PHP实现无限级分类(不使用递归)
在进行无限极分类中最常用的算法就是“递归”,熟悉PHP语言的朋友肯定知道,PHP不擅长递归 ,而且递归次数有限(100次左右,因操作系统和配置而异)。
所以本文将会给大家带来几种不使用递归实现无限级分类的代码。供大家来学习使用。
第一种:
无限级分类在开发中经常使用,例如:部门结构、文章分类。无限级分类的难点在于“输出”和“查询”,例如
将文章分类输出为
- 列表形式;
查找分类A下面所有分类包含的文章。
1.实现原理
几种常见的实现方法,各有利弊。其中“改进前序遍历树”数据结构,便于输出和查询,但是在移动分类和常规理解上有些复杂。
2.数据结构
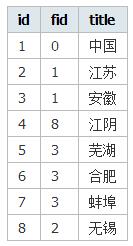
<?php $list = array( array('id'=>1, 'fid'=>0, 'title' => '中国'), array('id'=>2, 'fid'=>1, 'title' => '江苏'), array('id'=>3, 'fid'=>1, 'title' => '安徽'), array('id'=>4, 'fid'=>8, 'title' => '江阴'), array('id'=>5, 'fid'=>3, 'title' => '芜湖'), array('id'=>6, 'fid'=>3, 'title' => '合肥'), array('id'=>7, 'fid'=>3, 'title' => '蚌埠'), array('id'=>8, 'fid'=>8, 'title' => '无锡') ); ?>
由于所有的递归均可以使用循环实现,本文根据PHP语言特点编写了一套关于“无限级”分类的函数,相比递归实现而言效率更高。
3.输出ul列表形式
将上述数据输出为下面的HTML
<ul> <li class="first-child"> <p>江苏</p> <ul> <li class="first-child last-child"> <p>无锡</p> <ul> <li class="first-child last-child"> <p>江阴</p> </li> </ul> </li> </ul> </li> <li class="last-child"> <p>安徽</p> <ul> <li class="first-child"><p>芜湖</p></li> <li><p>合肥</p></li> <li class="last-child"><p>蚌埠</p></li> </ul> </li> </ul>
这种HTML结构在前端使用(使用JavaScript和CSS构造可折叠树)十分方便。具体实现程序如下:
<ul><?php echo get_tree_ul($list, 1); ?></ul>
4.输出option列表形式
<select> <option value="2">江苏</option> <option value="8"> 无锡</option> <option value="4"> 江阴</option> <option value="3">安徽</option> <option value="5"> 芜湖</option> <option value="6"> 合肥</option> <option value="7"> 蚌埠</option> </select>
具体实现程序如下:
<select>
<?php
// get_tree_option()返回数组,并为每个元素增加了“深度”(即depth)列,直接输出即可
$options = get_tree_option($list, 1);
foreach($options as $op) {
echo '<option value="' . $op['id'] .'">' . str_repeat(" ", $op['depth'] * 4) . $op['title'] . '<;/option>';
}
?>
<;/select>5. 查找某一分类的所有子类
<?php $children = get_tree_child($list, 0); echo implode(',', $children); // 输出:1,3,2,7,6,5,8,4 ?>
6. 查找某一分类的所有父类
<?php $children = get_tree_parent($list, 4); echo implode(',', $children); //8, 2, 10 ?>
7. 相关函数
<?php
function get_tree_child($data, $fid) {
$result = array();
$fids = array($fid);
do {
$cids = array();
$flag = false;
foreach($fids as $fid) {
for($i = count($data) - 1; $i >=0 ; $i--) {
$node = $data[$i];
if($node['fid'] == $fid) {
array_splice($data, $i , 1);
$result[] = $node['id'];
$cids[] = $node['id'];
$flag = true;
}
}
}
$fids = $cids;
} while($flag === true);
return $result;
}
function get_tree_parent($data, $id) {
$result = array();
$obj = array();
foreach($data as $node) {
$obj[$node['id']] = $node;
}
$value = isset($obj[$id]) ? $obj[$id] : null;
while($value) {
$id = null;
foreach($data as $node) {
if($node['id'] == $value['fid']) {
$id = $node['id'];
$result[] = $node['id'];
break;
}
}
if($id === null) {
$result[] = $value['fid'];
}
$value = isset($obj[$id]) ? $obj[$id] : null;
}
unset($obj);
return $result;
}
function get_tree_ul($data, $fid) {
$stack = array($fid);
$child = array();
$added_left = array();
$added_right= array();
$html_left = array();
$html_right = array();
$obj = array();
$loop = 0;
foreach($data as $node) {
