发布 .f `@xmldom/xmldom`
语境
xmldom 是一个 javascript ponyfill,用于向其他运行时提供现代浏览器中存在的以下 API:
- 将 XML 字符串转换为 DOM 树
new DOMParser().parseFromString(xml, mimeType) => Document登录后复制
- 创建、访问和修改 DOM 树
new DOMImplementation().createDocument(...) => Document登录后复制
- 将 DOM 树序列化回 XML 字符串
new XMLSerializer().serializeToString(node) => string登录后复制
来源:xmldom 自述文件
历史
自从我在 2020 年 6 月开始为分叉的 xmldom 库做出贡献以来,已经发布了 40 个版本。
这是一个非常有趣且具有挑战性的项目,并且很可能会在相当长的一段时间内保持这种状态。
据 GitHub 称,自分叉以来已有 50 多人为其做出了贡献。
再次感谢所有贡献者。
这并不包括所有设法从原始无作用域 xmldom 包迁移到有作用域 @xmldom/xmldom 包版本 0.7.0 以获得所有安全修复程序的人。
作为 lts 标签发布的最新版本是 0.7.13。
最后一个具有重大更改的版本是 0.8.0,发布于 2021 年 12 月 22 日,大约 3 年前。
最新发布的版本是0.8.10。
0.9.0 (2024-08-29)
但是我今天要讲的是自 2022 年 10 月以来在 next 标签下发布的所有内容。
我对这些变化感到非常兴奋,因为它们为未来潜在的变化提供了明确的基础。
TLDR:与规范更加一致,差异尽可能明确。
1. 强制mimeType交还控制权
使实现变得复杂的一个方面是解析 XML 与 HTML 的规则不同。
xmldom(在某种程度上)从一开始就“支持”这两种风格。甚至根本不需要传递 mimeType:应用什么规则是根据当前正在解析的 XML 字符串/节点的当前默认命名空间决定的。
这以 0.9.0 结束:从现在开始,DOMParser.parseFromString(xml, mimeType) 中的 mimeType 是强制性的,并且是唯一被检查以决定是否应用 XML 或 HTML 规则的东西。巴斯塔。
该信息会保留在生成的文档(新类型属性)中,因此在序列化它时,会再次应用正确的规则。
这是一个巨大的(并且可能是破坏性的)变化,但我真的很高兴它已经准备好了,因为它使大量相关的错误修复变得可能/更容易实现,并且还降低了 API 和实现的复杂性。
此外,它现在只接受指定的 mime 类型,并在任何其他情况下抛出 TypeError。
严格性和错误处理
我个人对原生浏览器 API 的错误处理感到困惑的是,它总是返回一个 Document,如果出现问题,parsererror 节点将是主体的第一个子节点:
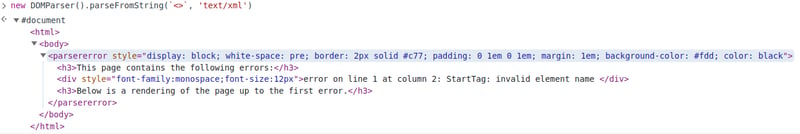
由于错误处理在 xmldom 中从来没有以这种方式工作,但现有的错误处理非常复杂、混乱且文档记录很差,0.9.0 对其进行了简化,现在对解析过程中发生的任何潜在错误具有(更加)一致的行为:
它抛出一个 ParseError ?,例如有下列情况之一的:
- 在以前的版本中,对于某些格式不正确的 XML 字符串,返回的 Document 可能没有 documentElement,这很可能会导致后面的代码出现 TypeErrors。
- 几个格式不正确的 XML 字符串现在将正确报告为 fatalError,现在总是阻止任何进一步的处理。
- 一些以前未报告为错误或仅报告为警告的事情现在也报告为 fatalError
仍然有一些情况会被报告为警告(尤其是在解析 HTML 时)或错误,但不会阻止数据的处理,但是新的错误处理可以很容易地决定代码的严格程度需要使用 xmldom。
可以传递给 DOMParser 构造函数的(不符合规范的)选项称为 onError。
它需要一个具有以下签名的函数:
function onError(level:ErrorLevel, message:string, context: DOMHandler):void;
- ErrorLevel 是警告、错误或 fatalError
- xmldom 已经为两个最常见的用例提供了实现:
- onErrorStopParsing 也会针对所有错误级别问题抛出 ParseError
- onWarningStopParsing 也会针对所有错误级别问题抛出 ParseError
建议应用其中一个来在出现任何意外的第一个信号时停止处理 XML:
// prevent parsing of XML that has `error`s
new DOMParser({onError: onErrorStopParsing}).parseFromString(...)
// prevent parsing of XML that has `warning`s
new DOMParser({onError: onWarningStopParsing}).parseFromString(...)
compareDocumentPosition, extended HTML entities , null instead of undefined, ...
Another fork of the original xmldom repository made it's way back into our repo by extending the HTML entities to the complete set (also available in 0.8.x) and porting over the implementation of the compareDocumentPosition API. Thank you, and welcome @zorkow
