Java自備的四種執行緒池是什麼?
java預先定義的哪四種執行緒池?
newSingleThreadExexcutor:單執行緒數的執行緒池(核心執行緒數=最大執行緒數=1)
newFixedThreadPool:固定執行緒數的執行緒池(核心執行緒數=最大執行緒數=自訂)
-
newCacheThreadPool:可快取的執行緒池(核心執行緒數=0,最大執行緒數=Integer.MAX_VALUE)
newScheduledThreadPool:支援定時或週期任務的執行緒池(核心執行緒數=自訂,最大執行緒數=Integer.MAX_VALUE)
#四個執行緒數池有什麼差別?
上面四種執行緒池類別都繼承ThreadPoolExecutor,在建立時都是直接回傳new ThreadPoolExecutor(參數),它們的差別是定義的ThreadPoolExecutor(參數)中參數不同,而ThreadPoolExecutor又繼承ExecutorService介面類別
newFixedThreadPool
定義:
xecutorService executorService=Executors.newFixedThreadPool(2);
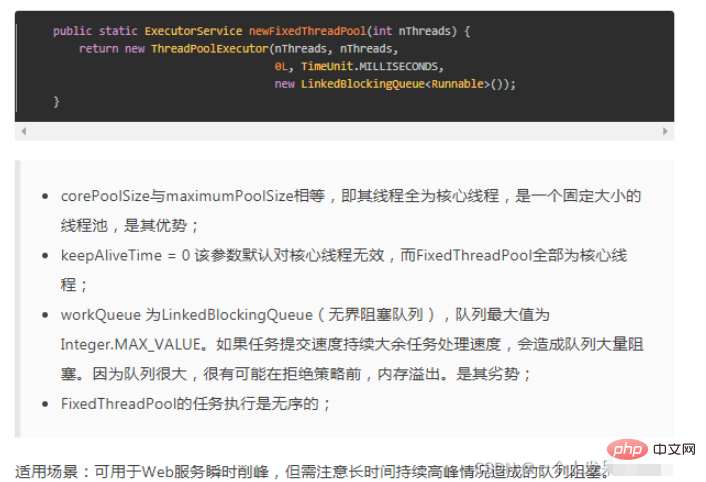
##缺點:使用了LinkBlockQueue的鍊錶型阻塞隊列,當任務的堆積速度大於處理速度時,容易堆積任務而導致OOM記憶體溢出
newSingleThreadExecutor
定義:ExecutorService executorService =Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor();
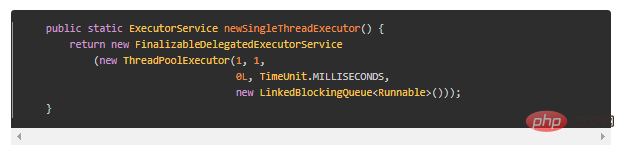
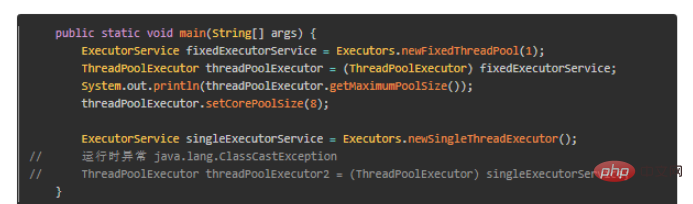 ##可知,fixedExecutorService的本質是ThreadPoolExecutor,所以fixedExecutorService可以強轉成ThreadPoolExecutor,但singleExecutorService與ThreadPoolExecutor沒有任何關係,所以強轉失敗,故newSingleThreadExecutor()建立後,無法再修改其執行緒池參數,真正做到single單一執行緒。
##可知,fixedExecutorService的本質是ThreadPoolExecutor,所以fixedExecutorService可以強轉成ThreadPoolExecutor,但singleExecutorService與ThreadPoolExecutor沒有任何關係,所以強轉失敗,故newSingleThreadExecutor()建立後,無法再修改其執行緒池參數,真正做到single單一執行緒。
缺點:使用了LinkBlockQueue的鍊錶型阻塞隊列,當任務的堆積速度大於處理速度時,容易堆積任務而導致OOM記憶體溢出
newCacheThreadPool
#定義:ExecutorService executorService=Executors.newCacheThreadPool();##缺點:SynchronousQueue是BlockingQueue的實現,它也是一個佇列,因為最大執行緒數為Integer.MAX_VALUE,所有當執行緒過多時容易OOM記憶體溢出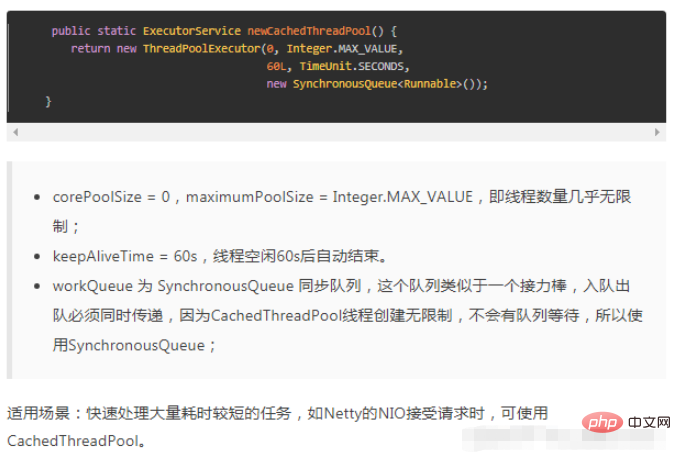
定義:ExecutorService executorService=Executors.newScheduledThreadPool(2);
##源码:
public static ScheduledExecutorService newScheduledThreadPool(int corePoolSize) {
//ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor继承ThreadPoolExecutor
return new ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor(corePoolSize);
}
public ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor(int corePoolSize) {
//ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor继承ThreadPoolExecutor,故super()会调用ThreadPoolExecutor的构造函数初始化并返回一个ThreadPoolExecutor,而ThreadPoolExecutor使实现ExecutorService接口的
//最终ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor也和上面几种线程池一样返回的是ExecutorService接口的实现类ThreadPoolExecutor
super(corePoolSize, Integer.MAX_VALUE, 0, NANOSECONDS,
new DelayedWorkQueue());
}線程池有哪幾個重要參數? ThreadPoolExecutor建構方法如下:
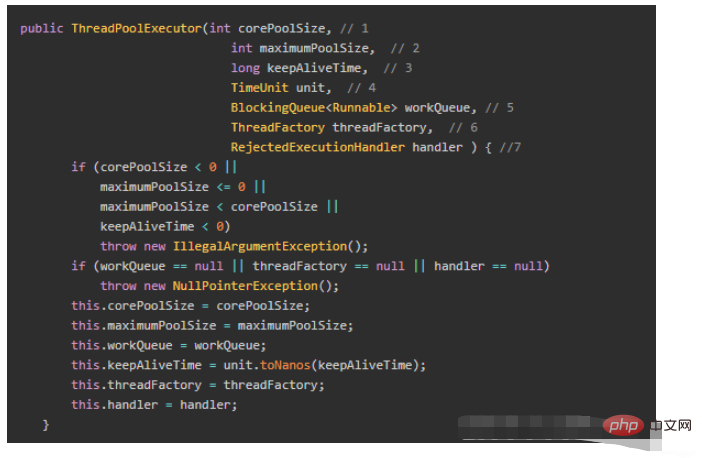
