循環調度的C程序
我們給定了n個進程及其對應的突發時間和時間量,任務是找到平均等待時間和平均週轉時間並顯示結果。
#什麼是循環調度?
輪循是一種專為分時系統設計的CPU調度演算法。它更像是 FCFS 調度演算法,但有一個變化是循環進程受量子時間大小的限制。一個小的時間單位被稱為時間量子或時間片。時間量的範圍可以是 10 到 100 毫秒。 CPU將就緒佇列視為循環佇列,以給定的時間片執行程序。它遵循搶佔式方法,因為固定時間被分配給進程。它唯一的缺點是上下文切換的開銷。
#我們需要計算什麼?
Completion Time#是行程所需的時間完成其執行
##週轉時間#是流程提交和完成之間的時間間隔。
週轉時間= 流程完成– 流程提交等待時間是週轉時間和突發時間之間的差等待時間= 週轉時間- 突發時間範例我們有3 個進程P1、P2 和P3 對應的突發時間為24、3 及3| #Burst Time | |
|---|---|
| 24 | |
| #3 | |
使用甘特圖,平均等待時間計算如下-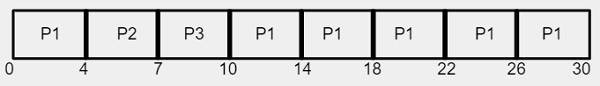
平均等待時間= 17/3 = 5.66 毫秒
演算法
Start
Step 1-> In function int turnarroundtime(int processes[], int n, int bt[], int wt[], int tat[])
Loop For i = 0 and i < n and i++
Set tat[i] = bt[i] + wt[i]
return 1
Step 2-> In function int waitingtime(int processes[], int n, int bt[], int wt[], int quantum)
Declare rem_bt[n]
Loop For i = 0 and i < n and i++
Set rem_bt[i] = bt[i]
Set t = 0
Loop While (1)
Set done = true
Loop For i = 0 and i < n and i++
If rem_bt[i] > 0 then,
Set done = false
If rem_bt[i] > quantum then,
Set t = t + quantum
Set rem_bt[i] = rem_bt[i] - quantum
Else
Set t = t + rem_bt[i]
Set wt[i] = t - bt[i]
Set rem_bt[i] = 0
If done == true then,
Break
Step 3->In function int findavgTime(int processes[], int n, int bt[], int quantum)
Declare and initialize wt[n], tat[n], total_wt = 0, total_tat = 0
Call function waitingtime(processes, n, bt, wt, quantum)
Call function turnarroundtime(processes, n, bt, wt, tat)
Print "Processes Burst Time Waiting Time turnaround time "
Loop For i=0 and i<n and i++
Set total_wt = total_wt + wt[i]
Set total_tat = total_tat + tat[i]
Print the value i+1, bt[i], wt[i], tat[i]
Print "Average waiting time = total_wt / n
Print "Average turnaround time =total_tat / n
Step 4-> In function int main()
Delcare and initialize processes[] = { 1, 2, 3}
Declare and initialize n = sizeof processes / sizeof processes[0]
Declare and initialize burst_time[] = {8, 6, 12}
Set quantum = 2
Call function findavgTime(processes, n, burst_time, quantum)實例示範
#include <stdio.h>
// Function to calculate turn around time
int turnarroundtime(int processes[], int n,
int bt[], int wt[], int tat[]) {
// calculating turnaround time by adding
// bt[i] + wt[i]
for (int i = 0; i < n ; i++)
tat[i] = bt[i] + wt[i];
return 1;
}
// Function to find the waiting time for all
// processes
int waitingtime(int processes[], int n,
int bt[], int wt[], int quantum) {
// Make a copy of burst times bt[] to store remaining
// burst times.
int rem_bt[n];
for (int i = 0 ; i < n ; i++)
rem_bt[i] = bt[i];
int t = 0; // Current time
// Keep traversing processes in round robin manner
// until all of them are not done.
while (1) {
bool done = true;
// Traverse all processes one by one repeatedly
for (int i = 0 ; i < n; i++) {
// If burst time of a process is greater than 0
// then only need to process further
if (rem_bt[i] > 0) {
done = false; // There is a pending process
if (rem_bt[i] > quantum) {
// Increase the value of t i.e. shows
// how much time a process has been processed
t += quantum;
// Decrease the burst_time of current process
// by quantum
rem_bt[i] -= quantum;
}
// If burst time is smaller than or equal to
// quantum. Last cycle for this process
else {
// Increase the value of t i.e. shows
// how much time a process has been processed
t = t + rem_bt[i];
// Waiting time is current time minus time
// used by this process
wt[i] = t - bt[i];
// As the process gets fully executed
// make its remaining burst time = 0
rem_bt[i] = 0;
}
}
}
// If all processes are done
if (done == true)
break;
}
return 1;
}
// Function to calculate average time
int findavgTime(int processes[], int n, int bt[],
int quantum) {
int wt[n], tat[n], total_wt = 0, total_tat = 0;
