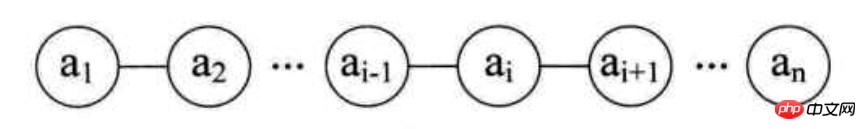
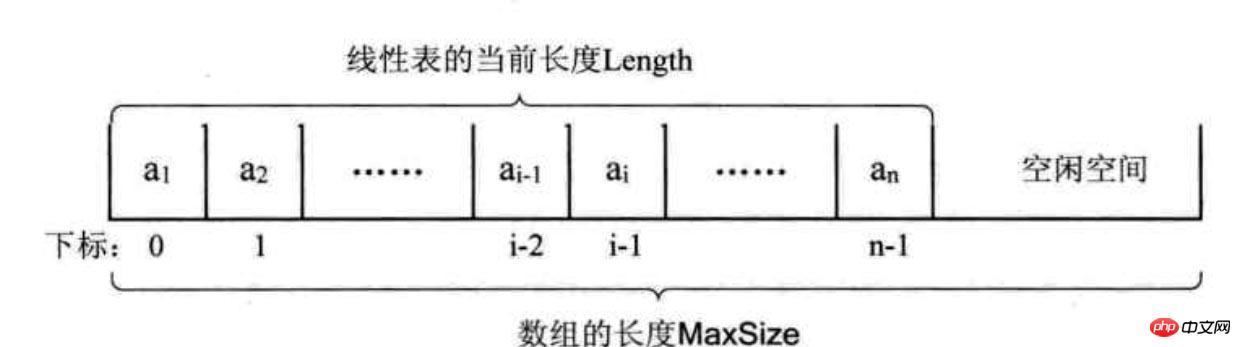
package online.jfree.base;
public class OrderedLineList<E> implements LineList<E> {
private static final int INIT_CAPACITY = 10;
private transient E[] elementData;
private transient int elementLength;
private int size;
public OrderedLineList() {
this(0);
}
public OrderedLineList(int initCapacity) {
init(initCapacity);
}
private void init(int initCapacity) {
if (initCapacity >= 0) {
this.elementData = (E[]) new Object[initCapacity];
this.elementLength = initCapacity;
} else {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal Capacity: " +
initCapacity);
}
this.size = 0;
}
private void dilatation() {
int oldCapacity = this.elementLength;
int newCapacity = oldCapacity;
if (oldCapacity <= this.size) {
newCapacity = oldCapacity + INIT_CAPACITY;
}else if(oldCapacity - INIT_CAPACITY > this.size){
newCapacity = oldCapacity - INIT_CAPACITY;
}
if (oldCapacity != newCapacity){
E[] newElementData = (E[]) new Object[newCapacity];
System.arraycopy(elementData, 0, newElementData, 0, oldCapacity);
this.elementLength = newCapacity;
this.elementData = newElementData;
}
}
private void checkCapacity(int index){
if (index > this.size - 1 || index < 0)
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(new StringBuffer("[index : ").append(index).append("] , [size : ").append(size).append("] ").toString());
}
@Override
public boolean isEmpty() {
return this.size == 0;
}
@Override
public void clear() {
this.init(0);
}
@Override
public E get(int index) {
this.checkCapacity(index);
return this.elementData[index];
}
@Override
public int indexOf(E e) {
for (int i = 0; i < this.size; i++){
if (e == null && elementData[i] == null || e.equals(elementData[i])){
return i;
}
}
return -1;
}
@Override
public boolean contains(E e) {
return this.indexOf(e) > 0;
}
@Override
public E set(int index, E e) {
this.checkCapacity(index);
this.dilatation();
E oldElement = this.elementData[index];
this.elementData[index] = e;
return oldElement;
}
@Override
public E remove(int index) {
this.dilatation();
E e = elementData[index];
if (index == size - 1) elementData[index] = null;
else {
int length = size - index - 1;
System.arraycopy(elementData, index + 1, elementData, index, length);
}
size --;
return e;
}
@Override
public E add(E e) {
return this.add(size, e);
}
@Override
public E add(int index, E e) {
this.dilatation();
if (index == size) elementData[index] = e;
else {
index++;
int lastLength = size - index;
E[] lastElementData = (E[]) new Object[lastLength];
System.arraycopy(elementData, index, lastElementData, 0, lastLength);
elementData[index] = e;
System.arraycopy(lastElementData, 0, elementData, index + 1, lastLength);
}
size ++ ;
return e;
}
@Override
public int size() {
return this.size;
}
}