GIT LFS迁移说明(实例详解)
本篇文章给大家带来了关于Git的相关知识,其中主要介绍了GIT LFS的相关问题,包括了GIT LFS服务端配置、GIT LFS客户端安装、迁移本地历史仓库等等,希望对大家有帮助。

推荐学习:《Git学习教程》
之前一些git项目上 CI/CD,发现jenkins git clone失败,设置depth及clone时间之类的无果。只能考虑仓库瘦身之类的策略。发现仓库有不少的二进制文件,且这些二进制文件变更还挺频繁,这种操作会导致git仓库成倍增长极速膨胀,git本身只适合管理文本文件。
另外说一则有趣的往事,之前有个同事是图形编程,这个语言源码是图片形式的,而且一个文件又特别大,上git管理,小公司项目变更又频繁,导致没多久公司内部搭的git服务器硬盘居然就给他的几个git仓库给占满了。
GIT LFS (Large File Storage)
虽然git一直不适合管理二进制文件,不过现在 git 也好像默认提供了git lfs 这个专门用来管理大文件的插件。
基本原理简单来说就是使用类似一个文件指针(文本)代替实际的文件存储,git只存储文件指针的变更历史而不是整个二进制文件,并且在使用的时候,自动提供hook,方便在如clone、pull、reset等操作会自动去获取这些文件指针的源二进制文件,同样更新二进制文件commit的时候,git 会自动将源文件转成文件指针进git log,同时源文件上传lfs。所以在用户层面,GIT LFS的使用其实是无感的。
迁移
上面简单介绍了一下GIT LFS,接下来直接将如何迁移,至于为什么直接讲迁移而不是从0开始如何使用LFS。
是因为往往是git仓库用着用着发现,仓库好大、clone好慢,然后才是想着用LFS。
迁移需要我们有仓库的管理员权限,并且将保护分支之类取消保护;
具体LFS迁移主要分为以下几步。
迁移前最好做好备份,并且和团队同事沟通好,毕竟操作涉及-f高危操作,容易背锅。
GIT LFS 服务端配置
部分自建git 服务的话,可能需要服务端配置开启LFS,比如gitlab。
GIT LFS 客户端安装
windows 的git安装包自带了该插件,不需要另外安装,其他平台可自行安装,链接。
在命令行尝试以下命令。
git lfs
如果有类似help文档信息输出,就是已经有git lfs客户端了。
git-lfs/2.11.0 (GitHub; windows amd64; go 1.14.2; git 48b28d97)git lfs <command> [<args>]Git LFS is a system for managing and versioning large files in association with a Git repository. Instead of storing the large files within the Git repository as blobs, Git LFS stores special "pointer files" in the repository, while storing the actual file contents on a Git LFS server. The contents of the large file are downloaded automatically when needed, for example