Python爬取天氣資料及視覺化分析的方法是什麼
1、資料取得
請求網站連結
先查看中國天氣網,這裡就造訪本地的天氣網址,如果想爬取不同的地區只要修改最後的101280701地區編號即可,前面的weather代表是7天的網頁,weather1d代表當天,weather15d代表未來14天。這裡就主要訪問7天和14天的中國天氣網。採用requests.get()方法,請求網頁,如果成功訪問,則得到的是網頁的所有字串文字。這就是請求過程。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 |
|
提取有用資訊
這裡採用BeautifulSoup庫對剛剛取得的字串進行資料擷取,首先對網頁進行檢查,找到需要取得資料的標籤:
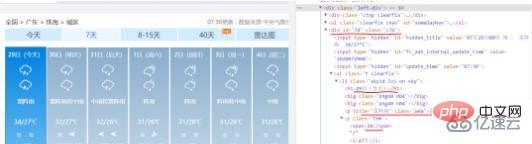
可以發現7天的資料資訊在div標籤中且id=“7d”,且日期、天氣、溫度、風級等資訊都在ul和li標籤中,所以我們可以使用BeautifulSoup將取得的網頁文字尋找div標籤id=“7d”,找出他包含的所有的ul和li標籤,之後提取標籤中對應的資料值,儲存到對應清單中。
這裡要注意一個細節就是有時日期沒有最高氣溫,對於沒有資料的情況要進行判斷和處理。另外對於一些資料保存的格式也要提前進行處理,例如溫度後面的攝氏度符號,日期數字的提取,和風級文字的提取,這需要用到字符查找及字符串切片處理。
1 2 3 4 5 6 |
|
下面爬取當天的數據
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 |
|
下面爬取7天的數據
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 |
|
同樣對於/weather15d:15天的信息,也做同樣的處理,這裡經過查看後發現他的15天網頁中只有8-14天,前面的1-7天在/weather中,這裡就分別訪問兩個網頁將爬取得到的數據進行合併得到最終14天的數據。 - 前面是未來14天的數據爬取過程,對於當天24小時的天氣資訊數據,經過查找發現他是一個json數據,可以透過json.loads()方法獲取當天的數據,進而對當天的天氣資訊進行提取。

