线程同步有几种方法

线程同步的方法有哪些?在linux下,系统提供了很多种方式来实现线程同步,其中最常用的便是互斥锁、条件变量和信号量这三种方式,可能还有很多伙伴对于这三种方法都不熟悉,下面就给大家详细介绍下。
Linux下实现线程同步的三种方法:
一、互斥锁(mutex)
通过锁机制实现线程间的同步。
1、初始化锁。在Linux下,线程的互斥量数据类型是pthread_mutex_t。在使用前,要对它进行初始化。
静态分配:pthread_mutex_t mutex = PTHREAD_MUTEX_INITIALIZER;
动态分配:int pthread_mutex_init(pthread_mutex_t *mutex, const pthread_mutex_attr_t *mutexattr);
2、加锁。对共享资源的访问,要对互斥量进行加锁,如果互斥量已经上了锁,调用线程会阻塞,直到互斥量被解锁。
int pthread_mutex_lock(pthread_mutex *mutex);
int pthread_mutex_trylock(pthread_mutex_t *mutex);
3、解锁。在完成了对共享资源的访问后,要对互斥量进行解锁。
int pthread_mutex_unlock(pthread_mutex_t *mutex);
4、销毁锁。锁在是使用完成后,需要进行销毁以释放资源。
int pthread_mutex_destroy(pthread_mutex *mutex);
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#include "iostream"
using namespace std;
pthread_mutex_t mutex = PTHREAD_MUTEX_INITIALIZER;
int tmp;
void* thread(void *arg)
{
cout << "thread id is " << pthread_self() << endl;
pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex);
tmp = 12;
cout << "Now a is " << tmp << endl;
pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex);
return NULL;
}
int main()
{
pthread_t id;
cout << "main thread id is " << pthread_self() << endl;
tmp = 3;
cout << "In main func tmp = " << tmp << endl;
if (!pthread_create(&id, NULL, thread, NULL))
{
cout << "Create thread success!" << endl;
}
else
{
cout << "Create thread failed!" << endl;
}
pthread_join(id, NULL);
pthread_mutex_destroy(&mutex);
return 0;
}
//编译:g++ -o thread testthread.cpp -lpthread相关推荐:《PHP入门教程》
二、条件变量(cond)
与互斥锁不同,条件变量是用来等待而不是用来上锁的。条件变量用来自动阻塞一个线程,直到某特殊情况发生为止。通常条件变量和互斥锁同时使用。条件变量分为两部分: 条件和变量。条件本身是由互斥量保护的。线程在改变条件状态前先要锁住互斥量。条件变量使我们可以睡眠等待某种条件出现。条件变量是利用线程间共享的全局变量进行同步的一种机制,主要包括两个动作:一个线程等待“条件变量的条件成立”而挂起;另一个线程使“条件成立”(给出条件成立信号)。条件的检测是在互斥锁的保护下进行的。如果一个条件为假,一个线程自动阻塞,并释放等待状态改变的互斥锁。如果另一个线程改变了条件,它发信号给关联的条件变量,唤醒一个或多个等待它的线程,重新获得互斥锁,重新评价条件。如果两进程共享可读写的内存,条件变量可以被用来实现这两进程间的线程同步。
1、初始化条件变量。
静态态初始化,pthread_cond_t cond = PTHREAD_COND_INITIALIER;
动态初始化,int pthread_cond_init(pthread_cond_t *cond, pthread_condattr_t *cond_attr);
2、等待条件成立。释放锁,同时阻塞等待条件变量为真才行。timewait()设置等待时间,仍未signal,返回ETIMEOUT(加锁保证只有一个线程wait)
int pthread_cond_wait(pthread_cond_t *cond, pthread_mutex_t *mutex);
int pthread_cond_timewait(pthread_cond_t *cond,pthread_mutex *mutex,const timespec *abstime);
3、激活条件变量。pthread_cond_signal,pthread_cond_broadcast(激活所有等待线程)
int pthread_cond_signal(pthread_cond_t *cond);
int pthread_cond_broadcast(pthread_cond_t *cond); //解除所有线程的阻塞
4、清除条件变量。无线程等待,否则返回EBUSY
int pthread_cond_destroy(pthread_cond_t *cond);
[cpp] view plain copy
#include <stdio.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#include "stdlib.h"
#include "unistd.h"
pthread_mutex_t mutex;
