationConfigApplicationContext = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(BeanConfig.class);
//获取Bean
Person bean = annotationConfigApplicationContext.getBean(Person.class);
//关闭容器
annotationConfigApplicationContext.close();
}
}
import com.dashu.bean.Person;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.*;
@Configuration
public class BeanConfig {
@Scope("prototype")
@Bean(initMethod = "init",destroyMethod = "destroy")
public Person person(){
return new Person();
}
}登入後複製
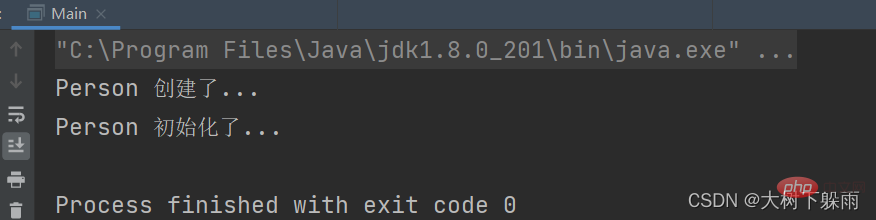
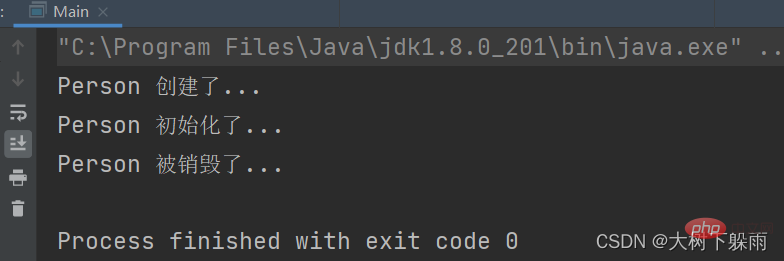
7、測試結果import com.dashu.bean.Person;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.*;
@Configuration
public class BeanConfig {
@Scope("prototype")
@Bean(initMethod = "init",destroyMethod = "destroy")
public Person person(){
return new Person();
}
}
import org.springframework.beans.factory.DisposableBean;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.InitializingBean;
public class Person implements InitializingBean, DisposableBean {
public Person(){
System.out.println("Person 创建了...");
}
@Override
public void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception {
System.out.println("Person 初始化了...");
}
@Override
public void destroy() throws Exception {
System.out.println("Person 被销毁了...");
}
}登入後複製
2、Bean註冊配置類別import org.springframework.beans.factory.DisposableBean;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.InitializingBean;
public class Person implements InitializingBean, DisposableBean {
public Person(){
System.out.println("Person 创建了...");
}
@Override
public void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception {
System.out.println("Person 初始化了...");
}
@Override
public void destroy() throws Exception {
System.out.println("Person 被销毁了...");
}
}import com.dashu.bean.Person;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.*;
@Configuration
public class BeanConfig {
@Bean
public Person person(){
return new Person();
}
} 3、測試結果四、透過註解@PostConstruct和@PreDestroy
3、測試結果四、透過註解@PostConstruct和@PreDestroy@PostConstruct:标注在Bean的初始化方法上
@PreDestroy:标注在Bean的销毁方法上