$pid = $node['fid'];
if(!isset($child[$pid])) {
$child[$pid] = array();
}
array_push($child[$pid], $node['id']);
$obj[$node['id']] = $node;
}
while (count($stack) > 0) {
$id = $stack[0];
$flag = false;
$node = isset($obj[$id]) ? $obj[$id] : null;
if (isset($child[$id])) {
$cids = $child[$id];
$length = count($cids);
for($i = $length - 1; $i >= 0; $i--) {
array_unshift($stack, $cids[$i]);
}
$obj[$cids[$length - 1]]['isLastChild'] = true;
$obj[$cids[0]]['isFirstChild'] = true;
$flag = true;
}
if ($id != $fid && $node && !isset($added_left[$id])) {
if(isset($node['isFirstChild']) && isset($node['isLastChild'])) {
$html_left[] = '<li class="first-child last-child">';
} else if(isset($node['isFirstChild'])) {
$html_left[] = '<li class="first-child">';
} else if(isset($node['isLastChild'])) {
$html_left[] = '<li class="last-child">';
} else {
$html_left[] = '<li>';
}
$html_left[] = ($flag === true) ? "<p>{$node['title']}</p><ul>" : "<p>{$node['title']}</p>";
$added_left[$id] = true;
}
if ($id != $fid && $node && !isset($added_right[$id])) {
$html_right[] = ($flag === true) ? '</ul></li>' : '</li>';
$added_right[$id] = true;
}
if ($flag == false) {
if($node) {
$cids = $child[$node['fid']];
for ($i = count($cids) - 1; $i >= 0; $i--) {
if ($cids[$i] == $id) {
array_splice($child[$node['fid']], $i, 1);
break;
}
}
if(count($child[$node['fid']]) == 0) {
$child[$node['fid']] = null;
}
}
array_push($html_left, array_pop($html_right));
array_shift($stack);
}
$loop++;
if($loop > 5000) return $html_left;
}
unset($child);
unset($obj);
return implode('', $html_left);
}
function get_tree_option($data, $fid) {
$stack = array($fid);
$child = array();
$added = array();
$options = array();
$obj = array();
$loop = 0;
$depth = -1;
foreach($data as $node) {
$pid = $node['fid'];
if(!isset($child[$pid])) {
$child[$pid] = array();
}
array_push($child[$pid], $node['id']);
$obj[$node['id']] = $node;
}
while (count($stack) > 0) {
$id = $stack[0];
$flag = false;
$node = isset($obj[$id]) ? $obj[$id] : null;
if (isset($child[$id])) {
for($i = count($child[$id]) - 1; $i >= 0; $i--) {
array_unshift($stack, $child[$id][$i]);
}
$flag = true;
}
if ($id != $fid && $node && !isset($added[$id])) {
$node['depth'] = $depth;
$options[] = $node;
$added[$id] = true;
}
if($flag == true){
$depth++;
} else {
if($node) {
for ($i = count($child[$node['fid']]) - 1; $i >= 0; $i--) {
if ($child[$node['fid']][$i] == $id) {
array_splice($child[$node['fid']], $i, 1);
break;
}
}
if(count($child[$node['fid']]) == 0) {
$child[$node['fid']] = null;
$depth--;
}
}
array_shift($stack);
}
$loop++;
if($loop > 5000) return $options;
}
unset($child);
unset($obj);
return $options;
}
?>第二种:
这是使用TP来制作的无限级分类。
算法复杂度为T(n)=O(2n),只遍历两次数组.
关键代码其实只有一行
$return[$v['pid']]['child'][$v['id']] = &$return[$k];
但是为了实现较为复杂的扩展,这里添加一些额外的信息
//索引要和ID一致,这不是废话么
//pid是父元素
//不要出现死循环嵌套,就是AB互为父子
//不要出现相同name
$list[0]=['id'=>0,'pid'=>-1,'name'=>'A@0'];//-1用于后面的根目录判断
$list[1]=['id'=>1,'pid'=>0,'name'=>'A@1'];
$list[2]=['id'=>2,'pid'=>0,'name'=>'A@2'];
