django进阶学习记录
前言: 这篇博客对上篇博客django进阶作下补充。
一、效果图
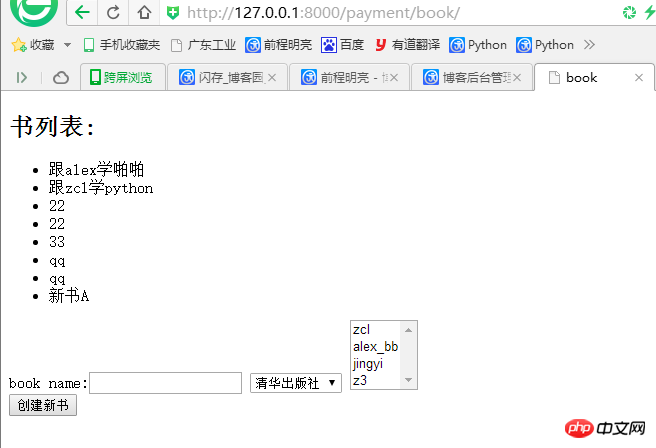
前端界面较简单(丑),有两个功能:
从数据库中取出书名 eg: 新书A
在form表单输入书名,选择出版社,选择作者(多选),输入完毕后一点击创建新书submit,就在数据库创建数据
二、实现
我们先来实现第一个功能,根据数据库数据在页面打印出书名。
1. 添加url路由
url(r'^book/', views.book),
2. 在views.py定义book方法
django默认使用GET方式,即获取数据;如果想创建/修改数据,比如待会要实现的第二个功能,就需要用POST方式。
def book(request):
books = models.Book.objects.all() #找到所有的书
publisher_list = models.Publisher.objects.all()
author_list = models.Author.objects.all()
print("---->:", request)
return render(request, "app01/book.html", {"books":books,
"publishers":publisher_list,
"authors":author_list})3. 在templates/app01下创建book.html:
books为数据库中所有书的对象集合,在html用个循环便可在前端页面显示书名。
<h2>书列表:</h2>
<ul>
{% for book in books %}
<li>{{ book.name }}</li>
{% endfor %}
</ul>接下来实现第二个功能,创建数据。
先来看前端的html:
<form method="post" action="/payment/book/"> {% csrf_token %}
book name:<input type="text" name="name"/>
<select name="publisher_id">
{% for publisher in publishers %}
<option value="{{ publisher.id }}">{{ publisher.name }}</option>
{% endfor %}
</select>
<select name="author_ids" multiple="multiple">
{% for author in authors %}
<option value="{{ author.id }}">{{ author.first_name }}</option>
{% endfor %}
</select>
<div>
<input type="submit" value="创建新书"/>
</div>
</form>注意:
因为是创建数据,所以提交方式要用post, action="/payment/book/"是一条url, 表示将数据提交到book方法,数据封装在request参数。
你在选择出版社时,要将出版社名传到后台?? 其实完全不用,你只要将选中id传到后台就可以了。因此我在option标签加上value属性,用来获致出版社的id, 当你一点击submit提交数据时,value中的id会提交给select标签的name属性,name属性再将数据提交到后台。
你会发现html代码第一行有{% csrf_token %},这个是什么意思我现在还不知道~_~,我将这句代码去掉会提交不了数据!!
再来看后台book方法
def book(request):
if request.method == "POST": #若是创建书的数据
print(request.POST)
book_name = request.POST.get("name")
publisher_id = request.POST.get("publisher_id")
# 即使在前端页面选择多个作者只会返回一个值,只能取到最后一个作者的id
#author_ids = request.POST.get("author_ids")
author_ids = request.POST.getlist("author_ids") #getlist 可取出所有作者的id
#生成一个书的对象
new_book = models.Book(
name = book_name,
publisher_id = publisher_id,
publish_date = "2017-3-18"
)
new_book.save() #同步到数据库
#new_book.authors.add(1,2) 添加作者
new_book.authors.add(*author_ids) #author_ids为列表,需在前面加上*转化为id
print("------->>:", book_name,publisher_id,author_ids)
books = models.Book.objects.all()
publisher_list = models.Publisher.objects.all()
author_list = models.Author.objects.all()
print("---->:", request)
return render(request, "app01/book.html", {"books":books,
"publishers":publisher_list,
"authors":author_list})当我在前端界面输入书名: 新书A, 选中第二个出版社,选中第2和第3个作者,为了方便看,我在后台打印出来了:
<QueryDict: {'name': ['新书A'], 'csrfmiddlewaretoken': ['V9OdHSJ10OFSq3r
vI41tggns1W2VxwV'], 'publisher_id': ['2'], 'author_ids': ['2', '3']}>
------->>: 新书A 2 ['2', '3']
---->: <WSGIRequest: POST '/payment/book/'>
[18/Mar/2017 14:06:23] "POST /payment/book/ HTTP/1.1" 200 1335根据打印结果知道author_ids是一个列表,当我为书添加作者时,用下面的代码:
new_book.authors.add(*author_ids)
为什么要在列表前加上*?不加上*是会曝错的! 加上*是为了将列表形式["2","3"]转化为作者id形式2,3。
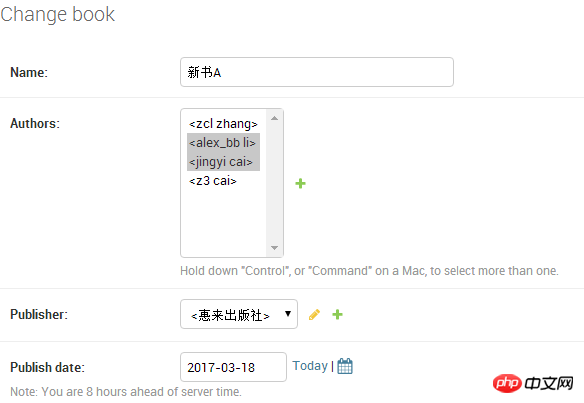
登陆admin后台查看刚刚创建的新书A:
以上是django进阶学习记录的详细内容。更多信息请关注PHP中文网其他相关文章!

