实例详解Java实现简易版的图书管理系统
本篇文章给大家带来了关于java的相关知识,其中主要整理了实现简易版的图书管理系统的相关问题,包括了分析图书管理系统的功能、在IDEA中进行功能类的创建、进行用户相关的处理等等内容,下面一起来看一下,希望对大家有帮助。

推荐学习:《java视频教程》
1.分析图书管理系统的功能
我们先分析一下,一个图书管理系统应该具备的功能,进行一个简单的框架搭建。
(1)登录
正常情况下图书管理系统只有两种人会使用,一种是学生,一种是图书管理员
这个就是我学校的网上图书馆的登录界面,学生查找书籍通过网络就可以查阅
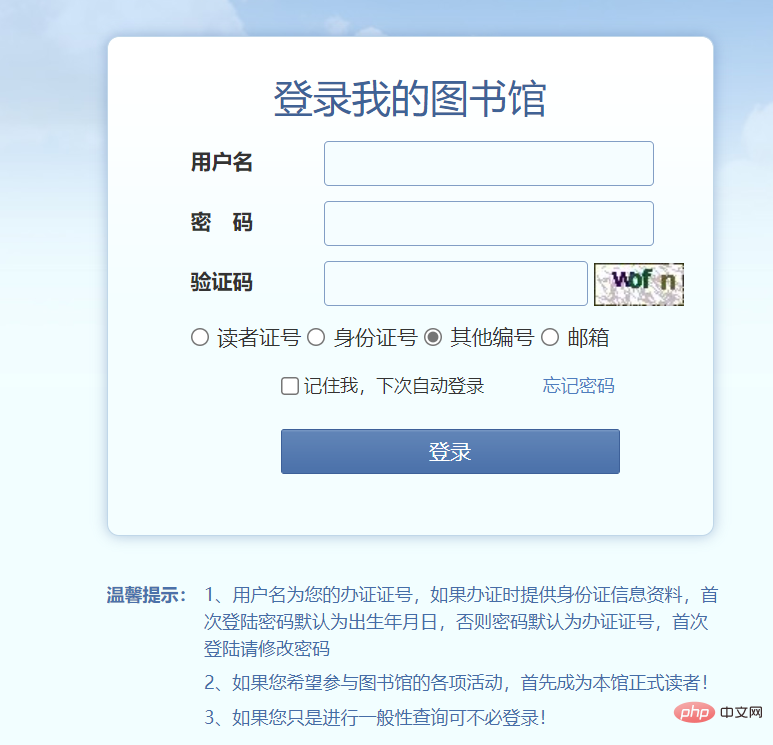
而管理员的登录界面,我这里看不到,但肯定会有后台的管理人员登录的窗口,进行系统维护
所以根据使用人员不同,就要在登录时进行选择,是普通用户还是管理员。
(2)分析功能
简单的图书管理系统应该具备的功能,

2.在IDEA中进行功能类的创建
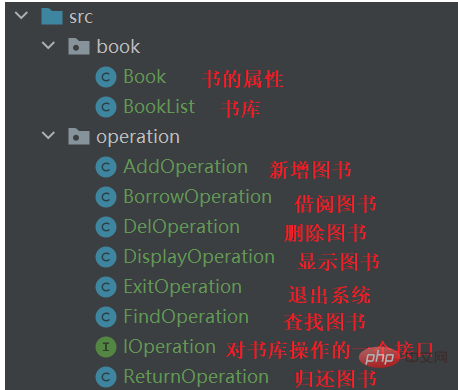
2.1 创建一个名为book的包,里面存放书相关的
(1)创建一个Book的类,来显示书的属性
对一个图书进行查找,应该一本书应该具有这些属性

