Java ArrayList 类
ArrayList是List接口的实现,它属于java中的集合框架,它允许我们动态地(即在运行时)增加数组的大小。该类在java.util.package内部可用,它使用数组数据结构。 ArrayList只允许java中的包装类,用户定义类。
开始您的免费软件开发课程
网络开发、编程语言、软件测试及其他
语法:
ArrayList<T> list = new ArrayList<>();
List<T> list = new ArrayList<>();
我们可以直接使用ArrayList的实例或者将其分配给List引用。
构造函数:
在数组列表中,我们有三个可用的构造函数,如下:
- ArrayList(int initialCapacity): 在此,我们可以指定数组列表的初始长度。但是如果大小超过提到的initialCapacity,ArrayList 类会处理它。
- ArrayList(): 通过这个,我们可以创建一个没有初始容量的空列表,所以在这种情况下,默认的initialCapacity将为10。
- ArrayList(Collection extends E> c): 集合列表。
Java ArrayList 类的方法
以下是java ArrayList类的方法:
- void trimToSize(): This method will trim the list to the current list size.
- Object[] toArray(): Return the array of object.
- boolean remove(Object o): This method is used to remove the object, but it will remove the first occurrence as the list contain duplicate.
- boolean removeAll(Collection c): This method is used to remove all the elements of the list.
- Boolean removeIf(Predicate filter): This method is used to remove the predicate passed. Used as a filter.
- Add (E e): This method s used to add elements to the list.
- Void add(int index, E element): It takes two-parameter and adds elements t the specific index we mentioned.
- Boolean addAll(Collection c): This takes a list as an argument and adds all the elements to the end of the current list.
- boolean addAll(int index, Collection c): This method adds all the elements to the current list at the specified index we pass.
- Get (int index): This method is used to get the element. It will return the element present at the specified position in the list.
- Int indexOf(Object o): This method is used to get the element’s index passed. It will always return the first occurrence of the element into the list because the list can contain duplicate elements.
-
ListIterator
listIterator(int index): This method returns an iterator with the specific index. - Remove (int index): This method removes the element. It will remove the element with the corresponding index passed.
- Protected void removeRange(int fromIndex, int toIndex): This removes the elements from a specified range.
- Boolean retainAll(Collection c): This method will retain all elements contained in the specified collection.
- Set (int index, E element): This method will set the element to the specified index.
- Void sort(Comparator c): This method is used to sort the collection element.
-
List
subList(int fromIndex, int toIndex): This method will be used to return the sublist from the specified index. - Void clear(): This mentioned is used to clear the elements in the list.
- Object clone(): These methods create a copy of the list.
- Boolean contains(Object o): This method is used to check whether the passing object is present in the list or not.
- Void ensureCapacity(int minCapacity): This method is used to increase the capacity of the array list.
- Boolean isEmpty(): This method is used to check whether the array list is empty or not.
-
Iterator
iterator(): This method returns iterator. - int lastIndexOf(Object o): This method returns the last index of the object passed. If the object does not present in the list, it will return -1.
-
ListIterator
listIterator(): This methods return iterator.
Examples of Java ArrayList Class
Examples of Java ArrayList Class are given below:
1. add an element in ArrayList
The below example will show how to add an element to an array list.
Code:
package com.cont.article;
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class ArratListTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add("abc");
list.add("xyz");
list.add("yyy");
list.add("some name");
list.add("other name");
System.out.println("list is :: " + list);
}
}Output:

2. Copying elements of list one to another list
Code:
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add("abc");
list.add("xyz");
list.add("yyy");
list.add("some name");
list.add("other name");
ArrayList<String> list2 = new ArrayList<>();
list2.addAll(list);
System.out.println("Elements in list one : " + list);
System.out.println("Elements in list two : " + list2);
}
}Output:
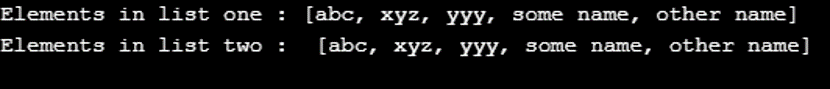
3. Remove element from ArrayList
Code:
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add("abc");
list.add("xyz");
list.add("yyy");
list.add("some name");
list.add("other name");
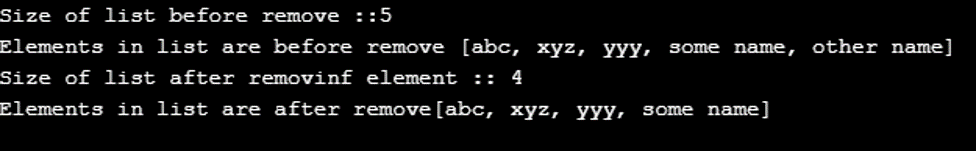
System.out.println("Size of list before remove ::" + list.size());
System.out.println("Elements in list are before remove " + list);
list.remove(4);
System.out.println("Size of list after removinf element :: " +list.size());
System.out.println("Elements in list are after remove" + list);
}
}Output:
4. Clear all the elements from ArrayList
Code:
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add("abc");
list.add("xyz");
list.add("yyy");
list.add("some name");
list.add("other name");
list.clear();
System.out.println("Clering all elements of list " +list.size());
}
}Output:

