一文搞懂 | Linux 時脈子系統
Clock 時鐘是 SoC 中的脈搏,它控制著各個部件按照各自的節奏運作。例如,CPU 主頻設定、串列埠的波特率設定、I2S 的取樣率設定、I2C 的速率設定等等。這些不同的 clock 設定都需要從某個或某幾個時鐘源頭而來,最後形成一顆時鐘樹。可以透過 cat /sys/kernel/debug/clk/clk_summary 指令查看這棵時鐘樹。
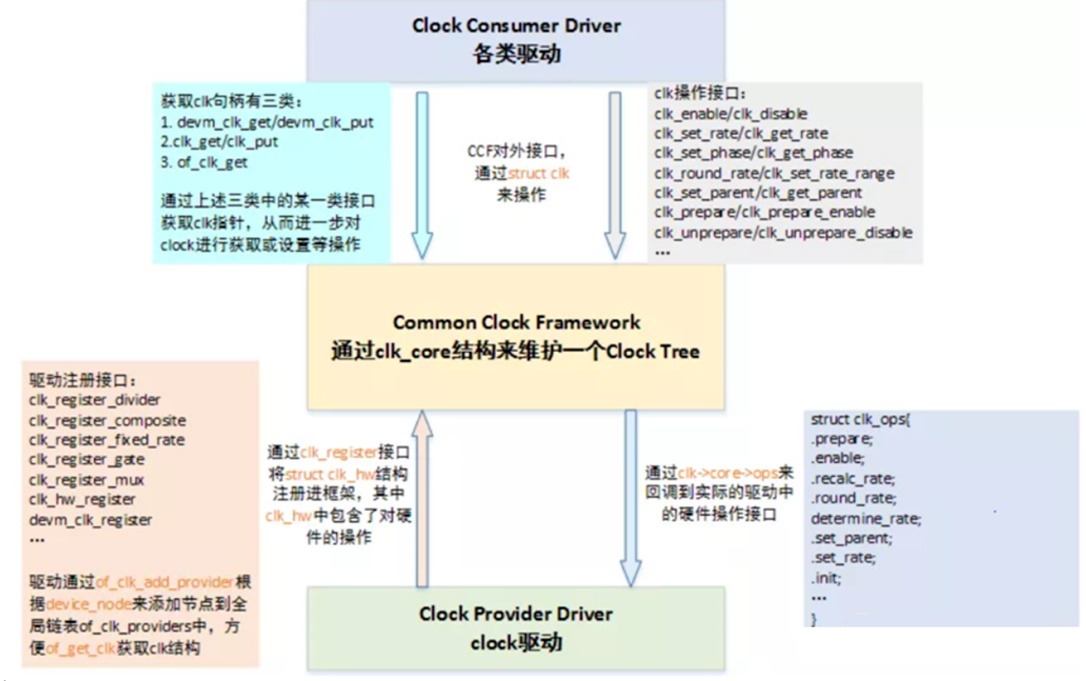
核心中使用 CCF 框架來管理 clock。如下圖所示,右邊是 clock 提供者,即 Clock Provider;中間是 CCF;左邊是裝置驅動的 clock 使用者,即 Clock Consumer。
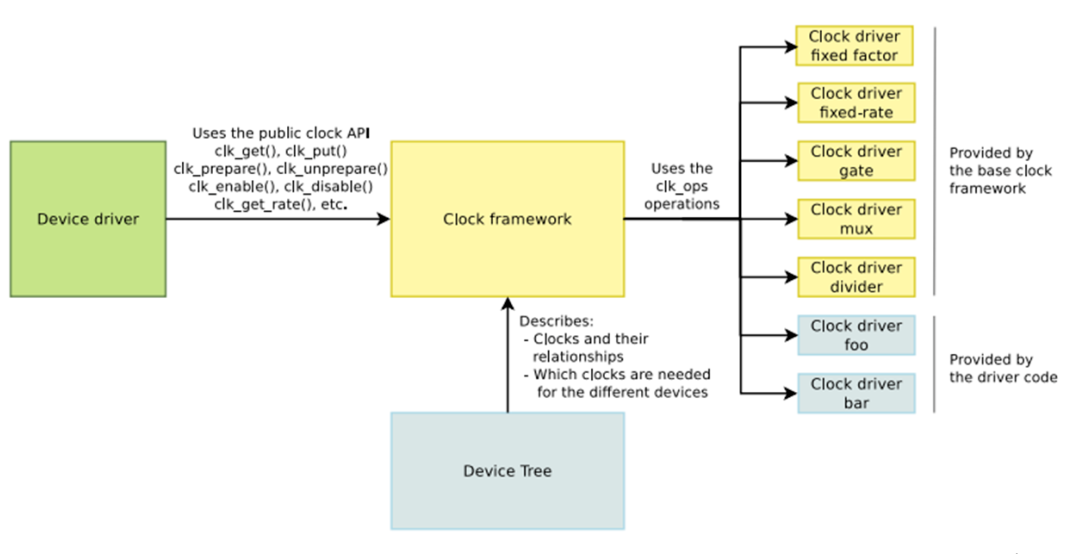
Clock Provider
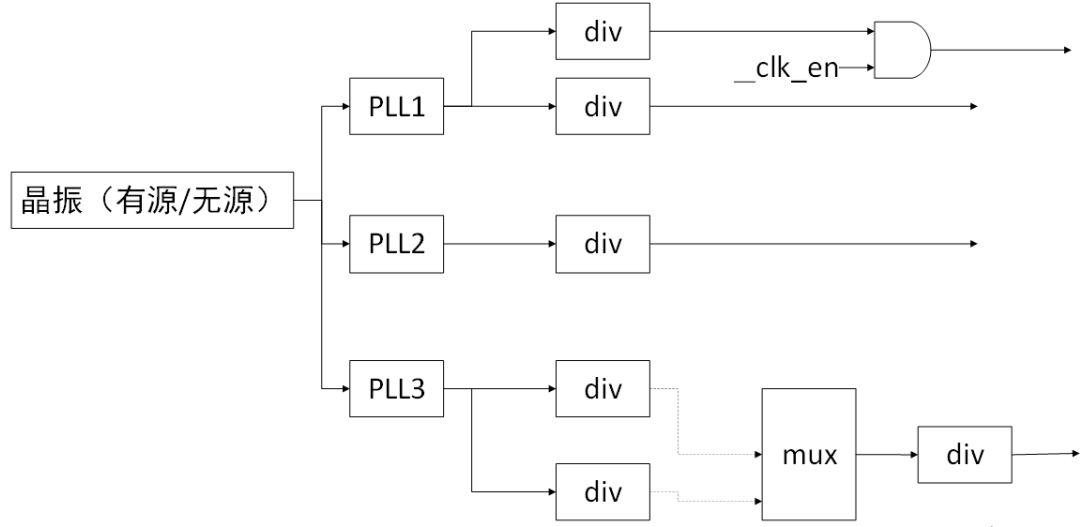
- 根節點一般是 Oscillator(主動振盪器)或 Crystal(被動振盪器)。
- 中間節點有很多種,包括PLL(鎖相環,用於提升頻率的),Divider(分頻器,用於降頻的),Mux(從多個clock path中選擇一個),Gate(用來控制ON/OFF的)。
- 葉節點是使用 clock 做為輸入的、有具體功能的 HW block。
根據 clock 的特點,clock framework 將 clock 分為 fixed rate、gate、devider、mux、fixed factor、composite 六類。
資料結構
#上面六類本質上都屬於clock device,核心把這些 clock HW block 的特性抽取出來,用 struct clk_hw 來表示,具體如下:
struct clk_hw {
//指向CCF模块中对应 clock device 实例
struct clk_core *core;
//clk是访问clk_core的实例。每当consumer通过clk_get对CCF中的clock device(也就是clk_core)发起访
问的时候都需要获取一个句柄,也就是clk
struct clk *clk;
//clock provider driver初始化时的数据,数据被用来初始化clk_hw对应的clk_core数据结构。
const struct clk_init_data *init;
};
struct clk_init_data {
//该clock设备的名字
const char *name;
//clock provider driver进行具体的 HW 操作
const struct clk_ops *ops;
//描述该clk_hw的拓扑结构
const char * const *parent_names;
const struct clk_parent_data *parent_data;
const struct clk_hw **parent_hws;
u8 num_parents;
unsigned long flags;
};
以固定頻率的振動器 fixed rate 為例,它的資料結構是:
struct clk_fixed_rate {
//下面是fixed rate这种clock device特有的成员
struct clk_hw hw;
//基类
unsigned long fixed_rate;
unsigned long fixed_accuracy;
u8 flags;
};
其他的特定的clock device大概都是如此,這裡就不贅述了。
這裡用一張圖來描述這些資料結構之間的關係:
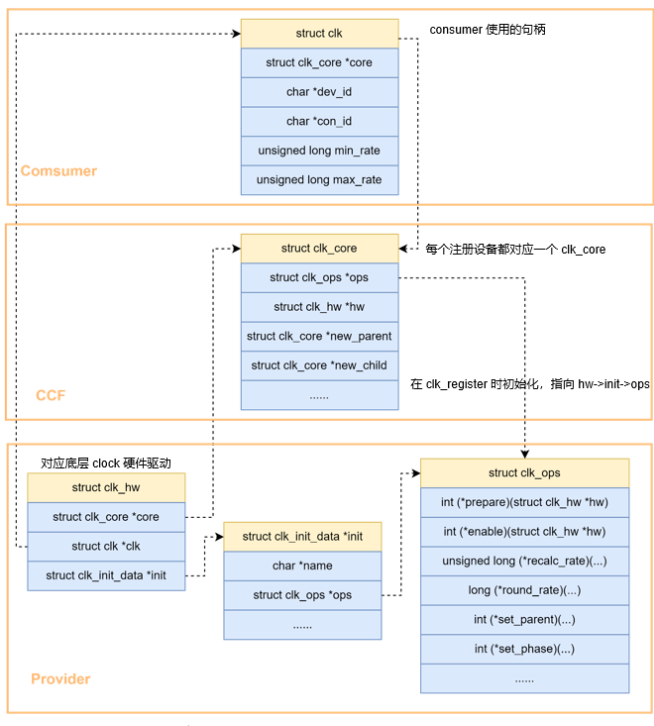
註冊方式
