基于binlog来分析mysql的行记录修改情况
最近写完mysql flashback,突然发现还有有这种使用场景:有些情况下,可能会统计在某个时间段内,MySQL修改了多少数据量?发生了多少事务?主要是哪些表格发生变动?变动的数量是怎么样的? 但是却不需要行记录的修改内容,只需要了解 行数据的 变动情况。故也整理了下。
昨晚写的脚本,因为个人python能力有限,本来想这不发这文,后来想想,没准会有哪位园友给出优化建议。
1 实现内容
有些情况下,可能会统计在某个时间段内,MySQL修改了多少数据量?发生了多少事务?主要是哪些表格发生变动?变动的数量是怎么样的? 但是却不需要行记录的修改内容,只需要了解 行数据的 变动情况。
这些情况部分可以通过监控来大致了解,但是也可以基于binlog来全盘分析,binlog的格式是row模式。
在写flashback的时候,顺带把这个也写了个脚步,使用python编写,都差不多原理,只是这个简单些,介于个人python弱的不行,性能可能还有很大的提升空间,也希望园友能协助优化下。
先贴python脚步的分析结果图如下,分为4个部分:事务耗时情况、事务影响行数情况、DML行数情况以及操作最频繁表格情况。
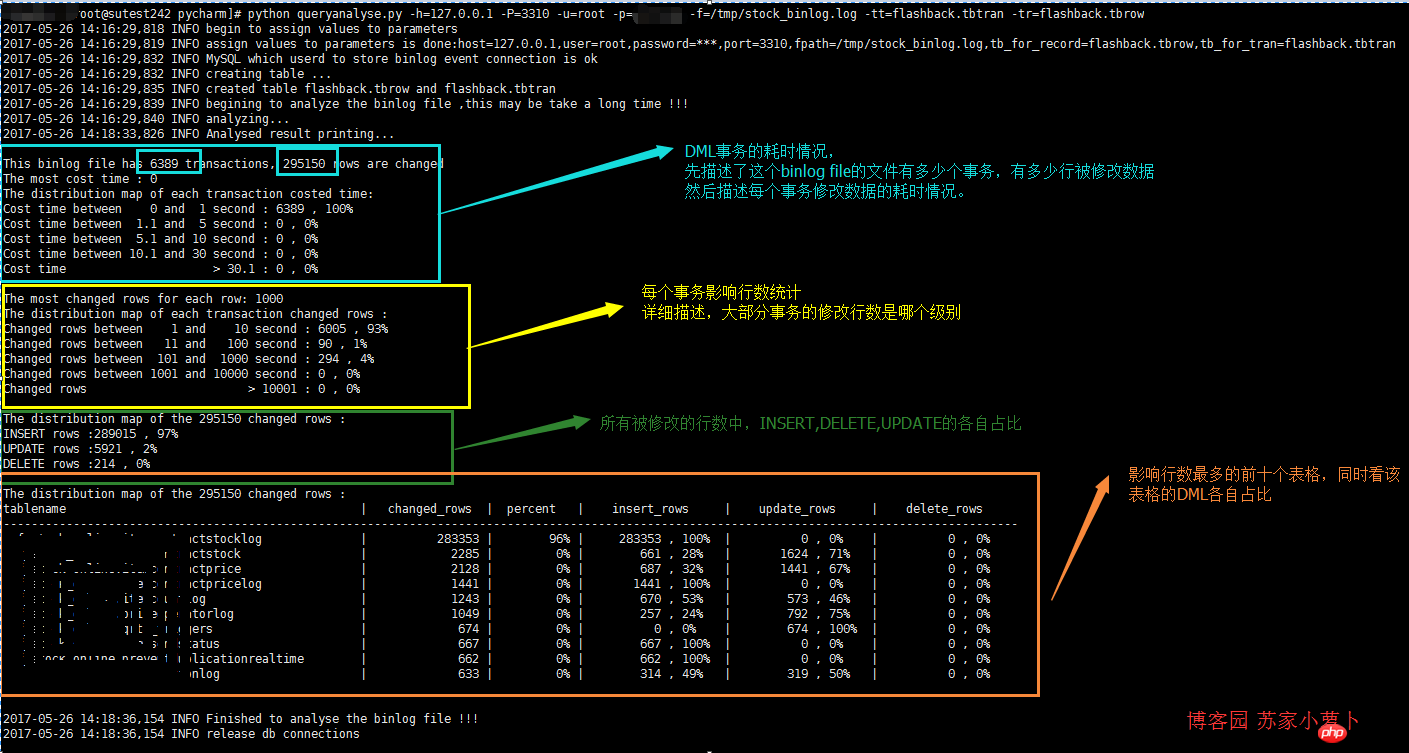
2 脚本简单描述
脚本依赖的模块中,pymysql需要自行安装。
创建类queryanalyse,其中有5个函数定义:_get_db、create_tab、rowrecord、binlogdesc跟closeconn。
2.1 _get_db
该函数用来解析输入参数值,参数值一共有7个,都是必须填写的。分别为host,user,password,port,table name for transaction,table name for records,对应的简写如下:
ALL options need to assign:
-h : host, the database host,which database will store the results after analysis
-u : user, the db user
-p : password, the db user's password
-P : port, the db port
-f : file path, the binlog file
-tr : table name for record , the table name to store the row record
-tt : table name for transaction, the table name to store transactions
比如,执行脚本:python queryanalyse.py -h=127.0.0.1 -P=3310 -u=root -p=password -f=/tmp/stock_binlog.log -tt=flashback.tbtran -tr=flashback.tbrow,该函数负责处理各个选项的参数值情况,并存储。
2.2 create_tab
创建两个表格,分别用来存储 binlog file文件的分析结果。一个用来存储事务的执行开始时间跟结束时间,由选项 -tt来赋值表名;一个是用来存储每一行记录的修改情况,由选项 -tr来赋值表名。
事务表记录内容:事务的开始时间及事务的结束时间。
行记录表的内容:库名,表名,DML类型以及事务对应事务表的编号。
root@localhost:mysql3310.sock 14:42:29 [flashback]>show create table tbrow \G*************************** 1. row *************************** Table: tbrowCreate Table: CREATE TABLE `tbrow` ( `auto_id` int(10) unsigned NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT, `sqltype` int(11) NOT NULL COMMENT '1 is insert,2 is update,3 is delete', `tran_num` int(11) NOT NULL COMMENT 'the transaction number', `dbname` varchar(50) NOT NULL, `tbname` varchar(50) NOT NULL, PRIMARY KEY (`auto_id`), KEY `sqltype` (`sqltype`), KEY `dbname` (`dbname`), KEY `tbname` (`tbname`) ) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=295151 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf81 row in set (0.00 sec) root@localhost:mysql3310.sock 14:42:31 [flashback]>SHOW CREATE TABLE TBTRAN \G*************************** 1. row *************************** Table: TBTRANCreate Table: CREATE TABLE `tbtran` ( `auto_id` int(10) unsigned NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT, `begin_time` datetime NOT NULL, `end_time` datetime NOT NULL, PRIMARY KEY (`auto_id`) ) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=6390 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf81 row in set (0.00 sec)
