儘管現代關係型資料庫越來越相似,但它們的實現背後可能有著截然不同的機制。實際使用方面,因為SQL語法規範的存在使得我們熟悉多種關係型資料庫並非難事,但是有多少種資料庫可能就有多少種鎖的實作方法。
Microsoft Sql Server2005之前只提供頁鎖,直到2005版本才開始支援樂觀並發、悲觀並發,樂觀模式下允許實現行級鎖,在Sql Server的設計中鎖是一種稀缺資源,鎖的數量越多,開銷就越大,為了避免因為鎖的數量快速攀升導致性能斷崖式下跌,其支持一種稱為鎖升級的機制,一旦行鎖升級為頁鎖,並發性能就又回到原點。
事實上,在同一個資料庫中,不同的執行引擎對鎖定功能的解釋仍然存在許多爭議。 MyISAM只支援表級鎖定,用於並發讀取還好,但在並發修改方面有一定限制。 Innodb則和Oracle非常相似,提供非鎖定一致性讀取、行鎖支持,與Sql Server明顯不同的是隨著鎖總數的上升,Innodb僅只需要付出一點點代價。
Innodb支援行鎖,且對於鎖的描述並不會有特別大的開銷。因此不需要鎖定升級此機製作為大量鎖定導致性能下降之後的搶救措施。
摘自lock0priv.h文件,Innodb對於行鎖的定義如下:
/** Record lock for a page */
struct lock_rec_t {
/* space id */
ulint space;
/* page number */
ulint page_no;
/**
* number of bits in the lock bitmap;
* NOTE: the lock bitmap is placed immediately after the lock struct
*/
ulint n_bits;
};雖然並發控制可以在行級別進行細化,但鎖的管理方式是以頁為單位進行組織的。 Innodb的設計中透過space id、page number兩個必要條件就可以確定唯一一個資料頁,n_bits表示描述該頁行鎖定資訊需要多少bit位元。
同一資料頁中每筆記錄都分配唯一的連續的遞增序號:heap_no,若要知道某一行記錄是否上鎖,則只需要判斷位圖heap_no位置的數字是否為一即可。由於lock bitmap根據資料頁的記錄數量進行記憶體空間分配的,因此沒有明確定義,且該頁記錄可能還會繼續增加,因此預留了LOCK_PAGE_BITMAP_MARGIN大小的空間。
/** * Safety margin when creating a new record lock: this many extra records * can be inserted to the page without need to create a lock with * a bigger bitmap */ #define LOCK_PAGE_BITMAP_MARGIN 64
假設space id = 20,page number = 100的資料頁目前有160筆記錄,heap_no為2、3、4的記錄已經被鎖,則對應的lock_rec_t結構與資料頁應該被這樣刻畫:
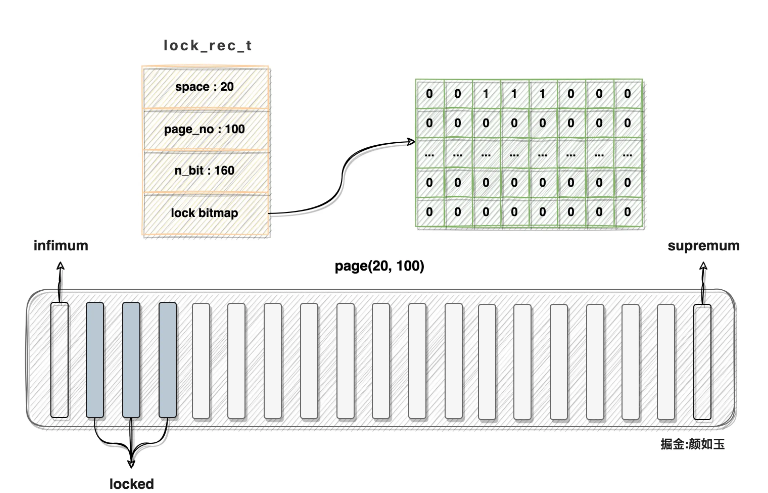
註:
#記憶體中的lock bitmap應該是線性分佈的,圖中所示二維結構是為了方便描述
bitmap與lock_rec_t結構是一個連續內存,圖中引用關係也是繪圖需要
可以看到該頁對應的bitmap第二三四位置全部置一,描述一個資料頁行鎖所消耗記憶體從感官上相當有限,那具體佔用多少呢?我們可以計算一下:
160 / 8 8 1 = 29byte。
160筆記錄對應160bit
# 8是因為需要預留64bit
1是因為原始碼中也預留了1位元組
為了避免結果數值偏小的問題,這裡額外增加了1。這樣可以避免整除會導致誤差產生。假如是161筆記錄如果不 1則計算出來的20byte不夠描述所有記錄的鎖定資訊(不動用預留位)。
摘自lock0priv.h檔:
/* lock_rec_create函数代码片段 */
n_bits = page_dir_get_n_heap(page) + LOCK_PAGE_BITMAP_MARGIN;
n_bytes = 1 + n_bits / 8;
/* 注意这里是分配的连续内存 */
lock = static_cast<lock_t*>(
mem_heap_alloc(trx->lock.lock_heap, sizeof(lock_t) + n_bytes)
);
/**
* Gets the number of records in the heap.
