在日常開發中只需要引入下面的依賴就可以開發Servlet進行存取了。
<dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId> </dependency>
那這是怎麼做到的呢?今天就來一探究竟
先新建一個maven專案rick-spring-boot,並建立兩個子專案分別是spring-boot和user,其中spring-boot專案就是模擬手寫一個簡單springboot,user就是用來測試手寫的spring-boot的。
user專案-測試工程
user專案包含pom.xml、UserController和UserService
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.rick.spring.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot</artifactId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>@RestController
public class UserController {
@Autowired
private UserService userService;
@GetMapping("/user")
public String getUser() {
return userService.getUser();
}
}
@Service
public class UserService {
public String getUser() {
return "rick";
}
}以及user專案的啟動類別RickApplication ,而RickSpringApplication.run()是需要手寫的啟動類別以及@RickSpringBootApplication註解,都是需要在spring-boot專案實現。
import com.rick.spring.boot.RickSpringApplication;
import com.rick.spring.boot.RickSpringBootApplication;
@RickSpringBootApplication
public class RickApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
RickSpringApplication.run(RickApplication.class);
}
}首先來看RickSpringApplication.run(RickApplication.class)方法需要做的事情:
(1)建立spring容器,並將傳入的class註冊到spring容器中
(2)啟動web服務,如tomcat,用來處理請求,並透過DispatchServlet將請求分發到Servlet進行處理。
public class RickSpringApplication {
public static void run(Class clz) {
AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext();
context.register(clz);
context.refresh();
start(context);
}
public static void start(WebApplicationContext applicationContext) {
System.out.println("start tomcat");
Tomcat tomcat = new Tomcat();
Server server = tomcat.getServer();
Service service = server.findService("Tomcat");
Connector connector = new Connector();
connector.setPort(8081);
Engine engine = new StandardEngine();
engine.setDefaultHost("localhost");
Host host = new StandardHost();
host.setName("localhost");
String contextPath = "";
Context context = new StandardContext();
context.setPath(contextPath);
context.addLifecycleListener(new Tomcat.FixContextListener());
host.addChild(context);
engine.addChild(host);
service.setContainer(engine);
service.addConnector(connector);
tomcat.addServlet(contextPath, "dispatcher", new DispatcherServlet(applicationContext));
context.addServletMappingDecoded("/*", "dispatcher");
try {
tomcat.start();
} catch (LifecycleException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}RickApplication是被@RickSpringBootApplication註解修飾的,從以下程式碼可以看出RickApplication是配置類,在被註冊到spring容器後,spring就會解析這個類別。
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Configuration
@ComponentScan
public @interface RickSpringBootApplication {
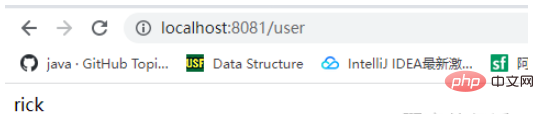
}啟動user專案RickApplication的main方法,
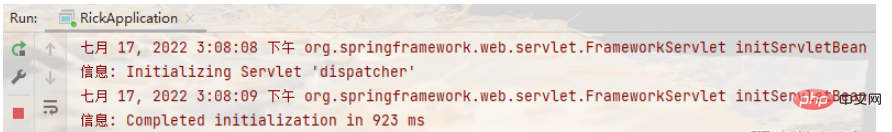
存取UserController
public interface WebServer {
void start();
}
public class JettyServer implements WebServer{
@Override
public void start() {
System.out.println("start jetty");
}
}public class TomcatServer implements WebServer, ApplicationContextAware {
private WebApplicationContext applicationContext;
@Override
public void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext applicationContext) throws BeansException {
this.applicationContext = (WebApplicationContext) applicationContext;
}
@Override
public void start() {
System.out.println("start tomcat");
...
tomcat.addServlet(contextPath, "dispatcher", new DispatcherServlet(applicationContext));
context.addServletMappingDecoded("/*", "dispatcher");
try {
tomcat.start();
} catch (LifecycleException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}public interface AutoConfiguration {
}
@Configuration
public class WebServerAutoConfiguration implements AutoConfiguration {
@Bean
@RickConditionalOnClass("org.apache.catalina.startup.Tomcat")
public TomcatServer tomcatServer() {
return new TomcatServer();
}
@Bean
@RickConditionalOnClass("org.eclipse.jetty.server.Server")
public JettyServer jettyWebServer() {
return new JettyServer();
}
}@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target(ElementType.METHOD)
@Conditional(RickOnClassConditional.class)
public @interface RickConditionalOnClass {
String value();
}
public class RickOnClassConditional implements Condition {
@Override
public boolean matches(ConditionContext context, AnnotatedTypeMetadata metadata) {
Map<String, Object> annotation = metadata.getAnnotationAttributes(RickConditionalOnClass.class.getName());
try {
context.getClassLoader().loadClass((String) annotation.get("value"));
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
return false;
}
return true;
}
}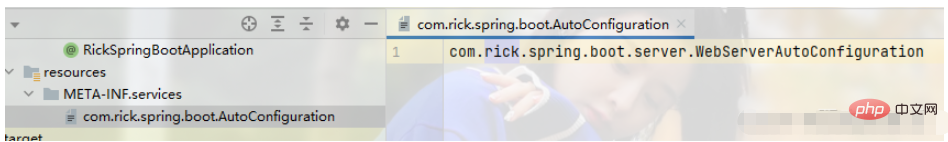
public class WebServerImportSelector implements DeferredImportSelector {
@Override
public String[] selectImports(AnnotationMetadata metadata) {
ServiceLoader<AutoConfiguration> load = ServiceLoader.load(AutoConfiguration.class);
List<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
for (AutoConfiguration loader : load) {
list.add(loader.getClass().getName());
}
return list.toArray(new String[list.size()]);
}
}<dependency>
<groupId>com.rick.spring.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot</artifactId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
<exclusions>
<exclusion>
<groupId>org.apache.tomcat.embed</groupId>
<artifactId>tomcat-embed-core</artifactId>
</exclusion>
</exclusions>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.eclipse.jetty</groupId>
<artifactId>jetty-server</artifactId>
<version>9.4.43.v20210629</version>
</dependency> #
#
以上是SpringBoot的底層原理是什麼的詳細內容。更多資訊請關注PHP中文網其他相關文章!




