FutureTask 是一個可取消的非同步計算。
FutureTask提供了對Future的基本實現,可以呼叫方法去開始和取消一個計算,可以查詢計算是否完成,並且取得計算結果。
FutureTask只能在計算完成後取得到計算結果,一旦計算完成,將無法重新啟動或取消,除非呼叫runAndReset方法。
FutureTask除了實作了Future介面以外,也實作了Runnable接口,因此FutureTask是可以交由執行緒池的Executor執行,也可以直接使用一個非同步執行緒呼叫執行(futureTask.run())。
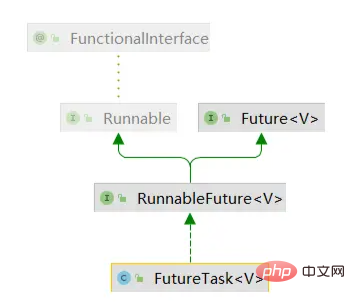
首先,我們看一下FutureTask類別的繼承結構,如下圖,它實現的是RunnableFuture接口,而RunnableFuture#繼承自Future和函數式介面Runnable,所以說FutureTask本質就是一個可運行的Future。
Future 介面約定了一些非同步運算類別必須實現的功能,原始碼如下:
package java.util.concurrent;
public interface Future<V> {
/**
* 尝试取消任务的执行,并返回取消结果。
* 参数mayInterruptIfRunning:是否中断线程。
*/
boolean cancel(boolean mayInterruptIfRunning);
/**
* 判断任务是否被取消(正常结束之前被被取消返回true)
*/
boolean isCancelled();
/**
* 判断当前任务是否执行完毕,包括正常执行完毕、执行异常或者任务取消。
*/
boolean isDone();
/**
* 获取任务执行结果,任务结束之前会阻塞。
*/
V get() throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException;
/**
* 在指定时间内尝试获取执行结果。若超时则抛出超时异常TimeoutException
*/
V get(long timeout, TimeUnit unit)
throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException, TimeoutException;
}Runnable 接口我們都很熟悉,他就是一個函數式接口,我們常用其創建一個線程。
package java.lang;
?
@FunctionalInterface
public interface Runnable {
? ?
? ?public abstract void run();
}FutureTask就是一個將要被執行的任務,它包含了上述介面具體的實現,FutureTask內部定義了任務的狀態state和一些狀態的常數,它的內部核心是一個Callable callable,我們透過建構函式可以傳入callable或是runnable,最後都會內部轉為callable,因為我們需要取得非同步任務的執行結果,而只有透過Callable所建立的執行緒才會回傳結果。
我們可以透過此時的狀態來判斷Future中isCancelled(),isDone()的回傳結果。
以下為FutureTask原始碼,內含核心原始碼分析註解
package java.util.concurrent;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.LockSupport;
public class FutureTask<V> implements RunnableFuture<V> {
/**
* 任务的运行状态
*/
private volatile int state;
private static final int NEW = 0; // 新建
private static final int COMPLETING = 1; // 完成
private static final int NORMAL = 2; // 正常
private static final int EXCEPTIONAL = 3; // 异常
private static final int CANCELLED = 4; // 取消
private static final int INTERRUPTING = 5; // 中断中
private static final int INTERRUPTED = 6; // 中断的
private Callable<V> callable;
/**
* 返回结果
*/
private Object outcome;
private volatile Thread runner;
private volatile WaitNode waiters;
...
