php内核分析(一)
这里阅读的php版本为PHP-7.1.0 RC3,阅读代码的平台为linux
首先是寻找php的入口,php有很多种模式,apache,php-fpm, cli模式,我要入手的话,只能先从最简单的cli模型开始。
那么,我需要先寻找
php -r 'echo 12;'
这个命令是如何执行的。
首先还是寻找main入口,由于我们看的是命令行的php程序。所以,这个入口在sapi/cli/php_cli.c中。
首先是定义一系列的变量
01 int c; 02 zend_file_handle file_handle; 03 int behavior = PHP_MODE_STANDARD; 04 char *reflection_what = NULL; 05 volatile int request_started = 0; 06 volatile int exit_status = 0; 07 char *php_optarg = NULL, *orig_optarg = NULL; 08 int php_optind = 1, orig_optind = 1; 09 char *exec_direct=NULL, *exec_run=NULL, *exec_begin=NULL, *exec_end=NULL; 10 char *arg_free=NULL, **arg_excp=&arg_free; 11 char *script_file=NULL, *translated_path = NULL; 12 int interactive=0; 13 int lineno = 0; 14 const char *param_error=NULL; 15 int hide_argv = 0;
然后是这个
sapi_module_struct *sapi_module = &cli_sapi_module;
这是一个sapi_module_struct结构,这个结构是sapi中最重要的数据结构。它的定义在main/SAPI.h中。
下面是增加了注释的代码:
01 struct _sapi_module_struct { // SAPI模块结构
02 char *name; // 应用层名称,比如cli,cgi等
03 char *pretty_name; // 应用层更易读的名字,比如cli对应的就是Command Line Interface
04
05 int (*startup)(struct _sapi_module_struct *sapi_module); // 当一个应用要调用php的时候,这个模块启动的时候会调用的函数
06 int (*shutdown)(struct _sapi_module_struct *sapi_module); // 当一个应用要调用php的时候,这个模块结束的时候会调用的函数
07
08 int (*activate)(void); // 在处理每个request的时候,激活需要调用的函数
09 int (*deactivate)(void); // 在处理完每个request的时候,收尾时候要调用的函数
10
11 size_t (*ub_write)(const char *str, size_t str_length); // 这个函数告诉php如何输出数据
12 void (*flush)(void *server_context); // 提供给php的刷新缓存的函数指针
13 zend_stat_t *(*get_stat)(void); // 用来判断要执行文件的权限,来判断是否有执行权限
14 char *(*getenv)(char *name, size_t name_len); // 获取环境变量的方法
15
16 void (*sapi_error)(int type, const char *error_msg, ...) ZEND_ATTRIBUTE_FORMAT(printf, 2, 3); // 错误处理方法
17
18 int (*header_handler)(sapi_header_struct *sapi_header, sapi_header_op_enum op, sapi_headers_struct *sapi_headers); // 这个函数会在我们调用header()的时候被调用
19 int (*send_headers)(sapi_headers_struct *sapi_headers); // 发送所有的header
20 void (*send_header)(sapi_header_struct *sapi_header, void *server_context); // 单独发送某一个header
21
22 size_t (*read_post)(char *buffer, size_t count_bytes); // 如何获取HTTP POST中的数据
23 char *(*read_cookies)(void); // 如何获取cookie中的数据
24
25 void (*register_server_variables)(zval *track_vars_array); // 这个函数可以给$_SERVER中获取变量
26 void (*log_message)(char *message, int syslog_type_int); // 输出错误信息函数
27 double (*get_request_time)(void); // 获取请求时间的函数
28 void (*terminate_process)(void); // TODO: 调用exit的时候调用的方法
29
30 char *php_ini_path_override; // PHP的ini文件被复写了所复写的地址
31
32 void (*default_post_reader)(void); // 这里和前面的read_post有个差别,read_post负责如何获取POST数据,而这里的函数负责如何解析POST数据
33 void (*treat_data)(int arg, char *str, zval *destArray); // 对数据进行处理,比如进行安全过滤等。 default_post_reader/tread_data/input_filter是三个能对输入进行过滤和处理的函数
34 char *executable_location; // 执行的地理位置
35
36 int php_ini_ignore; // 是否不使用任何ini配置文件,比如php -n 就将这个位置设置为1
37 int php_ini_ignore_cwd; // 不在当前路径寻找php.ini
38
39 int (*get_fd)(int *fd); // 获取执行文件的fd
40
41 int (*force_http_10)(void); // 强制使用http1.0
42
43 int (*get_target_uid)(uid_t *); // 获取执行程序的uid
44 int (*get_target_gid)(gid_t *); // 获取执行程序的gid
45
46 unsigned int (*input_filter)(int arg, char *var, char **val, size_t val_len, size_t *new_val_len); // 对输入进行过滤。比如将输入参数填充到自动全局变量$_GET, $_POST, $_COOKIE中
47
48 void (*ini_defaults)(HashTable *configuration_hash); // 默认的ini配置
49 int phpinfo_as_text; // 是否打印phpinfo信息
50
51 char *ini_entries; // 有没有附带的ini配置,比如使用php -d date.timezone=America/Adak,可以在命令行中设置时区
52 const zend_function_entry *additional_functions; // 每个SAPI模块特有的一些函数注册,比如cli的cli_get_process_title
53 unsigned int (*input_filter_init)(void); // TODO:
54 };有几个点可以总结:
cli模式是不需要发送header的,所以对应header处理的三个函数
1 sapi_cli_header_handler 2 sapi_cli_send_headers 3 sapi_cli_send_header
实际上都是空实现。
cookie也是同样道理
sapi_cli_read_cookies
其他的一些定义的函数,等到我们遇到的时候再分析吧。
main
回到main函数,根据上面的那个结构,我们就理解了
1 argv = save_ps_args(argc, argv); //这里获取一次当前执行进程的参数,环境变量等。为的是对特定平台,修正下argv变量以供后续使用。 2 3 cli_sapi_module.additional_functions = additional_functions; // cli模式特有的函数
signal
1 #ifdef HAVE_SIGNAL_H 2 #if defined(SIGPIPE) && defined(SIG_IGN) 3 // 忽略SIGPIPE是为了如果php是socket的客户端,那么当服务端关闭的话,会返回一个PIPE的信号,为的是当前的程序不会因为这个而结束 4 signal(SIGPIPE, SIG_IGN); 5 #endif 6 #endif
以上就是php内核分析(一)的内容,更多相关内容请关注PHP中文网(www.php.cn)!

