下面由Redis教程栏目给大家介绍关于spring redis注解实现缓存机制,希望对需要的朋友有所帮助!
1、xml配置
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 | <bean id="poolConfigTax" class="redis.clients.jedis.JedisPoolConfig">
<property name="maxIdle" value="${redis_tax.maxIdle}" />
<property name="minIdle" value="${redis_tax.minIdle}" />
<property name="maxTotal" value="${redis_tax.maxTotal}" />
<property name="testOnBorrow" value="${redis_tax.testOnBorrow}" />
</bean>
<!-- Tax redis 数据库 -->
<bean id="connectionFactoryTax" class="org.springframework.data.redis.connection.jedis.JedisConnectionFactory"
p:host-name="${redis_tax.host}" p:port="${redis_tax.port}" p:password="${redis_tax.pass}" p:pool-config-ref="poolConfigTax"
p:database="0"/>
<!--redis操作模版,使用该对象可以操作redis -->
<bean id="redisTemplateTax" class="org.springframework.data.redis.core.RedisTemplate" >
<property name="connectionFactory" ref="connectionFactoryTax" />
<!--如果不配置Serializer,那么存储的时候缺省使用String,如果用User类型存储,那么会提示错误User can't cast to String!! -->
<property name="keySerializer" >
<bean class="org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.StringRedisSerializer" />
</property>
<property name="valueSerializer" >
<bean class="org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.GenericJackson2JsonRedisSerializer" />
</property>
<property name="hashKeySerializer">
<bean class="org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.StringRedisSerializer"/>
</property>
<property name="hashValueSerializer">
<bean class="org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.GenericJackson2JsonRedisSerializer"/>
</property>
<!--开启事务 -->
<property name="enableTransactionSupport" value="false"></property>
</bean>
<!-- 配置RedisCacheManager -->
<bean id="redisCacheManager" class="org.springframework.data.redis.cache.RedisCacheManager">
<constructor-arg name="redisOperations" ref="redisTemplateTax" />
</bean>
<cache:annotation-driven cache-manager="redisCacheManager"/>
|
登录后复制
2、缓存注解@Cacheable、@CacheEvict、@CachePut详解
一、@Cacheable用法详解
1、用在哪里?用在方法或者类上。
2、这两种用法有什么区别?
用在方法上表示:该方法的返回值将被缓存起来
用在类上表示:表示该类的所有方法都支持该注解
3、使用后的结果是什么?下次使用相同方法和相同参数调用这个方法的时候将直接从缓存取值,而不需要再次执行该方法。
4、返回值在缓存中怎么存储的?以键值对的方式存储在缓存中,value就是返回值,key由两种策略生成:默认策略和自定义策略
5、默认策略和默认策略怎么用?
默认策略:在value值后双“::”拼接,形参列表,当形参是对象时,使用json格式:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 | @CacheConfig(cacheNames="enterprise")
public interface EnterpriseRepo extends JpaRepository<Enterprise, Integer>,JpaSpecificationExecutor<Enterprise>{
@Cacheable(value="cash1")
Enterprise findByid(Integer id);
@CachePut(value="cash1")
Enterprise save(Enterprise enterprise);
}
|
登录后复制
自定义策略:key属性是用来指定Spring缓存方法的返回结果时对应的key的。该属性支持SpringEL表达式。当我们没有指定该属性时,Spring将使用默认策略生成key。