// Function to find waiting time of all processes
waitingtime(processes, n, bt, wt, quantum);
// Function to find turn around time for all processes
turnarroundtime(processes, n, bt, wt, tat);
// Display processes along with all details
printf("Processes Burst Time Waiting Time turnaround time</p><p>");
// Calculate total waiting time and total turn
// around time
for (int i=0; i<n; i++) {
total_wt = total_wt + wt[i];
total_tat = total_tat + tat[i];
printf("\t%d\t\t\t%d\t\t\t%d\t\t\t%d</p><p>",i+1, bt[i], wt[i], tat[i]);
}
printf("Average waiting time = %f", (float)total_wt / (float)n);
printf("</p><p>Average turnaround time = %f</p><p>", (float)total_tat / (float)n);
return 1;
}
// main function
int main() {
// process id's
int processes[] = { 1, 2, 3};
int n = sizeof processes / sizeof processes[0];
// Burst time of all processes
int burst_time[] = {8, 6, 12};
// Time quantum
int quantum = 2;
findavgTime(processes, n, burst_time, quantum);
return 0;
}登入後複製輸出
#include <stdio.h>
// Function to calculate turn around time
int turnarroundtime(int processes[], int n,
int bt[], int wt[], int tat[]) {
// calculating turnaround time by adding
// bt[i] + wt[i]
for (int i = 0; i < n ; i++)
tat[i] = bt[i] + wt[i];
return 1;
}
// Function to find the waiting time for all
// processes
int waitingtime(int processes[], int n,
int bt[], int wt[], int quantum) {
// Make a copy of burst times bt[] to store remaining
// burst times.
int rem_bt[n];
for (int i = 0 ; i < n ; i++)
rem_bt[i] = bt[i];
int t = 0; // Current time
// Keep traversing processes in round robin manner
// until all of them are not done.
while (1) {
bool done = true;
// Traverse all processes one by one repeatedly
for (int i = 0 ; i < n; i++) {
// If burst time of a process is greater than 0
// then only need to process further
if (rem_bt[i] > 0) {
done = false; // There is a pending process
if (rem_bt[i] > quantum) {
// Increase the value of t i.e. shows
// how much time a process has been processed
t += quantum;
// Decrease the burst_time of current process
// by quantum
rem_bt[i] -= quantum;
}
// If burst time is smaller than or equal to
// quantum. Last cycle for this process
else {
// Increase the value of t i.e. shows
// how much time a process has been processed
t = t + rem_bt[i];
// Waiting time is current time minus time
// used by this process
wt[i] = t - bt[i];
// As the process gets fully executed
// make its remaining burst time = 0
rem_bt[i] = 0;
}
}
}
// If all processes are done
if (done == true)
break;
}
return 1;
}
// Function to calculate average time
int findavgTime(int processes[], int n, int bt[],
int quantum) {
int wt[n], tat[n], total_wt = 0, total_tat = 0;
// Function to find waiting time of all processes
waitingtime(processes, n, bt, wt, quantum);
// Function to find turn around time for all processes
turnarroundtime(processes, n, bt, wt, tat);
// Display processes along with all details
printf("Processes Burst Time Waiting Time turnaround time</p><p>");
// Calculate total waiting time and total turn
// around time
for (int i=0; i<n; i++) {
total_wt = total_wt + wt[i];
total_tat = total_tat + tat[i];
printf("\t%d\t\t\t%d\t\t\t%d\t\t\t%d</p><p>",i+1, bt[i], wt[i], tat[i]);
}
printf("Average waiting time = %f", (float)total_wt / (float)n);
printf("</p><p>Average turnaround time = %f</p><p>", (float)total_tat / (float)n);
return 1;
}
// main function
int main() {
// process id's
int processes[] = { 1, 2, 3};
int n = sizeof processes / sizeof processes[0];
// Burst time of all processes
int burst_time[] = {8, 6, 12};
// Time quantum
int quantum = 2;
findavgTime(processes, n, burst_time, quantum);
return 0;
}以上是循環調度的C程序的詳細內容。更多資訊請關注PHP中文網其他相關文章!