热AI工具

Undresser.AI Undress
人工智能驱动的应用程序,用于创建逼真的裸体照片

AI Clothes Remover
用于从照片中去除衣服的在线人工智能工具。

Undress AI Tool
免费脱衣服图片

Clothoff.io
AI脱衣机

AI Hentai Generator
免费生成ai无尽的。

热门文章

热工具

记事本++7.3.1
好用且免费的代码编辑器

SublimeText3汉化版
中文版,非常好用

禅工作室 13.0.1
功能强大的PHP集成开发环境

Dreamweaver CS6
视觉化网页开发工具

SublimeText3 Mac版
神级代码编辑软件(SublimeText3)

热门话题
 适用于 Ubuntu 和 Debian 的 PHP 8.4 安装和升级指南
Dec 24, 2024 pm 04:42 PM
适用于 Ubuntu 和 Debian 的 PHP 8.4 安装和升级指南
Dec 24, 2024 pm 04:42 PM
PHP 8.4 带来了多项新功能、安全性改进和性能改进,同时弃用和删除了大量功能。 本指南介绍了如何在 Ubuntu、Debian 或其衍生版本上安装 PHP 8.4 或升级到 PHP 8.4
 讨论 CakePHP
Sep 10, 2024 pm 05:28 PM
讨论 CakePHP
Sep 10, 2024 pm 05:28 PM
CakePHP 是 PHP 的开源框架。它的目的是使应用程序的开发、部署和维护变得更加容易。 CakePHP 基于类似 MVC 的架构,功能强大且易于掌握。模型、视图和控制器 gu
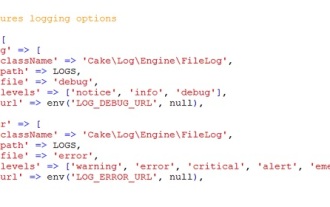 CakePHP 日志记录
Sep 10, 2024 pm 05:26 PM
CakePHP 日志记录
Sep 10, 2024 pm 05:26 PM
登录 CakePHP 是一项非常简单的任务。您只需使用一项功能即可。您可以记录任何后台进程(如 cronjob)的错误、异常、用户活动、用户采取的操作。在 CakePHP 中记录数据很容易。提供了 log() 函数
 如何设置 Visual Studio Code (VS Code) 进行 PHP 开发
Dec 20, 2024 am 11:31 AM
如何设置 Visual Studio Code (VS Code) 进行 PHP 开发
Dec 20, 2024 am 11:31 AM
Visual Studio Code,也称为 VS Code,是一个免费的源代码编辑器 - 或集成开发环境 (IDE) - 可用于所有主要操作系统。 VS Code 拥有针对多种编程语言的大量扩展,可以轻松编写










