.NET框架-双向链表(LinkedList)代码分析(图)
.NET框架中的LinkList,实现的是双向链表,总结下它的实现源码。
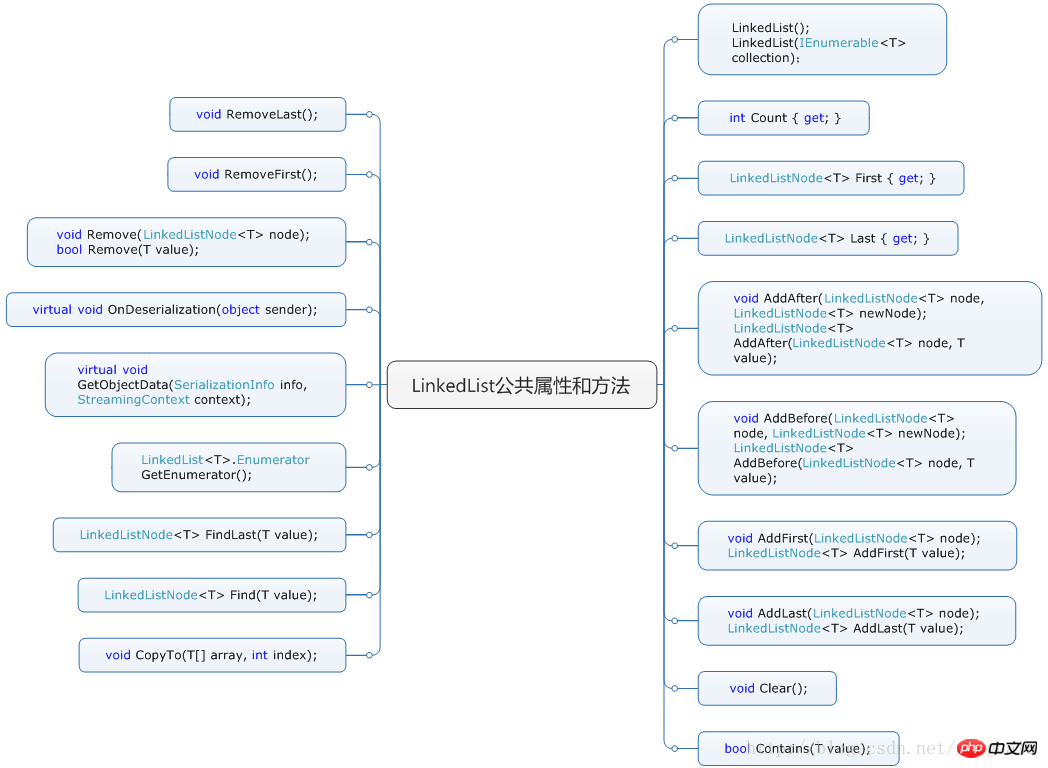
先看下LinkedList提供的公有属性和方法的导图:
1 LinkedList实现的接口:
public class LinkedList<T> : ICollection<T>, ICollection, IReadOnlyCollection<T>, ISerializable, IDeserializationCallback
2 LinkedList的全局变量包括,
head是封装的类内头节点;
// This LinkedList is a doubly-Linked circular list.
internal LinkedListNode<T> head;
internal int count;
internal int version;
private object _syncRoot;
//A temporary variable which we need during deserialization.
private SerializationInfo _siInfo;
// names for serialization
private const string VersionName = "Version";
private const string CountName = "Count";
private const string ValuesName = "Data";封装的每个节点的数据结构为:
public sealed class LinkedListNode<T>
{ public LinkedListNode(T value);
//获取LinkedListNode所属的LinkedList
public LinkedList<T> List { get; }
public LinkedListNode<T> Next { get; }
public LinkedListNode<T> Previous { get; }
//获取节点中包含的值。
public T Value { get; set; }
}3 构造函数:
public LinkedList() //默认的构造函数
{
} //带有参数的
public LinkedList(IEnumerable<T> collection)
{ if (collection == null)
{ throw new ArgumentNullException(nameof(collection));
} foreach (T item in collection)
{
AddLast(item);
}
}在构造IEnumerable类型的collection时,用到了AddLast(T)方法,它还有一个重载,工作细节如下:
public LinkedListNode<T> AddLast(T value)
{
LinkedListNode<T> result = new LinkedListNode<T>(this, value);
if (head == null)
{
InternalInsertNodeToEmptyList(result);
} else
{
InternalInsertNodeBefore(head, result);
} return result;
}
public void AddLast(LinkedListNode<T> node)
{
ValidateNewNode(node);
if (head == null)
{
InternalInsertNodeToEmptyList(node);
} else
{
InternalInsertNodeBefore(head, node);
}
node.list = this; //结合LinkedListNode看
}以上2个方法,语义是插入某个节点,
分插入新节点到空list中,InternalInsertNodeToEmptyList
插入新节点到不为空的list中,InternalInsertNodeBefore,并且给出在哪个节点前插入newNode,还判断了新插入的节点是不是一个有效的新节点。
internal void ValidateNewNode(LinkedListNode<T> node)
{ if (node == null)
{ throw new ArgumentNullException(nameof(node));
} if (node.list != null)
{ throw new InvalidOperationException(SR.LinkedListNodeIsAttached);
}
}同时,还给出判断一个节点是不是有效节点:
internal void ValidateNode(LinkedListNode<T> node)
{ if (node == null)
{ throw new ArgumentNullException(nameof(node));
} if (node.list != this)
{ throw new InvalidOperationException(SR.ExternalLinkedListNode);
}
}这是双向链表比较重要的内部方法,
InternalInsertNodeToEmptyList的实现细节:
private void InternalInsertNodeToEmptyList(LinkedListNode<T> newNode)
{
Debug.Assert(head == null && count == 0, "LinkedList must be empty when this method is called!");
newNode.next = newNode;
newNode.prev = newNode;
head = newNode;
version++;
count++;
}InternalInsertNodeBefore的实现细节:
private void InternalInsertNodeBefore(LinkedListNode<T> node, LinkedListNode<T> newNode)
{
newNode.next = node;
newNode.prev = node.prev;
node.prev.next = newNode;
node.prev = newNode;
version++;
count++;
}4 链表自然离不开插入某个节点的公有方法,
public LinkedListNode<T> AddAfter(LinkedListNode<T> node, T value)
{
ValidateNode(node);
LinkedListNode<T> result = new LinkedListNode<T>(node.list, value);
InternalInsertNodeBefore(node.next, result); return result;
} public void AddAfter(LinkedListNode<T> node, LinkedListNode<T> newNode)
{
ValidateNode(node);
ValidateNewNode(newNode);
InternalInsertNodeBefore(node.next, newNode);
newNode.list = this;
} public LinkedListNode<T> AddBefore(LinkedListNode<T> node, T value)
{
ValidateNode(node);
LinkedListNode<T> result = new LinkedListNode<T>(node.list, value);
InternalInsertNodeBefore(node, result); if (node == head)
{
head = result;
} return result;
} public void AddBefore(LinkedListNode<T> node, LinkedListNode<T> newNode)
{
ValidateNode(node);
ValidateNewNode(newNode);
InternalInsertNodeBefore(node, newNode);
newNode.list = this; if (node == head)
{
head = newNode;
}
} public LinkedListNode<T> AddFirst(T value)
{
LinkedListNode<T> result = new LinkedListNode<T>(this, value);
if (head == null)
{
InternalInsertNodeToEmptyList(result);
} else
{
InternalInsertNodeBefore(head, result);
head = result;
} return result;
} public void AddFirst(LinkedListNode<T> node)
{
ValidateNewNode(node); if (head == null)
{
InternalInsertNodeToEmptyList(node);
} else
{
InternalInsertNodeBefore(head, node);
head = node;
}
node.list = this;