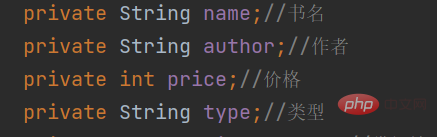
private String name;//书名 private String author;//作者 private int price;//价格 private String type;//类型 private boolean isBorrowed;//借阅情况
注意这里给书提供的控制符都是私有的,在类外是不能访问的
所以要再提供get()和set()对属性进行设置和获取
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getAuthor() {
return author;
}
public void setAuthor(String author) {
this.author = author;
}
public int getPrice() {
return price;
}
public void setPrice(int price) {
this.price = price;
}
public String getType() {
return type;
}
public void setType(String type) {
this.type = type;
}
public boolean isBorrowed() {
return isBorrowed;
}
public void setBorrowed(boolean borrowed) {
isBorrowed = borrowed;
}再给书的属性提供一个构造方法,
这里注意,在构造方法中不给书加isBorrowed,isBorrowed是boolean类型的,默认 false,也就是未被借出去。如果条件一本书,它默认就是没有被借出去
public Book(String name, String author, int price, String type) {
this.name = name;
this.author = author;
this.price = price;
this.type = type;
}最后,再提供一个toString方法来显示书的信息
@Override
public String toString() {
return "BookList{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", author='" + author + '\'' +
", price=" + price +
", type='" + type + '\'' +
", isBorrowed=" + isBorrowed +
'}';
}(2) 创建一个BookList的类,这个就是书库
因为是书库,要存放书,所以设置一个数组来存放书籍
//最多存放20本书 private Book[] books = new Book[20];
再提供一个成员变量,来实时记录当前books数组中书的个数
private int usedSize;//实时记录 当前Books这个数组中有多少本书
下面就可以提供一个构造方法,给里面先存上几本书
public BookList() {
books[0] = new Book("西游记","吴承恩",25,"小说");
books[1] = new Book("红楼梦","曹雪芹",26,"小说");
books[2] = new Book("三国演义","罗贯中",27,"小说");
books[3] = new Book("水浒传","施耐庵",28,"小说");
usedSize = 4;//当前有4本书
}提供一个方法,如果给一个合法的数组下标,就能找到这本书
public Book getBook(int pos) {
return books[pos];
}提供一个方法,给一个合法的数组下标,和一本书,就能存放这本书到书库中
public void setBooks(int pos,Book book) {
books[pos] = book;
}提供一个方法,给一个参数,来实时修改当前书架上的书的个数
public void setUsedSize(int size) {
usedSize = size;
}2.2 创建一个名为Operation的包,里面存放对书的所有操作
(1)创建一个IOperation的接口,实现对数组的操作引用
因为不论是管理员或是普通用户,对书的操作都是在BookList类的数组books中进行操作,

所以可以提供一个IOperation的接口,实现对数组的操作,
public interface IOperation {
/*
* 对书的所有操作都是通过BookList类里面的books数组进行操作
* 可以将这个写成一个接口
**/
void work(BookList bookList);
}(2)创建各种类,来实现对书的所有操作
比如说,普通用户和管理员都要对书进行显示操作,这个显示是一个效果,
所以只需写一个类,普通用户和管理员就都可以调用。
合起来,创建这些类就可以了,