* @return number of user records
*/
UNIV_INLINE ulint page_dir_get_n_heap(const page_t* page)
{
return(page_header_get_field(page, PAGE_N_HEAP) & 0x7fff);
}Innodb也支援表鎖,表鎖可分為兩大類:意向鎖,自增鎖其資料結構定義如下:
摘自lock0priv.h檔案
struct lock_table_t {
/* database table in dictionary cache */
dict_table_t* table;
/* list of locks on the same table */
UT_LIST_NODE_T(lock_t) locks;
};摘自ut0lst.h檔案
struct ut_list_node {
/* pointer to the previous node, NULL if start of list */
TYPE* prev;
/* pointer to next node, NULL if end of list */
TYPE* next;
};
#define UT_LIST_NODE_T(TYPE) ut_list_node<TYPE>上述lock_rec_t、lock_table_t結構只是單獨的定義,鎖產生於事務之中,因此每個事務對應的行鎖、表鎖會有一個對應的鎖的結構,其定義如下:
#摘自lock0priv.h檔
/** Lock struct; protected by lock_sys->mutex */
struct lock_t {
/* transaction owning the lock */
trx_t* trx;
/* list of the locks of the transaction */
UT_LIST_NODE_T(lock_t) trx_locks;
/**
* lock type, mode, LOCK_GAP or LOCK_REC_NOT_GAP,
* LOCK_INSERT_INTENTION, wait flag, ORed
*/
ulint type_mode;
/* hash chain node for a record lock */
hash_node_t hash;
/*!< index for a record lock */
dict_index_t* index;
/* lock details */
union {
/* table lock */
lock_table_t tab_lock;
/* record lock */
lock_rec_t rec_lock;
} un_member;
};lock_t是根據每個事務每個頁(或表)來定義的,但是一個事務往往涉及到多個頁,因此需要鍊錶trx_locks串聯起一個事務相關的所有鎖定資訊。除了需要根據事務查詢到所有鎖定信息,實際場景還要求系統必須能夠快速高效的檢測出某個行記錄是否已經上鎖。因此必須有一個全域變數支援對行記錄進行鎖定資訊的查詢。 Innodb選擇了雜湊表,定義如下:
摘自lock0lock.h檔案
/** The lock system struct */
struct lock_sys_t {
/* Mutex protecting the locks */
ib_mutex_t mutex;
/* 就是这里: hash table of the record locks */
hash_table_t* rec_hash;
/* Mutex protecting the next two fields */
ib_mutex_t wait_mutex;
/**
* Array of user threads suspended while waiting forlocks within InnoDB,
* protected by the lock_sys->wait_mutex
*/
srv_slot_t* waiting_threads;
/*
* highest slot ever used in the waiting_threads array,
* protected by lock_sys->wait_mutex
*/
srv_slot_t* last_slot;
/**
* TRUE if rollback of all recovered transactions is complete.
* Protected by lock_sys->mutex
*/
ibool rollback_complete;
/* Max wait time */
ulint n_lock_max_wait_time;
/**
* Set to the event that is created in the lock wait monitor thread.
* A value of 0 means the thread is not active
*/
os_event_t timeout_event;
/* True if the timeout thread is running */
bool timeout_thread_active;
};函數lock_sys_create在database start之際負責初始化lock_sys_t結構。 srv_lock_table_size變數決定了rec_hash中哈希槽數量的大小。 The key value of the rec_hash hash table is computed by using the space id and page number of the page.。
摘自lock0lock.ic、ut0rnd.ic 檔案
/**
* Calculates the fold value of a page file address: used in inserting or
* searching for a lock in the hash table.
