SpringBoot ApplicationContextAware拓展介面如何使用
ApplicationContextAware介面:
public interface ApplicationContextAware extends Aware {
void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext applicationContext) throws BeansException;
}首先Aware介面就知道這是springboot擴充給使用者使用的,這裡提供了方法setApplicationContext,參數就是傳遞spring容器上下文物件進來,我們可以接收這個上下文對象,我們要知道取得spring容器上下文ApplicationContext具體有什麼作用,這才是擴充介面的目的所在,取得上下文會根據上下文的特性做些什麼。
我們來看ApplicationContext物件的方法:
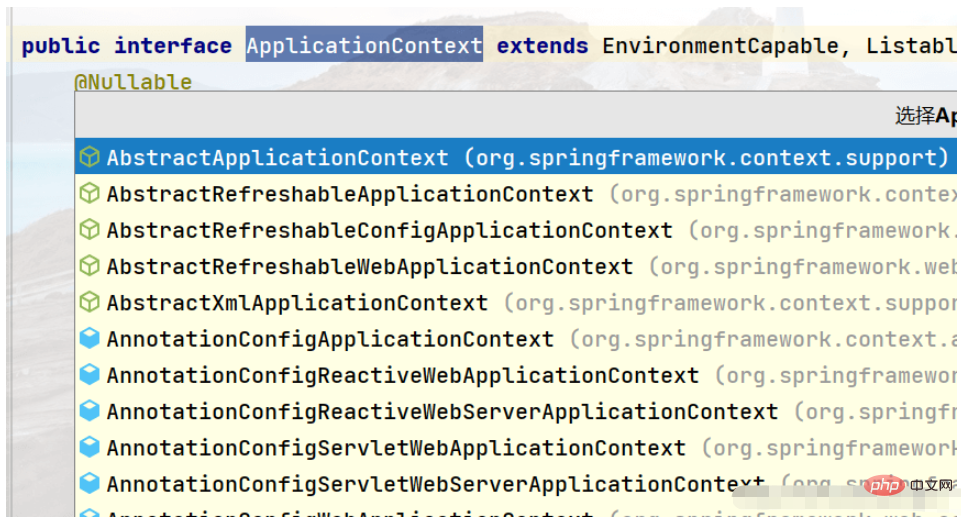
#來看看AbstractApplicationContext實作類別的方法:
public Object getBean(String name) throws BeansException {this.assertBeanFactoryActive();return this.getBeanFactory().getBean(name);}
public <T> T getBean(String name, Class<T> requiredType) throws BeansException {this.assertBeanFactoryActive();return this.getBeanFactory().getBean(name, requiredType);}
public Object getBean(String name, Object... args) throws BeansException {this.assertBeanFactoryActive();return this.getBeanFactory().getBean(name, args);}
public <T> T getBean(Class<T> requiredType) throws BeansException {this.assertBeanFactoryActive();return this.getBeanFactory().getBean(requiredType);}
public <T> T getBean(Class<T> requiredType, Object... args) throws BeansException {this.assertBeanFactoryActive();return this.getBeanFactory().getBean(requiredType, args);}
public <T> ObjectProvider<T> getBeanProvider(Class<T> requiredType) {this.assertBeanFactoryActive();return this.getBeanFactory().getBeanProvider(requiredType);}
public <T> ObjectProvider<T> getBeanProvider(ResolvableType requiredType) {this.assertBeanFactoryActive();return this.getBeanFactory().getBeanProvider(requiredType);}
public boolean containsBean(String name) {return this.getBeanFactory().containsBean(name);}
public boolean isSingleton(String name) throws NoSuchBeanDefinitionException {this.assertBeanFactoryActive();return this.getBeanFactory().isSingleton(name);}
public boolean isPrototype(String name) throws NoSuchBeanDefinitionException {this.assertBeanFactoryActive();return this.getBeanFactory().isPrototype(name);}這裡我們可以發現getBean ()方法很眼熟,因為在最開始學習spring時沒有用spring的腳手架創建項目,我們獲取bean的方法通常是classPathContextLoader掃描bean的xml文件解析組成ApplicationCOntext對象,再調用它的getBean方法獲取實例bean。
由此可以發現我們主要的應用途徑就是使用這個getBean的方法,那麼動態的注入bean我們通過很多方法就能實現,所以這裡不難想到,靜態方法中無法使用注入的bean的問題。
其次我們來復現這個問題,大家來看如下的程式碼:
public class JsonGetter {
@Resource
private UuidGetter uuidGetter;
public static string Test(){
return uuidGetter.getUuid();
}
public static JsONobject set0bjectToJsonObject(object data){
return JsoNobject.parseObject(String.valueof(JsONObject.toJSON(data)));
}
public static JsONObject setStringTO3son0bject(String data) { return JsONObject.parseObject(data);
