探索 JVM 虚拟线程机制中的固定
Java's virtual threads offer a lightweight alternative to traditional OS threads, enabling efficient concurrency management. But understanding their behavior is crucial for optimal performance. This blog post dives into pinning, a scenario that can impact virtual thread execution, and explores techniques to monitor and address it.
Virtual Threads: A Lightweight Concurrency Approach
Java's virtual threads are managed entities that run on top of the underlying operating system threads (carrier threads). They provide a more efficient way to handle concurrency compared to creating numerous OS threads, as they incur lower overhead. The JVM maps virtual threads to carrier threads dynamically, allowing for better resource utilization.
Managed by the JVM: Unlike OS threads that are directly managed by the operating system, virtual threads are created and scheduled by the Java Virtual Machine (JVM). This allows for finer-grained control and optimization within the JVM environment.
Reduced Overhead: Creating and managing virtual threads incurs significantly lower overhead compared to OS threads. This is because the JVM can manage a larger pool of virtual threads efficiently, utilizing a smaller number of underlying OS threads.
Compatibility with Existing Code: Virtual threads are designed to be seamlessly integrated with existing Java code. They can be used alongside traditional OS threads and work within the familiar constructs like Executor and ExecutorService for managing concurrent.
The figure below shows the relationship between virtual threads and platform threads:
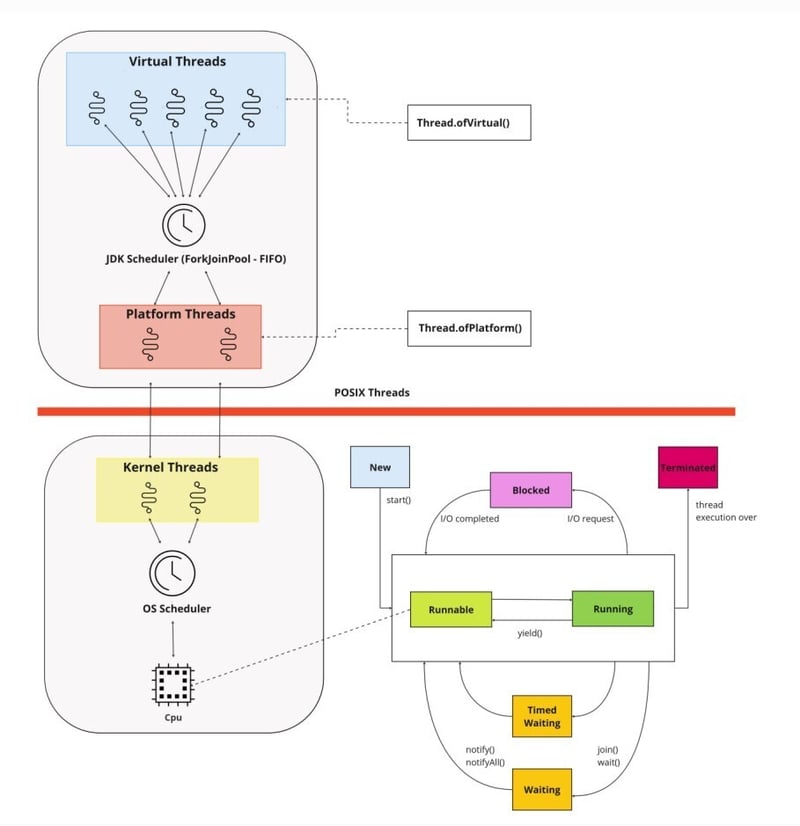
Pinning: When a Virtual Thread Gets Stuck
Pinning occurs when a virtual thread becomes tied to its carrier thread. This essentially means the virtual thread cannot be preempted (switched to another carrier thread) while it's in a pinned state. Here are common scenarios that trigger pinning:
- Synchronized Blocks and Methods: Executing code within a synchronized block or method leads to pinning. This ensures exclusive access to shared resources, preventing data corruption issues.
Code Example:
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
final Counter counter = new Counter();
Runnable task = () -> {
for (int i = 0; i < 1000; i++) {
counter.increment();
}
};
Thread thread1 = new Thread(task);
Thread thread2 = new Thread(task);
thread1.start();
thread2.start();
thread1.join();
thread2.join();
System.out.println("Final counter value: " + counter.getCount());
}
}
class Counter {
private int count = 0;
public synchronized void increment() {
count++;
}
public synchronized int getCount() {
return count;
}
}
In this example, when a virtual thread enters the synchronized block, it becomes pinned to its carrier thread, but this is not always true. Java's synchronized keyword alone is not enough to cause thread pinning in virtual threads. For thread pinning to occur, there must be a blocking point within a synchronized block that causes a virtual thread to trigger park, and ultimately disallows unmounting from its carrier thread. Thread pinning could cause a decrease in performance as it would negate the benefits of using lightweight/virtual threads.
Whenever a virtual thread encounters a blocking point, its state is transitioned to PARKING. This state transition is indicated by invoking the VirtualThread.park() method:
// JDK core code
void park() {
assert Thread.currentThread() == this;
// complete immediately if parking permit available or interrupted
if (getAndSetParkPermit(false) || interrupted)
return;
// park the thread
setState(PARKING);
try {
if (!yieldContinuation()) {
// park on the carrier thread when pinned
parkOnCarrierThread(false, 0);
}
} finally {
assert (Thread.currentThread() == this) && (state() == RUNNING);
}
}
Let's take a look at a code sample to illustrate this concept:
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Counter counter = new Counter();
Runnable task = () -> {
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
counter.increment();
}
};
Thread thread1 = Thread.ofVirtual().start(task);
Thread thread2 = Thread.ofVirtual().start(task);
try {
thread1.join();
thread2.join();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
System.out.println("Final counter value: " + counter.getCount());
}
}
class Counter {
private int count = 0;
public void increment() {
synchronized (this) {
try {
Thread.sleep(100); // This simulates a blocking call within the synchronized block
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
count++;
}
}
public synchronized int getCount() {
return count;
}
}
- Native Methods/Foreign Functions: Running native methods or foreign functions can also cause pinning. The JVM might not be able to efficiently manage the virtual thread's state during these operations.
Monitoring Pinning with -Djdk.tracePinnedThreads=full
The -Djdk.tracePinnedThreads=full flag is a JVM startup argument that provides detailed tracing information about virtual thread pinning. When enabled, it logs events like:
- Virtual thread ID involved in pinning
- Carrier thread ID to which the virtual thread is pinned
- Stack trace indicating the code section causing pinning
Use this flag judiciously during debugging sessions only, as it introduces performance overhead.
-
Compile the our demo code:
javac Main.java
登录后复制 -
Start the compiled code with the -Djdk.tracePinnedThreads=full flag:
java -Djdk.tracePinnedThreads=full Main
登录后复制 -
Observe the output in the console, which shows detailed information about virtual thread pinning:
Thread[#29,ForkJoinPool-1-worker-1,5,CarrierThreads] java.base/java.lang.VirtualThread$VThreadContinuation.onPinned(VirtualThread.java:183) java.base/jdk.internal.vm.Continuation.onPinned0(Continuation.java:393) java.base/java.lang.VirtualThread.parkNanos(VirtualThread.java:621) java.base/java.lang.VirtualThread.sleepNanos(VirtualThread.java:791) java.base/java.lang.Thread.sleep(Thread.java:507) Counter.increment(Main.java:38) <== monitors:1 Main.lambda$main\$0(Main.java:13) java.base/java.lang.VirtualThread.run(VirtualThread.java:309) Final counter value: 200
登录后复制
Fixing Pinning with Reentrant Locks
Pinning is an undesirable scenario which impedes the performance of virtual threads. Reentrant locks serve as an effective tool to counteract pinning. Here's how you can use Reentrant locks to mitigate pinning situations:
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantLock;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Counter counter = new Counter();
Runnable task = () -> {
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
counter.increment();
}
};
Thread thread1 = Thread.ofVirtual().start(task);
Thread thread2 = Thread.ofVirtual().start(task);
try {
thread1.join();
thread2.join();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
System.out.println("Final counter value: " + counter.getCount());
}
}
class Counter {
private int count = 0;
private final ReentrantLock lock = new ReentrantLock();
public void increment() {
lock.lock();
try {
Thread.sleep(100); // This simulates a blocking call
count++;
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
public int getCount() {
return count;
}
}
In the updated example, we use a ReentrantLock instead of a synchronized block. The thread can acquire the lock and release it immediately after it completes its operation, potentially reducing the duration of pinning compared to a synchronized block which might hold the lock for a longer period.
综上所述
Java 的虚拟线程是该语言的发展和功能的见证。它们为传统操作系统线程提供了一种全新的、轻量级的替代方案,为高效的并发管理提供了一座桥梁。花时间深入挖掘并理解线程固定等关键概念可以让开发人员掌握充分利用这些轻量级线程潜力的专业知识。这些知识不仅帮助开发人员为利用即将推出的功能做好准备,还使他们能够在当前项目中更有效地解决复杂的并发控制问题。
以上是探索 JVM 虚拟线程机制中的固定的详细内容。更多信息请关注PHP中文网其他相关文章!