熱AI工具

Undresser.AI Undress
人工智慧驅動的應用程序,用於創建逼真的裸體照片

AI Clothes Remover
用於從照片中去除衣服的線上人工智慧工具。

Undress AI Tool
免費脫衣圖片

Clothoff.io
AI脫衣器

Video Face Swap
使用我們完全免費的人工智慧換臉工具,輕鬆在任何影片中換臉!

熱門文章

熱工具

記事本++7.3.1
好用且免費的程式碼編輯器

SublimeText3漢化版
中文版,非常好用

禪工作室 13.0.1
強大的PHP整合開發環境

Dreamweaver CS6
視覺化網頁開發工具

SublimeText3 Mac版
神級程式碼編輯軟體(SublimeText3)
 如何在 macOS 中停用「按一下桌面顯示」功能
Nov 23, 2023 pm 02:31 PM
如何在 macOS 中停用「按一下桌面顯示」功能
Nov 23, 2023 pm 02:31 PM
預設情況下,macOSSonoma會在您按一下桌面桌布時隱藏所有活動視窗。如果您傾向於在桌面上有一堆需要存取的文件,這將很方便。但是,如果您發現這種行為令人抓狂,則有一種方法可以將其關閉。 Apple最新的macOSSonomaMac作業系統有一個新選項,稱為「點擊壁紙以顯示桌面」。預設情況下啟用,如果您傾向於打開多個窗口,並且想要訪問桌面上的文件或資料夾,而不必最小化或移動窗口,則該選項可能特別有用。啟用該功能並點擊桌面牆紙後,所有開啟的視窗都會暫時被掃到一邊,從而直接存取桌面。完成後,您可以再次
 C++程式以給定值為參數,找出雙曲正弦反函數的值
Sep 17, 2023 am 10:49 AM
C++程式以給定值為參數,找出雙曲正弦反函數的值
Sep 17, 2023 am 10:49 AM
雙曲函數是使用雙曲線而不是圓定義的,與普通三角函數相當。它從提供的弧度角傳回雙曲正弦函數中的比率參數。但要做相反的事,或者換句話說。如果我們想要根據雙曲正弦值計算角度,我們需要像雙曲反正弦運算一樣的反雙曲三角運算。本課程將示範如何使用C++中的雙曲反正弦(asinh)函數,並使用雙曲正弦值(以弧度為單位)計算角度。雙曲反正弦運算遵循下列公式-$$\mathrm{sinh^{-1}x\:=\:In(x\:+\:\sqrt{x^2\:+\:1})},其中\:In\:是\:自然對數\:(log_e\:k)
 C程式使用rename()函數更改檔名
Sep 21, 2023 pm 10:01 PM
C程式使用rename()函數更改檔名
Sep 21, 2023 pm 10:01 PM
rename函數將檔案或目錄從舊名稱變更為新名稱。此操作類似於移動操作。因此,我們也可以使用此rename函數來移動檔案。此函數存在於stdio.h庫頭檔中。 rename函數的語法如下:intrename(constchar*oldname,constchar*newname);rename()函數的函數它接受兩個參數。一個是oldname,一個是newname。這兩個參數都是指向常數字元的指針,用於定義檔案的舊名稱和新名稱。如果檔案重新命名成功,則傳回零;否則,傳回非零整數。在重新命名操作期間
 C++程式列印字典
Sep 11, 2023 am 10:33 AM
C++程式列印字典
