本篇文章带大家了解一下Nodejs异步编程中的Promise,介绍一下Promise比callback优秀在哪里。

【推荐学习:《nodejs 教程》】
Promise 是一种异步编程的解决方案!
(function () {
const res = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(() => {
resolve();
}, 500);
});
console.log("500ms", res);
setTimeout(() => {
console.log("800ms", res);
}, 800);
})();打印出如下内容
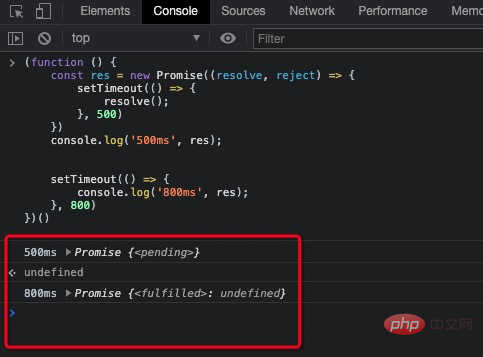
结果是符合我们的预期的
promise的结果,此时promise处于pending状态promise的结果,此时promise处于fulfilled状态(function () {
const res = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(() => {
reject(new Error("error"));
}, 500);
});
console.log("500ms", res);
setTimeout(() => {
console.log("800ms", res);
}, 800);
})();打印出如下内容
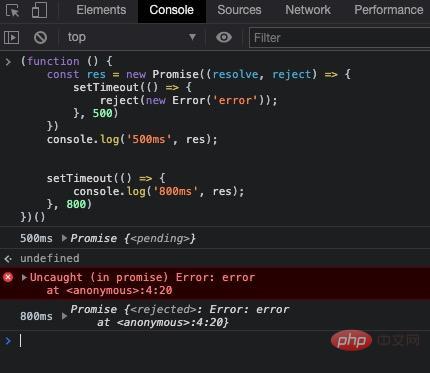
结果是符合我们的预期的
promise的结果,此时promise处于pending状态promise的结果,此时promise处于reject状态注意:如果当
pengding状态进入到reject状态,这个错误又没有正确捕获的话,这个错误就会被抛到 JS 的全局
(function () {
const res = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(() => {
resolve();
}, 300);
setTimeout(() => {
reject(new Error("error"));
}, 500);
});
console.log("500ms", res);
setTimeout(() => {
console.log("800ms", res);
}, 800);
})();打印出如下内容
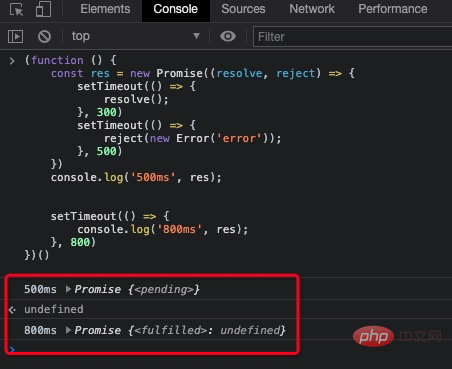
可以发现!
在 300ms 的时候promise的状态已经切换到了resolve, 切换后永远也无法到达reject状态
pending 只能流转到 resolve 或者 reject;resolve 和 reject 不能互相流转;(function () {
const res = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(() => {
resolve(3);
}, 300);
})
.then((result) => {
console.log("result", result);
})
.catch((error) => {
console.log("error", error);
});
console.log("300ms", res);
setTimeout(() => {
console.log("800ms", res);
}, 800);
})();打印出如下内容
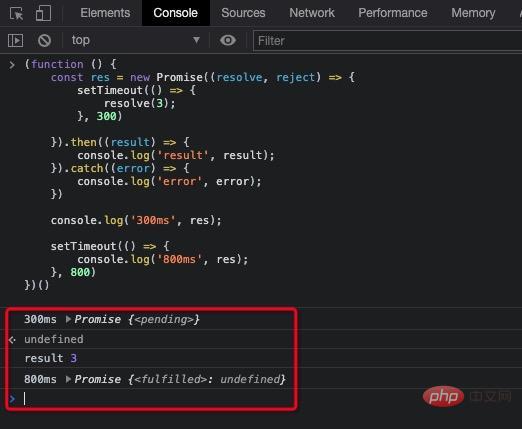
可以发现
then 是 promise 的状态流转到 reslove 状态可以拿到的结果(function () {
const res = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(() => {
reject(new Error("error-3"));
}, 300);
})
.then((result) => {
console.log("result", result);
})
.catch((error) => {
console.log("error", error);
});
console.log("300ms", res);
setTimeout(() => {
console.log("800ms", res);