儲存csv檔案
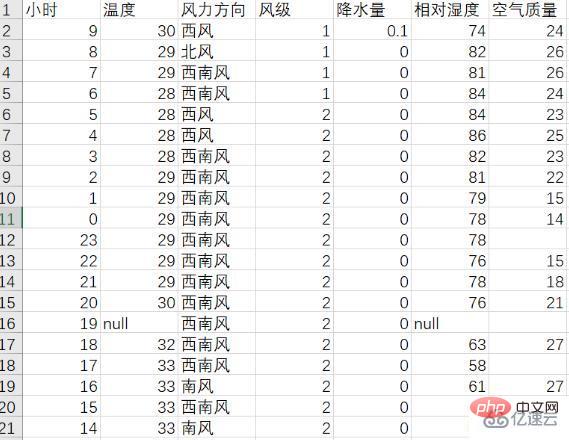
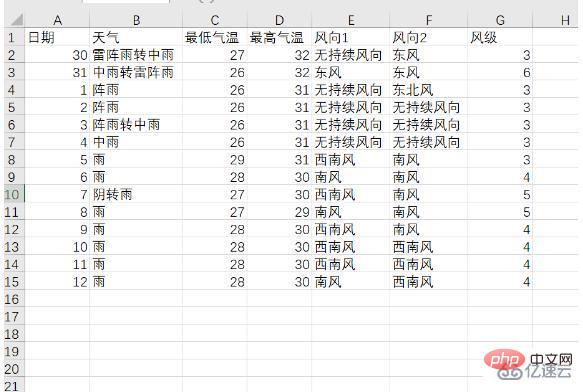
前面將爬取的資料加入到列表中,這裡引入csv函式庫,利用f_csv.writerow(header)和f_csv. writerows(data)方法,分別寫入表頭和每一行的數據,這裡將1天和未來14天的數據分開存儲,分別保存為weather1.csv和weather14.csv,下面是他們保存的表格圖:
2.可視化分析
#當天溫度變化曲線圖
採用matplotlib中plt.plot ()方法繪製出一天24小時的溫度變化曲線,並用plt.text()方法點出最高溫和最低溫,並畫出平均溫度線,下圖為溫度變化曲線圖:(代碼見附錄)
屌啊!接私活必備的 N 個開源專案!趕快收藏吧
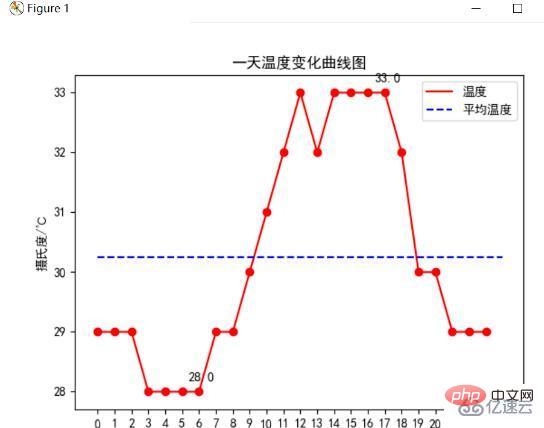
分析可以發現這一天最高溫度為33℃,最低溫度為28℃,且平均溫度在20.4℃左右,透過對時間分析,發現晝夜溫差5℃,低溫分佈在凌晨,高溫分佈在中午到下午的時段。
當天相對濕度變化曲線圖
採用matplotlib中plt.plot()方法繪製出一天24小時的濕度變化曲線,並畫出平均相對濕度線,下圖為濕度變化曲線圖:(代碼見附錄)
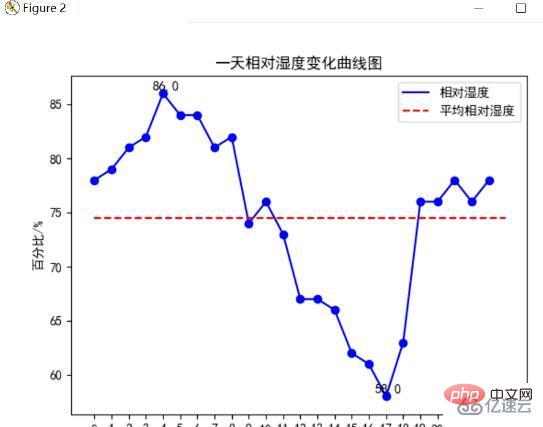
分析可以發現這一天最高相對濕度為86%,最低相對濕度為58℃,且平均相對濕度在75%左右,透過對時間分析,清晨的濕度比較大,而下午至黃昏濕度較小。
溫濕度相關性分析圖
經過前面兩個圖的分析我們可以感覺到溫度和濕度之間是有關係的,為了更清楚直觀地感受這種關係,使用plt.scatter()方法將溫度為橫座標、濕度為縱座標,每個時刻的點在圖中點出來,並且計算相關係數,下圖為結果圖:
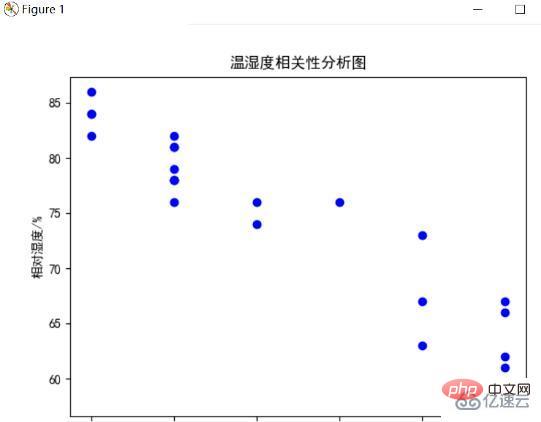
分析可以發現一天的溫度和濕度有強烈的相關性,他們呈現負相關,這表示他們時間是負相關關係,並且進一步分析,當溫度較低時,空氣中水分含量較多,濕度自然較高,而溫度較高時,水分蒸發,空氣就比較乾燥,濕度較低,符合平時氣候現象。
