使用 GitHub Actions 自动化构建、测试和部署流程
该项目是一个快速示例项目,演示了应用程序在推送到主分支时自动构建、测试和部署到暂存环境的过程。
为了充分演示 CI/CD 管道,我们将使用最少的代码创建一个简单的 Python 项目,然后将其集成到 GitHub Actions 中。
创建一个简单的 Python 项目
就像我之前所说的,我们将创建一个将在管道中使用的简单项目。我选择在 python 中执行此操作没有特殊原因,您可以使用您选择的任何其他编程语言,这个项目的主要目的是演示管道。
创建项目文件夹
所以继续创建项目文件夹并导航到该文件夹:
mkdir automated-testing cd automated-testing
编写申请文件
现在我们将编写简单的Python应用程序。在项目文件夹中创建一个新文件app.py。
touch app.py
将以下代码块添加到文件中:
def hello(): return "Hello, World!" if __name__ == "__main__": print(hello())
这是一个非常简单的 Python“Hello world”函数,作为可以在 CI 管道中测试的基本功能的示例。
def hello() 定义了一个名为 hello 的函数,它不带任何参数。调用此函数时,它返回字符串“Hello, World!”。
if __name__ == "__main__" 是一个标准的 Python 构造,用于确保某些代码仅在直接执行文件时运行(而不是作为模块导入时)。它充当脚本的入口点。
直接运行 app.py 时(例如,通过运行 python app.py),脚本将调用 hello() 函数并打印结果,即“Hello, World!”。
创建需求文件。
典型的项目会有依赖项,在 python 项目中,它们通常在requirements.txt 文件中定义。
创建新文件requirements.txt
touch requirements.txt
将其添加到文件中:
pytest
创建单元测试
现在我们将添加一个基本测试文件test_app.py来测试app.py中的功能。将以下内容添加到文件中:
from app import hello def test_hello(): assert hello() == "Hello, World!"
现在我们已准备好创建管道。
为 CI/CD 设置 GitHub 操作
要配置 GitHub 操作,我们需要在存储库中创建一个 .github/workflows 文件夹,这是我们向 GitHub 通知存储库中的 CI/CD 管道的方式。
创建一个新文件:
mkdir -p .github/workflows
您可以在一个存储库中拥有多个管道,因此请在 .github/workflows 文件夹中创建一个文件 proj.yml。我们将在这里定义构建、测试和部署 Python 项目的步骤。
将以下代码添加到您的文件中:
name: Build, Test and Deploy
# Trigger the workflow on pushes to the main branch
on:
push:
branches:
- main
jobs:
build-and-test:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
# Checkout the code from the repository
- name: Checkout repo
uses: actions/checkout@v4
# Set up Python environment
- name: Setup Python
uses: actions/setup-python@v5
with:
python-version: '3.x'
# Install dependencies
- name: Install Dependecies
run: |
python -m pip install --upgrade pip
pip install -r requirements.txt
# Build (this project deosn't require a build but we will simulate a build by creating a file)
- name: Build Project
run: |
mkdir -p build
# Simulate build output by creating a file
touch build/output_file.txt
# Run tests using pytest
- name: Run tests
run:
pytest
# Upload the build output as an artifact (we created a file in the build step to simulate an artifact)
- name: Upload build artifact
uses: actions/upload-artifact@v4
with:
name: build-artifact
path: build/
deploy:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
needs: build-and-test
if: success()
steps:
# Download the artifact from the build stage
- name: Download build artifact
uses: actions/download-artifact@v4
with:
name: build-artifact
path: build/
- name: Simulate Deployment
run: |
echo "Deploying to staging..."
ls build/
Breakdown of the CI/CD Pipeline Steps
- Trigger on Push to main: The pipeline is triggered whenever there is a push to the main branch.
- Checkout Code: This step uses GitHub’s checkout action to pull our code from the repository.
- Set Up Python: The pipeline sets up a Python environment on the CI runner (GitHub's virtual machine), ensuring that the correct Python version is used.