Sep 11, 2023 am 10:33 AM
映射是C++中的一種特殊類型的容器,其中每個元素都是一對兩個值,即鍵值和映射值。鍵值用於索引每個項目,映射值是與鍵關聯的值。無論映射值是否唯一,鍵始終是唯一的。要在C++中列印映射元素,我們必須使用迭代器。一組項目中的一個元素由迭代器物件指示。迭代器主要與陣列和其他類型的容器(例如向量)一起使用,並且它們具有一組特定的操作,可用於識別特定範圍內的特定元素。可以增加或減少迭代器來引用範圍或容器中存在的不同元素。迭代器指向範圍內特定元素的記憶體位置。使用迭代器在C++中列印地圖首先,我們先來看看如何定義
 C++程式來檢查一個字元是否為字母或非字母
Sep 14, 2023 pm 03:37 PM
C++程式來檢查一個字元是否為字母或非字母
Sep 14, 2023 pm 03:37 PM
在解決一些邏輯程式設計問題時,使用字串或字元有時非常有用。字串是字元的集合,字元是1位元組資料類型,用於保存ASCII值中的符號。符號可以是英文字母、數字或特殊字元。在本文中,我們將學習如何使用C++檢查一個字元是否是英文字母或字母表中的字母。檢查isalpha()函數要檢查數字是否為字母,我們可以使用ctype.h頭檔中的isalpha()函數。這將一個字元作為輸入,如果是字母表,則傳回true,否則傳回false。讓我們看看下面的C++實作來了解這個函數的用法。例子的中文翻譯為:示
 lambda表達式跳出循環
Feb 20, 2024 am 08:47 AM
lambda表達式跳出循環
Feb 20, 2024 am 08:47 AM
lambda表達式跳出循環,需要具體程式碼範例在程式設計中,循環結構是常用的一種重要語法。然而,在特定的情況下,我們可能希望在循環體內滿足某個條件時,跳出整個循環,而不是僅僅終止當前的循環迭代。在這個時候,lambda表達式的特性可以幫助我們達成跳脫循環的目標。 lambda表達式是一種匿名函數的宣告方式,它可以在內部定義簡單的函數邏輯。它與普通的函數聲明不同,
 C程序中的階乘程序
Sep 09, 2023 am 11:17 AM
C程序中的階乘程序
Sep 09, 2023 am 11:17 AM
給定數字n,任務是計算數字的階乘。數字的階乘是通過將數字與其小的存儲等整數值相乘來計算的。階乘的計算公式為−0!=11!=12!=2X1=23 !=3X2X1=64!=4X3X2X1=245!=5X4X3X2X1=120...N!=n*(n-1
 寫一個C程序,使用strncmp函式庫函數來比較兩個字串
Sep 09, 2023 pm 01:17 PM
寫一個C程序,使用strncmp函式庫函數來比較兩個字串
Sep 09, 2023 pm 01:17 PM
Strncmp是一個預先定義的函式庫函數,存在於string.h檔案中,它用於比較兩個字串並顯示哪個字串較大。 strcmp函數(字串比較)此函數比較兩個字串。它會傳回兩個字串中第一個不匹配字元的ASCII差異。語法intstrcmp(string1,string2);如果差異等於零,則string1=string2。如果差異為正,則string1>string2。如果差異為負,則string1<string2。範例strncmp函數此函數用於比較兩個字串的前n個字元。語法strn