了解資料結構,我們再看下每類 clock device 的註冊方式。
1. fixed rate clock
這一類clock有固定的頻率,不能開關、不能調整頻率、不能選擇parent,是最簡單的一類clock。可以直接透過 DTS 配置的方式支援。也可以透過接口,可以直接註冊 fixed rate clock,如下:
CLK_OF_DECLARE(fixed_clk, "fixed-clock", of_fixed_clk_setup); struct clk *clk_register_fixed_rate(struct device *dev, const char *name, const char *parent_name, unsigned long flags, unsigned long fixed_rate);
2. gate clock
這一類clock只可開關(會提供.enable/.disable回呼),可使用下面介面註冊:
struct clk *clk_register_gate(struct device *dev, const char *name, const char *parent_name, unsigned long flags, void __iomem *reg, u8 bit_idx, u8 clk_gate_flags, spinlock_t *lock);
3. divider clock
這一類clock可以設定分頻值(因而會提供.recalc_rate/.set_rate/.round_rate回呼),可透過下面兩個介面註冊:
struct clk *clk_register_divider(struct device *dev, const char *name, const char *parent_name, unsigned long flags, void __iomem *reg, u8 shift, u8 width, u8 clk_divider_flags, spinlock_t *lock); struct clk *clk_register_divider_table(struct device *dev, const char *name, const char *parent_name, unsigned long flags, void __iomem *reg, u8 shift, u8 width, u8 clk_divider_flags, const struct clk_div_table *table, spinlock_t *lock);
4. mux clock
這一類clock可以選擇多個parent,因為會實作.get_parent/.set_parent/.recalc_rate回調,可透過下面兩個介面註冊:
struct clk *clk_register_mux(struct device *dev, const char *name, const char **parent_names, u8 num_parents, unsigned long flags, void __iomem *reg, u8 shift, u8 width, u8 clk_mux_flags, spinlock_t *lock); struct clk *clk_register_mux_table(struct device *dev, const char *name, const char **parent_names, u8 num_parents, unsigned long flags, void __iomem *reg, u8 shift, u32 mask, u8 clk_mux_flags, u32 *table, spinlock_t *lock);