2.3 rowrecord
重点函数,分析binlog文件内容。这里有几个规律:
每个事务的结束点,是以 'Xid = ' 来查找
事务的开始时间,是事务内的第一个 'Table_map' 行里边的时间
事务的结束时间,是以 'Xid = '所在行的 里边的时间
每个行数据是属于哪个表格,是以 'Table_map'来查找
DML的类型是按照 行记录开头的情况是否为:'### INSERT INTO' 、'### UPDATE' 、'### DELETE FROM'
注意,单个事务可以包含多个表格多种DML多行数据修改的情况。
2.4 binlogdesc
描述分析结果,简单4个SQL分析。
分析修改行数据的 事务耗时情况
分析修改行数据的 事务影响行数情况
分析DML分布情况
分析 最多DML操作的表格 ,取前十个分析
2.5 closeconn
关闭数据库连接。
3 使用说明
首先,确保python安装了pymysql模块,把python脚本拷贝到文件 queryanalyse.py。
然后,把要分析的binlog文件先用 mysqlbinlog 指令分析存储,具体binlog的文件说明,可以查看之前的博文:关于binary log那些事——认真码了好长一篇。mysqlbinlog的指令使用方法,可以详细查看文档:https://dev.mysql.com/doc/refman/5.7/en/mysqlbinlog.html 。
比较常用通过指定开始时间跟结束时间来分析 binlog文件。
mysqlbinlog --start-datetime='2017-04-23 00:00:03' --stop-datetime='2017-04-23 00:30:00' --base64-output=decode-rows -v /data/mysql/logs/mysql-bin.007335 > /tmp/binlog_test.log
分析后,可以把这个 binlog_test.log文件拷贝到其他空闲服务器执行分析,只需要有个空闲的DB来存储分析记录即可。
假设这个时候,拷贝 binlog_test.log到测试服务器上,测试服务器上的数据库可以用来存储分析内容,则可以执行python脚本了,注意要进入到python脚本的目录中,或者指定python脚本路径。
python queryanalyse.py -h=127.0.0.1 -P=3310 -u=root -p=password -f= /tmp/binlog_test.log -tt=flashback.tbtran -tr=flashback.tbrow
没了,就等待输出吧。
性能是硬伤,在虚拟机上测试,大概500M的binlog文件需要分析2-3min,有待提高!
4 python脚本
1 import pymysql 2 from pymysql.cursors import DictCursor 3 import re 4 import os 5 import sys 6 import datetime 7 import time 8 import logging 9 import importlib 10 importlib.reload(logging) 11 logging.basicConfig(level=logging.DEBUG,format='%(asctime)s %(levelname)s %(message)s ') 12 13 14 usage=''' usage: python [script's path] [option] 15 ALL options need to assign: 16 17 -h : host, the database host,which database will store the results after analysis
18 -u : user, the db user 19 -p : password, the db user's password 20 -P : port, the db port 21 -f : file path, the binlog file 22 -tr : table name for record , the table name to store the row record 23 -tt : table name for transaction, the table name to store transactions 24 Example: python queryanalyse.py -h=127.0.0.1 -P=3310 -u=root -p=password -f=/tmp/stock_binlog.log -tt=flashback.tbtran -tr=flashback.tbrow 25 26 ''' 27 28 class queryanalyse: 29 def init(self): 30 #初始化 31 self.host='' 32 self.user='' 33 self.password='' 34 self.port='3306' 35 self.fpath='' 36 self.tbrow='' 