- Install Dependencies: It installs the required dependencies for our Python project (pytest in this case). This dependency was just added as an example of when a project has dependencies as this particular sample python application does not require any.
- Build: This stage was also just added for demonstration purposes, supposing this was a JavaScript/Node.js project this is where we would run the npm run build command and this will create an artifact we can upload and use in the deploy stage. Since this is a python project and it doesn't really require a build, we will create a file and folder in this stage. The file will serve as our artifact for the deploy stage.
- Run Tests: It runs the tests using pytest to validate the code.
- Upload Build Artifact: After running the tests, the build-and-test stage creates and saves a build artifact (in this case, a simulated output_file.txt in the build folder from the build step). The action upload-artifact is used to store this artifact. You can replace this with whatever actual build output your project creates.
- Deploy Stage: Our application will only be deployed if the test was successful which is why I have added the conditionals needs and if. Using “needs” we can require that the deploy job won’t even run unless the test job is successful. The download-artifact action retrieves the build artifact and the last step "Simulate Deployment" simulates deployment by printing a message and lists the artifact. If this was a live project we would have the actual deployment commands to deploy to a real staging environment here. You can replace the echo and ls commands with actual deployment commands (e.g., deploying to a cloud platform). This approach ensures that the output from the build-and-test stage is properly passed to the deploy stage, simulating how a real deployment would work with build artifacts.
Push to GitHub
If you haven't already, you need to initialize a git repository using the commands below:
git init git add . git commit -m "Create project as well as CI/CD pipeline"
Now we push to GitHub. Create a GitHub repository and push your code using the below commands:
git remote add origin <your-repo-url> git push -u origin main
Verify the Pipeline
After pushing the code, you can visit the Actions tab in your GitHub repository. You should see the pipeline triggered, running the steps defined in your proj.yml file.
If everything is set up correctly, the pipeline will build, test, and simulate deployment. You can changes things around in your project and make new pushes to see the the pipeline works, create errors intentional so you can see how the pipeline works when the tests fail.
On a successful run this is how your Actions tab should look.
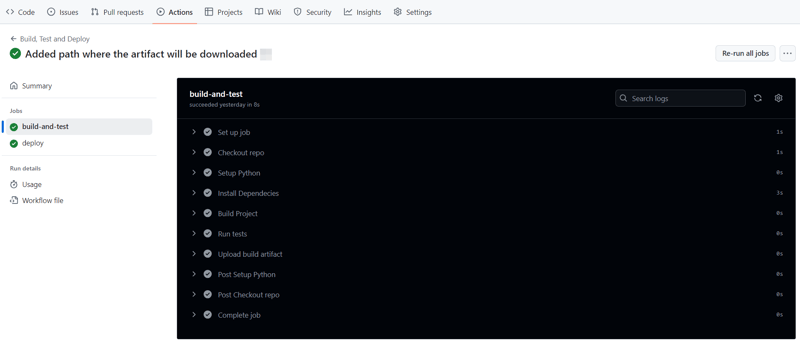
And that's it, this setup provides a working example of a CI/CD pipeline for a very basic Python project. If you found this helpful, please share with your connection and if you have any questions, do not hesitate to drop the question in the comments.
以上是使用 GitHub Actions 自动化构建、测试和部署流程的详细内容。更多信息请关注PHP中文网其他相关文章!