} public LinkedListNode<T> AddLast(T value)
{
LinkedListNode<T> result = new LinkedListNode<T>(this, value);
if (head == null)
{
InternalInsertNodeToEmptyList(result);
} else
{
InternalInsertNodeBefore(head, result);
} return result;
} public void AddLast(LinkedListNode<T> node)
{
ValidateNewNode(node); if (head == null)
{
InternalInsertNodeToEmptyList(node);
} else
{
InternalInsertNodeBefore(head, node);
}
node.list = this;
}5 再看下,清除链表所有节点,此处是设置所有节点不在指向内存堆,然后等GC回收,
public void Clear()
{
LinkedListNode<T> current = head;
while (current != null)
{
LinkedListNode<T> temp = current;
current = current.Next;
// use Next the instead of "next", otherwise it will loop forever
temp.Invalidate();
}
head = null;
count = 0;
version++;
}6 与只相对应的是移除某个节点的一些列接口,与添加类似,不再赘述,
Clear里面调用了Invalidate(),实现很简单:
internal void Invalidate()
{
list = null;
next = null;
prev = null;
}7 判断某个节点值为value的存在性,里面调用Find方法,
public bool Contains(T value)
{ return Find(value) != null;
}Find方法实现细节,类似的API还有FindLast,因为是双向链表,所以从尾部开始遍历链表即可,
public LinkedListNode<T> Find(T value)
{
LinkedListNode<T> node = head;
//调用默认相等比较器
EqualityComparer<T> c = EqualityComparer<T>.Default;
if (node != null)//链表为null
{
if (value != null)
{
do
{
if (c.Equals(node.item, value)) //Equals:某个节点node的item与value相等
{
return node;
}
node = node.next;
} while (node != head);
}
else
{
do
{
if (node.item == null)
{
return node;
}
node = node.next;
} while (node != head);
}
} return null; //链表为null,直接返回null
}8 再看一个复制数据到数组的实现:
public void CopyTo(T[] array, int index)
{
if (array == null)
{
throw new ArgumentNullException(nameof(array));
}
if (index < 0)
{
throw new ArgumentOutOfRangeException(nameof(index), index, SR.ArgumentOutOfRange_NeedNonNegNum);
}
if (index > array.Length)
{
throw new ArgumentOutOfRangeException(nameof(index), index, SR.ArgumentOutOfRange_BiggerThanCollection);
}
if (array.Length - index < Count)
{
throw new ArgumentException(SR.Arg_InsufficientSpace);
}
LinkedListNode<T> node = head;
if (node != null)
{
do
{
array[index++] = node.item;
node = node.next;
} while (node != head); //双向链表,再次遍历到头结点时
}
}以上是.NET框架-双向链表(LinkedList)代码分析(图)的详细内容。更多信息请关注PHP中文网其他相关文章!