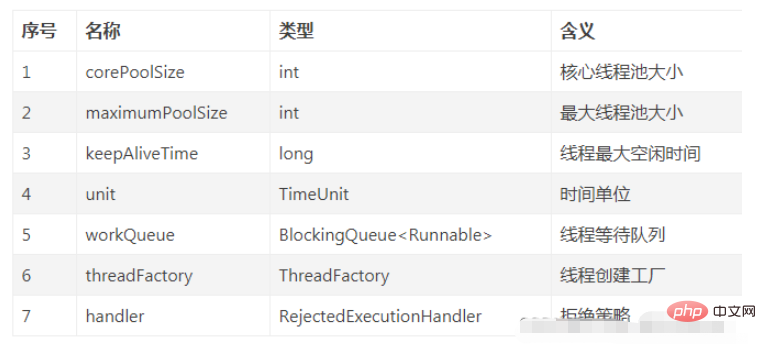 #keepAliveTime是指目前執行緒數位於[核心執行緒數,最大執行緒數] 之間的這些非核心執行緒等待多久空閒時間而沒有活乾時,就退出執行緒池;
#keepAliveTime是指目前執行緒數位於[核心執行緒數,最大執行緒數] 之間的這些非核心執行緒等待多久空閒時間而沒有活乾時,就退出執行緒池;
等待丟列的大小與最大執行緒數是沒有任何關係的,線程創建優先權=核心線程> 阻塞隊列> 擴容的線程(當前核心線程數小於最大線程數時才能擴容線程)
假如核心線程數5,等待隊列長度為3,最大線程數10:當線程數不斷在增加時,先創建5個核心線程,核心線程數滿了再把線程丟進等待丟列,等待隊列滿了(3個線程),此時會比較最大線程數(只有等待丟列滿了最大線程數才能出場),還可以繼續創建2個線程(5 3 2),若線程數超過了最大線程數,則執行拒絕策略;
假如核心執行緒數5,等待佇列長度為3,最大執行緒數7:當執行緒數不斷在增加時,先建立5個核心線程,核心執行緒數滿了再把線程丟進等待丟列,當等待隊列中有2個線程時達到了最大線程數(5 2=7),但是等待丟列還沒滿所以不用管最大線程數,直到等待丟列滿了(3個阻塞線程),此時會比較最大線程數(只有等待丟列滿了最大線程數才能出場),此時核心等待丟列=5 3=8>7=最大線程數,即已經達到最大執行緒數了,則執行拒絕策略;
如果把等待丟列設定為LinkedBlockingQueue無界丟列,這個丟列是無限大的,就永遠不會走到判斷最大線程數那一步了
如何自定义线程池
可以使用有界队列,自定义线程创建工厂ThreadFactory和拒绝策略handler来自定义线程池
public class ThreadTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException, IOException {
int corePoolSize = 2;
int maximumPoolSize = 4;
long keepAliveTime = 10;
TimeUnit unit = TimeUnit.SECONDS;
BlockingQueue<Runnable> workQueue = new ArrayBlockingQueue<>(2);
ThreadFactory threadFactory = new NameTreadFactory();
RejectedExecutionHandler handler = new MyIgnorePolicy();
ThreadPoolExecutor executor = new ThreadPoolExecutor(corePoolSize, maximumPoolSize, keepAliveTime, unit,
workQueue, threadFactory, handler);
executor.prestartAllCoreThreads(); // 预启动所有核心线程
for (int i = 1; i <= 10; i++) {
MyTask task = new MyTask(String.valueOf(i));
executor.execute(task);
}
System.in.read(); //阻塞主线程
}
static class NameTreadFactory implements ThreadFactory {
private final AtomicInteger mThreadNum = new AtomicInteger(1);
@Override
public Thread newThread(Runnable r) {
Thread t = new Thread(r, "my-thread-" + mThreadNum.getAndIncrement());
System.out.println(t.getName() + " has been created");
return t;
}
}
public static class MyIgnorePolicy implements RejectedExecutionHandler {
@Override
public void rejectedExecution(Runnable r, ThreadPoolExecutor e) {
doLog(r, e);
}
private void doLog(Runnable r, ThreadPoolExecutor e) {
// 可做日志记录等
System.err.println( r.toString() + " rejected");
// System.out.println("completedTaskCount: " + e.getCompletedTaskCount());
}
}
static class MyTask implements Runnable {
private String name;
public MyTask(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
@Override
public void run() {
try {
System.out.println(this.toString() + " is running!");
Thread.sleep(3000); //让任务执行慢点
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "MyTask [name=" + name + "]";
}
}
}运行结果:

其中7-10号线程被拒绝策略拒绝了,1、2号线程执行完后,3、6号线程进入核心线程池执行,此时4、5号线程在任务队列等待执行,3、6线程执行完再通知4、5线程执行
以上是Java自備的四種執行緒池是什麼?的詳細內容。更多資訊請關注PHP中文網其他相關文章!

熱AI工具

Undresser.AI Undress
人工智慧驅動的應用程序,用於創建逼真的裸體照片

AI Clothes Remover
用於從照片中去除衣服的線上人工智慧工具。

Undress AI Tool
免費脫衣圖片

Clothoff.io
AI脫衣器

AI Hentai Generator
免費產生 AI 無盡。

熱門文章

熱工具

記事本++7.3.1
好用且免費的程式碼編輯器

SublimeText3漢化版
中文版,非常好用

禪工作室 13.0.1
強大的PHP整合開發環境

Dreamweaver CS6
視覺化網頁開發工具

SublimeText3 Mac版
神級程式碼編輯軟體(SublimeText3)

熱門話題
 突破或從Java 8流返回?
Feb 07, 2025 pm 12:09 PM
突破或從Java 8流返回?
Feb 07, 2025 pm 12:09 PM
Java 8引入了Stream API,提供了一種強大且表達力豐富的處理數據集合的方式。然而,使用Stream時,一個常見問題是:如何從forEach操作中中斷或返回? 傳統循環允許提前中斷或返回,但Stream的forEach方法並不直接支持這種方式。本文將解釋原因,並探討在Stream處理系統中實現提前終止的替代方法。 延伸閱讀: Java Stream API改進 理解Stream forEach forEach方法是一個終端操作,它對Stream中的每個元素執行一個操作。它的設計意圖是處
 Java程序查找膠囊的體積
Feb 07, 2025 am 11:37 AM
Java程序查找膠囊的體積
Feb 07, 2025 am 11:37 AM
膠囊是一種三維幾何圖形,由一個圓柱體和兩端各一個半球體組成。膠囊的體積可以通過將圓柱體的體積和兩端半球體的體積相加來計算。本教程將討論如何使用不同的方法在Java中計算給定膠囊的體積。 膠囊體積公式 膠囊體積的公式如下: 膠囊體積 = 圓柱體體積 兩個半球體體積 其中, r: 半球體的半徑。 h: 圓柱體的高度(不包括半球體)。 例子 1 輸入 半徑 = 5 單位 高度 = 10 單位 輸出 體積 = 1570.8 立方單位 解釋 使用公式計算體積: 體積 = π × r2 × h (4












