Try natural language data analysis with Streamlit in Snowflake (SiS)
Introduction
Snowflake has released an LLM assistant feature called Snowflake Copilot as a preview feature. With Snowflake Copilot, you can analyze table data using natural language.
On the other hand, Streamlit in Snowflake (SiS) allows you to easily incorporate generative AI and securely access table data. This made me think: could we create a more proactive natural language data analysis tool? So, I developed an app that can analyze and visualize data using natural language.
Note: This post represents my personal views and not those of Snowflake.
Feature Overview
Goals
- Usable by business users unfamiliar with SQL
- Ability to select DB / schema / table via mouse operations for analysis
- Capable of analyzing with very ambiguous natural language queries
Actual Screenshots (Excerpts)
The following are excerpts from analysis results using Cortex LLM (snowflake-arctic).
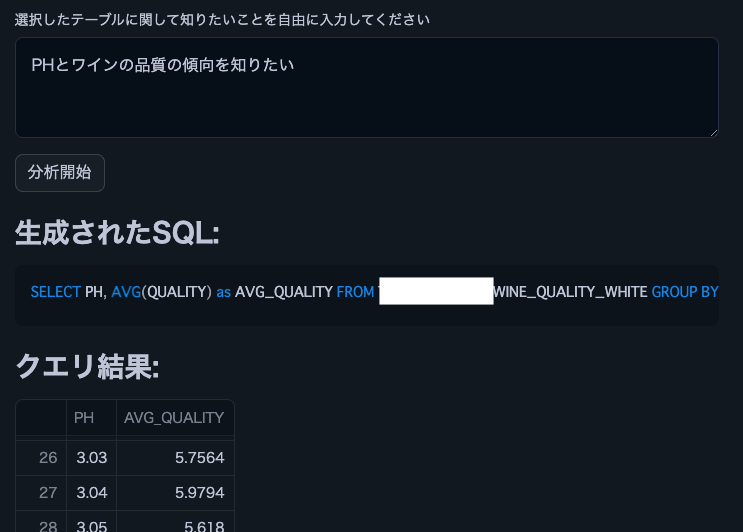
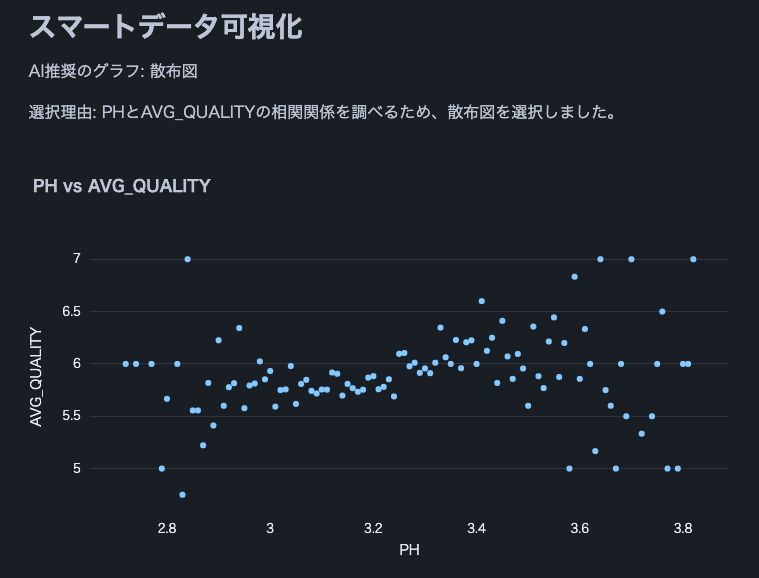