热AI工具

Undresser.AI Undress
人工智能驱动的应用程序,用于创建逼真的裸体照片

AI Clothes Remover
用于从照片中去除衣服的在线人工智能工具。

Undress AI Tool
免费脱衣服图片

Clothoff.io
AI脱衣机

Video Face Swap
使用我们完全免费的人工智能换脸工具轻松在任何视频中换脸!

热门文章

热工具

记事本++7.3.1
好用且免费的代码编辑器

SublimeText3汉化版
中文版,非常好用

禅工作室 13.0.1
功能强大的PHP集成开发环境

Dreamweaver CS6
视觉化网页开发工具

SublimeText3 Mac版
神级代码编辑软件(SublimeText3)
 公司安全软件导致应用无法运行?如何排查和解决?
Apr 19, 2025 pm 04:51 PM
公司安全软件导致应用无法运行?如何排查和解决?
Apr 19, 2025 pm 04:51 PM
公司安全软件导致部分应用无法正常运行的排查与解决方法许多公司为了保障内部网络安全,会部署安全软件。...
 如何将姓名转换为数字以实现排序并保持群组中的一致性?
Apr 19, 2025 pm 11:30 PM
如何将姓名转换为数字以实现排序并保持群组中的一致性?
Apr 19, 2025 pm 11:30 PM
将姓名转换为数字以实现排序的解决方案在许多应用场景中,用户可能需要在群组中进行排序,尤其是在一个用...
 如何使用MapStruct简化系统对接中的字段映射问题?
Apr 19, 2025 pm 06:21 PM
如何使用MapStruct简化系统对接中的字段映射问题?
Apr 19, 2025 pm 06:21 PM
系统对接中的字段映射处理在进行系统对接时,常常会遇到一个棘手的问题:如何将A系统的接口字段有效地映�...
 IntelliJ IDEA是如何在不输出日志的情况下识别Spring Boot项目的端口号的?
Apr 19, 2025 pm 11:45 PM
IntelliJ IDEA是如何在不输出日志的情况下识别Spring Boot项目的端口号的?
Apr 19, 2025 pm 11:45 PM
在使用IntelliJIDEAUltimate版本启动Spring...
 如何优雅地获取实体类变量名构建数据库查询条件?
Apr 19, 2025 pm 11:42 PM
如何优雅地获取实体类变量名构建数据库查询条件?
Apr 19, 2025 pm 11:42 PM
在使用MyBatis-Plus或其他ORM框架进行数据库操作时,经常需要根据实体类的属性名构造查询条件。如果每次都手动...
 Java对象如何安全地转换为数组?
Apr 19, 2025 pm 11:33 PM
Java对象如何安全地转换为数组?
Apr 19, 2025 pm 11:33 PM
Java对象与数组的转换:深入探讨强制类型转换的风险与正确方法很多Java初学者会遇到将一个对象转换成数组的�...
 电商平台SKU和SPU数据库设计:如何兼顾用户自定义属性和无属性商品?
Apr 19, 2025 pm 11:27 PM
电商平台SKU和SPU数据库设计:如何兼顾用户自定义属性和无属性商品?
Apr 19, 2025 pm 11:27 PM
电商平台SKU和SPU表设计详解本文将探讨电商平台中SKU和SPU的数据库设计问题,特别是如何处理用户自定义销售属...
 如何利用Redis缓存方案高效实现产品排行榜列表的需求?
Apr 19, 2025 pm 11:36 PM
如何利用Redis缓存方案高效实现产品排行榜列表的需求?
Apr 19, 2025 pm 11:36 PM
Redis缓存方案如何实现产品排行榜列表的需求?在开发过程中,我们常常需要处理排行榜的需求,例如展示一个�...