}我們發現在靜態的Test方法中調用注入的bean直接報錯,這裡解釋一下:歸功於類的載入機制與載入順序,靜態屬性與靜態程式碼區塊先載入(static靜態優先),這裡載入靜態方法是沒有bean實例給你用的,自然會報錯。
如何解決?我們可以採取Spring取得bean物件時呼叫getBean方法的思路,在容器載入時將spring容器的上下文進行靜態儲存:
@Component
@Lazy(value = false)
public class SpringContextHolder implements ApplicationContextAware, DisposableBean {
/**
* 将上下文静态设置,在初始化组件时就进行静态上下文的覆盖(这个覆盖是将远spring容器的上下文对象引用加到我们预定设置)
*/
private static ApplicationContext applicationContext = null;
public static ApplicationContext getApplicationContext() {
assertContextInjected();
return applicationContext;
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public static <T> T getBean(String name) {
assertContextInjected();
return (T) applicationContext.getBean(name);
}
public static <T> T getBean(Class<T> beanType) {
assertContextInjected();
return applicationContext.getBean(beanType);
}
@Override
public void setApplicationContext(@NotNull ApplicationContext applicationContext) throws BeansException {
SpringContextHolder.applicationContext = applicationContext;
}
@Override
public void destroy() {
applicationContext = null;
}
private static void assertContextInjected() {
Assert.notNull(applicationContext,
"applicationContext属性未注入, 请在applicationContext.xml中定义SpringContextHolder.");
}
public static void pushEvent(ApplicationEvent event){
assertContextInjected();
applicationContext.publishEvent(event);
}
}這裡只需要關注的是靜態成員變數ApplicationContext的定義、賦值與驗證:
/**
* 将上下文静态设置,在初始化组件时就进行静态上下文的覆盖(这个覆盖是将远spring容器的上下文对象引用加到我们预定设置)
*/
private static ApplicationContext applicationContext = null;重寫擴充介面的方法,實作靜態上下文的覆寫:
@Override
public void setApplicationContext(@NotNull ApplicationContext applicationContext) throws BeansException {
SpringContextHolder.applicationContext = applicationContext;
}將取得它的方法公有修飾,以便共享:
public static ApplicationContext getApplicationContext() {
assertContextInjected();
return applicationContext;
}寫到這裡還是不明白,這麼定義一個元件,將spring上下文物件靜態覆蓋到底有何作用?
不要慌,我們來看看這個類別的這個方法:
public class AppContext {
static transient ThreadLocal<Map<String, String>> contextMap = new ThreadLocal<>();
......省略n行业务代码
public static void fillLoginContext() {
DingAppInfo appInfo = SpringContextHolder.getBean(DingAppInfoService.class).findAppInfo(APP_CODE);
setDingVerifyInfo(appInfo);
CloudChatAppInfo cloudChatAppInfo = SpringContextHolder.getBean(CloudChatAppInfoService.class).findAppInfo(APP_CODE);
setCloudChatInfo(cloudChatAppInfo);
}
public static void clear() {
contextMap.remove(); //本地线程的remove方法极其重要,注意每次给它使用之后一定要调用remove清理,防止内存泄露。
}
}我們發現上例程式碼中進行了查庫的操作:
DingAppInfo appInfo = SpringContextHolder.getBean(DingAppInfoService.class).findAppInfo(APP_CODE);
以上是SpringBoot ApplicationContextAware拓展介面如何使用的詳細內容。更多資訊請關注PHP中文網其他相關文章!