$list[3]=['id'=>3,'pid'=>2,'name'=>'A@3'];
$list[4]=['id'=>4,'pid'=>3,'name'=>'A@4'];
$list[5]=['id'=>5,'pid'=>0,'name'=>'A@5'];
$list[6]=['id'=>6,'pid'=>1,'name'=>'A@6'];
//先初始化目录
$return=[];
foreach($list as $v)
$return[$v['name']]=[];
//将每个目录与父目录进行拼接,并找到根目录
foreach($list as $k=>$v)
{
if($v['pid']>=0)
$return[$list[$v['pid']]['name']][$v['name']]=&$return[$v['name']];
else
$parent=$v['name'];
}
//打印根目录
print_r($return[$parent]);输出1
Array(
[A@1] => Array
(
[A@6] => Array
(
)
)
[A@2] => Array
(
[A@3] => Array
(
[A@4] => Array
(
)
)
)
[A@5] => Array
(
)
)代码2
/**
* Created by PhpStorm.
* User: Nikaidou-Shinku
* Date: 16/9/14
* Time: 17:12
*/
$list[] = ['id' => 0, 'pid' => -1, 'name' => 'A@0'];//-1用于后面的根目录判断
$list[] = ['id' => 1, 'pid' => 0, 'name' => 'A@1'];
$list[] = ['id' => 2, 'pid' => 0, 'name' => 'A@2'];
$list[] = ['id' => 3, 'pid' => 2, 'name' => 'A@3'];
$list[] = ['id' => 4, 'pid' => 3, 'name' => 'A@4'];
$list[] = ['id' => 5, 'pid' => 0, 'name' => 'A@5'];
$list[] = ['id' => 6, 'pid' => 1, 'name' => 'A@6'];
//先初始化目录
$return = [];
$parent = '';
foreach ($list as $v)
$return[$v['id']] = [
'id' => $v['id'],
'name' => $v['name'],
'pid' => $v['pid'],
'child' => '',
];
//将每个目录与父目录进行拼接,并找到根目录
foreach ($return as $k => $v) {
if ($v['pid'] >= 0)
$return[$v['pid']]['child'][$v['id']] = &$return[$k];
else
$parent = &$return[$k];
}
//打印根目录
var_export($parent);输出2
$aa=[
'id' => 0,
'name' => 'A@0',
'pid' => -1,
'child' =>
[
1 =>
[
'id' => 1,
'name' => 'A@1',
'pid' => 0,
'child' =>
[
6 =>
[
'id' => 6,
'name' => 'A@6',
'pid' => 1,
'child' => '',
],
],
],
2 =>
[
'id' => 2,
'name' => 'A@2',
'pid' => 0,
'child' =>
[
3 =>
[
'id' => 3,
'name' => 'A@3',
'pid' => 2,
'child' =>
[
4 =>
[
'id' => 4,
'name' => 'A@4',
'pid' => 3,
'child' => '',
],
],
],
],
],
5 =>
[
'id' => 5,
'name' => 'A@5',
'pid' => 0,
'child' => '',
],
],
]第三种:
接下来这个无限级分类更为的简单。可以简化成使用5行代码就可以完成。
function generateTree($items){
$tree = array();
foreach($items as $item){
if(isset($items[$item['pid']])){
$items[$item['pid']]['son'][] = &$items[$item['id']];
}else{
$tree[] = &$items[$item['id']];
}
}
return $tree;
}
$items = array(
1 => array('id' => 1, 'pid' => 0, 'name' => '安徽省'),
2 => array('id' => 2, 'pid' => 0, 'name' => '浙江省'),
3 => array('id' => 3, 'pid' => 1, 'name' => '合肥市'),
4 => array('id' => 4, 'pid' => 3, 'name' => '长丰县'),
5 => array('id' => 5, 'pid' => 1, 'name' => '安庆市'),
);
print_r(generateTree($items));可以看到下面打印的结果:
Array
(
[0] => Array
(
[id] => 1
[pid] => 0
[name] => 安徽省
[son] => Array
(
[0] => Array
(
[id] => 3
[pid] => 1
[name] => 合肥市
[son] => Array
(
[0] => Array
(
[id] => 4
[pid] => 3
[name] => 长丰县
)
)
)
[1] => Array
(
[id] => 5
[pid] => 1
[name] => 安庆市
)
)
)
[1] => Array
(
[id] => 2
[pid] => 0
[name] => 浙江省
)
)上面生成树方法还可以精简到5行:
function generateTree($items){
foreach($items as $item)
$items[$item['pid']]['son'][$item['id']] = &$items[$item['id']];
return isset($items[0]['son']) ? $items[0]['son'] : array();
}但是上面的代码有个问题就是对数据库结构有点要求,每个节点要指明其父节点是谁,虽然实用性不高,但是还是能给大家带来启发,学习下不同类型的无限级分类。

