测量外部服务请求的执行时间对于性能监控和优化至关重要。但是,当对这些外部服务的连接进行池化时,您可能会无意中测量的不仅仅是请求时间。具体来说,如果请求花费的时间太长并且您耗尽了可用连接,则您的自定义逻辑可能会开始包括从池中获取连接的等待时间。这可能会导致误导性指标,导致您误解系统的性能。让我们深入研究一下这是如何发生的,以及如何避免被自己的指标愚弄。
当池中的所有连接都在使用时,其他请求必须等待,直到连接可用。如果不与实际请求时间分开衡量,此等待时间可能会扭曲您的指标。
如果您的自定义逻辑测量从发出请求到收到响应的总时间,则您将包括等待时间和请求时间。
为了说明如何在连接池环境中被自己的指标所欺骗,让我们来看一个使用 Spring Boot 和 Apache HttpClient 5 的实际示例。我们将设置一个简单的 Spring Boot 应用程序,该应用程序向外部服务,测量这些请求的执行时间,并演示连接池耗尽如何导致误导性指标。
为了模拟外部服务的延迟,我们将使用 httpbin Docker 镜像。 Httpbin 提供了一个易于使用的 HTTP 请求和响应服务,我们可以使用它来在请求中创建人为延迟。
@SpringBootApplication
@RestController
public class Server {
public static void main(String... args) {
SpringApplication.run(Server.class, args);
}
class TimeClientHttpRequestInterceptor implements ClientHttpRequestInterceptor {
@Override
public ClientHttpResponse intercept(HttpRequest request, byte[] body, ClientHttpRequestExecution execution)
throws IOException {
var t0 = System.currentTimeMillis();
try {
return execution.execute(request, body);
} finally {
System.out.println("Request took: " + (System.currentTimeMillis() - t0) + "ms");
}
}
}
@Bean
public RestClient restClient() {
var connectionManager = new PoolingHttpClientConnectionManager();
connectionManager.setMaxTotal(2); // Max number of connections in the pool
connectionManager.setDefaultMaxPerRoute(2); // Max number of connections per route
return RestClient.builder()//
.requestFactory(new HttpComponentsClientHttpRequestFactory(
HttpClients.custom().setConnectionManager(connectionManager).build()))
.baseUrl("http://localhost:9091")//
.requestInterceptor(new TimeClientHttpRequestInterceptor()).build();
}
@GetMapping("/")
String hello() {
return restClient().get().uri("/delay/2").retrieve().body(String.class);
}
}
在上面的代码中,我们创建了一个请求拦截器 (ClientHttpRequestInterceptor) 来测量我们认为对 httpbin 支持的外部服务的请求的执行时间。
我们还明确将池设置为非常小的 2 个连接,以便于重现问题。
现在我们只需要启动httpbin,运行我们的spring boot应用程序并使用ab进行简单的测试
$ docker run -p 9091:80 kennethreitz/httpbin
ab -n 10 -c 4 http://localhost:8080/ ... Percentage of the requests served within a certain time (ms) 50% 4049 66% 4054 75% 4055 80% 4055 90% 4057 95% 4057 98% 4057 99% 4057 100% 4057 (longest request)
Request took: 2021ms Request took: 2016ms Request took: 2022ms Request took: 4040ms Request took: 4047ms Request took: 4030ms Request took: 4037ms Request took: 4043ms Request took: 4050ms Request took: 4034ms
如果我们看一下数字,我们可以看到,即使我们为外部服务器人为设置了 2 秒的延迟,但对于大多数请求来说,实际上我们得到了 4 秒的延迟。此外,我们注意到只有第一个请求遵循配置的 2 秒延迟,而后续请求会导致 4 秒的延迟。
在遇到奇怪的代码行为时,分析至关重要,因为它可以识别性能瓶颈,发现内存泄漏等隐藏问题,并显示应用程序如何使用系统资源。
这次我们将在进行 ab 负载测试时使用 JFR 分析正在运行的应用程序。
$ jcmd <pid> JFR.start name=app-profile duration=60s filename=app-profile-$(date +%FT%H-%M-%S).jfr
$ ab -n 50 -c 4 http://localhost:8080/ ... Percentage of the requests served within a certain time (ms) 50% 4043 66% 4051 75% 4057 80% 4060 90% 4066 95% 4068 98% 4077 99% 4077 100% 4077 (longest request)
如果我们打开 JFR 文件并查看火焰图,我们可以看到大部分执行时间都花在了 HTTP 客户端上。客户端的执行时间分为等待我们的外部服务响应和等待从池中获取连接。
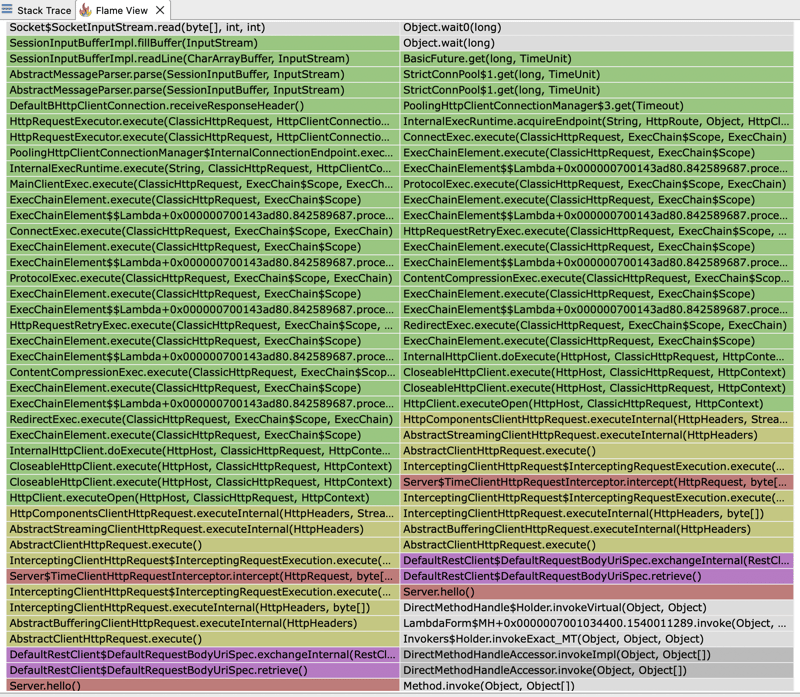
这解释了为什么我们看到的响应时间是我们为外部服务器设置的预期固定延迟 2 秒的两倍。我们配置了 2 个连接的池。然而,在我们的测试中,我们执行 4 个并发请求。因此,只有前 2 个请求将在 2 秒的预期时间内得到满足。后续请求将必须等待池释放连接,从而增加观察到的响应时间。
如果我们再次查看火焰图,我们还可以发现为什么我们的 ClientHttpRequestInterceptor 测量的时间并不反映外部服务器响应的时间,而是反映从池中获取连接所需的时间加上它所花费的时间向外部服务器执行实际请求。我们的拦截器实际上包装了一个堆栈跟踪,最终调用池管理器来获取连接:PoolingHttpClientConnectionManager
监控任何 HTTP 客户端的响应时间最好使用其内置指标来完成,因为这些指标是专门为捕获精确的计时信息而设计的。它们负责 HTTP 请求生命周期的各个方面,包括连接获取、数据传输和响应处理。这确保了测量结果准确且与客户的实际表现一致。
以上是指标可能会欺骗您:测量连接池环境中的执行时间的详细内容。更多信息请关注PHP中文网其他相关文章!