登入後複製
1、Person@PostConstruct:标注在Bean的初始化方法上 @PreDestroy:标注在Bean的销毁方法上
import javax.annotation.PostConstruct;
import javax.annotation.PreDestroy;
public class Person {
public Person(){
System.out.println("Person 创建了...");
}
@PostConstruct
public void init(){
System.out.println("Person 初始化了...");
}
@PreDestroy
public void destroy(){
System.out.println("Person 被销毁了...");
}
}登入後複製
2、測試結果import javax.annotation.PostConstruct;
import javax.annotation.PreDestroy;
public class Person {
public Person(){
System.out.println("Person 创建了...");
}
@PostConstruct
public void init(){
System.out.println("Person 初始化了...");
}
@PreDestroy
public void destroy(){
System.out.println("Person 被销毁了...");
}
}
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import javax.annotation.PostConstruct;
import javax.annotation.PreDestroy;
@Component
public class Person {
public Person(){
System.out.println("Person 创建了...");
}
@PostConstruct
public void init(){
System.out.println("Person 初始化了...");
}
@PreDestroy
public void destroy(){
System.out.println("Person 被销毁了...");
}
}import org.springframework.context.annotation.*;
@Configuration
@ComponentScan({"com.dashu"})
public class BeanConfig {
}import org.springframework.beans.BeansException;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.BeanPostProcessor;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor;
import org.springframework.lang.Nullable;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
/**
* 后置处理器:初始化前后进行处理工作
*/
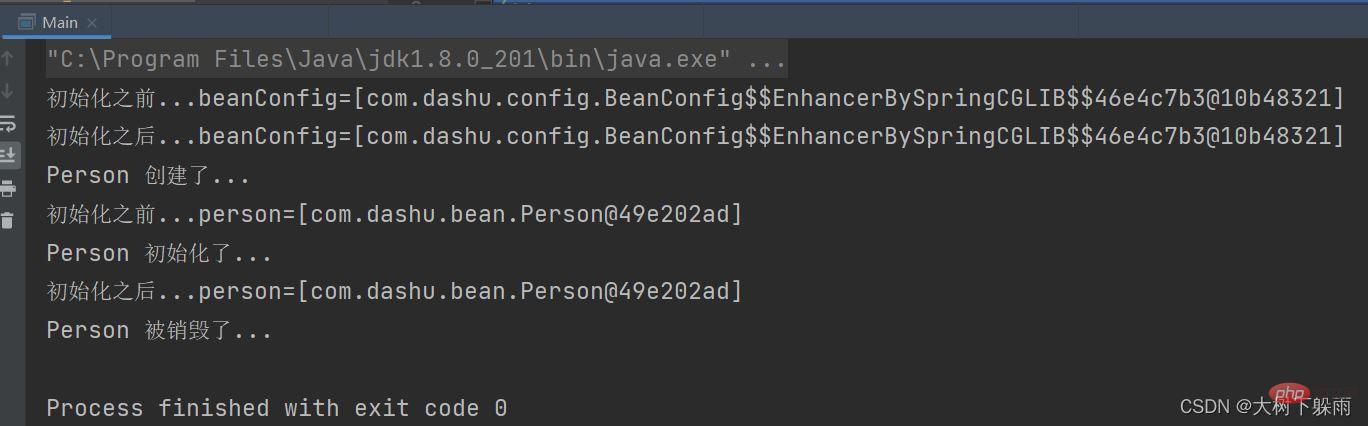
@Component
public class MyBeanPostProcessor implements BeanPostProcessor {
/**
* 初始化之前工作
* @param bean
* @param beanName
* @return
* @throws BeansException
*/
@Override
public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
System.out.println("初始化之前..."+beanName+"=["+bean+"]");
return bean;
}
/**
* 初始化之后工作
* @param bean
* @param beanName
* @return
* @throws BeansException
*/
@Override
public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
System.out.println("初始化之后..."+beanName+"=["+bean+"]");
return bean;
}
}以上是Java Spring Bean生命週期管理的範例分析的詳細內容。更多資訊請關注PHP中文網其他相關文章!

