編譯器為陣列的所有元素分配連續的記憶體位置。
基底位址是陣列中第一個元素的位置。
例如,int a [5] = {10, 20,30,40,50};
這五個元素的儲存如下所示−
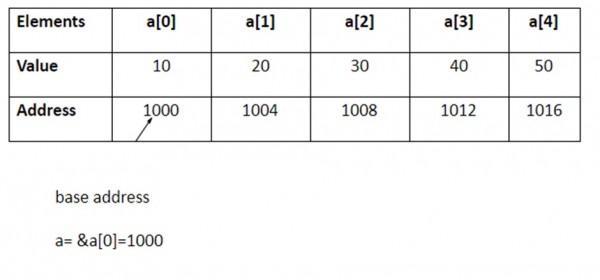
如果將&p'宣告為整數指針,則可以透過下列賦值指向數組&a' −
p=a or p=&a[0];
透過使用p 從一個元素移動到另一個元素來存取每個&a的值。當指標遞增時,它的值會增加指向的資料類型的大小。這個長度被稱為「比例因子」。
指標p和變數a之間的關係如下所示−
P = &a[0] = 1000 P+1 = &a[1] = 1004 P+2 = &a[2] = 1008 P+3 = &a[3] = 1012 P+4 = &a[4] = 1016
元素的位址是使用其索引和資料類型的比例因子計算的。
a[3]的位址=基底位址(3*a的比例因子int)
=1000 (3*4)
=1000 12
=1012
*(p+3) gives the value of a[3] a[i] = *(p+i)
#include<stdio.h>
main (){
int a[5];
int *p,i;
clrscr ();
printf (”Enter 5 lements”);
for (i=0; i<5; i++)
scanf (“%d”, &a[i]);
p = &a[0];
printf (“Elements of the array are”);
for (i=0; i<5; i++)
printf(“%d”, *(p+i));
getch();
}Enter 5 elements : 10 20 30 40 50 Elements of the array are : 10 20 30 40 50
以上是解釋C語言中指標和陣列的概念的詳細內容。更多資訊請關注PHP中文網其他相關文章!