然后就可以对这些类引用接口了,再重写一下
比如新增图书
public class AddOperation implements IOperation {
@Override
public void work(BookList bookList) {
System.out.println("新增图书!");
}
}3.进行用户相关的处理
也就是对普通用户和管理员进行处理
(1)创建一个user的包,在包中创建一个类
这里只创建一个类,是因为对于普通用户和管理员来说,他们两个都是用户
所以创建一个成员变量,来表示用户
//写protected是后面要继承 protected String name;//用户名
下面提供一个构造方法对其初始化
//提供一个构造方法,用来初始化当前对象name属性
public User(String name) {
this.name = name;
}(2)在user包中再创建两个类
子类NormalUser继承父类User,提供一个构造方法来显示帮助父类进行构造
public class NormalUser extends User{
public NormalUser(String name) {
super(name);
}
}子类AdminUser继承父类User和前面一样
下来就是打印菜单了,根据两个用户所需功能进行打印菜单
先看AdminUser管理员的
public int menu() {
System.out.println("hello " + this.name + "欢迎进入图书管理系统!");
System.out.println("1.查找图书!");
System.out.println("2.新增图书!");
System.out.println("3.删除图书!");
System.out.println("4.显示图书!");
System.out.println("0.退出系统!");
System.out.println("请输入你的操作:");
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
int choice = scanner.nextInt();
return choice;
//因为这个是个菜单,所以要把这个输入的值传出去,才能使用
}再看NormalUser普通用户的
System.out.println("hello " + this.name + "欢迎进入图书管理系统!");
System.out.println("1.查找图书!");
System.out.println("2.借阅图书!");
System.out.println("3.归还图书!");
System.out.println("0.退出系统!");
System.out.println("请输入你的操作:");
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
int choice = scanner.nextInt();
return choice;
//因为这个是个菜单,所以要把这个输入的值传出去,才能使用(3)单独创建一个Main的类,将前面所有整合起来
菜单用户都有了,下面就是要把这些都整合起来,
先准备图书
BookList bookList = new BookList();//准备图书
结下来就是登录了,
先写一个判断你是普通用户还是管理员的方法
public static User login() {
System.out.println("请输入你的姓名:");
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
String name = scanner.nextLine();
System.out.println("请输入你的身份:1:-》管理员.0:-》普通用户");
int choice = scanner.nextInt();
if (choice == 1) {
return new AdminUser(name);
}else {