空氣品質指數長條圖
空氣品質指數AQI是定量描述空氣品質狀況的指數,其數值越大說明空氣污染狀況越重,對人體健康的危害就越大。一般將空氣品質指數分為6個等級,等級越高說明污染越嚴重,下面使用plt.bar方法對一天24小時的空氣品質進行了長條圖繪製,並且根據6個等級的不同,相應的柱狀圖的顏色也從淺到深,也顯示污染逐步加重,更直觀的顯示污染情況,並且也將最高和最低的空氣質量指數標出,用虛線畫出平均的空氣質量指數,下圖是繪製結果圖:
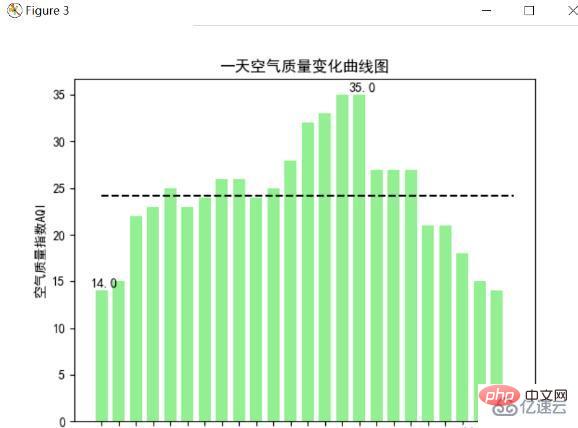
上面這張是南方珠海的控製品質圖,可以看出空氣品質指數最大也是在健康範圍,說明珠海空氣非常好,分析可以發現這一天最高空氣品質指數達到了35,最低則只有14,並且平均在25左右,通過時間也可以發現,基本上在清晨的時候是空氣最好的時候(4-9點),在下午是空氣污染最嚴重的時候,所以清晨一般可以去外面呼吸新鮮的空氣,那時污染最小。
而下面這個空氣品質圖是選取的北方的一個城市,可以看到這裡的環境遠遠比不上珠海。
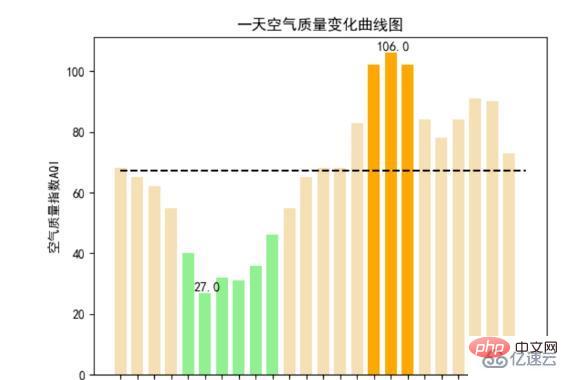
風向風級雷達圖
統計一天的風力和風向,由於風力風向使用極座標的方式展現較好,所以這裡採用的是極座標的方式展現一天的風力風向圖,將圓分為8份,每一份代表一個風向,半徑代表平均風力,並且隨著風級增高,藍色加深,最後結果如下所示:
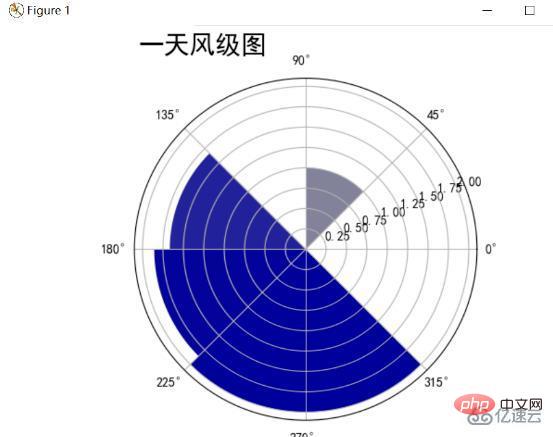
分析可以發現這一天西南風最多,平均風級達到了1.75級,東北風也有小部分1.0級,其餘空白方向無來風。
未來14天高低溫變化曲線圖
統計未來14天的高低溫變化,並繪製出他們的變化曲線圖,分別用虛線將他們的平均氣溫線繪製出來,最後結果如下所示:
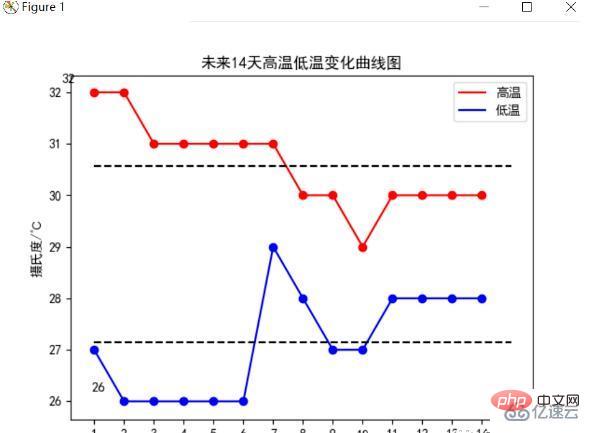
分析可以發現未來14天高溫平均氣溫為30.5℃,溫度還是比較高,但未來的第8天有降溫,需要做好降溫準備,低溫前方處於穩定趨勢,等到第8天開始下降,伴隨著高溫也下降,整體溫度下降,低溫平均在27℃左右。
