本文主要介绍了Ajax 高级功能之ajax向服务器发送数据的相关资料,需要的朋友可以参考下,希望能帮助到大家。
1. 准备向服务器发送数据
Ajax 最常见的一大用途是向服务器发送数据。最典型的情况是从 客户端发送表单数据,即用户在form元素所含的各个 input 元素里输入的值。下面代码展示了一张简单的表单:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>基本表单</title>
<style>
.table{display: table;}
.row{display: table-row;}
.cell{display: table-cell;padding: 5px;}
.lable{text-align: right;}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<form id="fruitform" method="post" action="http://127.0.0.1:8080/form">
<p class="lable">
<p class="row">
<p class="cell lable">Apples:</p>
<p class="cell"><input name="apples" value="5" /></p>
</p>
<p class="row">
<p class="cell lable">Bananas:</p>
<p class="cell"><input name="bananas" value="2" /></p>
</p>
<p class="row">
<p class="cell lable">Cherries:</p>
<p class="cell"><input name="cherries" value="20" /></p>
</p>
<p class="row">
<p class="cell lable">Total:</p>
<p id="results" class="cell">0 items</p>
</p>
</p>
<button id="submit" type="submit">Submit Form</button>
</form>
</body>
</html>这个例子中的表单包含三个input元素和一个提交button 。这些input元素让用户可以指定三种不同的说过各自要订购多少,button则会将表单提交给服务器。
1.1 定义服务器
显而易见,这里需要为这些示例创建处理请求的服务器。这里再一次使用Node.js,原因主要是它很简单,而且用的是Javascript。新建 fruitcalc.js脚本文件如下:
var http = require('http');
var querystring = require('querystring');
function writeResponse(res,data){
var total = 0;
for(fruit in data){
total += Number(data[fruit]);
}
res.writeHead(200,"OK",{
"Content-Type":"text/html",
"Access-Control-Allow-Origin":"http://localhost:63342"
});
res.write('<html><head><title>Fruit Total</title></head><body>');
res.write('<p>'+total+' item ordered</p></body></html>');
res.end();
}
http.createServer(function(req,res){
console.log("[200] "+req.method+" to "+req.url);
if(req.method == "OPTIONS"){
res.writeHead(200,"OK",{
"Access-Control-Allow-Header":"Content-Type",
"Access-Control-Allow-Methods":"*",
"Access-Control-Allow-Origin":"*"
});
res.end();
}else if(req.url == '/form'&& req.method == 'POST'){
var dataObj = new Object();
var contentType = req.headers["content-type"];
var fullBody = '';
if(contentType){
if(contentType.indexOf("application/x-www-form-urlencode") > -1){
req.on('data',function(chunk){
fullBody += chunk.toString();
});
req.on('end',function(){
var dBody = querystring.parse(fullBody);
dataObj.apples = dBody["apples"];
dataObj.bananas = dBody["bananas"];
dataObj.cherries = dBody["cherries"];
writeResponse(res,dataObj);
});
}else if(contentType.indexOf("application/json") > -1){
req.on('data',function(chunk){
fullBody += chunk.toString();
});
req.on('end',function(){
dataObj = JSON.parse(fullBody);
writeResponse(res,dataObj);
});
}
}
}
}).listen(8080);脚本中高亮部分:writeResponse函数。这个函数会在提取请求的表单值之后调用,它负责生产对浏览器的响应。当前,这个函数会创建简单的HTML文档,效果如下:
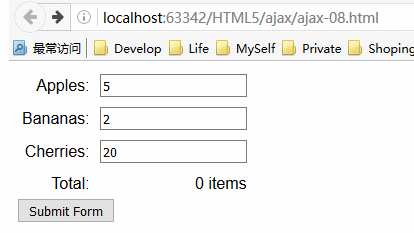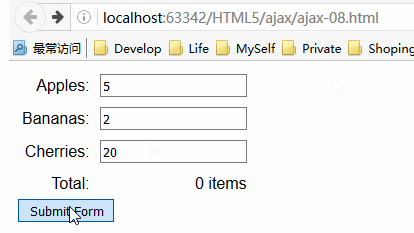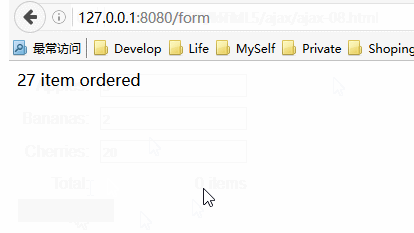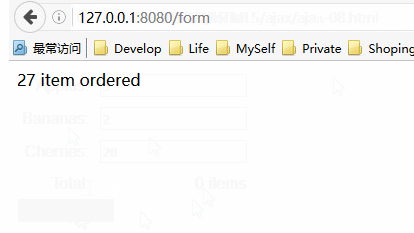
这个响应很简单,实现效果是让服务器计算出了用户通过form中各个input元素所订购的水果总数。服务器得端脚本的其余部分负责解码客户端用Ajax发送的各种可能数据格式。
1.2 理解问题所在
上面的图片清楚的描述了想要用Ajax解决的问题。
当提交表单后,浏览器会在新的页面显示结果。这意味着两点:
* 用户必须等待服务器处理数据并生成响应;
* 所有文档上下文信息都丢失了,因为结果是作为新文档进行显示的。
这就是应用Ajax的理想情形了。可以异步生成请求,这样用户就能在表单被处理时继续与文档进行交互。
2. 发送表单
向服务器发送数据的最基本方式是自己收集并格式化它。下面代码展示了添加到前面的HTML文档 example.html 的一段脚本。用的就是这种方式:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>手动收集和发送数据</title>
<style>
.table{display: table;}
.row{display: table-row;}
.cell{display: table-cell;padding: 5px;}
.lable{text-align: right;}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<form id="fruitform" method="post" action="http://127.0.0.1:8080/form">
<p class="lable">
<p class="row">
<p class="cell lable">Apples:</p>
<p class="cell"><input name="apples" value="5" /></p>
</p>
<p class="row">
<p class="cell lable">Bananas:</p>
<p class="cell"><input name="bananas" value="2" /></p>
</p>
<p class="row">
<p class="cell lable">Cherries:</p>
<p class="cell"><input name="cherries" value="20" /></p>
</p>
<p class="row">
<p class="cell lable">Total:</p>
<p id="results" class="cell">0 items</p>
</p>
</p>
<button id="submit" type="submit">Submit Form</button>
</form>
<script>
document.getElementById("submit").onclick = handleButtonPress;
var httpRequest;
function handleButtonPress(e){
//对表单里的button元素而言,其默认行为是用常规的非Ajax方式提交表单。这里不想让他发生,所以调用了preventDefault方法
e.preventDefault();
var form = document.getElementById("fruitform");
//收集并格式化各个input的值
var formData ="";
var inputElements = document.getElementsByTagName("input");
for (var i = 0; i < inputElements.length; i++){
formData += inputElements[i].name + "=" + inputElements[i].value +"&";
}
httpRequest = new XMLHttpRequest();
httpRequest.onreadystatechange = handleResponse;
//数据必须通过POST方法发送给服务器,并读取了HTMLFormElement的action属性获得了请求需要发送的URL
httpRequest.open("POST",form.action);
//添加标头来告诉服务器准备接受的数据格式
httpRequest.setRequestHeader('Content-Type','application/x-www-form-urlencoded');
//把想要发送给服务器的字符串作为参数传递给send方法
httpRequest.send(formData);
}
function handleResponse(){
if(httpRequest.readyState == 4 && httpRequest.status == 200){
document.getElementById("results").innerHTML = httpRequest.responseText;
}
}
</script>
</body>
</html>效果图如下:
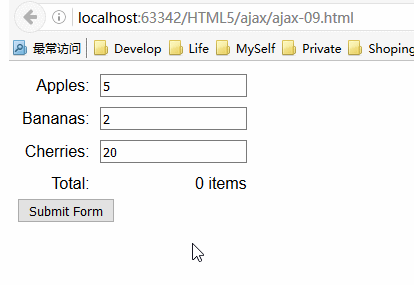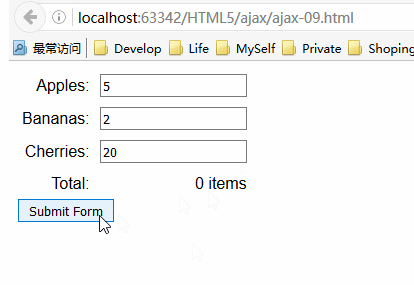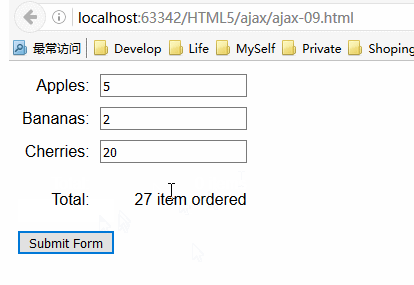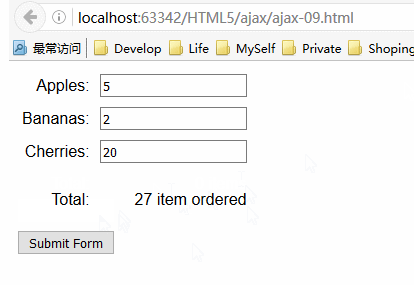
服务器响应表单提交后返回的HTML文档会显示在同一页,而且该请求是异步执行的。
3. 发送JSON数据