}, 800);
})();打印出如下内容
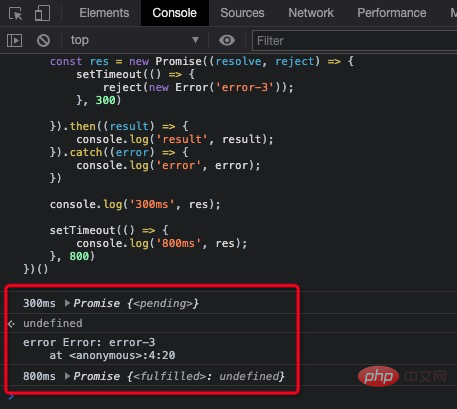
可以发现
catch 是 promise 的状态流转到 reject 状态可以拿到的结果, 并且之前全局的 JS 错误已经可以被 catch 捕获到了
.then .catch 总结
resolved 状态的 Promise 会回调后面的第一个 .thenrejected 状态的 Promise 会回调后面的第一个 .catchrejected 状态切后面没有 .catch 的 Promise 会造成 Js 环境的全局错误我们继续之前面试的例子
function interview() {
return new Promise(function (resolve, reject) {
setTimeout(() => {
if (Math.random() > 0.4) {
// resolve, reject 只能接受一个参数
resolve("success");
} else {
reject(new Error("fail"));
}
}, 1000);
});
}
(function () {
const res = interview();
res
.then((result) => {
console.log("面试成功!我笑了");
})
.catch((error) => {
console.log("面试失败!我哭了");
});
})();function interview() {
return new Promise(function (resolve, reject) {
setTimeout(() => {
if (Math.random() > 0.4) {
// resolve, reject 只能接受一个参数
resolve("success");
} else {
reject(new Error("fail"));
}
}, 500);
});
}
(function () {
const promsie1 = interview();
const promsie2 = promsie1.then((result) => {
throw new Error("面试成功!我笑了,但是我拒绝了");
});
setTimeout(() => {
console.log("promsie1", promsie1);
console.log("promsie2", promsie2);
}, 800);
})();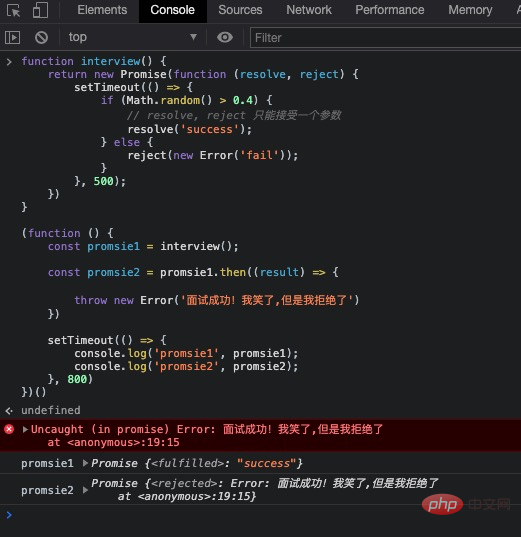
以上代码可以看出 ,**.then返回一个全新的 Promise, 此 Promise 的结果状态是由 .then 的回调函数的结果来决定的
throw, 则进入 rejectedreturn,则进入 resolvedfunction interview() {
return new Promise(function (resolve, reject) {
setTimeout(() => {
if (Math.random() > 0) {
// resolve, reject 只能接受一个参数
resolve("success");
} else {
reject(new Error("fail"));
}
}, 500);
});
}
(function () {
const promsie1 = interview();
const promsie2 = promsie1.catch((result) => {
return "虽然面试失败,但我还是笑了";
});
setTimeout(() => {
console.log("promsie1", promsie1);
console.log("promsie2", promsie2);
}, 800);
})();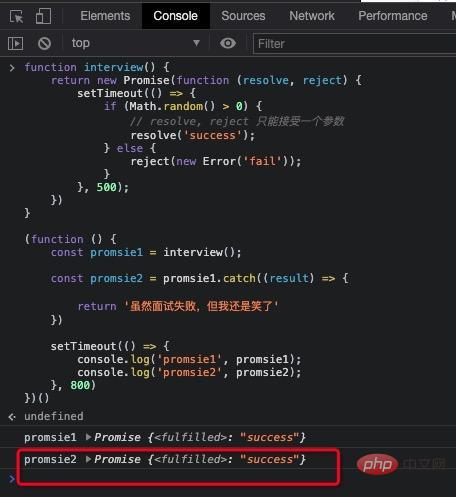
.catch 返回一个全新的 Promise, 此 Promise 的结果状态是由 .catch 的回调函数的结果来决定的
throw, 则进入 rejectedreturn,则进入 resolvedfunction interview() {
return new Promise(function (resolve, reject) {
setTimeout(() => {
