运算符被视为特殊字符或符号,用于对变量或值(操作数)执行某些操作。在Java中,有几个用于操作变量的运算符。它包括算术运算符、按位运算符、比较运算符、逻辑运算符、杂项。运算符、赋值运算符等。在本文中,我们将详细讨论 java 中的比较运算符。
以下是Java中的各种比较运算符。
广告 该类别中的热门课程 JAVA 掌握 - 专业化 | 78 课程系列 | 15 次模拟测试| Name of the Operator | Operator | Example |
| Equal to | = = | a= =b |
| Not equal to | != | a!=b |
| Less than | < | a |
| Greater than | > | a>b |
| Less than or equal to | <= | a<=b |
| Greater than or equal to | >= | a>=b |
该运算符检查运算符左侧的值是否等于右侧的值。
示例:
import java.util.Scanner;
public class ComparisonExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int x, y;
Scanner sc= new Scanner(System.in);
//take the value of x as input from user and store it in variable x
System.out.print("Enter the value of x : ");
x = sc.nextInt();
//take the value of y as input from user
System.out.print("Enter the value of y : ");
//store the value in variable y
y = sc.nextInt();
//checks whether x and y are equal; Return true if it is same, else returns false
System.out.println(x == y);
}
}输出:
情况 1:x = 3; y=5; 返回 false,因为它们不相等

情况 2:x = 4; y=4; 返回 true,因为它们相等

该运算符检查运算符左侧的值是否不等于右侧的值。
示例:
import java.util.Scanner;
public class ComparisonExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int x, y;
Scanner sc= new Scanner(System.in);
//take the value of x as input from user and store it in variable x
System.out.print("Enter the value of x : ");
x = sc.nextInt();
//take the value of y as input from user
System.out.print("Enter the value of y : ");
//store the value in variable y
y = sc.nextInt();
//checks whether x and y are not equal; Return true if it is not equal, else returns false
System.out.println(x != y);
}
}输出:
情况 1:x = 3; y=4; 返回 true,因为它们不相等
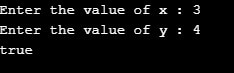
情况 2:x = 3; y=3; 返回 false,因为它们相等

该运算符检查运算符左侧的值是否小于右侧的值。
示例:
import java.util.Scanner;
public class ComparisonExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int x, y;
Scanner sc= new Scanner(System.in);
//take the value of x as input from user
System.out.print("Enter the value of x : ");
//store the value in variable x
x = sc.nextInt();
//take the value of y as input from user
System.out.print("Enter the value of y : ");
//store the value in variable y
y = sc.nextInt();
//Returns true if x is less than y, else false
System.out.println(x < y);
}
}输出:
情况 1:x = 4; y=6; 当 x 小于 y 时返回 true

情况 2:x = 44; y=32; 当 x 不小于 y
时返回 false
该运算符检查运算符左侧的值是否大于右侧的值。
示例:
import java.util.Scanner;
public class ComparisonExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int x, y;
Scanner sc= new Scanner(System.<em>in</em>);
//take the value of x as input from user
System.out.print("Enter the value of x : ");
//store the value in variable x
x = sc.nextInt();
//take the value of y as input from user
System.out.print("Enter the value of y : ");
//store the value in variable y
y = sc.nextInt();
//Returns true if x is greater than y, else false
System.out.println(x > y);
}
}输出:
情况 1:x = 67; y=66; 当 x 大于 y 时返回 true

情况 2:x = 43; y=57; 当 x 小于 y
时返回 false
该运算符检查运算符左侧的值是否小于或等于右侧的值。
示例:
import java.util.Scanner;
public class ComparisonExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int x, y;
Scanner sc= new Scanner(System.in);
//take the value of x as input from user and store it in variable x
System.out.print("Enter the value of x : ");
x = sc.nextInt();
//take the value of y as input from user and store it in variable y
System.out.print("Enter the value of y : ");
y = sc.nextInt();
//Returns true x is less than or equal to y, else false
System.out.println(x <= y);
}
}输出:
情况 1:x = 45; y=45; 当 x 等于 y
时返回 true
情况 2:x = 45; y=54; 当 x 小于 y 时返回 true

情况 3:x = 45; y=43; 当 x 大于 y
时返回 false
该运算符检查运算符左侧的值是否大于或等于右侧的值。
示例:
import java.util.Scanner;
public class ComparisonExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int x, y;
Scanner sc= new Scanner(System.in);
//take the value of x as input from user
System.out.print("Enter the value of x : ");
//store the value in variable x
x = sc.nextInt();
//take the value of y as input from user
System.out.print("Enter the value of y : ");
//store the value in variable y
y = sc.nextInt();
//Returns true x is greater than or equal to y, else false
System.out.println(x >= y);
}
}输出:
情况 1:x = 54; y=67; 当 x 小于 y
时返回 false
情况 2:x = 45; y=36; 当 x 大于 y 时返回 true

情况 3:x = 55; y=55; 当 x 等于 y
时返回 true
以上是Java 中的比较运算符的详细内容。更多信息请关注PHP中文网其他相关文章!