未來14天風向風級雷達圖
統計未來14天的風向和平均風力,並和前面一樣採用極座標形式,將圓週分為8個部分,代表8個方向,顏色越深代表風級越高,最後結果如下所示:
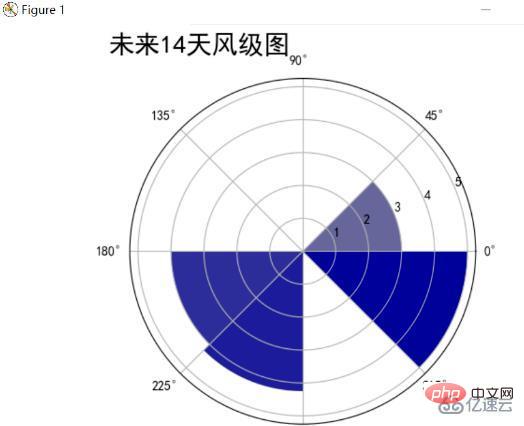
分析可以發現未來14天東南風、西南風所佔主要風向,風級最高達到了5級,最低的西風平均風級也有3級。
未來14天氣候分佈圓餅圖
統計未來14天的氣候,並求每個氣候的總天數,最後將各氣候的圓餅圖繪製出來,結果如下所示:
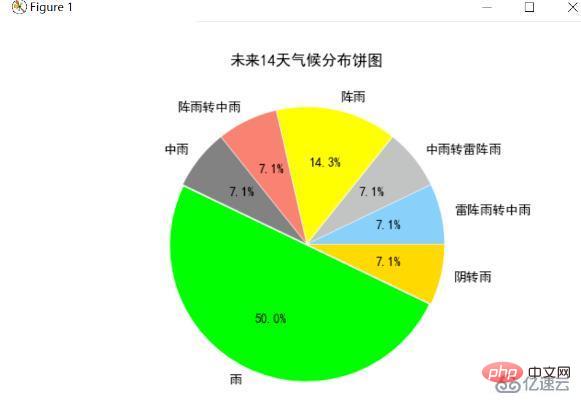
分析可以發現未來14天氣候基本上是“雨”、“陰轉雨”和“陣雨”,下雨的天數較多,結合前面的氣溫分佈圖可看出在第8-9天氣高溫下降,可以推測當天下雨,導致氣溫下降。
3、結論
1.首先根據爬取的溫濕度資料進行的分析,溫度從早上低到中午高再到晚上低,濕度和溫度的趨勢相反,透過相關係數發現溫度和濕度有強烈的負相關關係,經查閱資料發現因為隨著溫度升高水蒸汽蒸發加劇,空氣中水分降低濕度降低。當然,濕度同時受氣壓和雨水的影響,下雨濕度會明顯增加。
2.经查阅资料空气质量不仅跟工厂、汽车等排放的烟气、废气等有关,更为重要的是与气象因素有关。由于昼夜温差明显变化,当地面温度高于高空温度时,空气上升,污染物易被带到高空扩散;当地面温度低于一定高度的温度时,天空形成逆温层,它像一个大盖子一样压在地面上空,使地表空气中各种污染物不易扩散。一般在晚间和清晨影响较大,而当太阳出来后,地面迅速升温,逆温层就会逐渐消散,于是污染空气也就扩散了。
3.风是由气压在水平方向分布的不均匀导致的。风受大气环流、地形、水域等不同因素的综合影响,表现形式多种多样,如季风、地方性的海陆风、山谷风等,一天的风向也有不同的变化,根据未来14天的风向雷达图可以发现未来所有风向基本都有涉及,并且没有特别的某个风向,原因可能是近期没有降水和气文变化不大,导致风向也没有太大的变化规律。
4.天气是指某一个地区距离地表较近的大气层在短时间内的具体状态。跟某瞬时内大气中各种气象要素分布的综合表现。根据未来14天的天气和温度变化可以大致推断出某个时间的气候,天气和温度之间也是有联系的。