Note: We used this wine quality dataset.
Feature List
- Select Cortex LLM for analysis
- Choose DB / schema / table for analysis
- Display column information and sample data of the selected table
- Analysis using natural language input from users
- Automatic SQL generation for analysis
- Automatic execution of generated SQL
- Display of SQL query execution results
- Data insights provided by Cortex LLM
- Data visualization
- Appropriate graph selection and display by Cortex LLM
- Final data interpretation by Cortex LLM
Operating Conditions
- Snowflake account with access to Cortex LLM
- snowflake-ml-python 1.1.2 or later
Precautions
- Be cautious when using large datasets as no data limit is set
- Large result sets from generated SQL queries may take time to process
- Large result sets may cause LLM token limit errors
Source Code
from snowflake.snowpark.context import get_active_session
import streamlit as st
from snowflake.cortex import Complete as CompleteText
import snowflake.snowpark.functions as F
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
import json
import plotly.express as px
# Get current session
session = get_active_session()
# Application title
st.title("Natural Language Data Analysis App")
# Cortex LLM settings
st.sidebar.title("Cortex LLM Settings")
lang_model = st.sidebar.radio("Select the language model you want to use",
("snowflake-arctic", "reka-flash", "reka-core",
"mistral-large2", "mistral-large", "mixtral-8x7b", "mistral-7b",
"llama3.1-405b", "llama3.1-70b", "llama3.1-8b",
"llama3-70b", "llama3-8b", "llama2-70b-chat",
"jamba-instruct", "gemma-7b")
)
# Function to escape column names
def escape_column_name(name):
return f'"{name}"'
# Function to get table information
def get_table_info(database, schema, table):
# Get column information
columns = session.sql(f"DESCRIBE TABLE {database}.{schema}.{table}").collect()
# Create DataFrame
column_df = pd.DataFrame(columns)
# Get row count
row_count = session.sql(f"SELECT COUNT(*) as count FROM {database}.{schema}.{table}").collect()[0]['COUNT']
# Get sample data
sample_data = session.sql(f"SELECT * FROM {database}.{schema}.{table} LIMIT 5").collect()
sample_df = pd.DataFrame(sample_data)
return column_df, row_count, sample_df
# Data analysis function
def analyze(df, query):
st.subheader("Result Analysis")
# Display basic statistical information
st.subheader("Basic Statistics")
st.write(df.describe())
# Use AI for data analysis
analysis_prompt = f"""
Based on the following dataframe and original question, please perform data analysis.
Concisely explain in English the insights, trends, and anomalies derived from the data.
If possible, please also mention the following points:
1. Data distribution and characteristics
2. Presence of abnormal values or outliers
3. Correlations between columns (if there are multiple numeric columns)
4. Time-series trends (if there is date or time data)
5. Category-specific features (if data can be divided by categories)
Dataframe:
{df.to_string()}
Original question:
{query}
"""
analysis = CompleteText(lang_model, analysis_prompt)
st.write(analysis)
# Data visualization function
def smart_data_visualization(df):
st.subheader("Smart Data Visualization")
if df.empty:
st.warning("The dataframe is empty. There is no data to visualize.")
return
# Request AI for graph suggestion
columns_info = "\n".join([f"{col} - type: {df[col].dtype}" for col in df.columns])
sample_data = df.head().to_string()
visualization_prompt = f"""
Analyze the information of the following dataframe and suggest the most appropriate graph type and the columns to use for its x-axis and y-axis.
Consider the characteristics of the data to ensure a meaningful visualization.
Column information:
{columns_info}
Sample data:
{sample_data}
Please provide only the following JSON data format as your response:
{{
"graph_type": "One of: scatter plot, bar chart, line chart, histogram, box plot",
"x_axis": "Column name to use for x-axis",
"y_axis": "Column name to use for y-axis (if applicable)",
"explanation": "Brief explanation of the selection reason"
}}
"""
ai_suggestion = CompleteText(lang_model, visualization_prompt)
try:
suggestion = json.loads(ai_suggestion)
graph_type = suggestion['graph_type']
x_axis = suggestion['x_axis']
y_axis = suggestion.get('y_axis') # y-axis might not be needed in some cases
explanation = suggestion['explanation']
st.write(f"AI recommended graph: {graph_type}")
st.write(f"Selection reason: {explanation}")
if graph_type == "scatter plot":
fig = px.scatter(df, x=x_axis, y=y_axis, title=f"{x_axis} vs {y_axis}")
elif graph_type == "bar chart":
fig = px.bar(df, x=x_axis, y=y_axis, title=f"{y_axis} by {x_axis}")
elif graph_type == "line chart":
fig = px.line(df, x=x_axis, y=y_axis, title=f"{y_axis} over {x_axis}")
elif graph_type == "histogram":
fig = px.histogram(df, x=x_axis, title=f"Distribution of {x_axis}")
elif graph_type == "box plot":
fig = px.box(df, x=x_axis, y=y_axis, title=f"Distribution of {y_axis} by {x_axis}")
else:
st.warning(f"Unsupported graph type: {graph_type}")