37 self.tbtran='' 38 39 self._get_db() 40 logging.info('assign values to parameters is done:host={},user={},password=***,port={},fpath={},tb_for_record={},tb_for_tran={}'.format(self.host,self.user,self.port,self.fpath,self.tbrow,self.tbtran)) 41 42 self.mysqlconn = pymysql.connect(host=self.host, user=self.user, password=self.password, port=self.port,charset='utf8') 43 self.cur = self.mysqlconn.cursor(cursor=DictCursor) 44 logging.info('MySQL which userd to store binlog event connection is ok') 45 46 self.begin_time='' 47 self.end_time='' 48 self.db_name='' 49 self.tb_name='' 50 51 def _get_db(self): 52 #解析用户输入的选项参数值,这里对password的处理是明文输入,可以自行处理成是input格式, 53 #由于可以拷贝binlog文件到非线上环境分析,所以password这块,没有特殊处理 54 logging.info('begin to assign values to parameters') 55 if len(sys.argv) == 1: 56 print(usage) 57 sys.exit(1) 58 elif sys.argv[1] == '--help': 59 print(usage) 60 sys.exit() 61 elif len(sys.argv) > 2: 62 for i in sys.argv[1:]: 63 _argv = i.split('=') 64 if _argv[0] == '-h': 65 self.host = _argv[1] 66 elif _argv[0] == '-u': 67 self.user = _argv[1] 68 elif _argv[0] == '-P': 69 self.port = int(_argv[1]) 70 elif _argv[0] == '-f': 71 self.fpath = _argv[1] 72 elif _argv[0] == '-tr': 73 self.tbrow = _argv[1] 74 elif _argv[0] == '-tt': 75 self.tbtran = _argv[1] 76 elif _argv[0] == '-p': 77 self.password = _argv[1] 78 else: 79 print(usage) 80 81 def create_tab(self): 82 #创建两个表格:一个用户存储事务情况,一个用户存储每一行数据修改的情况 83 #注意,一个事务可以存储多行数据修改的情况 84 logging.info('creating table ...') 85 create_tb_sql ='''CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS {} ( 86 `auto_id` int(10) unsigned NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT, 87 `begin_time` datetime NOT NULL, 88 `end_time` datetime NOT NULL, 89 PRIMARY KEY (`auto_id`) 90 ) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8; 91 CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS {} ( 92 `auto_id` int(10) unsigned NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT, 93 `sqltype` int(11) NOT NULL COMMENT '1 is insert,2 is update,3 is delete', 94 `tran_num` int(11) NOT NULL COMMENT 'the transaction number', 95 `dbname` varchar(50) NOT NULL, 96 `tbname` varchar(50) NOT NULL, 97 PRIMARY KEY (`auto_id`), 98 KEY `sqltype` (`sqltype`), 99 KEY `dbname` (`dbname`),100 KEY `tbname` (`tbname`)101 ) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;102 truncate table {};103 truncate table {};104 '''.format(self.tbtran,self.tbrow,self.tbtran,self.tbrow)105 106 self.cur.execute(create_tb_sql)107 