淺析Python裝飾器中的@property
一、使用@property優點
將類別方法轉換為類別屬性,可以用來直接取得屬性值或將屬性賦值。
案例分析
範例:
class Exam(object):
def __init__(self, score):
self._score = score
def get_score(self):
return self._score
def set_score(self, val):
if val < 0:
self._score = 0
elif val > 100:
self._score = 100
else:
self._score = val
e = Exam(60)
print(e.get_score())
e.set_score(70)
print(e.get_score())
程式碼解析:
定義了一個Exam 類,為了避免直接對_score 屬性操作,提供了get_score 和set_score 方法,這樣起到了封裝的作用,把一些不想對外公開的屬性隱蔽起來,而只是提供方法給用戶操作,在方法裡面,可以檢查參數的合理性等。
Python 提供了 property 裝飾器,被裝飾的方法,可以將其『當作』屬性來用。
範例:
class Exam(object):
def __init__(self, score):
self._score = score
@property
def score(self):
return self._score
@score.setter
def score(self, val):
if val < 0:
self._score = 0
elif val > 100:
self._score = 100
else:
self._score = val
e = Exam(60)
print(e.score)
e.score = 90
print(e.score)
e.score = 200
print(e.score)
##class Exam(object):
def __init__(self, score):
self._score = score
@property
def score(self):
return self._score
e = Exam(60)
print(e.score)
e.score = 200 # score 是只读属性,不能设置值
print(e.score)
註:
###給方法score 加上了@property,於是可以把score 當成一個屬性來用,此時,又會創建新的score.setter,它可以把被裝飾的方法變成屬性來賦值。 ############另外,也不一定要用 score.setter 這個裝飾器,這時 score 就變成一個唯讀屬性:######
class Exam(object):
def __init__(self, score):
self._score = score
@property
def score(self):
return self._score
e = Exam(60)
print(e.score)
e.score = 200 # score 是只读属性,不能设置值
print(e.score)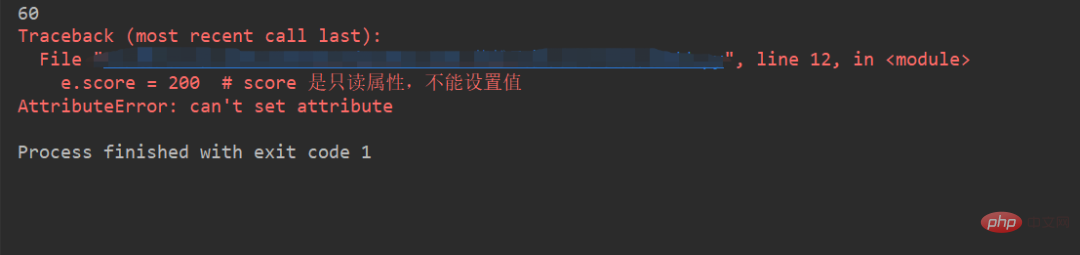
二、@property的力量
python处理上述问题的方法是使用property。可以这样来实现它。
例 :
class Celsius:
def __init__(self, temperature = 0):
self.temperature = temperature
def to_fahrenheit(self):
return (self.temperature * 1.8) + 32
def get_temperature(self):
print("获得的值")
return self._temperature
def set_temperature(self, value):
if value < -273:
raise ValueError("零下273度是不可能的")
print("设定值")
self._temperature = value
temperature = property(get_temperature,set_temperature)并且,一旦运行,在shell中发出以下代码。
c = Celsius() print(c.temperature)
创建对象时,将调用init ()方法。此方法的线为self.temperature = temperature。
此分配自动称为set_temperature()。

2. 属性的作用。
任何访问如c.temperature都会自动调用get_temperature()。
例:
c.temperature = 37 print(c.temperature) print(c.to_fahrenheit())

注:
温度值存储在私有变量_temperature中。temperature属性是一个属性对象,它提供了与此私有变量的接口。
三、深入了解property
在Python中,property()是一个内置函数,用于创建并返回属性对象。
语法
property(fget=None, fset=None, fdel=None, doc=None)
参数解析
fget为获取属性值的函数,fset为设置属性值的函数,fdel为删除属性的函数,doc为字符串(如注释)。从实现中可以看出,这些函数参数是可选的。
可以简单地按照以下方式创建属性对象。
property(fget=None, fset=None, fdel=None, doc=None) print(property())

1. 属性对象有三个方法,getter()、setter()和deleter()。
语法:
temperature = property(get_temperature,set_temperature)
用于稍后指定fget、fset和fdel。
# 创建空属性 temperature = property() # 设置 fget temperature = temperature.getter(get_temperature) # 设置 fset temperature = temperature.setter(set_temperature)
注:
这两段代码是等效的。
不定义名称get_temperature,set_temperature。
因为它们是不必要的,并且会影响类命名空间。为此,在定义getter和setter函数时重用了名称temperature。
2. 案例
例:
class Celsius:
def __init__(self, temperature = 0):
self._temperature = temperature
def to_fahrenheit(self):
return (self.temperature * 1.8) + 32
@property
def temperature(self):
print("获得值")
return self._temperature
@temperature.setter
def temperature(self, value):
if value < -273:
raise ValueError("零下273度是不可能的")
print("零下273度是不可能的")
self._temperature = value
c=Celsius()
c.temperature = 37
print(c.temperature)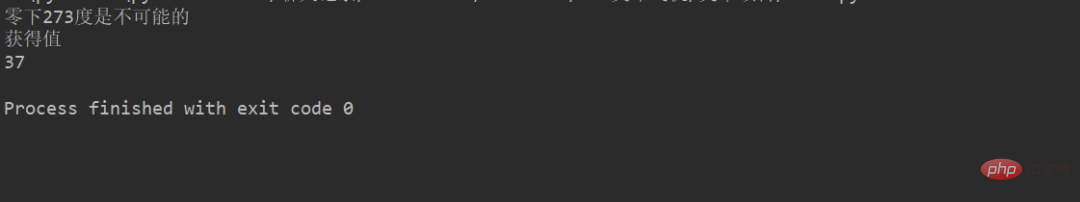
注:
实现是制作属性的简单方法和推荐方法。在Python中寻找属性时,很可能会遇到这些类型的构造。
四、总结
本文基于Python基础,介绍了@property 如何把方法变成了属性。通过案例的分析,代码的展示。介绍了@property的力量,以及提供了相应错误的解决方案处理方法。属性的作用。
以上是淺析Python裝飾器中的@property的詳細內容。更多資訊請關注PHP中文網其他相關文章!