热AI工具

Undresser.AI Undress
人工智能驱动的应用程序,用于创建逼真的裸体照片

AI Clothes Remover
用于从照片中去除衣服的在线人工智能工具。

Undress AI Tool
免费脱衣服图片

Clothoff.io
AI脱衣机

Video Face Swap
使用我们完全免费的人工智能换脸工具轻松在任何视频中换脸!

热门文章

热工具

记事本++7.3.1
好用且免费的代码编辑器

SublimeText3汉化版
中文版,非常好用

禅工作室 13.0.1
功能强大的PHP集成开发环境

Dreamweaver CS6
视觉化网页开发工具

SublimeText3 Mac版
神级代码编辑软件(SublimeText3)
 Python与C:学习曲线和易用性
Apr 19, 2025 am 12:20 AM
Python与C:学习曲线和易用性
Apr 19, 2025 am 12:20 AM
Python更易学且易用,C 则更强大但复杂。1.Python语法简洁,适合初学者,动态类型和自动内存管理使其易用,但可能导致运行时错误。2.C 提供低级控制和高级特性,适合高性能应用,但学习门槛高,需手动管理内存和类型安全。
 Python和时间:充分利用您的学习时间
Apr 14, 2025 am 12:02 AM
Python和时间:充分利用您的学习时间
Apr 14, 2025 am 12:02 AM
要在有限的时间内最大化学习Python的效率,可以使用Python的datetime、time和schedule模块。1.datetime模块用于记录和规划学习时间。2.time模块帮助设置学习和休息时间。3.schedule模块自动化安排每周学习任务。
 Python vs.C:探索性能和效率
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:20 AM
Python vs.C:探索性能和效率
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:20 AM
Python在开发效率上优于C ,但C 在执行性能上更高。1.Python的简洁语法和丰富库提高开发效率。2.C 的编译型特性和硬件控制提升执行性能。选择时需根据项目需求权衡开发速度与执行效率。
 学习Python:2小时的每日学习是否足够?
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:22 AM
学习Python:2小时的每日学习是否足够?
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:22 AM
每天学习Python两个小时是否足够?这取决于你的目标和学习方法。1)制定清晰的学习计划,2)选择合适的学习资源和方法,3)动手实践和复习巩固,可以在这段时间内逐步掌握Python的基本知识和高级功能。
 Python标准库的哪一部分是:列表或数组?
Apr 27, 2025 am 12:03 AM
Python标准库的哪一部分是:列表或数组?
Apr 27, 2025 am 12:03 AM
pythonlistsarepartofthestAndArdLibrary,herilearRaysarenot.listsarebuilt-In,多功能,和Rused ForStoringCollections,而EasaraySaraySaraySaraysaraySaraySaraysaraySaraysarrayModuleandleandleandlesscommonlyusedDduetolimitedFunctionalityFunctionalityFunctionality。
 Python:自动化,脚本和任务管理
Apr 16, 2025 am 12:14 AM
Python:自动化,脚本和任务管理
Apr 16, 2025 am 12:14 AM
Python在自动化、脚本编写和任务管理中表现出色。1)自动化:通过标准库如os、shutil实现文件备份。2)脚本编写:使用psutil库监控系统资源。3)任务管理:利用schedule库调度任务。Python的易用性和丰富库支持使其在这些领域中成为首选工具。
 Python vs. C:了解关键差异
Apr 21, 2025 am 12:18 AM
Python vs. C:了解关键差异
Apr 21, 2025 am 12:18 AM
Python和C 各有优势,选择应基于项目需求。1)Python适合快速开发和数据处理,因其简洁语法和动态类型。2)C 适用于高性能和系统编程,因其静态类型和手动内存管理。
 Web开发的Python:关键应用程序
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:20 AM
Web开发的Python:关键应用程序
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:20 AM
Python在Web开发中的关键应用包括使用Django和Flask框架、API开发、数据分析与可视化、机器学习与AI、以及性能优化。1.Django和Flask框架:Django适合快速开发复杂应用,Flask适用于小型或高度自定义项目。2.API开发:使用Flask或DjangoRESTFramework构建RESTfulAPI。3.数据分析与可视化:利用Python处理数据并通过Web界面展示。4.机器学习与AI:Python用于构建智能Web应用。5.性能优化:通过异步编程、缓存和代码优