return
st.plotly_chart(fig)
except json.JSONDecodeError:
st.error("Failed to parse AI suggestion. Please try again.")
except KeyError as e:
st.error(f"AI suggestion is missing necessary information: {str(e)}")
except Exception as e:
st.error(f"An error occurred while creating the graph: {str(e)}")
# AI interpretation of visualization
visualization_interpretation_prompt = f"""
Based on the following dataset and created graph, please provide a detailed interpretation of the data trends and characteristics in English.
Point out possible insights, patterns, anomalies, or areas that require additional analysis.
Dataset information:
Columns: {', '.join(df.columns)}
Number of rows: {len(df)}
Created graph:
Type: {graph_type}
X-axis: {x_axis}
Y-axis: {y_axis if y_axis else 'None'}
"""
ai_interpretation = CompleteText(lang_model, visualization_interpretation_prompt)
st.subheader("AI Interpretation of the Graph")
st.write(ai_interpretation)
# Function to handle cases where AI response is not just SQL query
def clean_sql_query(query):
# Remove leading and trailing whitespace
query = query.strip()
# If not starting with SQL keywords, remove everything up to the first SELECT
if not query.upper().startswith(('SELECT')):
keywords = ['SELECT']
for keyword in keywords:
if keyword in query.upper():
query = query[query.upper().index(keyword):]
break
return query
# Function for natural language querying of DB
def data_analysis_and_natural_language_query():
# Database selection
databases = session.sql("SHOW DATABASES").collect()
database_names = [row['name'] for row in databases]
selected_database = st.selectbox("Select a database", database_names)
if selected_database:
# Schema selection
schemas = session.sql(f"SHOW SCHEMAS IN DATABASE {selected_database}").collect()
schema_names = [row['name'] for row in schemas]
selected_schema = st.selectbox("Select a schema", schema_names)
if selected_schema:
# Table selection
tables = session.sql(f"SHOW TABLES IN {selected_database}.{selected_schema}").collect()
table_names = [row['name'] for row in tables]
selected_table = st.selectbox("Select a table", table_names)
if selected_table:
# Get table information
column_df, row_count, sample_df = get_table_info(selected_database, selected_schema, selected_table)
st.subheader("Table Information")
st.write(f"Table name: `{selected_database}.{selected_schema}.{selected_table}`")
st.write(f"Total rows: **{row_count:,}**")
st.subheader("Column Information")
st.dataframe(column_df)
st.subheader("Sample Data (showing only 5 rows)")
st.dataframe(sample_df)
# Stringify table information (for AI)
table_info = f"""
Table name: {selected_database}.{selected_schema}.{selected_table}
Total rows: {row_count}
Column information:
{column_df.to_string(index=False)}
Sample data:
{sample_df.to_string(index=False)}
"""
# Natural language input from user
user_query = st.text_area("Enter what you want to know about the selected table")
if st.button("Start Analysis"):
if user_query:
# Use AI to generate SQL
prompt = f"""
Based on the following table information and question, please generate an appropriate SQL query.
Return only the generated SQL query without any additional response.
Table information:
{table_info}
Question: {user_query}
Notes:
- Follow Snowflake SQL syntax.
- Use aggregate functions to keep the query result size manageable.
- Use {selected_database}.{selected_schema}.{selected_table} as the table name.
"""
generated_sql = CompleteText(lang_model, prompt)
generated_sql = clean_sql_query(generated_sql)
st.subheader("Generated SQL:")
st.code(generated_sql, language='sql')
try:
# Execute the generated SQL
result = session.sql(generated_sql).collect()
df = pd.DataFrame(result)
st.subheader("Query Result:")
st.dataframe(df)
# Analyze results
analyze(df, user_query)
# Smart data visualization
smart_data_visualization(df)
except Exception as e:
st.error(f"An error occurred while executing the query: {str(e)}")
else:
st.warning("Please enter a question.")
# Execution part
data_analysis_and_natural_language_query()
Conclusion
The ability to easily analyze table data using natural language without SQL or Python knowledge could significantly broaden the scope of data utilization in enterprises for business users. By adding features like joining multiple tables or increasing the variety of visualization graphs, even more complex analyses can be performed. I encourage everyone to try implementing data analysis democratization using Streamlit in Snowflake.
Announcements
Snowflake What's New Updates on X
I'm sharing Snowflake's What's New updates on X. Please feel free to follow if you're interested!
English Version
Snowflake What's New Bot (English Version)
https://x.com/snow_new_en
Japanese Version
Snowflake What's New Bot (Japanese Version)
https://x.com/snow_new_jp
Change History
(20240914) Initial post
Original Japanese Article
https://zenn.dev/tsubasa_tech/articles/2608c820294860
以上是Try natural language data analysis with Streamlit in Snowflake (SiS)的详细内容。更多信息请关注PHP中文网其他相关文章!