return new NormalUser(name);
}
}注意观察这段代码,返回类型是User,这是因为不论if中返回是AdminUser还是NormalUser,User作为父类都可以接收,这个过程就发生了向上转型
然后再在main方法中引用这个login()方法,就可以实现选择登录了
//登录-》user这个引用 引用哪个对象看前面if User user = login();
选择完你是哪种用户后,就打印对应功能菜单
但是注意,刚刚把菜单写在了对应子类中去了
如果现在要在父类中访问,是访问不了的,所以就要在父类中也引用出菜单
public abstract class User {
//写protected是后面要继承
protected String name;//用户名
//提供一个构造方法,用来初始化当前对象name属性
public User(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public abstract int menu();
}看代码中,只需将父类写成抽象类,然后在抽象类中,引出抽象方法的菜单,
就可以在Main类中通过父类访问到菜单,这就实现了动态绑定
public static void main(String[] args) {
//开始整合
BookList bookList = new BookList();//准备图书
//登录-》user这个引用 引用哪个对象看前面if
User user = login();
user.menu();//动态绑定
//要想访问子类中的菜单,那就要将父类写成抽象类,
//然后子类重写父类的方法,才可以访问菜单
}
}然后此时代码就可以运行了
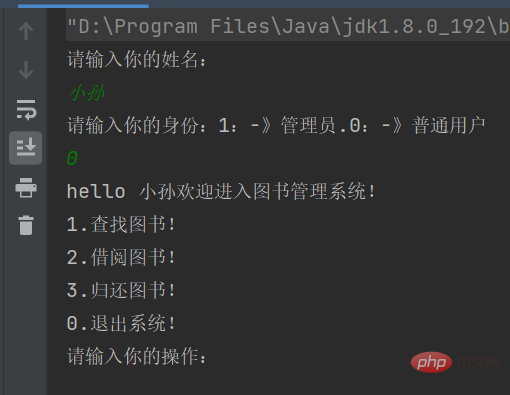
4.开始实现对书所有具体的操作功能
4.1先实现可以调用具体操作的功能方法
先在User中写一个方法,这个方法的作用是
通过某个用户,访问这个用户对应方法功能的数组下标,然后通过调用work方法,来实现功能
public void doOperation(int choice, BookList bookList) {
this.iOperations[choice].work(bookList);
}然后在mian中,通过选择用户引用这个方法
public static void main(String[] args) {
//开始整合
BookList bookList = new BookList();//准备图书
//登录-》user这个引用 引用哪个对象看前面if
User user = login();
int choice = user.menu();//动态绑定
user.doOperation(choice,bookList);
}细节可以看这个图片
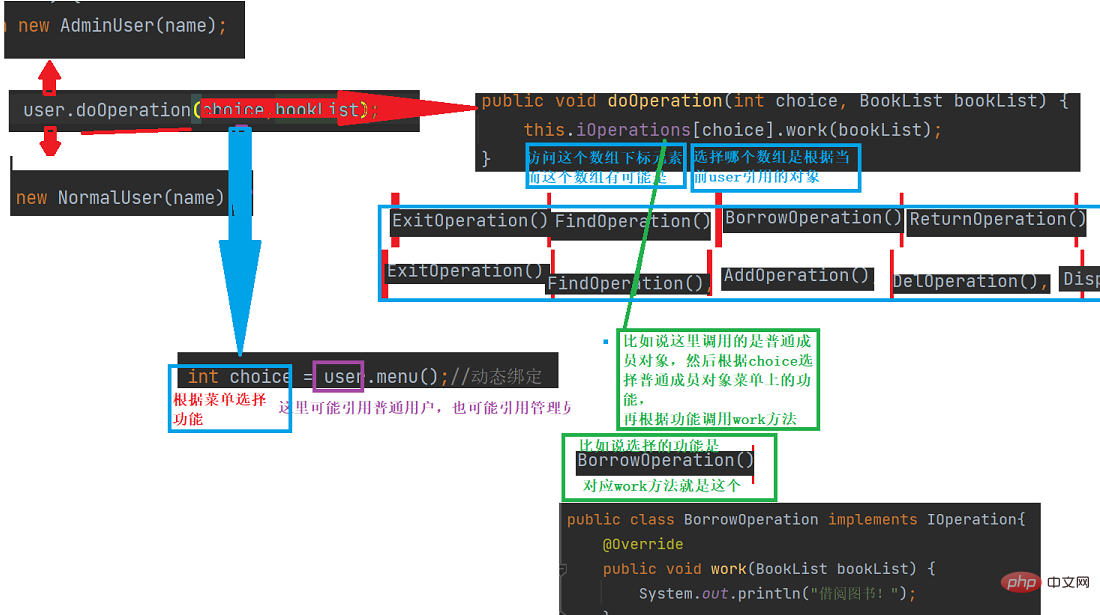
下面来看一下具体细节分析
(1)mian函数先调用
(2)现在user引用,有可能是两个对象
(3)
当引用doOperation时,根据菜单选择来访问数组元素
(4)具体选择哪个用户根据,前面login()中输入的选择对象
(5)根据前面选择需要的功能,调用work方法
比如这个
4.2 测试一下
现在已经整合完成了,就差具体操作功能实现了,先运行代码试试
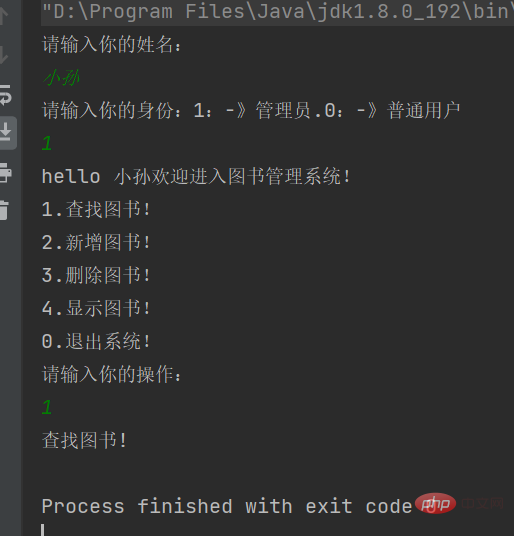
代码成功运行起来了,但是就用了一个功能就结束了,
所以我们可以加一个循环,来使用多个功能
public static void main(String[] args) {
//开始整合
BookList bookList = new BookList();//准备图书
//登录-》user这个引用 引用哪个对象看前面if
User user = login();
while(true){
int choice = user.menu();//动态绑定
user.doOperation(choice,bookList);
}
}4.3 实现单独具体的操作的功能
(1)新增图书 AppOperation类