热AI工具

Undresser.AI Undress
人工智能驱动的应用程序,用于创建逼真的裸体照片

AI Clothes Remover
用于从照片中去除衣服的在线人工智能工具。

Undress AI Tool
免费脱衣服图片

Clothoff.io
AI脱衣机

Video Face Swap
使用我们完全免费的人工智能换脸工具轻松在任何视频中换脸!

热门文章

热工具

记事本++7.3.1
好用且免费的代码编辑器

SublimeText3汉化版
中文版,非常好用

禅工作室 13.0.1
功能强大的PHP集成开发环境

Dreamweaver CS6
视觉化网页开发工具

SublimeText3 Mac版
神级代码编辑软件(SublimeText3)
 怎么看django版本
Dec 01, 2023 pm 02:25 PM
怎么看django版本
Dec 01, 2023 pm 02:25 PM
查看django版本步骤:1、打开终端或命令提示符窗口;2、确保已经安装了Django,如果没有安装Django,可以使用包管理工具来进行安装,输入pip install django命令即可;3、安装完成后,可以使用python -m django --version来查看Django的版本。
 Django vs. Flask:Python Web框架的对比分析
Jan 19, 2024 am 08:36 AM
Django vs. Flask:Python Web框架的对比分析
Jan 19, 2024 am 08:36 AM
Django和Flask都是PythonWeb框架中的佼佼者,它们都有着自己的优点和适用场景。本文将对这两个框架进行对比分析,并提供具体的代码示例。开发简介Django是一个全功能的Web框架,它的主要目的是为了快速开发复杂的Web应用。Django提供了许多内置的功能,比如ORM(对象关系映射)、表单、认证、管理后台等。这些功能使得Django在处理大型
 Django框架的优点和缺点:您需要知道的一切
Jan 19, 2024 am 09:09 AM
Django框架的优点和缺点:您需要知道的一切
Jan 19, 2024 am 09:09 AM
Django是一个完整的开发框架,该框架涵盖了Web开发生命周期的各个方面。目前,这个框架是全球范围内最流行的Web框架之一。如果你打算使用Django来构建自己的Web应用程序,那么你需要了解Django框架的优点和缺点。以下是您需要知道的一切,包括具体代码示例。Django优点:1.快速开发-Djang可以快速开发Web应用程序。它提供了丰富的库和内
 如何升级Django版本:步骤和注意事项
Jan 19, 2024 am 10:16 AM
如何升级Django版本:步骤和注意事项
Jan 19, 2024 am 10:16 AM
如何升级Django版本:步骤和注意事项,需要具体代码示例引言:Django是一个功能强大的PythonWeb框架,它持续地进行更新和升级,以提供更好的性能和更多的功能。然而,对于使用较旧版本Django的开发者来说,升级Django可能会面临一些挑战。本文将介绍如何升级Django版本的步骤和注意事项,并提供具体的代码示例。一、备份项目文件在升级Djan
 django版本区别是什么
Nov 20, 2023 pm 04:33 PM
django版本区别是什么
Nov 20, 2023 pm 04:33 PM
区别是:1、Django 1.x系列:这是Django的早期版本,包括1.0、1.1、1.2、1.3、1.4、1.5、1.6、1.7、1.8和1.9等版本。这些版本主要提供基本的Web开发功能;2、Django 2.x系列:这是Django的中期版本,包括2.0、2.1、2.2等版本;3、Django 3.x系列:这是Django的最新版本系列,包括3.0、3等版本。
 怎么查看django版本
Nov 30, 2023 pm 03:08 PM
怎么查看django版本
Nov 30, 2023 pm 03:08 PM
查看django版本的方法:1、通过命令行查看,在终端或命令行窗口中输入“python -m django --version”命令;2、在Python交互式环境中查看,输入“import django print(django.get_version())”代码;3、检查Django项目的设置文件,找到名为INSTALLED_APPS的列表,其中包含已安装的应用程序信息。
 django是前端还是后端
Nov 21, 2023 pm 02:36 PM
django是前端还是后端
Nov 21, 2023 pm 02:36 PM
django是后端。详细介绍:尽管Django主要是一个后端框架,但它与前端开发密切相关。通过Django的模板引擎、静态文件管理和RESTful API等功能,前端开发人员可以与后端开发人员协作,共同构建功能强大、可扩展的Web应用程序。
 Django、Flask和FastAPI:哪个框架适合初学者?
Sep 27, 2023 pm 09:06 PM
Django、Flask和FastAPI:哪个框架适合初学者?
Sep 27, 2023 pm 09:06 PM
Django、Flask和FastAPI:哪个框架适合初学者?引言:在Web应用开发领域,有许多优秀的Python框架可供选择。本文将重点介绍Django、Flask和FastAPI这三款最受欢迎的框架。我们将评估它们的特点,并讨论哪个框架最适合初学者使用。同时,我们还将提供一些具体的代码示例,以帮助初学者更好地理解这几个框架。一、Django:Django