热AI工具

Undresser.AI Undress
人工智能驱动的应用程序,用于创建逼真的裸体照片

AI Clothes Remover
用于从照片中去除衣服的在线人工智能工具。

Undress AI Tool
免费脱衣服图片

Clothoff.io
AI脱衣机

Video Face Swap
使用我们完全免费的人工智能换脸工具轻松在任何视频中换脸!

热门文章

热工具

记事本++7.3.1
好用且免费的代码编辑器

SublimeText3汉化版
中文版,非常好用

禅工作室 13.0.1
功能强大的PHP集成开发环境

Dreamweaver CS6
视觉化网页开发工具

SublimeText3 Mac版
神级代码编辑软件(SublimeText3)
 Python与C:学习曲线和易用性
Apr 19, 2025 am 12:20 AM
Python与C:学习曲线和易用性
Apr 19, 2025 am 12:20 AM
Python更易学且易用,C 则更强大但复杂。1.Python语法简洁,适合初学者,动态类型和自动内存管理使其易用,但可能导致运行时错误。2.C 提供低级控制和高级特性,适合高性能应用,但学习门槛高,需手动管理内存和类型安全。
 学习Python:2小时的每日学习是否足够?
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:22 AM
学习Python:2小时的每日学习是否足够?
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:22 AM
每天学习Python两个小时是否足够?这取决于你的目标和学习方法。1)制定清晰的学习计划,2)选择合适的学习资源和方法,3)动手实践和复习巩固,可以在这段时间内逐步掌握Python的基本知识和高级功能。
 Python vs.C:探索性能和效率
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:20 AM
Python vs.C:探索性能和效率
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:20 AM
Python在开发效率上优于C ,但C 在执行性能上更高。1.Python的简洁语法和丰富库提高开发效率。2.C 的编译型特性和硬件控制提升执行性能。选择时需根据项目需求权衡开发速度与执行效率。
 Python vs. C:了解关键差异
Apr 21, 2025 am 12:18 AM
Python vs. C:了解关键差异
Apr 21, 2025 am 12:18 AM
Python和C 各有优势,选择应基于项目需求。1)Python适合快速开发和数据处理,因其简洁语法和动态类型。2)C 适用于高性能和系统编程,因其静态类型和手动内存管理。
 Python标准库的哪一部分是:列表或数组?
Apr 27, 2025 am 12:03 AM
Python标准库的哪一部分是:列表或数组?
Apr 27, 2025 am 12:03 AM
pythonlistsarepartofthestAndArdLibrary,herilearRaysarenot.listsarebuilt-In,多功能,和Rused ForStoringCollections,而EasaraySaraySaraySaraysaraySaraySaraysaraySaraysarrayModuleandleandleandlesscommonlyusedDduetolimitedFunctionalityFunctionalityFunctionality。
 Python:自动化,脚本和任务管理
Apr 16, 2025 am 12:14 AM
Python:自动化,脚本和任务管理
Apr 16, 2025 am 12:14 AM
Python在自动化、脚本编写和任务管理中表现出色。1)自动化:通过标准库如os、shutil实现文件备份。2)脚本编写:使用psutil库监控系统资源。3)任务管理:利用schedule库调度任务。Python的易用性和丰富库支持使其在这些领域中成为首选工具。
 科学计算的Python:详细的外观
Apr 19, 2025 am 12:15 AM
科学计算的Python:详细的外观
Apr 19, 2025 am 12:15 AM
Python在科学计算中的应用包括数据分析、机器学习、数值模拟和可视化。1.Numpy提供高效的多维数组和数学函数。2.SciPy扩展Numpy功能,提供优化和线性代数工具。3.Pandas用于数据处理和分析。4.Matplotlib用于生成各种图表和可视化结果。
 Web开发的Python:关键应用程序
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:20 AM
Web开发的Python:关键应用程序
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:20 AM
Python在Web开发中的关键应用包括使用Django和Flask框架、API开发、数据分析与可视化、机器学习与AI、以及性能优化。1.Django和Flask框架:Django适合快速开发复杂应用,Flask适用于小型或高度自定义项目。2.API开发:使用Flask或DjangoRESTFramework构建RESTfulAPI。3.数据分析与可视化:利用Python处理数据并通过Web界面展示。4.机器学习与AI:Python用于构建智能Web应用。5.性能优化:通过异步编程、缓存和代码优