新增一本图书我们需要考虑输入这些
不用考虑isBorrowed 因为默认状态是未被借出的
将这些属性进行输入
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入图书的名字:");
String name = scanner.nextLine();
System.out.println("请输入图书的作者:");
String author = scanner.nextLine();
System.out.println("请输入图书的价格:");
int price = scanner.nextInt();
System.out.println("请输入图书的类型:");
String type = scanner.nextLine();然后将这些属性存放到new Book中
Book book = new Book(name,author,price,type);
获取当前下标,然后赋给currentSize,将前面输入的那本书放到数组下标为currentSize中,
然后给 currentSize加1
int currentSize = bookList.getUsedSize(); bookList.setBooks(currentSize,book); bookList.getUsedSize(currentSize+1);
运行一下,试试看
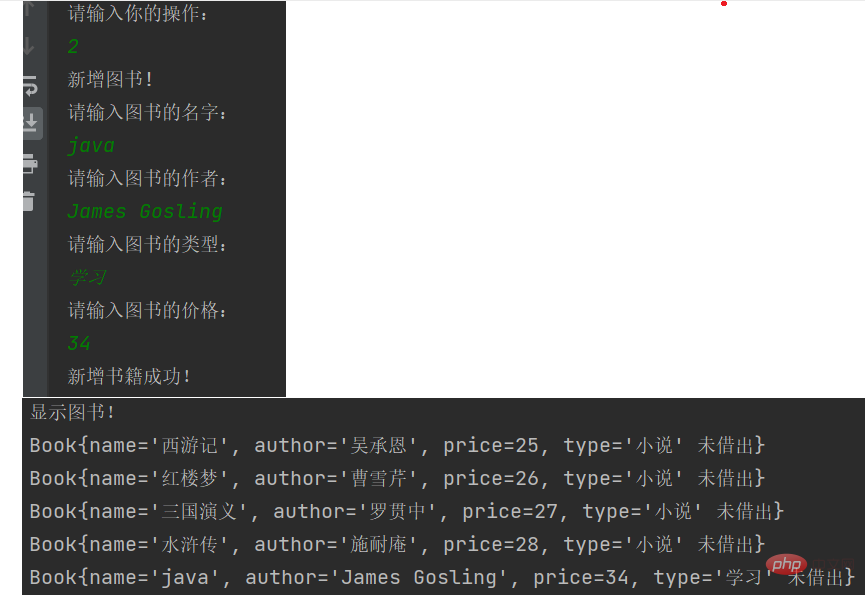
新增图书 AppOperation类的所有代码
public class AddOperation implements IOperation {
@Override
public void work(BookList bookList) {
System.out.println("新增图书!");
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入图书的名字:");
String name = scanner.nextLine();
System.out.println("请输入图书的作者:");
String author = scanner.nextLine();
System.out.println("请输入图书的类型:");
String type = scanner.nextLine();
System.out.println("请输入图书的价格:");
int price = scanner.nextInt();
Book book = new Book(name,author,price,type);
int currentSize = bookList.getUsedSize();
bookList.setBooks(currentSize,book);
bookList.getUsedSize(currentSize+1);
System.out.println("新增书籍成功!");
}
}(2)借阅图书 orrowOperation类
先输入要借阅图书的名字
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入借阅图书的名字:");
String name = scanner.nextLine();通过for循环遍历一遍,然后将遍历的每一本书赋给变量 book ,
再通过equals,来判断book和输入的书的名字是否相同,
如果相同就通过setBorrowed修改此时借阅状态,显示借阅成功
如果不同就显示没有这本书
int currentSize = bookList.getUsedSize();
for (int i = 0; i < currentSize; i++) {
Book book = bookList.getBook(i);
if(book.getName().equals(name)){
book.setBorrowed(true);
System.out.println("借阅成功!");
return;
}
}
System.out.println("没有这本书!");运行一下,试试看