5. fixed factor clock
#這一類clock具有固定的factor(即multiplier和divider),clock的頻率是由parent clock的頻率,乘以mul,除以div,多用於一些具有固定分頻係數的clock。由於parent clock的頻率可以改變,因而fix factor clock也可該改變頻率,因此也會提供.recalc_rate/.set_rate/.round_rate等回呼。可透過下面介面註冊:
struct clk *clk_register_fixed_factor(struct device *dev, const char *name, const char *parent_name, unsigned long flags, unsigned int mult, unsigned int div);
6. composite clock
顧名思義,就是mux、divider、gate等clock的組合,可透過下面介面註冊:
struct clk *clk_register_composite(struct device *dev, const char *name, const char **parent_names, int num_parents, struct clk_hw *mux_hw, const struct clk_ops *mux_ops, struct clk_hw *rate_hw, const struct clk_ops *rate_ops, struct clk_hw *gate_hw, const struct clk_ops *gate_ops, unsigned long flags);
這些註冊函數最終都會透過函數 clk_register 註冊到 Common Clock Framework 中,傳回為 struct clk 指標。如下圖所示:
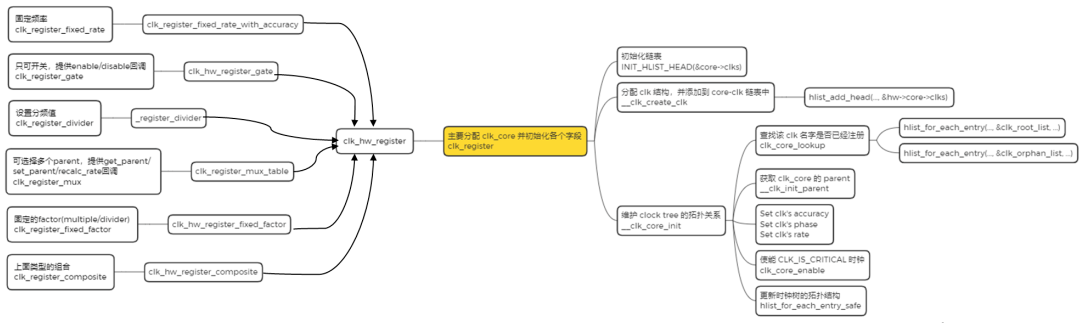
接著將傳回的 struct clk 指針,儲存在一個數組中,並呼叫 of_clk_add_provider 接口,告知 Common Clock Framework。
Clock Consumer
获取 clock
即通过 clock 名称获取 struct clk 指针的过程,由 clk_get、devm_clk_get、clk_get_sys、of_clk_get、of_clk_get_by_name、of_clk_get_from_provider 等接口负责实现,这里以 clk_get 为例,分析其实现过程:
struct clk *clk_get(struct device *dev, const char *con_id)
{
const char *dev_id = dev ? dev_name(dev) : NULL;
struct clk *clk;
if (dev) {
//通过扫描所有“clock-names”中的值,和传入的name比较,如果相同,获得它的index(即“clock-names”中的
第几个),调用of_clk_get,取得clock指针。
clk = __of_clk_get_by_name(dev->of_node, dev_id, con_id);
if (!IS_ERR(clk) || PTR_ERR(clk) == -EPROBE_DEFER)
return clk;
}
return clk_get_sys(dev_id, con_id);
}
struct clk *of_clk_get(struct device_node *np, int index)
{
struct of_phandle_args clkspec;
struct clk *clk;