when a Git branch containing the large file is checked out.Git LFS works by using a "smudge" filter to look up the large file contents based on the pointer file, and a "clean" filter to create a new version of the pointer file when the large file's contents change.It also uses a pre-push hook to upload the large file contents to the Git LFS server whenever a commit containing a new large file version is about to be pushed to the corresponding Git server.
而后需要执行以下命令配置LFS全局环境,只需要配置一次,同时也会去更新当前仓库的hooks
git lfs install
迁移本地历史仓库
lfs迁移基本思想:lfs重写本地历史—>force push覆写远端,达到迁移的效果。
所以我们最好将本地仓库与远端同步,并且将所有的远端分支都创建本地分支;
而后cd到自己本地仓库,执行以下下命令,–include里面是glob表达式,自行添加想LFS管理的文件名,–everything代表所有本地分支
git lfs migrate import --include="*.bin,*.lib,*.so,*.dll,*.a,*.param,*.zip,*.gz" --everything
migrate: Sorting commits: ..., done. migrate: Rewriting commits: 100% (193/193), done. develop bacb490a80ea46d73bd3866c2e7cf7ad199ce5eb -> 72884bcb4629417bad73ea3d485d08a0708909cd feature/npu-platform a3645632756becc527c7f4d58514b3c479f824d3 -> e227900a3903b3a6955e4dffee48daeceac6cdff master 1ccdecdcb4b5d6224a6e24c6f87793bfcc15ee4c -> 1d9fc2139600ef3d92a20d65bb5db89021b8c488 0.1.0 07c6b2aa732506f1cc88cedb551f37f376b6efa6 -> 8e55193221dfca9f6bb28ccd9cca85af9c5958c9 1.0.0 0f694efcd7aa9df641836e1ea6eebbb730b940b5 -> 3f9e77575120b6e56b34790c998a362116da75f5 migrate: Updating refs: ..., done.
重写完本地分支、tag之类的,
我们在这里可以先执行 git lfs ls-files查看有哪些文件被转成了lfs管理,检查是否有遗漏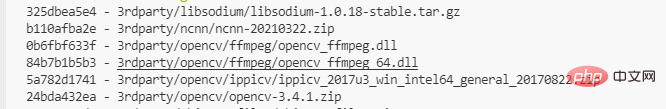