借阅图书 orrowOperation类的所有代码
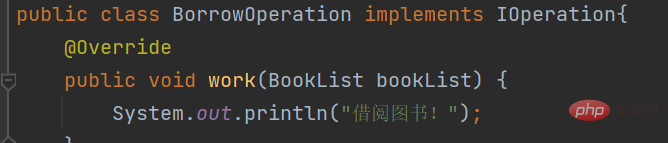
public class BorrowOperation implements IOperation{
@Override
public void work(BookList bookList) {
System.out.println("借阅图书!");
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入借阅图书的名字:");
String name = scanner.nextLine();
int currentSize = bookList.getUsedSize();
for (int i = 0; i < currentSize; i++) {
Book book = bookList.getBook(i);
if(book.getName().equals(name)){
book.setBorrowed(true);
System.out.println("借阅成功!");
return;
}
}
System.out.println("没有这本书!");
}
}(3)删除图书 DelOperation类
输入删除图书的名字
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入删除图书的名字:");
String name = scanner.nextLine();找到图书,然后删除
int currentSize = bookList.getUsedSize();
for (int i = 0; i < currentSize; i++) {
Book book = bookList.getBook(i);
if(book.getName().equals(name)){
for (int j = i; j < currentSize; j++) {
bookList.getBook(j);
}
bookList.getUsedSize(currentSize-1);//不要忘记更新图书种类
bookList.getUsedSize(currentSize-1);
System.out.println("删除成功!");
return;
}
}
System.out.println("没有找到要删除的图书!");运行程序,试试看
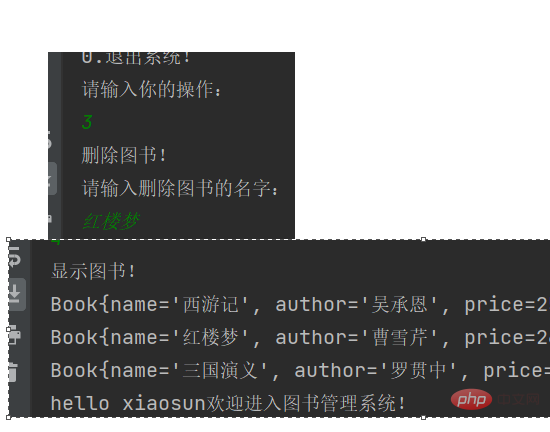
删除图书 DelOperation类的全部代码
public class DelOperation implements IOperation{
@Override
public void work(BookList bookList) {
System.out.println("删除图书!");
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入删除图书的名字:");
String name = scanner.nextLine();
int currentSize = bookList.getUsedSize();
for (int i = 0; i < currentSize; i++) {
Book book = bookList.getBook(i);
if(book.getName().equals(name)){
for (int j = i; j < currentSize; j++) {
bookList.getBook(j);
}
bookList.getUsedSize(currentSize-1);//不要忘记更新图书种类
bookList.getUsedSize(currentSize-1);
System.out.println("删除成功!");
return;
}
}
System.out.println("没有找到要删除的图书!");
}
}(4)显示图书 DisplayOperation类
将当前有几本书记录下来
int currentSize = bookList.getUsedSize();
然后for循环全部遍历一遍就可以了 ,直接看代码吧
public class DisplayOperation implements IOperation{
@Override
public void work(BookList bookList) {
System.out.println("显示图书!");
int currentSize = bookList.getUsedSize();
for (int i = 0; i < currentSize; i++) {
System.out.println(bookList.getBook(i));
}
}
}运行结果就是这样