public FutureTask(Callable<V> callable) {
if (callable == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
this.callable = callable;
this.state = NEW;
}
public FutureTask(Runnable runnable, V result) {
this.callable = Executors.callable(runnable, result);
this.state = NEW;
}
public boolean isCancelled() {
return state >= CANCELLED;
}
public boolean isDone() {
return state != NEW;
}
/*
* 取消任务实现
* 如果任务还没有启动就调用了cancel(true),任务将永远不会被执行。
* 如果任务已经启动,参数mayInterruptIfRunning将决定任务是否应该中断执行该任务的线程,以尝试中断该任务。
* 如果任务任务已经取消、已经完成或者其他原因不能取消,尝试将失败。
*/
public boolean cancel(boolean mayInterruptIfRunning) {
if (!(state == NEW &&
UNSAFE.compareAndSwapInt(this, stateOffset, NEW,
mayInterruptIfRunning ? INTERRUPTING : CANCELLED)))
return false;
try { // in case call to interrupt throws exception
if (mayInterruptIfRunning) {
try {
Thread t = runner;
if (t != null)
t.interrupt();
} finally { // final state
UNSAFE.putOrderedInt(this, stateOffset, INTERRUPTED);
}
}
} finally {
finishCompletion();
}
return true;
}
/*
* 等待获取结果
* 获取当前状态,判断是否执行完成。并且判断时间是否超时
* 如果任务没有执行完成,就阻塞等待完成,若超时抛出超时等待异常。
*/
public V get() throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException {
int s = state;
if (s <= COMPLETING)
s = awaitDone(false, 0L);
return report(s);
}
/*
* 等待获取结果
* 获取当前状态,判断是否执行完成。
* 如果任务没有执行完成,就阻塞等待完成。
*/
public V get(long timeout, TimeUnit unit)
throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException, TimeoutException {
if (unit == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
int s = state;
if (s <= COMPLETING &&
(s = awaitDone(true, unit.toNanos(timeout))) <= COMPLETING)
throw new TimeoutException();
return report(s);
}
/**
* 根据状态判断返回结果还是异常
*/
private V report(int s) throws ExecutionException {
Object x = outcome;
if (s == NORMAL)
return (V)x;
if (s >= CANCELLED)
throw new CancellationException();
throw new ExecutionException((Throwable)x);
}
protected void done() { }
/**
* 设置结果借助CAS确认状态是否完成状态
*/
protected void set(V v) {
if (UNSAFE.compareAndSwapInt(this, stateOffset, NEW, COMPLETING)) {
outcome = v;
UNSAFE.putOrderedInt(this, stateOffset, NORMAL); // final state
finishCompletion();
}
}
/**
* 设置异常,当运行完成出现异常,设置异常状态
*/
protected void setException(Throwable t) {
if (UNSAFE.compareAndSwapInt(this, stateOffset, NEW, COMPLETING)) {
outcome = t;
UNSAFE.putOrderedInt(this, stateOffset, EXCEPTIONAL); // final state
finishCompletion();
}
}
/*
* 执行callable获取结果,或者异常
* 判断状态是不是启动过的,如果是新建才可以执行run方法
*/
public void run() {
if (state != NEW ||
!UNSAFE.compareAndSwapObject(this, runnerOffset,
null, Thread.currentThread()))
return;
try {
Callable<V> c = callable;
if (c != null && state == NEW) {
V result;
boolean ran;
try {
result = c.call();
ran = true;
} catch (Throwable ex) {
result = null;
ran = false;
setException(ex);
}
if (ran)
set(result);
}
} finally {
runner = null;
int s = state;
if (s >= INTERRUPTING)
handlePossibleCancellationInterrupt(s);
}
}
/**
* 重新执行
*/
protected boolean runAndReset() {
if (state != NEW ||
!UNSAFE.compareAndSwapObject(this, runnerOffset,
null, Thread.currentThread()))
return false;
boolean ran = false;
int s = state;
try {
Callable<V> c = callable;
if (c != null && s == NEW) {
try {
c.call(); // don't set result
ran = true;
} catch (Throwable ex) {
setException(ex);
}
}
} finally {
runner = null;
s = state;
if (s >= INTERRUPTING)
handlePossibleCancellationInterrupt(s);
}
return ran && s == NEW;
}
/*
* 处理可能取消的中断
*/
private void handlePossibleCancellationInterrupt(int s) {
if (s == INTERRUPTING)
while (state == INTERRUPTING)
Thread.yield();
}
static final class WaitNode {
volatile Thread thread;
volatile WaitNode next;
WaitNode() { thread = Thread.currentThread(); }
}
/**
* 移除并唤醒所有等待线程,执行done,置空callable
*/
private void finishCompletion() {
// assert state > COMPLETING;
for (WaitNode q; (q = waiters) != null;) {
if (UNSAFE.compareAndSwapObject(this, waitersOffset, q, null)) {
for (;;) {
Thread t = q.thread;
if (t != null) {
q.thread = null;
LockSupport.unpark(t);
}
WaitNode next = q.next;
if (next == null)
break;
q.next = null; // unlink to help gc
q = next;
}
break;
}
}
done();
callable = null; // to reduce footprint
}
/**
* 等待完成
* 首先判断是否超时
* 处理中断的,然后处理异常状态的,处理完成的...