*
* @return folded value
*/
UNIV_INLINE ulint lock_rec_fold(ulint space, ulint page_no)
{
return(ut_fold_ulint_pair(space, page_no));
}
/**
* Folds a pair of ulints.
*
* @return folded value
*/
UNIV_INLINE ulint ut_fold_ulint_pair(ulint n1, ulint n2)
{
return (
(
(((n1 ^ n2 ^ UT_HASH_RANDOM_MASK2) << 8) + n1)
^ UT_HASH_RANDOM_MASK
)
+ n2
);
}這將意味著無法提供一個手段使得我們可以直接得知某一行是否上鎖。而是應該先透過其所在的頁得到space id、page number透過lock_rec_fold函數得出key值而後經過hash查詢得到lock_rec_t,而後根據heap_no掃描bit map,最後確定鎖定資訊。 lock_rec_get_first函式實作了上述邏輯:
这里返回的其实是lock_t对象,摘自lock0lock.cc文件
/**
* Gets the first explicit lock request on a record.
*
* @param block : block containing the record
* @param heap_no : heap number of the record
*
* @return first lock, NULL if none exists
*/
UNIV_INLINE lock_t* lock_rec_get_first(const buf_block_t* block, ulint heap_no)
{
lock_t* lock;
ut_ad(lock_mutex_own());
for (lock = lock_rec_get_first_on_page(block); lock;
lock = lock_rec_get_next_on_page(lock)
) {
if (lock_rec_get_nth_bit(lock, heap_no)) {
break;
}
}
return(lock);
}以页面为粒度进行锁维护并非最直接有效的方式,它明显是时间换空间,不过这种设计使得锁开销很小。某一事务对任一行上锁的开销都是一样的,锁数量的上升也不会带来额外的内存消耗。
对应每个事务的内存对象trx_t中,包含了该事务的锁信息链表和等待的锁信息。因此存在如下两种途径对锁进行查询:
根据事务: 通过trx_t对象的trx_locks链表,再通过lock_t对象中的trx_locks遍历可得某事务持有、等待的所有锁信息。
根据记录: 根据记录所在的页,通过space id、page number在lock_sys_t结构中定位到lock_t对象,扫描bitmap找到heap_no对应的bit位。
上述各种数据结构,对其整理关系如下图所示:
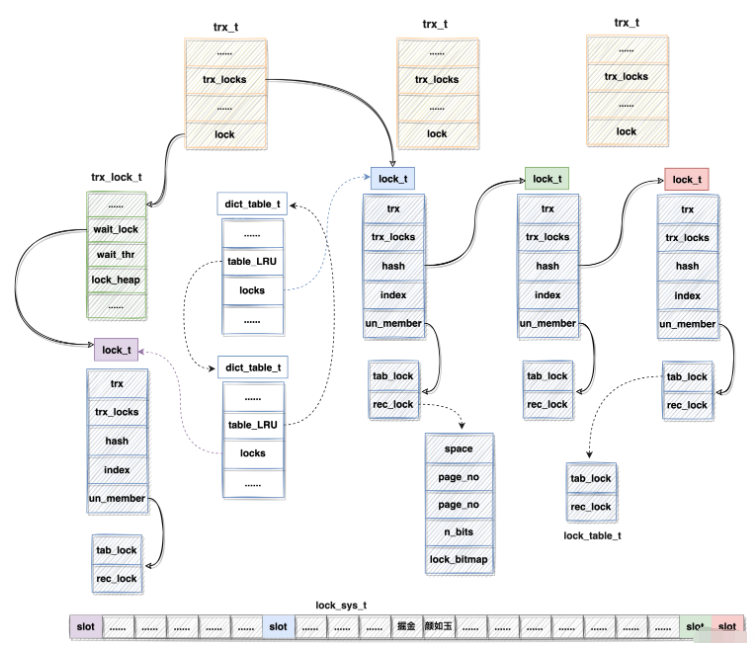
注:
lock_sys_t中的slot颜色与lock_t颜色相同则表明lock_sys_t slot持有lock_t 指针信息,实在是没法连线,不然图很混乱
以上是Mysql鎖內部實作機制是什麼的詳細內容。更多資訊請關注PHP中文網其他相關文章!