int rc;
if (index return ERR_PTR(-EINVAL);
rc = of_parse_phandle_with_args(np, "clocks", "#clock-cells", index,
&clkspec);
if (rc)
return ERR_PTR(rc);
//获取clock指针
clk = of_clk_get_from_provider(&clkspec);
of_node_put(clkspec.np);
return clk;
}
of_clk_get_from_provider 通过便利 of_clk_providers 链表,并调用每一个 provider 的 get 回调函数,获取 clock 指针。如下:
struct clk *of_clk_get_from_provider(struct of_phandle_args *clkspec)
{
struct of_clk_provider *provider;
struct clk *clk = ERR_PTR(-ENOENT);
/* Check if we have such a provider in our array */
mutex_lock(&of_clk_lock);
list_for_each_entry(provider, &of_clk_providers, link) {
if (provider->node == clkspec->np)
clk = provider->get(clkspec, provider->data);
if (!IS_ERR(clk))
break;
}
mutex_unlock(&of_clk_lock);
return clk;
}
至此,Consumer 与 Provider 里讲的 of_clk_add_provider 对应起来了。
操作 clock
//启动clock前的准备工作/停止clock后的善后工作。可能会睡眠。 int clk_prepare(struct clk *clk) void clk_unprepare(struct clk *clk) //启动/停止clock。不会睡眠。 static inline int clk_enable(struct clk *clk) static inline void clk_disable(struct clk *clk) //clock频率的获取和设置 static inline unsigned long clk_get_rate(struct clk *clk) static inline int clk_set_rate(struct clk *clk, unsigned long rate) static inline long clk_round_rate(struct clk *clk, unsigned long rate) //获取/选择clock的parent clock static inline int clk_set_parent(struct clk *clk, struct clk *parent) static inline struct clk *clk_get_parent(struct clk *clk) //将clk_prepare和clk_enable组合起来,一起调用。将clk_disable和clk_unprepare组合起来,一起调用 static inline int clk_prepare_enable(struct clk *clk) static inline void clk_disable_unprepare(struct clk *clk)
总结
以上是一文搞懂 | Linux 時脈子系統的詳細內容。更多資訊請關注PHP中文網其他相關文章!

