如何用SpringBoot+SpringSecurity實現基於真實資料的授權認證
(一)概述
Spring Security是一個功能強大且高度可自訂的身份驗證和存取控制框架,Spring Security主要做兩個事情,認證、授權。我之前寫過一篇關於SpringSecurity的博客,但是當時只是介紹了基於mock數據的案例,本期就來介紹一下基於真實數據的認證授權實現。
(二)前期專案搭建
為了更好的展示SpringSecurity,我們先建造一個簡單的web專案出來。引入thymeleaf依賴
<dependency> <groupid>org.springframework.boot</groupid> <artifactid>spring-boot-starter-thymeleaf</artifactid> </dependency> <dependency> <groupid>org.thymeleaf</groupid> <artifactid>thymeleaf-spring5</artifactid> </dependency> <dependency> <groupid>org.thymeleaf.extras</groupid> <artifactid>thymeleaf-extras-java8time</artifactid> </dependency>
新建一個登陸頁,一個首頁,然後幾個不同等級的展示頁面: login.html
nbsp;html> <meta> <title>登陆页</title> <div> <form> <h3 id="登陆页">登陆页</h3> <input> <input> <button>登陆</button> </form> </div>
index.html
nbsp;html> <meta> <title>首页</title> <div> <h3 id="首页">首页</h3> <a>登陆</a> <div> <div> <h4 id="level">level1</h4> <a>level-1-1</a> <hr> <a>level-1-2</a> </div> <div> <h4 id="level">level2</h4> <a>level-2-1</a> <hr> <a>level-2-2</a> </div> <div> <h4 id="level">level3</h4> <a>level-3-1</a> <hr> <a>level-3-2</a> </div> </div> </div>
另外還有幾個不同等級的頁面
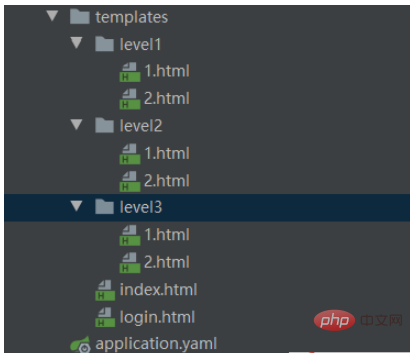
分別在body中寫上自己對應的編號。
nbsp;html> <meta> <title>Title</title> level-1-1
最後寫一個controller來接收請求:
@Controller
public class RouteController {
@RequestMapping({"/","/index"})
public String index(){
return "index";
}
@RequestMapping("/login")
public String toLogin(){
return "login";
}
@RequestMapping("/level1/{id}")
public String level1(@PathVariable("id")String id){
return "level1/"+id;
}
@RequestMapping("/level2/{id}")
public String level2(@PathVariable("id")String id){
return "level2/"+id;
}
@RequestMapping("/level3/{id}")
public String level3(@PathVariable("id")String id){
return "level3/"+id;
}
}最終的效果如下:
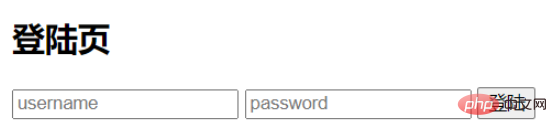
最終實作等級不同的level頁面根據不同權限進行跳轉。

