本文的目的是幫助您開始在 python 中繪製資料。我們將創建一個條形圖來繪製給定文字檔案中字元的頻率。在這種情況下,文字檔包含了《了不起的蓋茨比》的內容。

這個專案的環境會比較小。虛擬環境可讓您為工作區添加額外的功能,而不會影響電腦的其餘部分!
建立一個目錄並在程式碼編輯器和終端機(執行命令的地方)中開啟它。
讓我們運行:
$ python3 -m venv venv $ source venv/bin/activate
我們可以安裝我們必要的依賴項
$ pip3 install matplotlib
我們還要建立兩個文件,read.txt 和wordcount.py。
我們將使用 wordcount.py 來分析 read.txt 中的文字。
我們可以比較簡單的開始,
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt # plot
from collections import OrderedDict # this will be used for sorting later
file = open('read.txt')
text = file.read()
file.close()這就是我們「讀取」文件並將內容儲存在變數中所需的全部內容。
我們可以追蹤字元的最佳方法是使用 python 字典(在其他程式語言中稱為 hashmap)。
字典是一種非常有用的資料儲存方式。就像真正的字典一樣,它會有一個“單字”列表,您可以查看單字以查看定義。
在程式設計中,這個概念被推廣到「鍵/值」對。這意味著我們可以設定字典,當我向字典詢問“a”時,它將返回“a”出現的總次數。
所以讓我們來編碼吧!
charDict = {} # dictionaries are defined by curly braces
def count_letter(character):
character = character.lower()
if character.isspace():
return
if character in charDict:
charDict[character] = charDict[character] + 1
else:
charDict[character] = 1
# loop through text
for i in text:
count_letter(i)
charDict = OrderedDict(sorted(charDict.items()))讓我們回顧一下這裡發生了什麼。
現在我們的資料集已創建,讓我們將其組織成軸並繪製它!
我們將建立一個清單來表示每個軸
num_list = []
char_list = []
這些清單將相互對應,因此如果char_list 中的第1 項是“a”,則num_list 中的第1 項將是對應的頻率。讓我們也把它編碼出來。
char_list = [] # character num_list = [] # frequency # create x and y axes for x,y in charDict.items(): char_list.append(x) num_list.append(y)
我們使用兩個變數循環遍歷我們創建的字典中的鍵/值對,然後將它們添加到我們的資料列表中。
最後讓我們使用 matplotlib 建立並儲存這個長條圖。
fig = plt.figure() # create a new figure
ax = fig.add_subplot() # create a new bar graph within the figure
fig.canvas.manager.set_window_title('The Great Gatsby') # title of window
ax.bar(char_list, num_list) # add the data to the graph
plt.savefig('chars.png') # download an image of the bar graph
plt.show() # show the image##是時候測試它了!
使用下面的程式碼運行您的文件,為我們的結果做好準備! 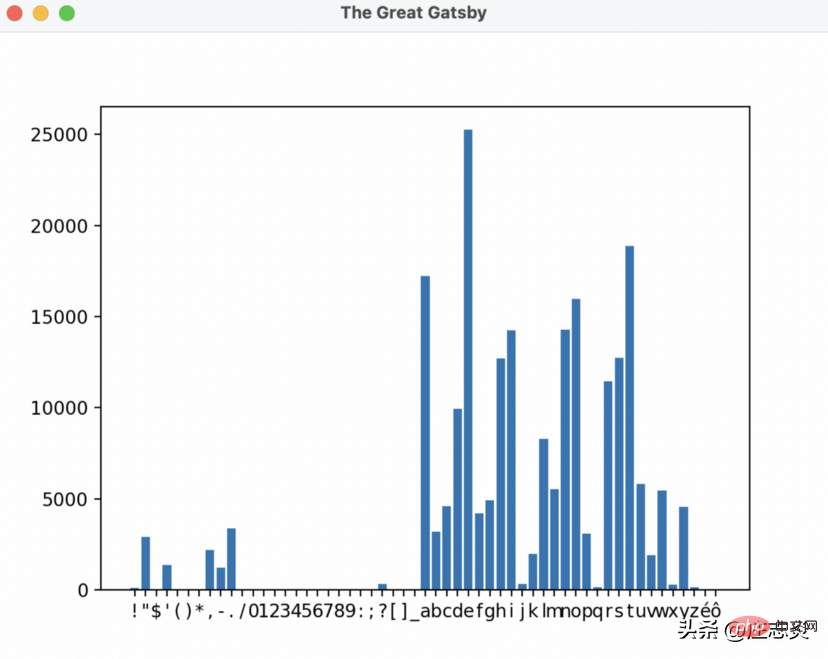
$ python3 wordcount.py
所以要回答我在文章開頭提出的問題,字母 e 在《了不起的蓋茨比》中被使用了超過 25,000 次!哇!
在本文結束時,我希望您對 matplotlib 和資料科學有所了解。
以上是使用 Python 和 Matplotlib 在文字中繪製字符的詳細內容。更多資訊請關注PHP中文網其他相關文章!