熱AI工具

Undresser.AI Undress
人工智慧驅動的應用程序,用於創建逼真的裸體照片

AI Clothes Remover
用於從照片中去除衣服的線上人工智慧工具。

Undress AI Tool
免費脫衣圖片

Clothoff.io
AI脫衣器

Video Face Swap
使用我們完全免費的人工智慧換臉工具,輕鬆在任何影片中換臉!

熱門文章

熱工具

記事本++7.3.1
好用且免費的程式碼編輯器

SublimeText3漢化版
中文版,非常好用

禪工作室 13.0.1
強大的PHP整合開發環境

Dreamweaver CS6
視覺化網頁開發工具

SublimeText3 Mac版
神級程式碼編輯軟體(SublimeText3)
 Linux體系結構:揭示5個基本組件
Apr 20, 2025 am 12:04 AM
Linux體系結構:揭示5個基本組件
Apr 20, 2025 am 12:04 AM
Linux系統的五個基本組件是:1.內核,2.系統庫,3.系統實用程序,4.圖形用戶界面,5.應用程序。內核管理硬件資源,系統庫提供預編譯函數,系統實用程序用於系統管理,GUI提供可視化交互,應用程序利用這些組件實現功能。
 git怎麼查看倉庫地址
Apr 17, 2025 pm 01:54 PM
git怎麼查看倉庫地址
Apr 17, 2025 pm 01:54 PM
要查看 Git 倉庫地址,請執行以下步驟:1. 打開命令行並導航到倉庫目錄;2. 運行 "git remote -v" 命令;3. 查看輸出中的倉庫名稱及其相應的地址。
 notepad怎麼運行java代碼
Apr 16, 2025 pm 07:39 PM
notepad怎麼運行java代碼
Apr 16, 2025 pm 07:39 PM
雖然 Notepad 無法直接運行 Java 代碼,但可以通過借助其他工具實現:使用命令行編譯器 (javac) 編譯代碼,生成字節碼文件 (filename.class)。使用 Java 解釋器 (java) 解釋字節碼,執行代碼並輸出結果。
 sublime寫好代碼後如何運行
Apr 16, 2025 am 08:51 AM
sublime寫好代碼後如何運行
Apr 16, 2025 am 08:51 AM
在 Sublime 中運行代碼的方法有六種:通過熱鍵、菜單、構建系統、命令行、設置默認構建系統和自定義構建命令,並可通過右鍵單擊項目/文件運行單個文件/項目,構建系統可用性取決於 Sublime Text 的安裝情況。
 Linux的主要目的是什麼?
Apr 16, 2025 am 12:19 AM
Linux的主要目的是什麼?
Apr 16, 2025 am 12:19 AM
Linux的主要用途包括:1.服務器操作系統,2.嵌入式系統,3.桌面操作系統,4.開發和測試環境。 Linux在這些領域表現出色,提供了穩定性、安全性和高效的開發工具。
 laravel安裝代碼
Apr 18, 2025 pm 12:30 PM
laravel安裝代碼
Apr 18, 2025 pm 12:30 PM
要安裝 Laravel,需依序進行以下步驟:安裝 Composer(適用於 macOS/Linux 和 Windows)安裝 Laravel 安裝器創建新項目啟動服務訪問應用程序(網址:http://127.0.0.1:8000)設置數據庫連接(如果需要)
 VSCode怎麼用
Apr 15, 2025 pm 11:21 PM
VSCode怎麼用
Apr 15, 2025 pm 11:21 PM
Visual Studio Code (VSCode) 是一款跨平台、開源且免費的代碼編輯器,由微軟開發。它以輕量、可擴展性和對眾多編程語言的支持而著稱。要安裝 VSCode,請訪問官方網站下載並運行安裝程序。使用 VSCode 時,可以創建新項目、編輯代碼、調試代碼、導航項目、擴展 VSCode 和管理設置。 VSCode 適用於 Windows、macOS 和 Linux,支持多種編程語言,並通過 Marketplace 提供各種擴展。它的優勢包括輕量、可擴展性、廣泛的語言支持、豐富的功能和版