熱AI工具

Undresser.AI Undress
人工智慧驅動的應用程序,用於創建逼真的裸體照片

AI Clothes Remover
用於從照片中去除衣服的線上人工智慧工具。

Undress AI Tool
免費脫衣圖片

Clothoff.io
AI脫衣器

Video Face Swap
使用我們完全免費的人工智慧換臉工具,輕鬆在任何影片中換臉!

熱門文章

熱工具

記事本++7.3.1
好用且免費的程式碼編輯器

SublimeText3漢化版
中文版,非常好用

禪工作室 13.0.1
強大的PHP整合開發環境

Dreamweaver CS6
視覺化網頁開發工具

SublimeText3 Mac版
神級程式碼編輯軟體(SublimeText3)
 說明PHP中的安全密碼散列(例如,password_hash,password_verify)。為什麼不使用MD5或SHA1?
Apr 17, 2025 am 12:06 AM
說明PHP中的安全密碼散列(例如,password_hash,password_verify)。為什麼不使用MD5或SHA1?
Apr 17, 2025 am 12:06 AM
在PHP中,應使用password_hash和password_verify函數實現安全的密碼哈希處理,不應使用MD5或SHA1。1)password_hash生成包含鹽值的哈希,增強安全性。 2)password_verify驗證密碼,通過比較哈希值確保安全。 3)MD5和SHA1易受攻擊且缺乏鹽值,不適合現代密碼安全。
 PHP和Python:比較兩種流行的編程語言
Apr 14, 2025 am 12:13 AM
PHP和Python:比較兩種流行的編程語言
Apr 14, 2025 am 12:13 AM
PHP和Python各有優勢,選擇依據項目需求。 1.PHP適合web開發,尤其快速開發和維護網站。 2.Python適用於數據科學、機器學習和人工智能,語法簡潔,適合初學者。
 PHP行動:現實世界中的示例和應用程序
Apr 14, 2025 am 12:19 AM
PHP行動:現實世界中的示例和應用程序
Apr 14, 2025 am 12:19 AM
PHP在電子商務、內容管理系統和API開發中廣泛應用。 1)電子商務:用於購物車功能和支付處理。 2)內容管理系統:用於動態內容生成和用戶管理。 3)API開發:用於RESTfulAPI開發和API安全性。通過性能優化和最佳實踐,PHP應用的效率和可維護性得以提升。
 PHP類型提示如何起作用,包括標量類型,返回類型,聯合類型和無效類型?
Apr 17, 2025 am 12:25 AM
PHP類型提示如何起作用,包括標量類型,返回類型,聯合類型和無效類型?
Apr 17, 2025 am 12:25 AM
PHP類型提示提升代碼質量和可讀性。 1)標量類型提示:自PHP7.0起,允許在函數參數中指定基本數據類型,如int、float等。 2)返回類型提示:確保函數返回值類型的一致性。 3)聯合類型提示:自PHP8.0起,允許在函數參數或返回值中指定多個類型。 4)可空類型提示:允許包含null值,處理可能返回空值的函數。
 PHP的持久相關性:它還活著嗎?
Apr 14, 2025 am 12:12 AM
PHP的持久相關性:它還活著嗎?
Apr 14, 2025 am 12:12 AM
PHP仍然具有活力,其在現代編程領域中依然佔據重要地位。 1)PHP的簡單易學和強大社區支持使其在Web開發中廣泛應用;2)其靈活性和穩定性使其在處理Web表單、數據庫操作和文件處理等方面表現出色;3)PHP不斷進化和優化,適用於初學者和經驗豐富的開發者。
 PHP和Python:解釋了不同的範例
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:26 AM
PHP和Python:解釋了不同的範例
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:26 AM
PHP主要是過程式編程,但也支持面向對象編程(OOP);Python支持多種範式,包括OOP、函數式和過程式編程。 PHP適合web開發,Python適用於多種應用,如數據分析和機器學習。
 您如何防止PHP中的SQL注入? (準備的陳述,PDO)
Apr 15, 2025 am 12:15 AM
您如何防止PHP中的SQL注入? (準備的陳述,PDO)
Apr 15, 2025 am 12:15 AM
在PHP中使用預處理語句和PDO可以有效防範SQL注入攻擊。 1)使用PDO連接數據庫並設置錯誤模式。 2)通過prepare方法創建預處理語句,使用佔位符和execute方法傳遞數據。 3)處理查詢結果並確保代碼的安全性和性能。
 PHP和Python:代碼示例和比較
Apr 15, 2025 am 12:07 AM
PHP和Python:代碼示例和比較
Apr 15, 2025 am 12:07 AM
PHP和Python各有優劣,選擇取決於項目需求和個人偏好。 1.PHP適合快速開發和維護大型Web應用。 2.Python在數據科學和機器學習領域佔據主導地位。