pthread_cond_t cond;
void hander(void *arg)
{
free(arg);
(void)pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex);
}
void *thread1(void *arg)
{
pthread_cleanup_push(hander, &mutex);
while(1)
{
printf("thread1 is running\n");
pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex);
pthread_cond_wait(&cond, &mutex);
printf("thread1 applied the condition\n");
pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex);
sleep(4);
}
pthread_cleanup_pop(0);
}
void *thread2(void *arg)
{
while(1)
{
printf("thread2 is running\n");
pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex);
pthread_cond_wait(&cond, &mutex);
printf("thread2 applied the condition\n");
pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex);
sleep(1);
}
}
int main()
{
pthread_t thid1,thid2;
printf("condition variable study!\n");
pthread_mutex_init(&mutex, NULL);
pthread_cond_init(&cond, NULL);
pthread_create(&thid1, NULL, thread1, NULL);
pthread_create(&thid2, NULL, thread2, NULL);
sleep(1);
do
{
pthread_cond_signal(&cond);
}while(1);
sleep(20);
pthread_exit(0);
return 0;
}#include <pthread.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include "stdio.h"
#include "stdlib.h"
static pthread_mutex_t mtx = PTHREAD_MUTEX_INITIALIZER;
static pthread_cond_t cond = PTHREAD_COND_INITIALIZER;
struct node
{
int n_number;
struct node *n_next;
}*head = NULL;
static void cleanup_handler(void *arg)
{
printf("Cleanup handler of second thread./n");
free(arg);
(void)pthread_mutex_unlock(&mtx);
}
static void *thread_func(void *arg)
{
struct node *p = NULL;
pthread_cleanup_push(cleanup_handler, p);
while (1)
{
//这个mutex主要是用来保证pthread_cond_wait的并发性
pthread_mutex_lock(&mtx);
while (head == NULL)
{
//这个while要特别说明一下,单个pthread_cond_wait功能很完善,为何
//这里要有一个while (head == NULL)呢?因为pthread_cond_wait里的线
//程可能会被意外唤醒,如果这个时候head != NULL,则不是我们想要的情况。
//这个时候,应该让线程继续进入pthread_cond_wait
// pthread_cond_wait会先解除之前的pthread_mutex_lock锁定的mtx,
//然后阻塞在等待对列里休眠,直到再次被唤醒(大多数情况下是等待的条件成立
//而被唤醒,唤醒后,该进程会先锁定先pthread_mutex_lock(&mtx);,再读取资源
//用这个流程是比较清楚的
pthread_cond_wait(&cond, &mtx);
p = head;
head = head->n_next;
printf("Got %d from front of queue/n", p->n_number);
free(p);
}
pthread_mutex_unlock(&mtx); //临界区数据操作完毕,释放互斥锁
}
pthread_cleanup_pop(0);
return 0;
}
int main(void)
{
pthread_t tid;
int i;
struct node *p;
//子线程会一直等待资源,类似生产者和消费者,但是这里的消费者可以是多个消费者,而
//不仅仅支持普通的单个消费者,这个模型虽然简单,但是很强大
pthread_create(&tid, NULL, thread_func, NULL);
sleep(1);
for (i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
p = (struct node*)malloc(sizeof(struct node));
p->n_number = i;
pthread_mutex_lock(&mtx); //需要操作head这个临界资源,先加锁,
p->n_next = head;
head = p;
pthread_cond_signal(&cond);
