一、线性表
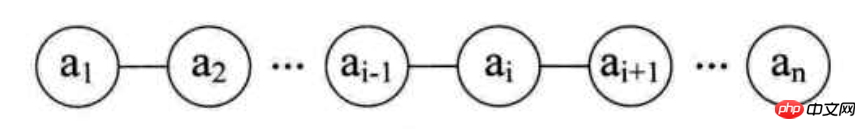
原理:零个或多个同类数据元素的有限序列
原理图:
特点 :
1、有序性
2、有限性
3、同类型元素
4、第一个元素无前驱,最后一个元素无后继,中间的元素有一个前驱并且有一个后继
线性表是一种逻辑上的数据结构,在物理上一般有两种实现 顺序实现和链表实现
二、基于数组的 线性表顺序实现
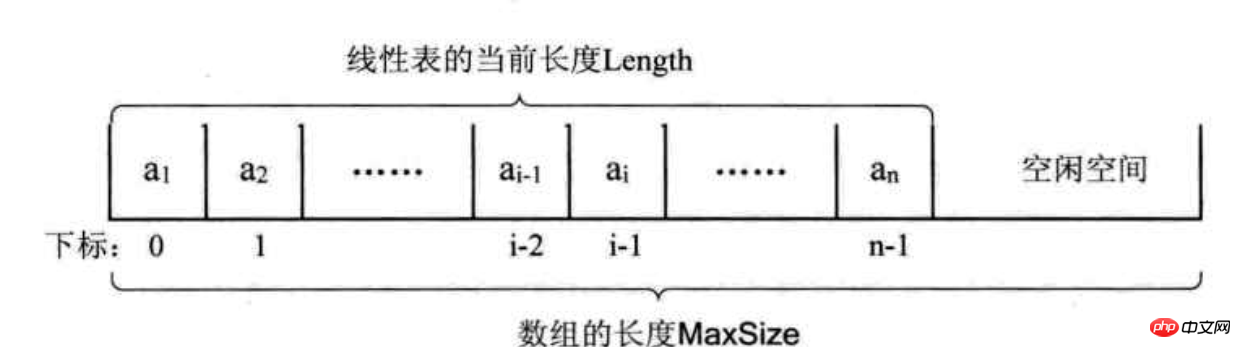
原理 : 用一段地址连续的存储单元依次存储线性表数据元素。
原理图:
算法原理:
1、初始化一个定长的数组空间 elementData[] , size 存储长度 存储元素
2、通过索引来快速存取元素
3、通过数组复制实现元素的插入和删除
总结:
1、无需为表示表中元素之间的逻辑关系增加额外的存储空间
2、可以快速存取表中任一位置元素
3、插入和删除需要进行数组复制(即大量元素的移动)
4、线性表长度变化较大时,需要频繁扩容,并造成存储空间碎片
实现代码:
接口定义:

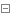
1 package online.jfree.base; 2 3 /** 4 * author : Guo LiXiao 5 * date : 2017-6-14 11:46 6 */ 7 8 public interface LineList <E>{ 9 10 /**11 * lineList 是否为空12 * @return13 */14 boolean isEmpty();15 16 /**17 * 清空 lineList18 */19 void clear();20 21 /**22 * 获取指定位置元素23 * @param index24 * @return25 */26 E get(int index);27 28 /**29 * 获取元素第一次出现的位置30 * @param e31 * @return32 */33 int indexOf(E e);34 35 /**36 * 判断 lineList是否包含指定元素37 * @param e38 * @return39 */40 boolean contains(E e);41 42 /**43 * 设置指定位置数据,如数据已存在 则覆盖原数据44 * @param index45 * @param e46 * @return47 */48 E set(int index, E e);49 50 /**51 * 移除指定位置元素52 * @param index53 * @return54 */55 E remove(int index);56 57 /**58 * 在lineList结尾插入元素59 * @param e60 * @return61 */62 E add(E e);63 64 /**65 * 在index后面插入元素66 * @param index67 * @param e68 * @return69 */70 E add(int index, E e);71 72 /**73 * 返回lineList长度74 * @return75 */76 int size();77 78 79 80 }算法实现:
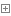

1 package online.jfree.base; 2 3 /** 4 * author : Guo LiXiao 5 * date : 2017-6-15 13:44 6 */ 7 8 public class OrderedLineList<E> implements LineList<E> { 9 10 private static final int INIT_CAPACITY = 10; 11 12 private transient E[] elementData; 13 14 private transient int elementLength; 15 16 private int size; 17 18 public OrderedLineList() { 19 this(0); 20 } 21 22 public OrderedLineList(int initCapacity) { 23 init(initCapacity); 24 } 25 26 private void init(int initCapacity) { 27 if (initCapacity >= 0) { 28 this.elementData = (E[]) new Object[initCapacity]; 29 this.elementLength = initCapacity; 30 } else { 31 throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal Capacity: " + 32 initCapacity); 33 } 34 this.size = 0; 35 } 36 37 /** 38 * 扩容 39 */ 40 private void dilatation() { 41 int oldCapacity = this.elementLength; 42 int newCapacity = oldCapacity; 43 if (oldCapacity <= this.size) { 44 newCapacity = oldCapacity + INIT_CAPACITY; 45 }else if(oldCapacity - INIT_CAPACITY > this.size){ 46 newCapacity = oldCapacity - INIT_CAPACITY; 47 } 48 if (oldCapacity != newCapacity){ 49 E[] newElementData = (E[]) new Object[newCapacity]; 50 System.arraycopy(elementData, 0, newElementData, 0, oldCapacity); 51 this.elementLength = newCapacity; 52 this.elementData = newElementData; 53 } 54 } 55 56 /** 57 * 校验列表索引越界 58 * @param index 59 */ 60 private void checkCapacity(int index){ 61 if (index > this.size - 1 || index < 0) 62 throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(new StringBuffer("[index : ").append(index).append("] , [size : ").append(size).append("] ").toString()); 63 } 64 65 @Override 66 public boolean isEmpty() { 67 return this.size == 0; 68 } 69 70 @Override 71 public void clear() { 72 this.init(0); 73 } 74 75 @Override 76 public E get(int index) { 77 this.checkCapacity(index); 78 return this.elementData[index]; 79 } 80 81 @Override 82 public int indexOf(E e) { 83 for (int i = 0; i < this.size; i++){ 84 if (e == null && elementData[i] == null || e.equals(elementData[i])){ 85 return i; 86 } 87 } 88 return -1; 89 } 90 91 @Override 92 public boolean contains(E e) { 93 return this.indexOf(e) > 0; 94 } 95 96 @Override 97 public E set(int index, E e) { 98 this.checkCapacity(index); 99 this.dilatation();100 E oldElement = this.elementData[index];101 this.elementData[index] = e;102 return oldElement;103 }104 105 @Override106 public E remove(int index) {107 this.dilatation();108 E e = elementData[index];109 if (index == size - 1) elementData[index] = null;110 else {111 int length = size - index - 1;112 System.arraycopy(elementData, index + 1, elementData, index, length);113 }114 size --;115 return e;116 }117 118 @Override119 public E add(E e) {120 return this.add(size, e);121 }122 123 @Override124 public E add(int index, E e) {125 this.dilatation();126 if (index == size) elementData[index] = e;127 else {128 index++;129 int lastLength = size - index;130 E[] lastElementData = (E[]) new Object[lastLength];131 System.arraycopy(elementData, index, lastElementData, 0, lastLength);132 elementData[index] = e;133 System.arraycopy(lastElementData, 0, elementData, index + 1, lastLength);134 }135 size ++ ;136 return e;137 }138 139 @Override140 public int size() {141 return this.size;142 }143 144 }
以上是浅析线性表的原理及简单实现的详细内容。更多信息请关注PHP中文网其他相关文章!