热AI工具

Undresser.AI Undress
人工智能驱动的应用程序,用于创建逼真的裸体照片

AI Clothes Remover
用于从照片中去除衣服的在线人工智能工具。

Undress AI Tool
免费脱衣服图片

Clothoff.io
AI脱衣机

Video Face Swap
使用我们完全免费的人工智能换脸工具轻松在任何视频中换脸!

热门文章

热工具

记事本++7.3.1
好用且免费的代码编辑器

SublimeText3汉化版
中文版,非常好用

禅工作室 13.0.1
功能强大的PHP集成开发环境

Dreamweaver CS6
视觉化网页开发工具

SublimeText3 Mac版
神级代码编辑软件(SublimeText3)
 使用LinkedList类的removeLast()方法删除链表中的最后一个元素
Jul 24, 2023 pm 05:13 PM
使用LinkedList类的removeLast()方法删除链表中的最后一个元素
Jul 24, 2023 pm 05:13 PM
使用LinkedList类的removeLast()方法删除链表中的最后一个元素LinkedList是Java集合框架中常见的一种数据结构,它以双向链表的形式存储元素。通过LinkedList类提供的方法,我们可以方便地对链表进行操作,例如添加、删除和修改元素。在某些场景下,我们可能需要删除链表中的最后一个元素。LinkedList类提供了removeLas
 Java程序向LinkedList添加元素
Aug 26, 2023 pm 10:21 PM
Java程序向LinkedList添加元素
Aug 26, 2023 pm 10:21 PM
LinkedList是JavaCollectionFramework的通用类,它实现了List、Deque和Queue三个接口。它提供了LinkedList数据结构的功能,LinkedList是一种线性数据结构,其中每个元素相互链接。我们可以对LinkedList执行多种操作,包括添加、删除和遍历元素。要将元素添加到LinkedList集合中,我们可以使用各种内置方法,例如add()、addFirst()和addLast()。我们将探索如何使用这些方法将元素添加到LinkedList。在Java
 使用C++按给定大小将双向链表分组反转
Sep 04, 2023 am 09:49 AM
使用C++按给定大小将双向链表分组反转
Sep 04, 2023 am 09:49 AM
在这个问题中,我们得到一个指向链表头部的指针和一个整数k。在大小为k的组中,我们需要反转链表。例如-Input:1<->2<->3<->4<->5(doublylinkedlist),k=3Output:3<->2<->1<->5<->4寻找解决方案的方法在这个问题中,我们将制定一个递归算法来解决这个问题。在这种方法中,我们将使用递归并使用递归来解决问题。示例#include<iostream&
 Java中如何使用LinkedList.addFirst()方法将元素添加到链表头部?
Nov 18, 2023 pm 03:51 PM
Java中如何使用LinkedList.addFirst()方法将元素添加到链表头部?
Nov 18, 2023 pm 03:51 PM
Java中的LinkedList类提供了addFirst()方法,可以将元素添加到链表的头部。该方法的作用是在链表的开头添加一个元素,并将原链表的其他元素后移。下面是使用LinkedList.addFirst()方法将元素添加到链表头部的示例代码:importjava.util.LinkedList;publicclassMain{pu
 Java文档解读:LinkedList类的addFirst()方法功能解析
Nov 03, 2023 am 09:09 AM
Java文档解读:LinkedList类的addFirst()方法功能解析
Nov 03, 2023 am 09:09 AM
Java文档解读:LinkedList类的addFirst()方法功能解析LinkedList是Java集合框架中的一个双向链表实现类,它提供了一系列在列表中进行添加、删除和查找操作的方法。其中,addFirst()方法是LinkedList类中的一个重要方法之一。本文将深入解析addFirst()方法的功能,并附带具体的代码示例。addFirst()方法的
 Java文档解读:LinkedList类的addLast()方法功能解析
Nov 03, 2023 pm 02:26 PM
Java文档解读:LinkedList类的addLast()方法功能解析
Nov 03, 2023 pm 02:26 PM
Java文档解读:LinkedList类的addLast()方法功能解析在Java的集合框架中,LinkedList类是一个双向链表实现的List接口。LinkedList类提供了许多操作链表的方法,其中包括addLast()方法。本文将对LinkedList的addLast()方法进行详细解析,并提供具体的代码示例。addLast()方法的功能是将指定的元
 如何在Java中将LinkedList转换为Array?
Aug 29, 2023 pm 11:09 PM
如何在Java中将LinkedList转换为Array?
Aug 29, 2023 pm 11:09 PM
LinkedList类的toArray()方法将当前的LinkedList对象转换为对象类型的数组并返回它。该数组按正确顺序(从第一个元素到最后一个元素)包含此列表中的所有元素。它充当基于数组和基于集合的API之间的桥梁。因此,将LinkedList转换为数组-实例化LinkedList类。使用add()方法填充它。调用上面创建的链表上的toArray()方法并检索对象数组。将对象数组的每个元素转换为字符串。示例 实时演示importjava.util.Arrays;importjava.uti
 。
Mar 31, 2025 pm 04:07 PM
。
Mar 31, 2025 pm 04:07 PM
.NET异步编程、LINQ和EFCore的核心概念分别是:1.异步编程通过async和await提高应用响应性;2.LINQ通过统一语法简化数据查询;3.EFCore通过ORM简化数据库操作。