这个时候无论在哪个分支,都会出现 .gitattributes 文件,且都会被添加上类似以下内容。
*.bin filter=lfs diff=lfs merge=lfs -text *.lib filter=lfs diff=lfs merge=lfs -text *.so filter=lfs diff=lfs merge=lfs -text *.dll filter=lfs diff=lfs merge=lfs -text *.a filter=lfs diff=lfs merge=lfs -text *.param filter=lfs diff=lfs merge=lfs -text *.zip filter=lfs diff=lfs merge=lfs -text *.gz filter=lfs diff=lfs merge=lfs -text
同时可以看到我们二进制文件全部都转成了以下形式文本
version https://git-lfs.github.com/spec/v1 oid sha256:9171c8350d72ccca6ad60ac80b577157ad1f9fd44ca05744216e02ccbfcdf491 size 10260
确认无误,之后就可以推送到远端;
由于lfs的迁移会重写所有的commit,并且修改hash值,因此需要我们需要加上–froce
这步需要取消保护分支(保护分支无法-f)
git push --force --all
这样远程仓库的lfs迁移就完成了
迁移一些补充说明
- 迁移者的本地仓库lfs文件转源文件:经过以上步骤,由于我们将所有文件都已经转成文件指针,我们需要将文件下载回来才能正常使用该仓库。
需要注意,其他人重新clone 或者同步 lfs迁移过的remote仓库 是不需要该步,只针对迁移作者本地的仓库。
git lfs pull
- 团队中其他成员迁移前的本地仓库同步: 由于远程仓库的历史已经被全部重写,所以无法直接同步,最好是删除本地分支,重新拉取远程分支,如果本地已经有部分commit需要提交,可以重名本地分支,拉取远程再做cherry pick。git tag 同理,删除迁移前的tag。
- 本地仓库清理:上面的迁移成功将二进制文件迁移成git lfs 对象,git log 也不在存储源文件文件变更而是指针变更,但是在本地.git文件夹中仍存在之前不再需要的git log 缓存,执行以下命令做清理。
git reflog expire --expire-unreachable=now --all git gc --prune=now
清理前后仓库对比
lfs直观来讲更多的是针对仓库大clone慢的问题,我这边lfs迁移前后各备份各一个小型远程仓库做测试,
用的测试仓库二进制文件比较小,总大50m内,且变更次数也在个位数。
clone下来的仓库大小对比。
和我预估差不多,总的来说更适合二进制文件频繁变更,如果单纯是文件大,但文件不变更的话,在clone的时候区别不大,毕竟lfs在clone仍有下载源文件的步骤,除开下载,操作文件指针对git来说理论仍会有性能提升,但是可能感知不强。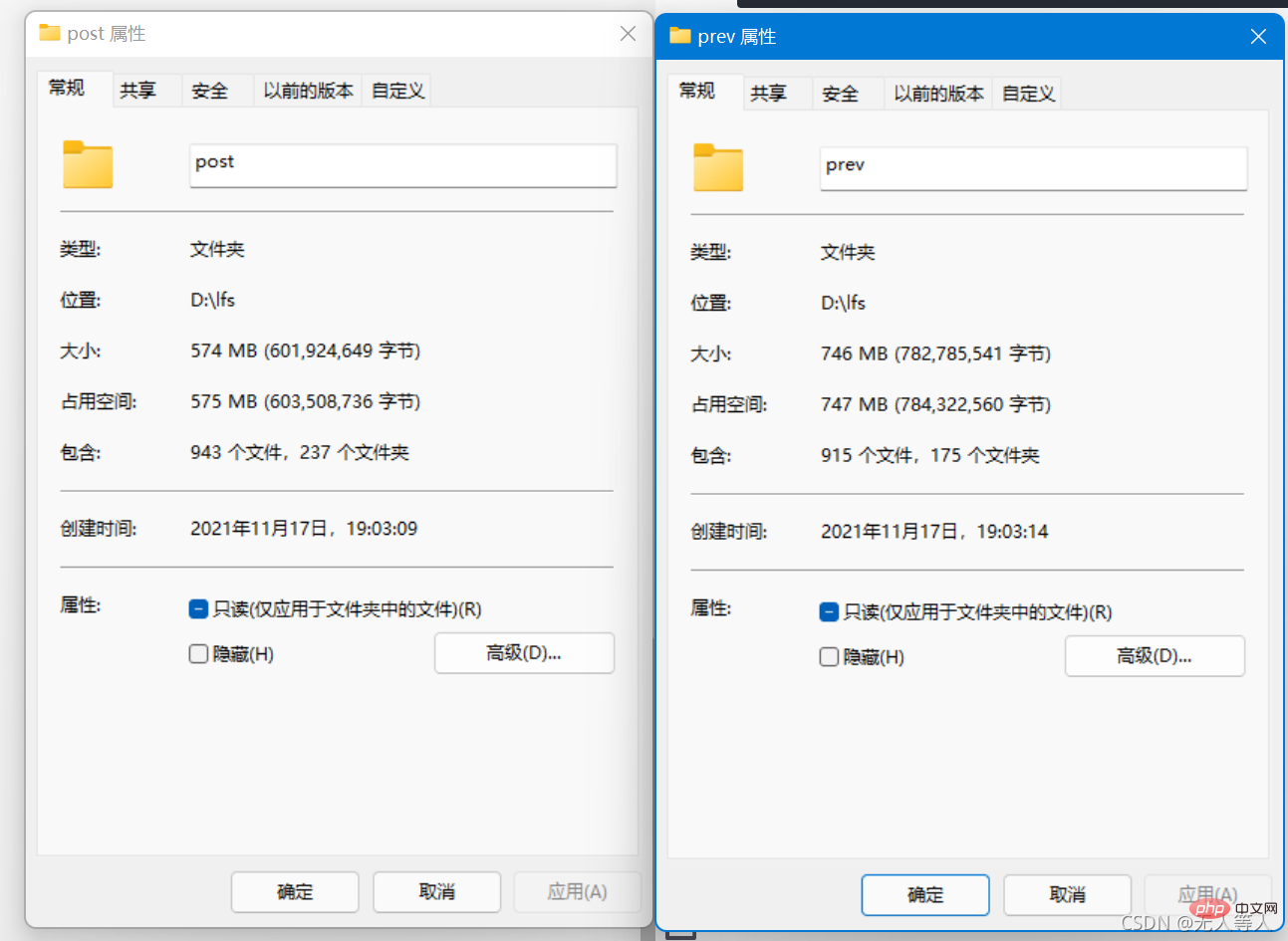 推荐学习:《Git教程》
推荐学习:《Git教程》
以上是GIT LFS迁移说明(实例详解)的详细内容。更多信息请关注PHP中文网其他相关文章!