熱AI工具

Undresser.AI Undress
人工智慧驅動的應用程序,用於創建逼真的裸體照片

AI Clothes Remover
用於從照片中去除衣服的線上人工智慧工具。

Undress AI Tool
免費脫衣圖片

Clothoff.io
AI脫衣器

Video Face Swap
使用我們完全免費的人工智慧換臉工具,輕鬆在任何影片中換臉!

熱門文章

熱工具

記事本++7.3.1
好用且免費的程式碼編輯器

SublimeText3漢化版
中文版,非常好用

禪工作室 13.0.1
強大的PHP整合開發環境

Dreamweaver CS6
視覺化網頁開發工具

SublimeText3 Mac版
神級程式碼編輯軟體(SublimeText3)
 Springboot怎麼整合Jasypt實現設定檔加密
Jun 01, 2023 am 08:55 AM
Springboot怎麼整合Jasypt實現設定檔加密
Jun 01, 2023 am 08:55 AM
Jasypt介紹Jasypt是一個java庫,它允許開發員以最少的努力為他/她的專案添加基本的加密功能,並且不需要對加密工作原理有深入的了解用於單向和雙向加密的高安全性、基於標準的加密技術。加密密碼,文本,數字,二進位檔案...適合整合到基於Spring的應用程式中,開放API,用於任何JCE提供者...添加如下依賴:com.github.ulisesbocchiojasypt-spring-boot-starter2. 1.1Jasypt好處保護我們的系統安全,即使程式碼洩露,也可以保證資料來源的
 SpringBoot怎麼整合Redisson實現延遲隊列
May 30, 2023 pm 02:40 PM
SpringBoot怎麼整合Redisson實現延遲隊列
May 30, 2023 pm 02:40 PM
使用場景1、下單成功,30分鐘未支付。支付超時,自動取消訂單2、訂單簽收,簽收後7天未進行評估。訂單超時未評價,系統預設好評3、下單成功,商家5分鐘未接單,訂單取消4、配送超時,推播簡訊提醒…對於延時比較長的場景、即時性不高的場景,我們可以採用任務調度的方式定時輪詢處理。如:xxl-job今天我們採
 怎麼在SpringBoot中使用Redis實現分散式鎖
Jun 03, 2023 am 08:16 AM
怎麼在SpringBoot中使用Redis實現分散式鎖
Jun 03, 2023 am 08:16 AM
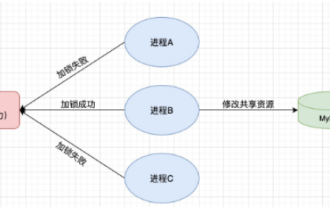
一、Redis實現分散式鎖原理為什麼需要分散式鎖在聊分散式鎖之前,有必要先解釋一下,為什麼需要分散式鎖。與分散式鎖相對就的是單機鎖,我們在寫多執行緒程式時,避免同時操作一個共享變數產生資料問題,通常會使用一把鎖來互斥以保證共享變數的正確性,其使用範圍是在同一個進程中。如果換做是多個進程,需要同時操作一個共享資源,如何互斥?現在的業務應用通常是微服務架構,這也意味著一個應用會部署多個進程,多個進程如果需要修改MySQL中的同一行記錄,為了避免操作亂序導致髒數據,此時就需要引入分佈式鎖了。想要實現分
 springboot讀取檔案打成jar包後存取不到怎麼解決
Jun 03, 2023 pm 04:38 PM
springboot讀取檔案打成jar包後存取不到怎麼解決
Jun 03, 2023 pm 04:38 PM
springboot讀取文件,打成jar包後訪問不到最新開發出現一種情況,springboot打成jar包後讀取不到文件,原因是打包之後,文件的虛擬路徑是無效的,只能通過流去讀取。文件在resources下publicvoidtest(){Listnames=newArrayList();InputStreamReaderread=null;try{ClassPathResourceresource=newClassPathResource("name.txt");Input
 Springboot+Mybatis-plus不使用SQL語句進行多表新增怎麼實現
Jun 02, 2023 am 11:07 AM
Springboot+Mybatis-plus不使用SQL語句進行多表新增怎麼實現
Jun 02, 2023 am 11:07 AM
在Springboot+Mybatis-plus不使用SQL語句進行多表添加操作我所遇到的問題準備工作在測試環境下模擬思維分解一下:創建出一個帶有參數的BrandDTO對像模擬對後台傳遞參數我所遇到的問題我們都知道,在我們使用Mybatis-plus中進行多表操作是極其困難的,如果你不使用Mybatis-plus-join這一類的工具,你只能去配置對應的Mapper.xml文件,配置又臭又長的ResultMap,然後再寫對應的sql語句,這種方法雖然看上去很麻煩,但具有很高的靈活性,可以讓我們
 SpringBoot怎麼自訂Redis實作快取序列化
Jun 03, 2023 am 11:32 AM
SpringBoot怎麼自訂Redis實作快取序列化
Jun 03, 2023 am 11:32 AM
1.自訂RedisTemplate1.1、RedisAPI預設序列化機制基於API的Redis快取實作是使用RedisTemplate範本進行資料快取操作的,這裡開啟RedisTemplate類,查看該類別的源碼資訊publicclassRedisTemplateextendsRedisAccessorimplementsRedisOperations,BeanClassLoaderAware{//聲明了value的各種序列化方式,初始值為空@NullableprivateRedisSe
 SpringBoot與SpringMVC的比較及差別分析
Dec 29, 2023 am 11:02 AM
SpringBoot與SpringMVC的比較及差別分析
Dec 29, 2023 am 11:02 AM
SpringBoot和SpringMVC都是Java開發中常用的框架,但它們之間有一些明顯的差異。本文將探究這兩個框架的特點和用途,並對它們的差異進行比較。首先,我們來了解一下SpringBoot。 SpringBoot是由Pivotal團隊開發的,它旨在簡化基於Spring框架的應用程式的建立和部署。它提供了一種快速、輕量級的方式來建立獨立的、可執行
 SpringBoot+Dubbo+Nacos 開發實戰教程
Aug 15, 2023 pm 04:49 PM
SpringBoot+Dubbo+Nacos 開發實戰教程
Aug 15, 2023 pm 04:49 PM
本文來寫個詳細的例子來說下dubbo+nacos+Spring Boot開發實戰。本文不會講述太多的理論的知識,會寫一個最簡單的例子來說明dubbo如何與nacos整合,快速建構開發環境。