熱AI工具

Undresser.AI Undress
人工智慧驅動的應用程序,用於創建逼真的裸體照片

AI Clothes Remover
用於從照片中去除衣服的線上人工智慧工具。

Undress AI Tool
免費脫衣圖片

Clothoff.io
AI脫衣器

Video Face Swap
使用我們完全免費的人工智慧換臉工具,輕鬆在任何影片中換臉!

熱門文章

熱工具

記事本++7.3.1
好用且免費的程式碼編輯器

SublimeText3漢化版
中文版,非常好用

禪工作室 13.0.1
強大的PHP整合開發環境

Dreamweaver CS6
視覺化網頁開發工具

SublimeText3 Mac版
神級程式碼編輯軟體(SublimeText3)
 突破或從Java 8流返回?
Feb 07, 2025 pm 12:09 PM
突破或從Java 8流返回?
Feb 07, 2025 pm 12:09 PM
Java 8引入了Stream API,提供了一種強大且表達力豐富的處理數據集合的方式。然而,使用Stream時,一個常見問題是:如何從forEach操作中中斷或返回? 傳統循環允許提前中斷或返回,但Stream的forEach方法並不直接支持這種方式。本文將解釋原因,並探討在Stream處理系統中實現提前終止的替代方法。 延伸閱讀: Java Stream API改進 理解Stream forEach forEach方法是一個終端操作,它對Stream中的每個元素執行一個操作。它的設計意圖是處
 PHP:網絡開發的關鍵語言
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:08 AM
PHP:網絡開發的關鍵語言
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:08 AM
PHP是一種廣泛應用於服務器端的腳本語言,特別適合web開發。 1.PHP可以嵌入HTML,處理HTTP請求和響應,支持多種數據庫。 2.PHP用於生成動態網頁內容,處理表單數據,訪問數據庫等,具有強大的社區支持和開源資源。 3.PHP是解釋型語言,執行過程包括詞法分析、語法分析、編譯和執行。 4.PHP可以與MySQL結合用於用戶註冊系統等高級應用。 5.調試PHP時,可使用error_reporting()和var_dump()等函數。 6.優化PHP代碼可通過緩存機制、優化數據庫查詢和使用內置函數。 7
 PHP與Python:了解差異
Apr 11, 2025 am 12:15 AM
PHP與Python:了解差異
Apr 11, 2025 am 12:15 AM
PHP和Python各有優勢,選擇應基於項目需求。 1.PHP適合web開發,語法簡單,執行效率高。 2.Python適用於數據科學和機器學習,語法簡潔,庫豐富。
 PHP與其他語言:比較
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:19 AM
PHP與其他語言:比較
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:19 AM
PHP適合web開發,特別是在快速開發和處理動態內容方面表現出色,但不擅長數據科學和企業級應用。與Python相比,PHP在web開發中更具優勢,但在數據科學領域不如Python;與Java相比,PHP在企業級應用中表現較差,但在web開發中更靈活;與JavaScript相比,PHP在後端開發中更簡潔,但在前端開發中不如JavaScript。
 PHP與Python:核心功能
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:16 AM
PHP與Python:核心功能
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:16 AM
PHP和Python各有優勢,適合不同場景。 1.PHP適用於web開發,提供內置web服務器和豐富函數庫。 2.Python適合數據科學和機器學習,語法簡潔且有強大標準庫。選擇時應根據項目需求決定。
 PHP的影響:網絡開發及以後
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:10 AM
PHP的影響:網絡開發及以後
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:10 AM
PHPhassignificantlyimpactedwebdevelopmentandextendsbeyondit.1)ItpowersmajorplatformslikeWordPressandexcelsindatabaseinteractions.2)PHP'sadaptabilityallowsittoscaleforlargeapplicationsusingframeworkslikeLaravel.3)Beyondweb,PHPisusedincommand-linescrip
 PHP:許多網站的基礎
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:07 AM
PHP:許多網站的基礎
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:07 AM
PHP成為許多網站首選技術棧的原因包括其易用性、強大社區支持和廣泛應用。 1)易於學習和使用,適合初學者。 2)擁有龐大的開發者社區,資源豐富。 3)廣泛應用於WordPress、Drupal等平台。 4)與Web服務器緊密集成,簡化開發部署。
 PHP與Python:用例和應用程序
Apr 17, 2025 am 12:23 AM
PHP與Python:用例和應用程序
Apr 17, 2025 am 12:23 AM
PHP適用於Web開發和內容管理系統,Python適合數據科學、機器學習和自動化腳本。 1.PHP在構建快速、可擴展的網站和應用程序方面表現出色,常用於WordPress等CMS。 2.Python在數據科學和機器學習領域表現卓越,擁有豐富的庫如NumPy和TensorFlow。