Ajax不止用来发送表单数据,几乎可以发送任何数据,包括JavaScript对象表示法(JavaScript Object Notation,JSON)数据,而它几乎已经成为一种流行的数据格式了。Ajax扎根于XML,但这一格式很繁琐。当运行的Web应用程序必须传输大量XML文档时,繁琐就意味着带宽和系统容量方面的实际成本。
JSON经常被称为XML的“脱脂”替代品。JSON易于阅读和编写,比XML更紧凑,而且已经获得了广泛支持。JSON发源于JavaScript,但它的发展已经超越了 JavaScript,被无数的程序包和系统理解并使用。
以下是一个简单的JavaScript对象用JSON表达的例子:
{"bananas":"2","apples":"5","cherries":"20"}这个对象有三个属性:bananas、apples和cherries。这些属性的值分别是2、5和20。
JSON的功能不如XML丰富,但对许多应用程序来说,那些功能是用不到的。JSON简单、轻量和富有表现力。下面例子演示了发送JSON数据到服务器有多简单,修改前例的JavaScript部分如下:
<script>
document.getElementById("submit").onclick = handleButtonPress;
var httpRequest;
function handleButtonPress(e){
e.preventDefault();
var form = document.getElementById("fruitform");
var formData = new Object();
var inputElements = document.getElementsByTagName("input");
for(var i=0;i<inputElements.length;i++){
formData[inputElements[i].name] = inputElements[i].value;
}
httpRequest = new XMLHttpRequest();
httpRequest.onreadystatechange = handleResponse;
httpRequest.open("POST",form.action);
httpRequest.setRequestHeader("Content-Type","application/json");
httpRequest.send(JSON.stringify(formData));
}
function handleResponse(){
if(httpRequest.readyState == 4 && httpRequest.status == 200){
document.getElementById("results").innerHTML = httpRequest.responseText;
}
}
</script>这段脚本,创建了一个新的Object,并定义了一些属性来对应表单内各个input元素的name属性值。可以使用任何数据,但 input元素很方便,而且能和之前的例子保持一致。
为了告诉服务器正在发送JSON数据,把请求的Content-Type标头设为 application/json,就像这样:
httpRequest.setRequestHeader("Content-Type","application/json");
用JSON对象和JSON格式进行相互的转换。(大多数浏览器能直接支持这个对象,但也可以用下面的网址里的脚本来给旧版的浏览器添加同样的功能:https://github.com/douglascrockford/JSON-js/blob/master/json2.js )JSON对象提供了两个方法:

在上面的例子中,使用了stringify方法,然后把结果传递给XMLHttpRequest 对象的send方法。此例中只有数据的编码方式发生了变化。提交表单的效果还是一样。
4. 使用FormData对象发送表单数据
另一种更简洁的表单收集方式是使用一个FormData对象,它是在XMLHttpRequest的第二级规范中定义的。
由于原来的Node.js代码有点问题,此处用C#新建文件 fruitcalc.aspx作为处理请求的服务器。其cs代码如下:
using System;
namespace Web4Luka.Web.ajax.html5
{
public partial class fruitcalc : System.Web.UI.Page
{
protected void Page_Load(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
int total = 0;
if (Request.HttpMethod == "POST")
{
if (Request.ContentType.IndexOf("multipart/form-data") > -1)
{
for (int i = 0; i < Request.Form.Count; i++)
{
total += Int32.Parse(Request.Form[i]);
}
}
writeResponse(Response, total);
}
}
private void writeResponse(System.Web.HttpResponse Response, int total)
{
string strHtml;
Response.AddHeader("Access-Control-Allow-Origin", "http://localhost:63342");
strHtml = total + " item ordered";
Response.Write(strHtml);
}
}
}4.1 创建 FormData 对象
创建FormData对象时可以传递一个HTMLFormElement对象,这样表单里所有的元素的值都会被自动收集起来。示例如下:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>使用FormData对象</title>
<style>
.row{display: table-row;}