热AI工具

Undresser.AI Undress
人工智能驱动的应用程序,用于创建逼真的裸体照片

AI Clothes Remover
用于从照片中去除衣服的在线人工智能工具。

Undress AI Tool
免费脱衣服图片

Clothoff.io
AI脱衣机

Video Face Swap
使用我们完全免费的人工智能换脸工具轻松在任何视频中换脸!

热门文章

热工具

记事本++7.3.1
好用且免费的代码编辑器

SublimeText3汉化版
中文版,非常好用

禅工作室 13.0.1
功能强大的PHP集成开发环境

Dreamweaver CS6
视觉化网页开发工具

SublimeText3 Mac版
神级代码编辑软件(SublimeText3)
 git怎么下载项目到本地
Apr 17, 2025 pm 04:36 PM
git怎么下载项目到本地
Apr 17, 2025 pm 04:36 PM
要通过 Git 下载项目到本地,请按以下步骤操作:安装 Git。导航到项目目录。使用以下命令克隆远程存储库:git clone https://github.com/username/repository-name.git
 git怎么更新代码
Apr 17, 2025 pm 04:45 PM
git怎么更新代码
Apr 17, 2025 pm 04:45 PM
更新 git 代码的步骤:检出代码:git clone https://github.com/username/repo.git获取最新更改:git fetch合并更改:git merge origin/master推送更改(可选):git push origin master
 git commit怎么用
Apr 17, 2025 pm 03:57 PM
git commit怎么用
Apr 17, 2025 pm 03:57 PM
Git Commit 是一种命令,将文件变更记录到 Git 存储库中,以保存项目当前状态的快照。使用方法如下:添加变更到暂存区域编写简洁且信息丰富的提交消息保存并退出提交消息以完成提交可选:为提交添加签名使用 git log 查看提交内容
 git怎么合并代码
Apr 17, 2025 pm 04:39 PM
git怎么合并代码
Apr 17, 2025 pm 04:39 PM
Git 代码合并过程:拉取最新更改以避免冲突。切换到要合并的分支。发起合并,指定要合并的分支。解决合并冲突(如有)。暂存和提交合并,提供提交消息。
 git下载不动怎么办
Apr 17, 2025 pm 04:54 PM
git下载不动怎么办
Apr 17, 2025 pm 04:54 PM
解决 Git 下载速度慢时可采取以下步骤:检查网络连接,尝试切换连接方式。优化 Git 配置:增加 POST 缓冲区大小(git config --global http.postBuffer 524288000)、降低低速限制(git config --global http.lowSpeedLimit 1000)。使用 Git 代理(如 git-proxy 或 git-lfs-proxy)。尝试使用不同的 Git 客户端(如 Sourcetree 或 Github Desktop)。检查防火
 git怎么删除仓库
Apr 17, 2025 pm 04:03 PM
git怎么删除仓库
Apr 17, 2025 pm 04:03 PM
要删除 Git 仓库,请执行以下步骤:确认要删除的仓库。本地删除仓库:使用 rm -rf 命令删除其文件夹。远程删除仓库:导航到仓库设置,找到“删除仓库”选项,确认操作。
 如何解决PHP项目中的高效搜索问题?Typesense助你实现!
Apr 17, 2025 pm 08:15 PM
如何解决PHP项目中的高效搜索问题?Typesense助你实现!
Apr 17, 2025 pm 08:15 PM
在开发一个电商网站时,我遇到了一个棘手的问题:如何在大量商品数据中实现高效的搜索功能?传统的数据库搜索效率低下,用户体验不佳。经过一番研究,我发现了Typesense这个搜索引擎,并通过其官方PHP客户端typesense/typesense-php解决了这个问题,大大提升了搜索性能。
 git怎么更新本地代码
Apr 17, 2025 pm 04:48 PM
git怎么更新本地代码
Apr 17, 2025 pm 04:48 PM
如何更新本地 Git 代码?用 git fetch 从远程仓库拉取最新更改。用 git merge origin/<远程分支名称> 将远程变更合并到本地分支。解决因合并产生的冲突。用 git commit -m "Merge branch <远程分支名称>" 提交合并更改,应用更新。