logging.info('created table {} and {}'.format(self.tbrow,self.tbtran))108 109 def rowrecord(self):110 #处理每一行binlog111 #事务的结束采用 'Xid =' 来划分112 #分析结果,按照一个事务为单位存储提交一次到db113 try:114 tran_num=1 #事务数115 record_sql='' #行记录的insert sql116 tran_sql='' #事务的insert sql117 118 self.create_tab()119 120 with open(self.fpath,'r') as binlog_file:121 logging.info('begining to analyze the binlog file ,this may be take a long time !!!')122 logging.info('analyzing...')123 124 for bline in binlog_file:125 126 if bline.find('Table_map:') != -1:127 l = bline.index('server')128 n = bline.index('Table_map')129 begin_time = bline[:l:].rstrip(' ').replace('#', '20')130 131 if record_sql=='':132 self.begin_time = begin_time[0:4] + '-' + begin_time[4:6] + '-' + begin_time[6:]133 134 self.db_name = bline[n::].split(' ')[1].replace('`', '').split('.')[0]135 self.tb_name = bline[n::].split(' ')[1].replace('`', '').split('.')[1]136 bline=''137 138 elif bline.startswith('### INSERT INTO'):139 record_sql=record_sql+"insert into {}(sqltype,tran_num,dbname,tbname) VALUES (1,{},'{}','{}');".format(self.tbrow,tran_num,self.db_name,self.tb_name)140 141 elif bline.startswith('### UPDATE'):142 record_sql=record_sql+"insert into {}(sqltype,tran_num,dbname,tbname) VALUES (2,{},'{}','{}');".format(self.tbrow,tran_num,self.db_name,self.tb_name)143 144 elif bline.startswith('### DELETE FROM'):145 record_sql=record_sql+"insert into {}(sqltype,tran_num,dbname,tbname) VALUES (3,{},'{}','{}');".format(self.tbrow,tran_num,self.db_name,self.tb_name)146 147 elif bline.find('Xid =') != -1:148 149 l = bline.index('server')150 end_time = bline[:l:].rstrip(' ').replace('#', '20')151 self.end_time = end_time[0:4] + '-' + end_time[4:6] + '-' + end_time[6:]152 tran_sql=record_sql+"insert into {}(begin_time,end_time) VALUES ('{}','{}')".format(self.tbtran,self.begin_time,self.end_time)153 154 self.cur.execute(tran_sql)155 self.mysqlconn.commit()156 record_sql = ''157 tran_num += 1158 159 except Exception:160 return 'funtion rowrecord error'161 162 def binlogdesc(self):163 sql=''164 t_num=0165 r_num=0166 logging.info('Analysed result printing...\n')167 #分析总的事务数跟行修改数量168 sql="select 'tbtran' name,count(*) nums from {} union all select 'tbrow' name,count(*) nums from {};".format(self.tbtran,self.tbrow)169 self.cur.execute(sql)170 rows=self.cur.fetchall()171 for row in rows:172 if row['name']=='tbtran':173 t_num = row['nums']174 else:175 r_num = row['nums']176 print('This binlog file has {} transactions, {} rows are changed '.format(t_num,r_num))177 178 # 计算 最耗时 的单个事务179 # 分析每个事务的耗时情况,分为5个时间段来描述180 # 这里正常应该是 以毫秒来分析的,但是binlog中,只精确时间到second181 sql='''select