pthread_mutex_unlock(&mtx); //解锁
sleep(1);
}
printf("thread 1 wanna end the line.So cancel thread 2./n");
//关于pthread_cancel,有一点额外的说明,它是从外部终止子线程,子线程会在最近的取消点,退出
//线程,而在我们的代码里,最近的取消点肯定就是pthread_cond_wait()了。
pthread_cancel(tid);
pthread_join(tid, NULL);
printf("All done -- exiting/n");
return 0;
}三、信号量(sem)
如同进程一样,线程也可以通过信号量来实现通信,虽然是轻量级的。信号量函数的名字都以“sem_”打头。线程使用的基本信号量函数有四个。
1、信号量初始化。
int sem_init (sem_t *sem , int pshared, unsigned int value);
这是对由sem指定的信号量进行初始化,设置好它的共享选项(linux 只支持为0,即表示它是当前进程的局部信号量),然后给它一个初始值VALUE。
2、等待信号量。给信号量减1,然后等待直到信号量的值大于0。
int sem_wait(sem_t *sem);
3、释放信号量。信号量值加1。并通知其他等待线程。
int sem_post(sem_t *sem);
4、销毁信号量。我们用完信号量后都它进行清理。归还占有的一切资源。
int sem_destroy(sem_t *sem);
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <semaphore.h>
#include <errno.h>
#define return_if_fail(p) if((p) == 0){printf ("[%s]:func error!/n", __func__);return;}
typedef struct _PrivInfo
{
sem_t s1;
sem_t s2;
time_t end_time;
}PrivInfo;
static void info_init (PrivInfo* thiz);
static void info_destroy (PrivInfo* thiz);
static void* pthread_func_1 (PrivInfo* thiz);
static void* pthread_func_2 (PrivInfo* thiz);
int main (int argc, char** argv)
{
pthread_t pt_1 = 0;
pthread_t pt_2 = 0;
int ret = 0;
PrivInfo* thiz = NULL;
thiz = (PrivInfo* )malloc (sizeof (PrivInfo));
if (thiz == NULL)
{
printf ("[%s]: Failed to malloc priv./n");
return -1;
}
info_init (thiz);
ret = pthread_create (&pt_1, NULL, (void*)pthread_func_1, thiz);
if (ret != 0)
{
perror ("pthread_1_create:");
}
ret = pthread_create (&pt_2, NULL, (void*)pthread_func_2, thiz);
if (ret != 0)
{
perror ("pthread_2_create:");
}
pthread_join (pt_1, NULL);
pthread_join (pt_2, NULL);
info_destroy (thiz);
return 0;
}
static void info_init (PrivInfo* thiz)
{
return_if_fail (thiz != NULL);
thiz->end_time = time(NULL) + 10;
sem_init (&thiz->s1, 0, 1);
sem_init (&thiz->s2, 0, 0);
return;
}
static void info_destroy (PrivInfo* thiz)
{
return_if_fail (thiz != NULL);
sem_destroy (&thiz->s1);
sem_destroy (&thiz->s2);
free (thiz);
thiz = NULL;
return;
}
static void* pthread_func_1 (PrivInfo* thiz)
{
return_if_fail(thiz != NULL);
while (time(NULL) < thiz->end_time)
{
sem_wait (&thiz->s2);
printf ("pthread1: pthread1 get the lock./n");
sem_post (&thiz->s1);
printf ("pthread1: pthread1 unlock/n");
sleep (1);
}
return;
}
static void* pthread_func_2 (PrivInfo* thiz)
{
return_if_fail (thiz != NULL);
while (time (NULL) < thiz->end_time)
{
sem_wait (&thiz->s1);
printf ("pthread2: pthread2 get the unlock./n");
sem_post (&thiz->s2);
printf ("pthread2: pthread2 unlock./n");
sleep (1);
}
return;
}以上便是Linux下实现线程同步常用的三种方法,大家都知道,线程的最大的亮点便是资源共享性,而资源共享中的线程同步问题却是一大难点。
以上是线程同步有几种方法的详细内容。更多信息请关注PHP中文网其他相关文章!