熱AI工具

Undresser.AI Undress
人工智慧驅動的應用程序,用於創建逼真的裸體照片

AI Clothes Remover
用於從照片中去除衣服的線上人工智慧工具。

Undress AI Tool
免費脫衣圖片

Clothoff.io
AI脫衣器

Video Face Swap
使用我們完全免費的人工智慧換臉工具,輕鬆在任何影片中換臉!

熱門文章

熱工具

記事本++7.3.1
好用且免費的程式碼編輯器

SublimeText3漢化版
中文版,非常好用

禪工作室 13.0.1
強大的PHP整合開發環境

Dreamweaver CS6
視覺化網頁開發工具

SublimeText3 Mac版
神級程式碼編輯軟體(SublimeText3)
 PHP和Python:解釋了不同的範例
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:26 AM
PHP和Python:解釋了不同的範例
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:26 AM
PHP主要是過程式編程,但也支持面向對象編程(OOP);Python支持多種範式,包括OOP、函數式和過程式編程。 PHP適合web開發,Python適用於多種應用,如數據分析和機器學習。
 在PHP和Python之間進行選擇:指南
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:24 AM
在PHP和Python之間進行選擇:指南
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:24 AM
PHP適合網頁開發和快速原型開發,Python適用於數據科學和機器學習。 1.PHP用於動態網頁開發,語法簡單,適合快速開發。 2.Python語法簡潔,適用於多領域,庫生態系統強大。
 Python vs. JavaScript:學習曲線和易用性
Apr 16, 2025 am 12:12 AM
Python vs. JavaScript:學習曲線和易用性
Apr 16, 2025 am 12:12 AM
Python更適合初學者,學習曲線平緩,語法簡潔;JavaScript適合前端開發,學習曲線較陡,語法靈活。 1.Python語法直觀,適用於數據科學和後端開發。 2.JavaScript靈活,廣泛用於前端和服務器端編程。
 PHP和Python:深入了解他們的歷史
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:25 AM
PHP和Python:深入了解他們的歷史
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:25 AM
PHP起源於1994年,由RasmusLerdorf開發,最初用於跟踪網站訪問者,逐漸演變為服務器端腳本語言,廣泛應用於網頁開發。 Python由GuidovanRossum於1980年代末開發,1991年首次發布,強調代碼可讀性和簡潔性,適用於科學計算、數據分析等領域。
 vs code 可以在 Windows 8 中運行嗎
Apr 15, 2025 pm 07:24 PM
vs code 可以在 Windows 8 中運行嗎
Apr 15, 2025 pm 07:24 PM
VS Code可以在Windows 8上運行,但體驗可能不佳。首先確保系統已更新到最新補丁,然後下載與系統架構匹配的VS Code安裝包,按照提示安裝。安裝後,注意某些擴展程序可能與Windows 8不兼容,需要尋找替代擴展或在虛擬機中使用更新的Windows系統。安裝必要的擴展,檢查是否正常工作。儘管VS Code在Windows 8上可行,但建議升級到更新的Windows系統以獲得更好的開發體驗和安全保障。
 visual studio code 可以用於 python 嗎
Apr 15, 2025 pm 08:18 PM
visual studio code 可以用於 python 嗎
Apr 15, 2025 pm 08:18 PM
VS Code 可用於編寫 Python,並提供許多功能,使其成為開發 Python 應用程序的理想工具。它允許用戶:安裝 Python 擴展,以獲得代碼補全、語法高亮和調試等功能。使用調試器逐步跟踪代碼,查找和修復錯誤。集成 Git,進行版本控制。使用代碼格式化工具,保持代碼一致性。使用 Linting 工具,提前發現潛在問題。
 notepad 怎麼運行python
Apr 16, 2025 pm 07:33 PM
notepad 怎麼運行python
Apr 16, 2025 pm 07:33 PM
在 Notepad 中運行 Python 代碼需要安裝 Python 可執行文件和 NppExec 插件。安裝 Python 並為其添加 PATH 後,在 NppExec 插件中配置命令為“python”、參數為“{CURRENT_DIRECTORY}{FILE_NAME}”,即可在 Notepad 中通過快捷鍵“F6”運行 Python 代碼。
 vscode 擴展是否是惡意的
Apr 15, 2025 pm 07:57 PM
vscode 擴展是否是惡意的
Apr 15, 2025 pm 07:57 PM
VS Code 擴展存在惡意風險,例如隱藏惡意代碼、利用漏洞、偽裝成合法擴展。識別惡意擴展的方法包括:檢查發布者、閱讀評論、檢查代碼、謹慎安裝。安全措施還包括:安全意識、良好習慣、定期更新和殺毒軟件。