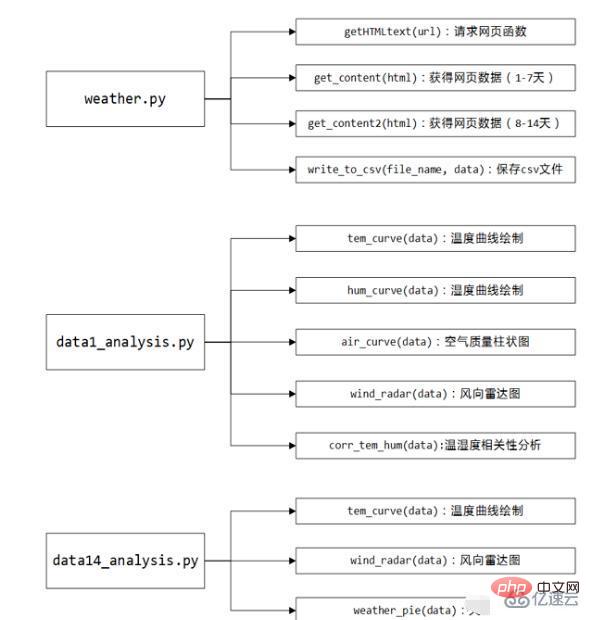
4、代码框架
代码主要分为weather.py:对中国天气网进行爬取天气数据并保存csv文件;data1_analysis.py:对当天的天气信息进行可视化处理;data14_analysis.py:对未来14天的天气信息进行可视化处理。下面是代码的结构图:
附源代码
weather.py
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 |
|
data1_analysis.py:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 160 161 162 163 164 165 166 167 168 169 170 171 172 173 174 175 176 177 178 179 180 181 182 183 184 185 186 187 188 189 190 191 192 193 194 195 196 197 198 199 200 201 202 203 204 205 206 207 208 209 210 211 212 213 214 215 216 217 218 219 220 221 222 223 224 225 226 227 228 229 230 231 232 233 234 235 236 237 238 239 240 241 242 243 244 245 246 247 248 249 250 251 252 253 254 255 256 257 258 259 260 261 262 263 264 265 266 267 268 269 270 271 272 273 274 275 276 277 278 279 280 281 282 283 284 285 286 287 288 289 290 291 292 293 294 295 296 297 |
|
以上是Python爬取天氣資料及視覺化分析的方法是什麼的詳細內容。更多資訊請關注PHP中文網其他相關文章!