.cell{display: table-cell;padding: 5px;}
.lable{text-align: right;}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<form id="fruitform" method="post" action="http://localhost:53396/ajax/html5/fruitcalc.aspx">
<p class="lable">
<p class="row">
<p class="cell lable">Apples:</p>
<p class="cell"><input name="apples" value="5" /></p>
</p>
<p class="row">
<p class="cell lable">Bananas:</p>
<p class="cell"><input name="bananas" value="2" /></p>
</p>
<p class="row">
<p class="cell lable">Cherries:</p>
<p class="cell"><input name="cherries" value="20" /></p>
</p>
<p class="row">
<p class="cell lable">Total:</p>
<p id="results" class="cell">0 items</p>
</p>
</p>
<button id="submit" type="submit">Submit Form</button>
</form>
<script>
document.getElementById("submit").onclick = handleButtonPress;
var httpRequest;
function handleButtonPress(e){
e.preventDefault();
var form = document.getElementById("fruitform");
var formData = new FormData(form);
httpRequest = new XMLHttpRequest();
httpRequest.onreadystatechange = handleResponse;
httpRequest.open("POST",form.action);
httpRequest.send(formData);
}
function handleResponse(){
if(httpRequest.readyState == 4 && httpRequest.status == 200){
document.getElementById("results").innerHTML = httpRequest.responseText;
}
}
</script>
</body>
</html>当然,关键的变化是使用了FormData对象:
var formData = new FormData(form);
其他需要注意的地方是不再设置Content-Type标头的值了。如果使用FormData对象,数据总是会被编码为multipart/form-data 。本例提交表单后,显示效果如下:
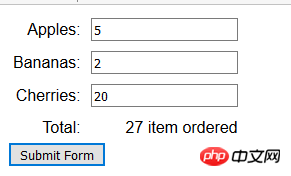
4.2 修改FormData对象
FormData对象定义了一个方法,它允许给要发送到服务器的数据添加名称/值对。

可以用append方法增补从表单中收集的数据,也可以在不使用HTMLFormElement的情况下创建FormData对象。这就意味着可以使用append方法来选择向客户端发送哪些数据值。修改上一示例的JavaScript代码如下:
<script>
document.getElementById("submit").onclick = handleButtonPress;
var httpRequest;
function handleButtonPress(e){
e.preventDefault();
var form = document.getElementById("fruitform");
var formData = new FormData();
var inputElements = document.getElementsByTagName("input");
for(var i=0;i<inputElements.length;i++){
if(inputElements[i].name != "cherries"){
formData.append(inputElements[i].name,inputElements[i].value);
}
}
httpRequest = new XMLHttpRequest();
httpRequest.onreadystatechange = handleResponse;
httpRequest.open("POST",form.action);
httpRequest.send(formData);
}
function handleResponse(){
if(httpRequest.readyState == 4 && httpRequest.status == 200){
document.getElementById("results").innerHTML = httpRequest.responseText;
}
}
</script>此段脚本里,创建FormData对象时并没有提供HTMLFormElement对象。随后用DOM找到文档里所有的input元素,并为那些name属性的值不是cherries的元素添加名称/值对。此例提交表单后,显示效果如下:
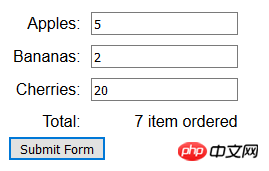
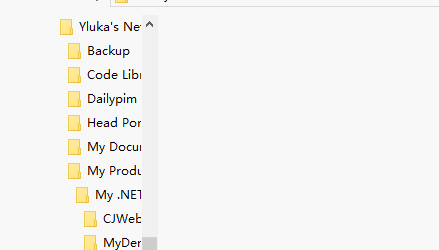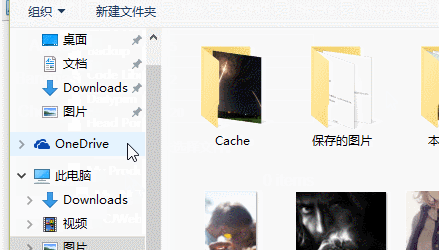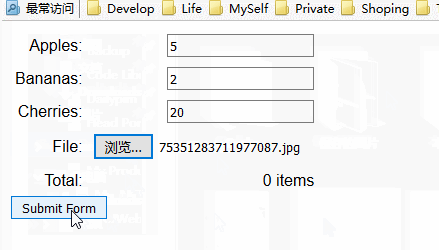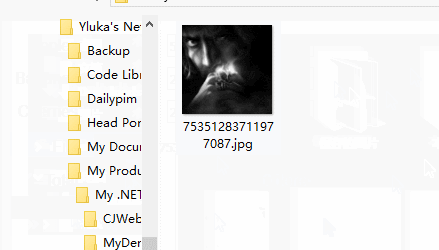