自定义策略是指我们可以通过Spring的EL表达式来指定我们的key。这里的EL表达式可以使用方法参数及它们对应的属性。使用方法参数时我们可以直接使用“#参数名”或者“#p参数index”。下面是几个使用参数作为key的示例。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 | @Cacheable(value="users", key="#id")
public User find(Integer id) {
return null;
}
@Cacheable(value="users", key="#p0")
public User find(Integer id) {
return null;
}
@Cacheable(value="users", key="#user.id")
public User find(User user) {
return null;
}
@Cacheable(value="users", key="#p0.id")
public User find(User user) {
return null;
}
|
登录后复制
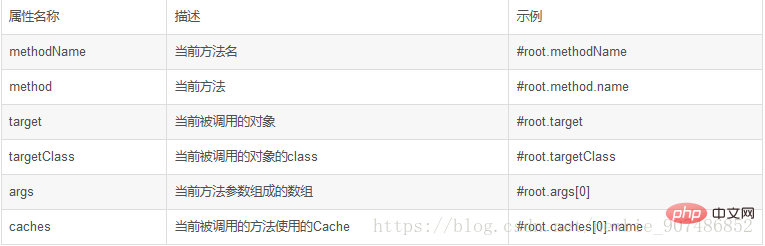
除了上述使用方法参数作为key之外,Spring还为我们提供了一个root对象可以用来生成key。通过该root对象我们可以获取到以下信息。

当我们要使用root对象的属性作为key时我们也可以将“#root”省略,因为Spring默认使用的就是root对象的属性。如:
1 2 3 4 5 | @Cacheable(value={"users", "xxx"}, key="caches[1].name")
public User find(User user) {
return null;
}
|
登录后复制
6、condition属性指定发生的条件
有的时候我们可能并不希望缓存一个方法所有的返回结果。通过condition属性可以实现这一功能。condition属性默认为空,表示将缓存所有的调用情形。其值是通过SpringEL表达式来指定的,当为true时表示进行缓存处理;当为false时表示不进行缓存处理,即每次调用该方法时该方法都会执行一次。如下示例表示只有当user的id为偶数时才会进行缓存。
1 2 3 4 5 | @Cacheable(value={"users"}, key="#user.id", condition="#user.id%2==0")
public User find(User user) {
System.out.println("find user by user " + user);
return user;
}
|
登录后复制
二、@CachePut
在支持Spring Cache的环境下,对于使用@Cacheable标注的方法,Spring在每次执行前都会检查Cache中是否存在相同key的缓存元素,如果存在就不再执行该方法,而是直接从缓存中获取结果进行返回,否则才会执行并将返回结果存入指定的缓存中。@CachePut也可以声明一个方法支持缓存功能。与@Cacheable不同的是使用@CachePut标注的方法在执行前不会去检查缓存中是否存在之前执行过的结果,而是每次都会执行该方法,并将执行结果以键值对的形式存入指定的缓存中。
一般使用在保存,更新方法中。
@CachePut也可以标注在类上和方法上。使用@CachePut时我们可以指定的属性跟@Cacheable是一样的。
@CachePut(“users”)//每次都会执行方法,并将结果存入指定的缓存中
1 2 3 | public User find(Integer id) {
return null;
}
|
登录后复制
三、@CacheEvict
@CacheEvict是用来标注在需要清除缓存元素的方法或类上的。当标记在一个类上时表示其中所有的方法的执行都会触发缓存的清除操作。@CacheEvict可以指定的属性有value、key、condition、allEntries和beforeInvocation。其中value、key和condition的语义与@Cacheable对应的属性类似。即value表示清除操作是发生在哪些Cache上的(对应Cache的名称);key表示需要清除的是哪个key,如未指定则会使用默认策略生成的key;condition表示清除操作发生的条件。下面我们来介绍一下新出现的两个属性allEntries和beforeInvocation。
1、 allEntries属性
allEntries是boolean类型,表示是否需要清除缓存中的所有元素。默认为false,表示不需要。当指定了allEntries为true时,Spring Cache将忽略指定的key。有的时候我们需要Cache一下清除所有的元素,这比一个一个清除元素更有效率。
1 2 3 4 | @CacheEvict(value="users", allEntries=true)
public void delete(Integer id) {
System.out.println("delete user by id: " + id);
}
|
登录后复制
2、beforeInvocation属性
清除操作默认是在对应方法成功执行之后触发的,即方法如果因为抛出异常而未能成功返回时也不会触发清除操作。使用beforeInvocation可以改变触发清除操作的时间,当我们指定该属性值为true时,Spring会在调用该方法之前清除缓存中的指定元素。
1 2 3 4 | @CacheEvict(value="users", beforeInvocation=true)
public void delete(Integer id) {
System.out.println("delete user by id: " + id);
}
|
登录后复制
以上是关于spring redis注解实现缓存机制的详细内容。更多信息请关注PHP中文网其他相关文章!