5. Iterate all the elements of ArrayList
Code:
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add("abc");
list.add("xyz");
list.add("yyy");
list.add("some name");
list.add("other name");
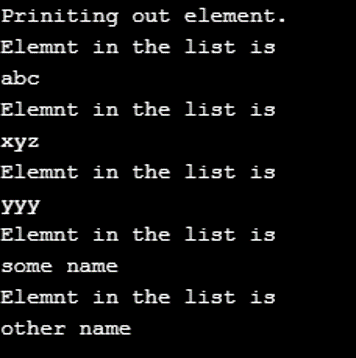
System.out.println("Priniting out element.");
for (String string : list) {
System.out.println("Elemnt in the list is");
System.out.println(string);
}
}
}Output:
The array list in java does not contain duplicate elements. Also, the insertion order is maintained in a list, which means we put over elements that will generate the output in the same sequence. Some detailed points which need to be remembered for the array list in java are as follows:
It implements various interfaces:
- Serializable,
- Iterable
, - Cloneable,
- Collection
, - List
, - RandomAccess
The class hierarchy is as follows:
java.lang.Object >> java.util.AbstractCollection<E> >> java.util.AbstractList<E> >> java.util.ArrayList<E>
By default, the array list is not synchronized in nature and is not thread-safe, But we can make them synchronized using the collections class synchronized method. The syntax is described below for reference :
List arrList = Collections.synchronizedList (new ArrayList(...));
以上是Java ArrayList 类的详细内容。更多信息请关注PHP中文网其他相关文章!

热AI工具

Undresser.AI Undress
人工智能驱动的应用程序,用于创建逼真的裸体照片

AI Clothes Remover
用于从照片中去除衣服的在线人工智能工具。

Undress AI Tool
免费脱衣服图片

Clothoff.io
AI脱衣机

Video Face Swap
使用我们完全免费的人工智能换脸工具轻松在任何视频中换脸!

热门文章

热工具

记事本++7.3.1
好用且免费的代码编辑器

SublimeText3汉化版
中文版,非常好用

禅工作室 13.0.1
功能强大的PHP集成开发环境

Dreamweaver CS6
视觉化网页开发工具

SublimeText3 Mac版
神级代码编辑软件(SublimeText3)
 PHP:网络开发的关键语言
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:08 AM
PHP:网络开发的关键语言
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:08 AM
PHP是一种广泛应用于服务器端的脚本语言,特别适合web开发。1.PHP可以嵌入HTML,处理HTTP请求和响应,支持多种数据库。2.PHP用于生成动态网页内容,处理表单数据,访问数据库等,具有强大的社区支持和开源资源。3.PHP是解释型语言,执行过程包括词法分析、语法分析、编译和执行。4.PHP可以与MySQL结合用于用户注册系统等高级应用。5.调试PHP时,可使用error_reporting()和var_dump()等函数。6.优化PHP代码可通过缓存机制、优化数据库查询和使用内置函数。7
 PHP与Python:了解差异
Apr 11, 2025 am 12:15 AM
PHP与Python:了解差异
Apr 11, 2025 am 12:15 AM
PHP和Python各有优势,选择应基于项目需求。1.PHP适合web开发,语法简单,执行效率高。2.Python适用于数据科学和机器学习,语法简洁,库丰富。
 突破或从Java 8流返回?
Feb 07, 2025 pm 12:09 PM
突破或从Java 8流返回?
Feb 07, 2025 pm 12:09 PM
Java 8引入了Stream API,提供了一种强大且表达力丰富的处理数据集合的方式。然而,使用Stream时,一个常见问题是:如何从forEach操作中中断或返回? 传统循环允许提前中断或返回,但Stream的forEach方法并不直接支持这种方式。本文将解释原因,并探讨在Stream处理系统中实现提前终止的替代方法。 延伸阅读: Java Stream API改进 理解Stream forEach forEach方法是一个终端操作,它对Stream中的每个元素执行一个操作。它的设计意图是处
 PHP与其他语言:比较
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:19 AM
PHP与其他语言:比较
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:19 AM
PHP适合web开发,特别是在快速开发和处理动态内容方面表现出色,但不擅长数据科学和企业级应用。与Python相比,PHP在web开发中更具优势,但在数据科学领域不如Python;与Java相比,PHP在企业级应用中表现较差,但在web开发中更灵活;与JavaScript相比,PHP在后端开发中更简洁,但在前端开发中不如JavaScript。
 PHP与Python:核心功能
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:16 AM
PHP与Python:核心功能
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:16 AM
PHP和Python各有优势,适合不同场景。1.PHP适用于web开发,提供内置web服务器和丰富函数库。2.Python适合数据科学和机器学习,语法简洁且有强大标准库。选择时应根据项目需求决定。
 PHP的影响:网络开发及以后
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:10 AM
PHP的影响:网络开发及以后
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:10 AM
PHPhassignificantlyimpactedwebdevelopmentandextendsbeyondit.1)ItpowersmajorplatformslikeWordPressandexcelsindatabaseinteractions.2)PHP'sadaptabilityallowsittoscaleforlargeapplicationsusingframeworkslikeLaravel.3)Beyondweb,PHPisusedincommand-linescrip
 PHP:许多网站的基础
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:07 AM
PHP:许多网站的基础
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:07 AM
PHP成为许多网站首选技术栈的原因包括其易用性、强大社区支持和广泛应用。1)易于学习和使用,适合初学者。2)拥有庞大的开发者社区,资源丰富。3)广泛应用于WordPress、Drupal等平台。4)与Web服务器紧密集成,简化开发部署。
 PHP与Python:用例和应用程序
Apr 17, 2025 am 12:23 AM
PHP与Python:用例和应用程序
Apr 17, 2025 am 12:23 AM
PHP适用于Web开发和内容管理系统,Python适合数据科学、机器学习和自动化脚本。1.PHP在构建快速、可扩展的网站和应用程序方面表现出色,常用于WordPress等CMS。2.Python在数据科学和机器学习领域表现卓越,拥有丰富的库如NumPy和TensorFlow。