後台基於Mybatis和Mysql資料庫實現,因此我們除了引入SpringSecurity的依賴之外,還需要引入Mybatis相關依賴:
<dependency> <groupid>org.springframework.boot</groupid> <artifactid>spring-boot-starter-security</artifactid> </dependency> <dependency> <groupid>org.springframework.boot</groupid> <artifactid>spring-boot-starter-jdbc</artifactid> </dependency> <dependency> <groupid>mysql</groupid> <artifactid>mysql-connector-java</artifactid> <scope>runtime</scope> </dependency> <dependency> <groupid>org.mybatis.spring.boot</groupid> <artifactid>mybatis-spring-boot-starter</artifactid> <version>2.1.3</version> </dependency>
在設定文件中新增資料來源相關信息,以及Mybatis的配置:
spring.datasource.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/security?serverTimezone=UTC&useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf-8 spring.datasource.username=root spring.datasource.password=123456 spring.datasource.driver-class-name=com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver mybatis.mapper-locations=classpath:mapper/*.xml
(三)認證與授權的實現
3.1 表結構設計
認證和授權在表設計上應該分在兩個表內,一個表存儲用戶信息包括密碼等,另一個表存儲授權信息,還需要一個表建立用戶和授權之間的關聯,給出最終的表結構:
CREATE TABLE `roles` ( `id` int(4) NOT NULL, `rolename` varchar(255) DEFAULT NULL, PRIMARY KEY (`id`) ) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8mb4; CREATE TABLE `sysuser` ( `id` int(4) NOT NULL, `username` varchar(255) NOT NULL, `password` varchar(255) NOT NULL, PRIMARY KEY (`id`) ) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8mb4; CREATE TABLE `user_role` ( `id` int(4) NOT NULL, `user_id` int(4) DEFAULT NULL, `role_id` int(4) DEFAULT NULL, PRIMARY KEY (`id`) ) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8mb4;
接下來是針對這三張表的實體類,Mapper介面以及xml文件,你可以不看程式碼,主要實作一個透過使用者名稱來尋找使用者以及相關權限的操作:
@Data
public class Roles {
private Integer id;
private String roleName;
}
@Data
public class SysUser {
private Integer id;
private String userName;
private String password;
private List<roles> roles;
}</roles>Mapper介面:
public interface UserMapper {
public SysUser getUserByUserName(@Param("userName") String userName);
}xml實作:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
nbsp;mapper PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN" "http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<mapper>
<resultmap>
<id></id>
<result></result>
<result></result>
<collection>
<result></result>
</collection>
</resultmap>
<select>
select sysuser.*,roles.rolename
from sysuser
LEFT JOIN user_role on sysuser.id= user_role.user_id
LEFT JOIN roles on user_role.role_id=roles.id
where username= #{userName}
</select>
</mapper>3.2 認證過程
SpringSecurity的認證過程是這樣的,首先透過用戶名或其他唯一的ID在資料庫裡找到這個用戶,用戶的密碼以非對稱加密的方式儲存。取到用戶後將前台傳入的密碼加密後和資料庫中已經加密好的欄位進行對比,從而通過認證。
上面這個過程中的第一步透過使用者名稱找到使用者的操作需要透過Service服務來實現,而這個Service服務需要繼承SpringSecurity中的UserDetailsService介面。這個介面回傳一個SpringSecurity的User物件。
@Service
public class UserService implements UserDetailsService {
@Resource
private UserMapper userMapper;
//根据用户名找到对应的用户信息
@Override
public UserDetails loadUserByUsername(String s) throws UsernameNotFoundException {
SysUser sysUser = userMapper.getUserByUserName(s);
if (sysUser!=null){
List<grantedauthority> roles=new ArrayList();
sysUser.getRoles().stream().forEach(x->{
roles.add(new SimpleGrantedAuthority(x.getRoleName()));
});
return new User(sysUser.getUserName(),sysUser.getPassword(),roles);
}
throw new UsernameNotFoundException("用户未找到");
}
}</grantedauthority>3.3 Security攔截設定
上面的步驟都完成後就開始設定Security了,寫一個設定方法SecurityConfig,程式碼層面很簡單,認證傳入userService對象,會自動把資料庫中取出的密碼和前端傳過來的密碼進行對照。同時在userService中也傳入了roles集合,在授權處為不同的頁面附上不同的權限即可。
@EnableWebSecurity
public class SecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
@Autowired
private UserService userService;
//授权
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
//首页所有人都能访问,level页面只有有权限的人才能访问
http.authorizeRequests()
.antMatchers("/").permitAll()
.antMatchers("/level1/**").hasRole("vip1")
.antMatchers("/level2/**").hasRole("vip2")
.antMatchers("/level3/**").hasRole("vip3");
//没有权限默认跳到登陆页,默认会重定向到/login
http.formLogin();
}
//认证
@Override
protected void configure(AuthenticationManagerBuilder auth) throws Exception {
auth.userDetailsService(userService).passwordEncoder(new BCryptPasswordEncoder());
}
}3.4 其他注意點
我在認證的時候使用的密碼加密方式是BCryptPasswordEncoder,因此存入資料庫中的密碼也需要被加密,常用的方式就是在註冊時通過同樣的方式將密碼加密存入資料庫:
String password="xxx"; BCryptPasswordEncoder bCryptPasswordEncoder = new BCryptPasswordEncoder(); String encode=bCryptPasswordEncoder.encode(password);
以上是如何用SpringBoot+SpringSecurity實現基於真實資料的授權認證的詳細內容。更多資訊請關注PHP中文網其他相關文章!

熱AI工具

Undresser.AI Undress
人工智慧驅動的應用程序,用於創建逼真的裸體照片

AI Clothes Remover
用於從照片中去除衣服的線上人工智慧工具。

Undress AI Tool
免費脫衣圖片

Clothoff.io
AI脫衣器

Video Face Swap
使用我們完全免費的人工智慧換臉工具,輕鬆在任何影片中換臉!