*/
private int awaitDone(boolean timed, long nanos)
throws InterruptedException {
final long deadline = timed ? System.nanoTime() + nanos : 0L;
WaitNode q = null;
boolean queued = false;
for (;;) {
if (Thread.interrupted()) {
removeWaiter(q);
throw new InterruptedException();
}
int s = state;
if (s > COMPLETING) {
if (q != null)
q.thread = null;
return s;
}
else if (s == COMPLETING) // cannot time out yet
Thread.yield();
else if (q == null)
q = new WaitNode();
else if (!queued)
queued = UNSAFE.compareAndSwapObject(this, waitersOffset,
q.next = waiters, q);
else if (timed) {
nanos = deadline - System.nanoTime();
if (nanos <= 0L) {
removeWaiter(q);
return state;
}
LockSupport.parkNanos(this, nanos);
}
else
LockSupport.park(this);
}
}
/**
* 去除等待
*/
private void removeWaiter(WaitNode node) {
if (node != null) {
node.thread = null;
retry:
for (;;) { // restart on removeWaiter race
for (WaitNode pred = null, q = waiters, s; q != null; q = s) {
s = q.next;
if (q.thread != null)
pred = q;
else if (pred != null) {
pred.next = s;
if (pred.thread == null) // check for race
continue retry;
}
else if (!UNSAFE.compareAndSwapObject(this, waitersOffset,
q, s))
continue retry;
}
break;
}
}
}
// Unsafe mechanics
private static final sun.misc.Unsafe UNSAFE;
private static final long stateOffset;
private static final long runnerOffset;
private static final long waitersOffset;
static {
try {
UNSAFE = sun.misc.Unsafe.getUnsafe();
Class<?> k = FutureTask.class;
stateOffset = UNSAFE.objectFieldOffset
(k.getDeclaredField("state"));
runnerOffset = UNSAFE.objectFieldOffset
(k.getDeclaredField("runner"));
waitersOffset = UNSAFE.objectFieldOffset
(k.getDeclaredField("waiters"));
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new Error(e);
}
}
}一般來說,我們可以認為FutureTask具有以下三種狀態:
未啟動:新建的FutureTask,在run()沒執行之前,FutureTask處於未啟動狀態。
private static final int NEW = 0; // 新建
已啟動:FutureTask物件的run方法啟動並執行的過程中,FutureTask處於已啟動狀態。
已完成:FutureTask正常執行結束,或FutureTask執行被取消(FutureTask物件cancel方法),或是FutureTask物件run方法執行拋出例外而導致中斷而結束,FutureTask都處於已完成狀態。
private static final int COMPLETING = 1; // 完成 private static final int NORMAL = 2; // 完成后正常设置结果 private static final int EXCEPTIONAL = 3; // 完成后异常设置异常 private static final int CANCELLED = 4; // 执行取消 private static final int INTERRUPTING = 5; // 中断中 private static final int INTERRUPTED = 6; // 中断的
使用一(直接新建一個執行緒呼叫):
FutureTask<Integer> task = new FutureTask<>(new Callable() {
@Override
public Integer call() throws Exception {
return sum();
}
});
new Thread(task).stat();
Integer result = task.get();使用二(結合執行緒池使用)
FutureTask<Integer> task = new FutureTask<>(new Callable() {
@Override
public Integer call() throws Exception {
return sum();
}
});
Executors.newCachedThreadPool().submit(task);
Integer result = task.get();以上是Java FutureTask源碼分析及使用詳解的詳細內容。更多資訊請關注PHP中文網其他相關文章!