熱AI工具

Undresser.AI Undress
人工智慧驅動的應用程序,用於創建逼真的裸體照片

AI Clothes Remover
用於從照片中去除衣服的線上人工智慧工具。

Undress AI Tool
免費脫衣圖片

Clothoff.io
AI脫衣器

Video Face Swap
使用我們完全免費的人工智慧換臉工具,輕鬆在任何影片中換臉!

熱門文章

熱工具

記事本++7.3.1
好用且免費的程式碼編輯器

SublimeText3漢化版
中文版,非常好用

禪工作室 13.0.1
強大的PHP整合開發環境

Dreamweaver CS6
視覺化網頁開發工具

SublimeText3 Mac版
神級程式碼編輯軟體(SublimeText3)
 PHP和Python:解釋了不同的範例
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:26 AM
PHP和Python:解釋了不同的範例
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:26 AM
PHP主要是過程式編程,但也支持面向對象編程(OOP);Python支持多種範式,包括OOP、函數式和過程式編程。 PHP適合web開發,Python適用於多種應用,如數據分析和機器學習。
 在PHP和Python之間進行選擇:指南
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:24 AM
在PHP和Python之間進行選擇:指南
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:24 AM
PHP適合網頁開發和快速原型開發,Python適用於數據科學和機器學習。 1.PHP用於動態網頁開發,語法簡單,適合快速開發。 2.Python語法簡潔,適用於多領域,庫生態系統強大。
 sublime怎麼運行代碼python
Apr 16, 2025 am 08:48 AM
sublime怎麼運行代碼python
Apr 16, 2025 am 08:48 AM
在 Sublime Text 中運行 Python 代碼,需先安裝 Python 插件,再創建 .py 文件並編寫代碼,最後按 Ctrl B 運行代碼,輸出會在控制台中顯示。
 PHP和Python:深入了解他們的歷史
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:25 AM
PHP和Python:深入了解他們的歷史
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:25 AM
PHP起源於1994年,由RasmusLerdorf開發,最初用於跟踪網站訪問者,逐漸演變為服務器端腳本語言,廣泛應用於網頁開發。 Python由GuidovanRossum於1980年代末開發,1991年首次發布,強調代碼可讀性和簡潔性,適用於科學計算、數據分析等領域。
 Python vs. JavaScript:學習曲線和易用性
Apr 16, 2025 am 12:12 AM
Python vs. JavaScript:學習曲線和易用性
Apr 16, 2025 am 12:12 AM
Python更適合初學者,學習曲線平緩,語法簡潔;JavaScript適合前端開發,學習曲線較陡,語法靈活。 1.Python語法直觀,適用於數據科學和後端開發。 2.JavaScript靈活,廣泛用於前端和服務器端編程。
 Golang vs. Python:性能和可伸縮性
Apr 19, 2025 am 12:18 AM
Golang vs. Python:性能和可伸縮性
Apr 19, 2025 am 12:18 AM
Golang在性能和可擴展性方面優於Python。 1)Golang的編譯型特性和高效並發模型使其在高並發場景下表現出色。 2)Python作為解釋型語言,執行速度較慢,但通過工具如Cython可優化性能。
 vscode在哪寫代碼
Apr 15, 2025 pm 09:54 PM
vscode在哪寫代碼
Apr 15, 2025 pm 09:54 PM
在 Visual Studio Code(VSCode)中編寫代碼簡單易行,只需安裝 VSCode、創建項目、選擇語言、創建文件、編寫代碼、保存並運行即可。 VSCode 的優點包括跨平台、免費開源、強大功能、擴展豐富,以及輕量快速。
 notepad 怎麼運行python
Apr 16, 2025 pm 07:33 PM
notepad 怎麼運行python
Apr 16, 2025 pm 07:33 PM
在 Notepad 中運行 Python 代碼需要安裝 Python 可執行文件和 NppExec 插件。安裝 Python 並為其添加 PATH 後,在 NppExec 插件中配置命令為“python”、參數為“{CURRENT_DIRECTORY}{FILE_NAME}”,即可在 Notepad 中通過快捷鍵“F6”運行 Python 代碼。