熱門文章

熱工具

記事本++7.3.1
好用且免費的程式碼編輯器

SublimeText3漢化版
中文版,非常好用

禪工作室 13.0.1
強大的PHP整合開發環境

Dreamweaver CS6
視覺化網頁開發工具

SublimeText3 Mac版
神級程式碼編輯軟體(SublimeText3)
 Springboot怎麼整合Jasypt實現設定檔加密
Jun 01, 2023 am 08:55 AM
Springboot怎麼整合Jasypt實現設定檔加密
Jun 01, 2023 am 08:55 AM
Jasypt介紹Jasypt是一個java庫,它允許開發員以最少的努力為他/她的專案添加基本的加密功能,並且不需要對加密工作原理有深入的了解用於單向和雙向加密的高安全性、基於標準的加密技術。加密密碼,文本,數字,二進位檔案...適合整合到基於Spring的應用程式中,開放API,用於任何JCE提供者...添加如下依賴:com.github.ulisesbocchiojasypt-spring-boot-starter2. 1.1Jasypt好處保護我們的系統安全,即使程式碼洩露,也可以保證資料來源的
 怎麼在SpringBoot中使用Redis實現分散式鎖
Jun 03, 2023 am 08:16 AM
怎麼在SpringBoot中使用Redis實現分散式鎖
Jun 03, 2023 am 08:16 AM
一、Redis實現分散式鎖原理為什麼需要分散式鎖在聊分散式鎖之前,有必要先解釋一下,為什麼需要分散式鎖。與分散式鎖相對就的是單機鎖,我們在寫多執行緒程式時,避免同時操作一個共享變數產生資料問題,通常會使用一把鎖來互斥以保證共享變數的正確性,其使用範圍是在同一個進程中。如果換做是多個進程,需要同時操作一個共享資源,如何互斥?現在的業務應用通常是微服務架構,這也意味著一個應用會部署多個進程,多個進程如果需要修改MySQL中的同一行記錄,為了避免操作亂序導致髒數據,此時就需要引入分佈式鎖了。想要實現分
 SpringBoot怎麼整合Redisson實現延遲隊列
May 30, 2023 pm 02:40 PM
SpringBoot怎麼整合Redisson實現延遲隊列
May 30, 2023 pm 02:40 PM
使用場景1、下單成功,30分鐘未支付。支付超時,自動取消訂單2、訂單簽收,簽收後7天未進行評估。訂單超時未評價,系統預設好評3、下單成功,商家5分鐘未接單,訂單取消4、配送超時,推播簡訊提醒…對於延時比較長的場景、即時性不高的場景,我們可以採用任務調度的方式定時輪詢處理。如:xxl-job今天我們採
 springboot讀取檔案打成jar包後存取不到怎麼解決
Jun 03, 2023 pm 04:38 PM
springboot讀取檔案打成jar包後存取不到怎麼解決
Jun 03, 2023 pm 04:38 PM
springboot讀取文件,打成jar包後訪問不到最新開發出現一種情況,springboot打成jar包後讀取不到文件,原因是打包之後,文件的虛擬路徑是無效的,只能通過流去讀取。文件在resources下publicvoidtest(){Listnames=newArrayList();InputStreamReaderread=null;try{ClassPathResourceresource=newClassPathResource("name.txt");Input
 Springboot+Mybatis-plus不使用SQL語句進行多表新增怎麼實現
Jun 02, 2023 am 11:07 AM
Springboot+Mybatis-plus不使用SQL語句進行多表新增怎麼實現
Jun 02, 2023 am 11:07 AM
在Springboot+Mybatis-plus不使用SQL語句進行多表添加操作我所遇到的問題準備工作在測試環境下模擬思維分解一下:創建出一個帶有參數的BrandDTO對像模擬對後台傳遞參數我所遇到的問題我們都知道,在我們使用Mybatis-plus中進行多表操作是極其困難的,如果你不使用Mybatis-plus-join這一類的工具,你只能去配置對應的Mapper.xml文件,配置又臭又長的ResultMap,然後再寫對應的sql語句,這種方法雖然看上去很麻煩,但具有很高的靈活性,可以讓我們
 SpringBoot與SpringMVC的比較及差別分析
Dec 29, 2023 am 11:02 AM
SpringBoot與SpringMVC的比較及差別分析
Dec 29, 2023 am 11:02 AM
SpringBoot和SpringMVC都是Java開發中常用的框架,但它們之間有一些明顯的差異。本文將探究這兩個框架的特點和用途,並對它們的差異進行比較。首先,我們來了解一下SpringBoot。 SpringBoot是由Pivotal團隊開發的,它旨在簡化基於Spring框架的應用程式的建立和部署。它提供了一種快速、輕量級的方式來建立獨立的、可執行
 SpringBoot怎麼自訂Redis實作快取序列化
Jun 03, 2023 am 11:32 AM
SpringBoot怎麼自訂Redis實作快取序列化
Jun 03, 2023 am 11:32 AM
1.自訂RedisTemplate1.1、RedisAPI預設序列化機制基於API的Redis快取實作是使用RedisTemplate範本進行資料快取操作的,這裡開啟RedisTemplate類,查看該類別的源碼資訊publicclassRedisTemplateextendsRedisAccessorimplementsRedisOperations,BeanClassLoaderAware{//聲明了value的各種序列化方式,初始值為空@NullableprivateRedisSe
 springboot怎麼取得application.yml裡值
Jun 03, 2023 pm 06:43 PM
springboot怎麼取得application.yml裡值
Jun 03, 2023 pm 06:43 PM
在專案中,很多時候需要用到一些配置信息,這些信息在測試環境和生產環境下可能會有不同的配置,後面根據實際業務情況有可能還需要再做修改。我們不能將這些設定在程式碼中寫死,最好是寫到設定檔中,例如可以把這些資訊寫到application.yml檔案中。那麼,怎麼在程式碼裡取得或使用這個位址呢?有2個方法。方法一:我們可以透過@Value註解的${key}即可取得設定檔(application.yml)中和key對應的value值,這個方法適用於微服務比較少的情形方法二:在實際專案中,遇到業務繁瑣,邏