182 count(case when cost_sec between 0 and 1 then 1 end ) cos_1,183 count(case when cost_sec between 1.1 and 5 then 1 end ) cos_5,184 count(case when cost_sec between 5.1 and 10 then 1 end ) cos_10,185 count(case when cost_sec between 10.1 and 30 then 1 end ) cos_30,186 count(case when cost_sec >30.1 then 1 end ) cos_more,187 max(cost_sec) cos_max188 from
189 (190 select
191 auto_id,timestampdiff(second,begin_time,end_time) cost_sec192 from {}193 ) a;'''.format(self.tbtran)194 self.cur.execute(sql)195 rows=self.cur.fetchall()196 197 for row in rows:198 print('The most cost time : {} '.format(row['cos_max']))199 print('The distribution map of each transaction costed time: ')200 print('Cost time between 0 and 1 second : {} , {}%'.format(row['cos_1'],int(row['cos_1']*100/t_num)))201 print('Cost time between 1.1 and 5 second : {} , {}%'.format(row['cos_5'], int(row['cos_5'] * 100 / t_num)))202 print('Cost time between 5.1 and 10 second : {} , {}%'.format(row['cos_10'], int(row['cos_10'] * 100 / t_num)))203 print('Cost time between 10.1 and 30 second : {} , {}%'.format(row['cos_30'], int(row['cos_30'] * 100 / t_num)))204 print('Cost time > 30.1 : {} , {}%\n'.format(row['cos_more'], int(row['cos_more'] * 100 / t_num)))205 206 # 计算 单个事务影响行数最多 的行数量207 # 分析每个事务 影响行数 情况,分为5个梯度来描述208 sql='''select
209 count(case when nums between 0 and 10 then 1 end ) row_1,210 count(case when nums between 11 and 100 then 1 end ) row_2,211 count(case when nums between 101 and 1000 then 1 end ) row_3,212 count(case when nums between 1001 and 10000 then 1 end ) row_4,213 count(case when nums >10001 then 1 end ) row_5,214 max(nums) row_max215 from
216 (217 select
218 count(*) nums219 from {} group by tran_num220 ) a;'''.format(self.tbrow)221 self.cur.execute(sql)222 rows=self.cur.fetchall()223 224 for row in rows:225 print('The most changed rows for each row: {} '.format(row['row_max']))226 print('The distribution map of each transaction changed rows : ')227 print('Changed rows between 1 and 10 second : {} , {}%'.format(row['row_1'],int(row['row_1']*100/t_num)))228 print('Changed rows between 11 and 100 second : {} , {}%'.format(row['row_2'], int(row['row_2'] * 100 / t_num)))229 print('Changed rows between 101 and 1000 second : {} , {}%'.format(row['row_3'], int(row['row_3'] * 100 / t_num)))230 print('Changed rows between 