Along the way several places where xmldom so far returned undefined instead of null, have been fixed to adhere to the spec.
And I discovered that the former author seems to have preferred iterating from the end of a list in so many places, that attributes were processed in the reverse order in multiple places, which is now fixed.
The implementation of the removeChild API changed quite a bit, to comply to the spec and throws a DOMException when it should.
And 3 related bugs were fixed in a way that clearly states what the future direction of xmldom is:
Support for lax HTML parsing rules will only be provided if proper strict XML parsing doesn't suffer from it.
The former (broken) "support" for automatic self closing tags in HTML is gone.
coctype internalSubset
More recently @shunkica invested a huge amount of time end effort to fix tons of issues in the former handling of the internalSubset part of the !DOCTYPE.
It is now preserved as part of the internalSubset property of the doctype of a Document and many wrong doctype declarations are now correctly detected as such and reported as a fatalError.
Also thanks to @kboshold for the latest bug fix in this area.
Along the way we created a new module containing regular expressions for the relevant grammar, and correctness checks are based on those and they are properly covered by tests.
It is not the goal of xmldom to become a validating parser, but this a great step to support those documents that come with more complex DTDs.
And there is even more
Up to now development was done using Node v10, since this is also the lowest version xmldom currently supports. As part of the work on the upcoming version, I decided to switch to v18 for development, since more and more devDependencies also made this a minimum requirement. This will be the new minimum runtime version for the time being starting with this release.
I initiated a public poll / dicussion to ask people which version of Node or other runtimes they need support for.
The next breaking release will most likely drop support for some older Node versions, if there is no feedback indicating something different.
Along the way plenty of APIs have received jsdoc comments with proper types.
Thank you
for taking the time to read through all of this.
Those are quite some changes, and I'm very excited to be able to ship those.
I hope you are as excited as I am :)
If you need more details you can go through the very detailed changelog, or head over to the repository and join or start a discussion or file an issue.
以上是发布 .f `@xmldom/xmldom`的详细内容。更多信息请关注PHP中文网其他相关文章!