5. 发送文件
可以使用FormData 对象和type 属性为 file 的input 元素向服务器发送文件。当表单提交时,FormData对象会自动确保用户选择的文件内容与其他的表单值一同上传。下面的例子展示了如何以这种方式使用FormData对象。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>使用FormData对象发送文件到服务器</title>
<style>
.row{display: table-row;}
.cell{display: table-cell;padding: 5px;}
.lable{text-align: right;}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<form id="fruitform" method="post" action="http://localhost:53396/ajax/html5/fruitcalc.aspx">
<p class="lable">
<p class="row">
<p class="cell lable">Apples:</p>
<p class="cell"><input name="apples" value="5" /></p>
</p>
<p class="row">
<p class="cell lable">Bananas:</p>
<p class="cell"><input name="bananas" value="2" /></p>
</p>
<p class="row">
<p class="cell lable">Cherries:</p>
<p class="cell"><input name="cherries" value="20" /></p>
</p>
<p class="row">
<p class="cell lable">File:</p>
<p class="cell"><input type="file" name="file" /></p>
</p>
<p class="row">
<p class="cell lable">Total:</p>
<p id="results" class="cell">0 items</p>
</p>
</p>
<button id="submit" type="submit">Submit Form</button>
</form>
<script>
document.getElementById("submit").onclick = handleButtonPress;
var httpRequest;
function handleButtonPress(e){
e.preventDefault();
var form = document.getElementById("fruitform");
var formData = new FormData(form);
httpRequest = new XMLHttpRequest();
httpRequest.onreadystatechange = handleResponse;
httpRequest.open("POST",form.action);
httpRequest.send(formData);
}
function handleResponse(){
if(httpRequest.readyState == 4 && httpRequest.status == 200){
document.getElementById("results").innerHTML = httpRequest.responseText;
}
}
</script>
</body>
</html>此例里,最明显的变化发生在 form元素上。添加了input元素后,FormData对象就会上传用户所选的任意文件。
修改 fruitcalc.aspx 的cs文件如下:
using System;
using System.Web;
namespace Web4Luka.Web.ajax.html5
{
public partial class fruitcalc : System.Web.UI.Page
{
protected void Page_Load(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
int total = 0;
if (Request.HttpMethod == "POST")
{
if (Request.ContentType.IndexOf("multipart/form-data") > -1)
{
for (int i = 0; i < Request.Form.Count; i++)
{
total += Int32.Parse(Request.Form[i]);
}
if (Request.Files["file"] != null)
{
HttpPostedFile file = Request.Files["file"];
file.SaveAs(Server.MapPath("/upload/pictures/" + file.FileName));
}
}
writeResponse(Response, total);
}
}
private void writeResponse(System.Web.HttpResponse Response, int total)
{
string strHtml;
Response.AddHeader("Access-Control-Allow-Origin", "http://localhost:63342");
strHtml = total + " item ordered";
Response.Write(strHtml);
}
}
}此例的显示效果如下:
相关推荐:
以上是ajax向服务器发送数据的详细内容。更多信息请关注PHP中文网其他相关文章!