1001 and 10000 second : {} , {}%'.format(row['row_4'], int(row['row_4'] * 100 / t_num)))231 print('Changed rows > 10001 : {} , {}%\n'.format(row['row_5'], int(row['row_5'] * 100 / t_num)))232 233 # 分析 各个行数 DML的类型情况234 # 描述 delete,insert,update的分布情况235 sql='select sqltype ,count(*) nums from {} group by sqltype ;'.format(self.tbrow)236 self.cur.execute(sql)237 rows=self.cur.fetchall()238 239 print('The distribution map of the {} changed rows : '.format(r_num))240 for row in rows:241 242 if row['sqltype']==1:243 print('INSERT rows :{} , {}% '.format(row['nums'],int(row['nums']*100/r_num)))244 if row['sqltype']==2:245 print('UPDATE rows :{} , {}% '.format(row['nums'],int(row['nums']*100/r_num)))246 if row['sqltype']==3:247 print('DELETE rows :{} , {}%\n '.format(row['nums'],int(row['nums']*100/r_num)))248 249 # 描述 影响行数 最多的表格250 # 可以分析是哪些表格频繁操作,这里显示前10个table name251 sql = '''select
252 dbname,tbname ,253 count(*) ALL_rows,254 count(*)*100/{} per,255 count(case when sqltype=1 then 1 end) INSERT_rows,256 count(case when sqltype=2 then 1 end) UPDATE_rows,257 count(case when sqltype=3 then 1 end) DELETE_rows258 from {}
259 group by dbname,tbname
260 order by ALL_rows desc
261 limit 10;'''.format(r_num,self.tbrow)262 self.cur.execute(sql)263 rows = self.cur.fetchall()264 265 print('The distribution map of the {} changed rows : '.format(r_num))266 print('tablename'.ljust(50),267 '|','changed_rows'.center(15),268 '|','percent'.center(10),269 '|','insert_rows'.center(18),270 '|','update_rows'.center(18),271 '|','delete_rows'.center(18)272 )273 print('-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------')274 for row in rows:275 print((row['dbname']+'.'+row['tbname']).ljust(50),276 '|',str(row['ALL_rows']).rjust(15),277 '|',(str(int(row['per']))+'%').rjust(10),278 '|',str(row['INSERT_rows']).rjust(10)+' , '+(str(int(row['INSERT_rows']*100/row['ALL_rows']))+'%').ljust(5),279 '|',str(row['UPDATE_rows']).rjust(10)+' , '+(str(int(row['UPDATE_rows']*100/row['ALL_rows']))+'%').ljust(5),280 '|',str(row['DELETE_rows']).rjust(10)+' , '+(str(int(row['DELETE_rows']*100/row['ALL_rows']))+'%').ljust(5),281 )282 print('\n')283 284 logging.info('Finished to analyse the binlog file !!!')285 286 def closeconn(self):287 self.cur.close()288 logging.info('release db connections\n')289 290 def main():291 p = queryanalyse()292 p.rowrecord()293 p.binlogdesc()294 p.closeconn()295 296 if name == "main":297 main()以上是基于binlog来分析mysql的行记录修改情况的详细内容。更多信息请关注PHP中文网其他相关文章!