热AI工具

Undresser.AI Undress
人工智能驱动的应用程序,用于创建逼真的裸体照片

AI Clothes Remover
用于从照片中去除衣服的在线人工智能工具。

Undress AI Tool
免费脱衣服图片

Clothoff.io
AI脱衣机

Video Face Swap
使用我们完全免费的人工智能换脸工具轻松在任何视频中换脸!

热门文章

热工具

记事本++7.3.1
好用且免费的代码编辑器

SublimeText3汉化版
中文版,非常好用

禅工作室 13.0.1
功能强大的PHP集成开发环境

Dreamweaver CS6
视觉化网页开发工具

SublimeText3 Mac版
神级代码编辑软件(SublimeText3)
 Python vs. JavaScript:学习曲线和易用性
Apr 16, 2025 am 12:12 AM
Python vs. JavaScript:学习曲线和易用性
Apr 16, 2025 am 12:12 AM
Python更适合初学者,学习曲线平缓,语法简洁;JavaScript适合前端开发,学习曲线较陡,语法灵活。1.Python语法直观,适用于数据科学和后端开发。2.JavaScript灵活,广泛用于前端和服务器端编程。
 JavaScript和Web:核心功能和用例
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:19 AM
JavaScript和Web:核心功能和用例
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:19 AM
JavaScript在Web开发中的主要用途包括客户端交互、表单验证和异步通信。1)通过DOM操作实现动态内容更新和用户交互;2)在用户提交数据前进行客户端验证,提高用户体验;3)通过AJAX技术实现与服务器的无刷新通信。
 JavaScript在行动中:现实世界中的示例和项目
Apr 19, 2025 am 12:13 AM
JavaScript在行动中:现实世界中的示例和项目
Apr 19, 2025 am 12:13 AM
JavaScript在现实世界中的应用包括前端和后端开发。1)通过构建TODO列表应用展示前端应用,涉及DOM操作和事件处理。2)通过Node.js和Express构建RESTfulAPI展示后端应用。
 了解JavaScript引擎:实施详细信息
Apr 17, 2025 am 12:05 AM
了解JavaScript引擎:实施详细信息
Apr 17, 2025 am 12:05 AM
理解JavaScript引擎内部工作原理对开发者重要,因为它能帮助编写更高效的代码并理解性能瓶颈和优化策略。1)引擎的工作流程包括解析、编译和执行三个阶段;2)执行过程中,引擎会进行动态优化,如内联缓存和隐藏类;3)最佳实践包括避免全局变量、优化循环、使用const和let,以及避免过度使用闭包。
 Python vs. JavaScript:社区,图书馆和资源
Apr 15, 2025 am 12:16 AM
Python vs. JavaScript:社区,图书馆和资源
Apr 15, 2025 am 12:16 AM
Python和JavaScript在社区、库和资源方面的对比各有优劣。1)Python社区友好,适合初学者,但前端开发资源不如JavaScript丰富。2)Python在数据科学和机器学习库方面强大,JavaScript则在前端开发库和框架上更胜一筹。3)两者的学习资源都丰富,但Python适合从官方文档开始,JavaScript则以MDNWebDocs为佳。选择应基于项目需求和个人兴趣。
 Python vs. JavaScript:开发环境和工具
Apr 26, 2025 am 12:09 AM
Python vs. JavaScript:开发环境和工具
Apr 26, 2025 am 12:09 AM
Python和JavaScript在开发环境上的选择都很重要。1)Python的开发环境包括PyCharm、JupyterNotebook和Anaconda,适合数据科学和快速原型开发。2)JavaScript的开发环境包括Node.js、VSCode和Webpack,适用于前端和后端开发。根据项目需求选择合适的工具可以提高开发效率和项目成功率。
 C/C在JavaScript口译员和编译器中的作用
Apr 20, 2025 am 12:01 AM
C/C在JavaScript口译员和编译器中的作用
Apr 20, 2025 am 12:01 AM
C和C 在JavaScript引擎中扮演了至关重要的角色,主要用于实现解释器和JIT编译器。 1)C 用于解析JavaScript源码并生成抽象语法树。 2)C 负责生成和执行字节码。 3)C 实现JIT编译器,在运行时优化和编译热点代码,显着提高JavaScript的执行效率。
 Python vs. JavaScript:比较用例和应用程序
Apr 21, 2025 am 12:01 AM
Python vs. JavaScript:比较用例和应用程序
Apr 21, 2025 am 12:01 AM
Python更适合数据科学和自动化,JavaScript更适合前端和全栈开发。1.Python在数据科学和机器学习中表现出色,使用NumPy、Pandas等库进行数据处理和建模。2.Python在自动化和脚本编写方面简洁高效。3.JavaScript在前端开发中不可或缺,用于构建动态网页和单页面应用。4.JavaScript通过Node.js在后端开发中发挥作用,支持全栈开发。






