连通圆问题是判断二维平面内的所有圆是否连通。这个问题可以使用深度优先遍历来解决。 DFS算法有很多应用。本节应用DFS算法来解决连通圆问题。
在连通圆问题中,您需要确定二维平面中的所有圆是否都是连通的。如果所有圆都相连,则将它们绘制为实心圆,如下图(a)所示。否则,它们不会被填充,如下图(b)所示。
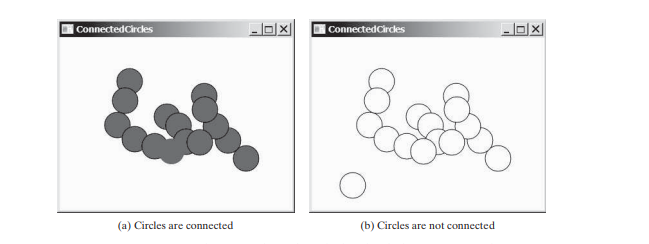
我们将编写一个程序,让用户通过在当前未被圆圈覆盖的空白区域中单击鼠标来创建一个圆圈。添加圆圈时,如果圆圈已连接,则会重新绘制填充,否则未填充。
我们将创建一个图表来模拟问题。每个圆都是图中的一个顶点。如果两个圆重叠,则它们是相连的。我们在图中应用 DFS,如果在深度优先搜索中找到所有顶点,则图是连通的。
程序在下面的代码中给出。
import javafx.application.Application;
import javafx.geometry.Point2D;
import javafx.scene.Node;
import javafx.scene.Scene;
import javafx.scene.layout.Pane;
import javafx.scene.paint.Color;
import javafx.scene.shape.Circle;
import javafx.stage.Stage;
public class ConnectedCircles extends Application {
@Override // Override the start method in the Application class
public void start(Stage primaryStage) {
// Create a scene and place it in the stage
Scene scene = new Scene(new CirclePane(), 450, 350);
primaryStage.setTitle("ConnectedCircles"); // Set the stage title
primaryStage.setScene(scene); // Place the scene in the stage
primaryStage.show(); // Display the stage
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Application.launch(args);
}
/** Pane for displaying circles */
class CirclePane extends Pane {
public CirclePane() {
this.setOnMouseClicked(e -> {
if (!isInsideACircle(new Point2D(e.getX(), e.getY()))) {
// Add a new circle
getChildren().add(new Circle(e.getX(), e.getY(), 20));
colorIfConnected();
}
});
}
/** Returns true if the point is inside an existing circle */
private boolean isInsideACircle(Point2D p) {
for (Node circle: this.getChildren())
if (circle.contains(p))
return true;
return false;
}
/** Color all circles if they are connected */
private void colorIfConnected() {
if (getChildren().size() == 0)
return; // No circles in the pane
// Build the edges
java.util.List<AbstractGraph.Edge> edges = new java.util.ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < getChildren().size(); i++)
for (int j = i + 1; j < getChildren().size(); j++)
if (overlaps((Circle)(getChildren().get(i)), (Circle)(getChildren().get(j)))) {
edges.add(new AbstractGraph.Edge(i, j));
edges.add(new AbstractGraph.Edge(j, i));
}
// Create a graph with circles as vertices
Graph<Node> graph = new UnweightedGraph<>((java.util.List<Node>)getChildren(), edges);
AbstractGraph<Node>.Tree tree = graph.dfs(0); // a DFS tree
boolean isAllCirclesConnected = getChildren().size() == tree.getNumberOfVerticesFound();
for (Node circle: getChildren()) {
if (isAllCirclesConnected) { // All circles are connected
((Circle)circle).setFill(Color.RED);
}
else {
((Circle)circle).setStroke(Color.BLACK);
((Circle)circle).setFill(Color.WHITE);
}
}
}
}
public static boolean overlaps(Circle circle1, Circle circle2) {
return new Point2D(circle1.getCenterX(), circle1.getCenterY()).distance(circle2.getCenterX(), circle2.getCenterY()) <= circle1.getRadius() + circle2.getRadius();
}
}
JavaFX Circle 类包含数据字段 x、y 和 radius,它们指定圆的中心位置和半径。它还定义了 contains 用于测试点是否在圆中。 overlaps 方法(第 76-80 行)检查两个圆是否重叠。
当用户在任何现有圆圈之外单击鼠标时,将以鼠标点为中心创建一个新圆圈,并将该圆圈添加到窗格中(第 26 行)。
为了检测圆是否相连,程序构建了一个图(第 46-59 行)。圆圈是图的顶点。边缘在第 49-55 行中构建。如果两个圆顶点重叠,则它们是相连的(第 51 行)。该图的 DFS 生成一棵树(第 60 行)。树的 getNumberOfVerticesFound() 返回搜索到的顶点数。如果它等于圆的数量,则所有圆都相连(第 61-62 行)。
以上是案例研究:连通圆问题的详细内容。更多信息请关注PHP中文网其他相关文章!