热AI工具

Undresser.AI Undress
人工智能驱动的应用程序,用于创建逼真的裸体照片

AI Clothes Remover
用于从照片中去除衣服的在线人工智能工具。

Undress AI Tool
免费脱衣服图片

Clothoff.io
AI脱衣机

Video Face Swap
使用我们完全免费的人工智能换脸工具轻松在任何视频中换脸!

热门文章

热工具

记事本++7.3.1
好用且免费的代码编辑器

SublimeText3汉化版
中文版,非常好用

禅工作室 13.0.1
功能强大的PHP集成开发环境

Dreamweaver CS6
视觉化网页开发工具

SublimeText3 Mac版
神级代码编辑软件(SublimeText3)
 怎么删除微信好友?删除微信好友的方法
Mar 04, 2024 am 11:10 AM
怎么删除微信好友?删除微信好友的方法
Mar 04, 2024 am 11:10 AM
微信是主流的聊天工具之一,我们可以通过微信认识新的朋友,联系老的朋友,维系朋友之间的情谊。正如天下没有不散的宴席,人与人之间的相处难免会发生意见不合的时候。当一个人极其影响你的情绪,或者在相处的时候发现三观不合,没办法再继续沟通,那么我们可能需要删除微信好友的方法。怎么删除微信好友?删除微信好友的方法第一步:在微信主界面轻触【通讯录】;第二步:点击对应要删除的好友,进入【详细资料】;第三步:点击右上角【...】;第四步:点击下方【删除】即可;第五步:了解后页面提示后,点击【删除联系人】即可;温馨
 微信删除的人如何找回(简单教程告诉你如何恢复被删除的联系人)
May 01, 2024 pm 12:01 PM
微信删除的人如何找回(简单教程告诉你如何恢复被删除的联系人)
May 01, 2024 pm 12:01 PM
而后悔莫及、人们常常会因为一些原因不小心将某些联系人删除、微信作为一款广泛使用的社交软件。帮助用户解决这一问题,本文将介绍如何通过简单的方法找回被删除的联系人。1.了解微信联系人删除机制这为我们找回被删除的联系人提供了可能性、微信中的联系人删除机制是将其从通讯录中移除,但并未完全删除。2.使用微信内置“通讯录恢复”功能微信提供了“通讯录恢复”节省时间和精力,用户可以通过该功能快速找回之前被删除的联系人,功能。3.进入微信设置页面点击右下角,打开微信应用“我”再点击右上角设置图标、进入设置页面,,
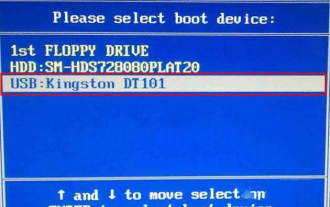 七彩虹主板怎么进入bios?教你两种方法
Mar 13, 2024 pm 06:01 PM
七彩虹主板怎么进入bios?教你两种方法
Mar 13, 2024 pm 06:01 PM
七彩虹主板在中国国内市场享有较高的知名度和市场占有率,但是有些七彩虹主板的用户还不清楚怎么进入bios进行设置呢?针对这一情况,小编专门为大家带来了两种进入七彩虹主板bios的方法,快来试试吧! 方法一:使用u盘启动快捷键直接进入u盘装系统 七彩虹主板一键启动u盘的快捷键是ESC或F11,首先使用黑鲨装机大师制作一个黑鲨U盘启动盘,然后开启电脑,当看到开机画面的时候,连续按下键盘上的ESC或F11键以后将会进入到一个启动项顺序选择的窗口,将光标移动到显示“USB”的地方,然
 怎么在番茄免费小说app中写小说 分享番茄小说写小说方法教程
Mar 28, 2024 pm 12:50 PM
怎么在番茄免费小说app中写小说 分享番茄小说写小说方法教程