热AI工具

Undresser.AI Undress
人工智能驱动的应用程序,用于创建逼真的裸体照片

AI Clothes Remover
用于从照片中去除衣服的在线人工智能工具。

Undress AI Tool
免费脱衣服图片

Clothoff.io
AI脱衣机

Video Face Swap
使用我们完全免费的人工智能换脸工具轻松在任何视频中换脸!

热门文章

热工具

记事本++7.3.1
好用且免费的代码编辑器

SublimeText3汉化版
中文版,非常好用

禅工作室 13.0.1
功能强大的PHP集成开发环境

Dreamweaver CS6
视觉化网页开发工具

SublimeText3 Mac版
神级代码编辑软件(SublimeText3)
 phpmyadmin怎么打开
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:51 PM
phpmyadmin怎么打开
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:51 PM
可以通过以下步骤打开 phpMyAdmin:1. 登录网站控制面板;2. 找到并点击 phpMyAdmin 图标;3. 输入 MySQL 凭据;4. 点击 "登录"。
 MySQL:世界上最受欢迎的数据库的简介
Apr 12, 2025 am 12:18 AM
MySQL:世界上最受欢迎的数据库的简介
Apr 12, 2025 am 12:18 AM
MySQL是一种开源的关系型数据库管理系统,主要用于快速、可靠地存储和检索数据。其工作原理包括客户端请求、查询解析、执行查询和返回结果。使用示例包括创建表、插入和查询数据,以及高级功能如JOIN操作。常见错误涉及SQL语法、数据类型和权限问题,优化建议包括使用索引、优化查询和分表分区。
 MySQL的位置:数据库和编程
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:18 AM
MySQL的位置:数据库和编程
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:18 AM
MySQL在数据库和编程中的地位非常重要,它是一个开源的关系型数据库管理系统,广泛应用于各种应用场景。1)MySQL提供高效的数据存储、组织和检索功能,支持Web、移动和企业级系统。2)它使用客户端-服务器架构,支持多种存储引擎和索引优化。3)基本用法包括创建表和插入数据,高级用法涉及多表JOIN和复杂查询。4)常见问题如SQL语法错误和性能问题可以通过EXPLAIN命令和慢查询日志调试。5)性能优化方法包括合理使用索引、优化查询和使用缓存,最佳实践包括使用事务和PreparedStatemen
 为什么要使用mysql?利益和优势
Apr 12, 2025 am 12:17 AM
为什么要使用mysql?利益和优势
Apr 12, 2025 am 12:17 AM
选择MySQL的原因是其性能、可靠性、易用性和社区支持。1.MySQL提供高效的数据存储和检索功能,支持多种数据类型和高级查询操作。2.采用客户端-服务器架构和多种存储引擎,支持事务和查询优化。3.易于使用,支持多种操作系统和编程语言。4.拥有强大的社区支持,提供丰富的资源和解决方案。
 apache怎么连接数据库
Apr 13, 2025 pm 01:03 PM
apache怎么连接数据库
Apr 13, 2025 pm 01:03 PM
Apache 连接数据库需要以下步骤:安装数据库驱动程序。配置 web.xml 文件以创建连接池。创建 JDBC 数据源,指定连接设置。从 Java 代码中使用 JDBC API 访问数据库,包括获取连接、创建语句、绑定参数、执行查询或更新以及处理结果。
 docker怎么启动mysql
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:09 PM
docker怎么启动mysql
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:09 PM
在 Docker 中启动 MySQL 的过程包含以下步骤:拉取 MySQL 镜像创建并启动容器,设置根用户密码并映射端口验证连接创建数据库和用户授予对数据库的所有权限
 MySQL的角色:Web应用程序中的数据库
Apr 17, 2025 am 12:23 AM
MySQL的角色:Web应用程序中的数据库
Apr 17, 2025 am 12:23 AM
MySQL在Web应用中的主要作用是存储和管理数据。1.MySQL高效处理用户信息、产品目录和交易记录等数据。2.通过SQL查询,开发者能从数据库提取信息生成动态内容。3.MySQL基于客户端-服务器模型工作,确保查询速度可接受。
 centos安装mysql
Apr 14, 2025 pm 08:09 PM
centos安装mysql
Apr 14, 2025 pm 08:09 PM
在 CentOS 上安装 MySQL 涉及以下步骤:添加合适的 MySQL yum 源。执行 yum install mysql-server 命令以安装 MySQL 服务器。使用 mysql_secure_installation 命令进行安全设置,例如设置 root 用户密码。根据需要自定义 MySQL 配置文件。调整 MySQL 参数和优化数据库以提升性能。