if (Math.random() > 0.4) {
// resolve, reject 只能接受一个参数
resolve("success");
} else {
reject(new Error("fail"));
}
}, 500);
});
}
(function () {
const promsie1 = interview();
const promsie2 = promsie1
.then((result) => {
return new Promise(function (resolve, reject) {
setTimeout(() => {
resolve("面试成功!,给我400ms 总结一下");
}, 400);
});
})
.catch((result) => {
return new Promise(function (resolve, reject) {
setTimeout(() => {
resolve("面试失败,给我400ms 总结一下");
}, 400);
});
});
setTimeout(() => {
console.log("800ms promsie1", promsie1);
console.log("800ms promsie2", promsie2);
}, 800);
setTimeout(() => {
console.log("1000ms promsie1", promsie1);
console.log("1000ms promsie2", promsie2);
}, 1000);
})();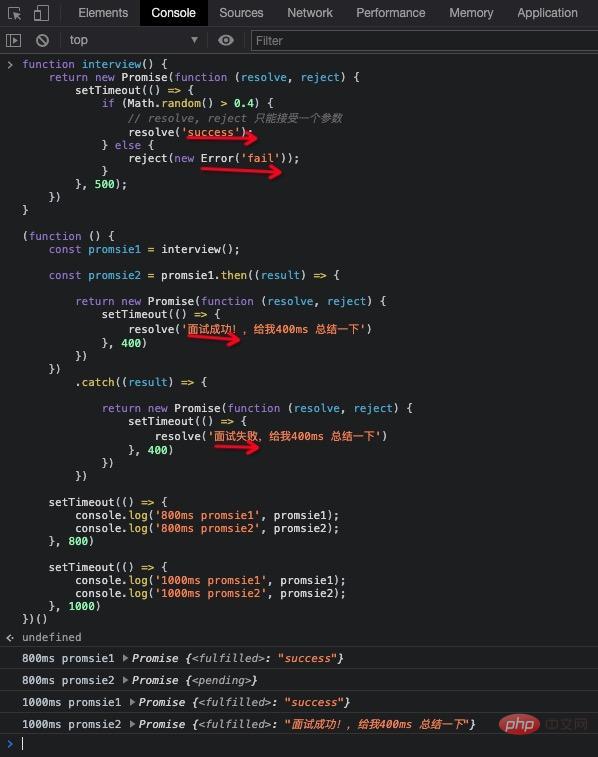
如果在 .catch,.then 中 返回 Promise, 则会等待此 Promise 的执行结果
如果回调函数最终 return 了 Promise,该 promise 和回调函数的 return 的 Promsie 状态保持一致, 这就表示了可以 在 Promise 的链式调用里面串行的执行多个异步任务!
// round 面试第几轮
function interview(round) {
return new Promise(function (resolve, reject) {
setTimeout(() => {
if (Math.random() > 0.4) {
// resolve, reject 只能接受一个参数
resolve("success");
} else {
const error = new Error("fail");
reject({ round, error });
}
}, 500);
});
}
(function () {
interview(1)
.then(() => {
return interview(2);
})
.then(() => {
return interview(3);
})
.then(() => {
console.log("每轮面试都成功!我开心的笑了");
})
.catch((err) => {
console.log(`第${err.round}轮面试失败了`);
});
})();Promise 的 .then .catch 把回调地狱变成了一段线性的代码!
// round 面试第几轮
function interview(name) {
return new Promise(function (resolve, reject) {
setTimeout(() => {
if (Math.random() > 0.4) {
// resolve, reject 只能接受一个参数
resolve("success");
} else {
const error = new Error("fail");
reject({ name, error });
}
}, 500);
});
}
(function () {
Promise.all([interview("tenxun"), interview("ali"), interview("baidu")])
.then(() => {
console.log("每家公司都面试成功了");
})
.catch((err) => {
console.log(`面试${err.name}失败了`);
});
})();更多编程相关知识,请访问:编程视频!!
以上是深入浅析Nodejs异步编程中的Promise的详细内容。更多信息请关注PHP中文网其他相关文章!