Mar 28, 2024 pm 12:50 PM
番茄小说是一款非常热门的小说阅读软件,我们在番茄小说中经常会有新的小说和漫画可以去阅读,每一本小说和漫画都很有意思,很多小伙伴也想着要去写小说来赚取赚取零花钱,在把自己想要写的小说内容编辑成文字,那么我们要怎么样在这里面去写小说呢?小伙伴们都不知道,那就让我们一起到本站本站中花点时间来看写小说的方法介绍吧。分享番茄小说写小说方法教程 1、首先在手机上打开番茄免费小说app,点击个人中心——作家中心 2、跳转到番茄作家助手页面——点击创建新书在小说的结
 手机版龙蛋孵化方法大揭秘(一步一步教你如何成功孵化手机版龙蛋)
May 04, 2024 pm 06:01 PM
手机版龙蛋孵化方法大揭秘(一步一步教你如何成功孵化手机版龙蛋)
May 04, 2024 pm 06:01 PM
手机游戏成为了人们生活中不可或缺的一部分,随着科技的发展。它以其可爱的龙蛋形象和有趣的孵化过程吸引了众多玩家的关注,而其中一款备受瞩目的游戏就是手机版龙蛋。帮助玩家们在游戏中更好地培养和成长自己的小龙,本文将向大家介绍手机版龙蛋的孵化方法。1.选择合适的龙蛋种类玩家需要仔细选择自己喜欢并且适合自己的龙蛋种类,根据游戏中提供的不同种类的龙蛋属性和能力。2.提升孵化机的等级玩家需要通过完成任务和收集道具来提升孵化机的等级,孵化机的等级决定了孵化速度和孵化成功率。3.收集孵化所需的资源玩家需要在游戏中
 Win11管理员权限获取方法汇总
Mar 09, 2024 am 08:45 AM
Win11管理员权限获取方法汇总
Mar 09, 2024 am 08:45 AM
Win11管理员权限获取方法汇总在Windows11操作系统中,管理员权限是非常重要的权限之一,可以让用户对系统进行各种操作。有时候,我们可能需要获取管理员权限来完成一些操作,比如安装软件、修改系统设置等。下面就为大家总结了一些获取Win11管理员权限的方法,希望能帮助到大家。1.使用快捷键在Windows11系统中,可以通过快捷键的方式快速打开命令提
 Oracle版本查询方法详解
Mar 07, 2024 pm 09:21 PM
Oracle版本查询方法详解
Mar 07, 2024 pm 09:21 PM
Oracle版本查询方法详解Oracle是目前世界上最流行的关系型数据库管理系统之一,它提供了丰富的功能和强大的性能,广泛应用于企业中。在进行数据库管理和开发过程中,了解Oracle数据库的版本是非常重要的。本文将详细介绍如何查询Oracle数据库的版本信息,并给出具体的代码示例。查询数据库版本的SQL语句在Oracle数据库中,可以通过执行简单的SQL语句
 手机字体大小设置方法(轻松调整手机字体大小)
May 07, 2024 pm 03:34 PM
手机字体大小设置方法(轻松调整手机字体大小)
May 07, 2024 pm 03:34 PM
字体大小的设置成为了一项重要的个性化需求,随着手机成为人们日常生活的重要工具。以满足不同用户的需求、本文将介绍如何通过简单的操作,提升手机使用体验,调整手机字体大小。为什么需要调整手机字体大小-调整字体大小可以使文字更清晰易读-适合不同年龄段用户的阅读需求-方便视力不佳的用户使用手机系统自带字体大小设置功能-如何进入系统设置界面-在设置界面中找到并进入"显示"选项-找到"字体大小"选项并进行调整第三方应用调整字体大小-下载并安装支持字体大小调整的应用程序-打开应用程序并进入相关设置界面-根据个人