(5)退出系统 ExitOperation类
直接调用状态码exit来退出系统
public class ExitOperation implements IOperation{
@Override
public void work(BookList bookList) {
System.out.println("退出系统!");
System.exit(0);
}
}
(6)查找图书 FindOperation类
要查找图书,肯定是先要输入你需要查找书的名字
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入图书的名字:");
String name = scanner.nextLine();通过for循环遍历一遍,然后将遍历的每一本书赋给变量 book ,
再通过equals,来判断book和输入的书的名字是否相同,
如果相同就打印,并显示找到了,如果不相同,就直接显示没有找到,
但这里有一个问题在前面给每一本书默认都是false,现在打印还是这样,所以要修改一下
在Book类中,修改toString,给借阅状态一个三目运算符,来判断是否借出了
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Book{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", author='" + author + '\'' +
", price=" + price +
", type='" + type + '\'' +
((isBorrowed == true)?" 已经借出":" 未借出")+
'}';
}运行一下,试试
 查找图书 FindOperation类的全部代码就是
查找图书 FindOperation类的全部代码就是
public class FindOperation implements IOperation{
@Override
public void work(BookList bookList) {
System.out.println("查找图书!");
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入图书的名字:");
String name = scanner.nextLine();
int currentSize = bookList.getUsedSize();
for (int i = 0; i < currentSize; i++) {
Book book = bookList.getBook(i);
if(book.getName().equals(name)){
System.out.println("这本书找到了!");
System.out.println(book);
return;
}
}
System.out.println("这本书没有找到!");
}
}(7)归还图书 ReturnOperation类
先输入要归还图书的名字
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入归还图书的名字:");
String name = scanner.nextLine();和前面借阅基本一样,修改一下setBorrowed的状态就可以了
int currentSize = bookList.getUsedSize();
for (int i = 0; i < currentSize; i++) {
Book book = bookList.getBook(i);
if(book.getName().equals(name)){
book.setBorrowed(false);
System.out.println("归还成功!");
return;
}
}运行代码,试试看
<br>
归还图书 ReturnOperation类的全部代码
public class ReturnOperation implements IOperation{
@Override
public void work(BookList bookList) {
System.out.println("归还图书!");
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入归还图书的名字:");
String name = scanner.nextLine();
int currentSize = bookList.getUsedSize();
for (int i = 0; i < currentSize; i++) {
Book book = bookList.getBook(i);
if(book.getName().equals(name)){
book.setBorrowed(false);
System.out.println("归还成功!");
return;
}
}
}
}推荐学习:《java视频教程》
以上是实例详解Java实现简易版的图书管理系统的详细内容。更多信息请关注PHP中文网其他相关文章!

热AI工具

Undresser.AI Undress
人工智能驱动的应用程序,用于创建逼真的裸体照片

AI Clothes Remover
用于从照片中去除衣服的在线人工智能工具。

Undress AI Tool
免费脱衣服图片

Clothoff.io
AI脱衣机

Video Face Swap
使用我们完全免费的人工智能换脸工具轻松在任何视频中换脸!

热门文章

热工具

记事本++7.3.1
好用且免费的代码编辑器

SublimeText3汉化版
中文版,非常好用

禅工作室 13.0.1
功能强大的PHP集成开发环境

Dreamweaver CS6
视觉化网页开发工具

SublimeText3 Mac版
神级代码编辑软件(SublimeText3)
 突破或从Java 8流返回?
Feb 07, 2025 pm 12:09 PM
突破或从Java 8流返回?
Feb 07, 2025 pm 12:09 PM
Java 8引入了Stream API,提供了一种强大且表达力丰富的处理数据集合的方式。然而,使用Stream时,一个常见问题是:如何从forEach操作中中断或返回? 传统循环允许提前中断或返回,但Stream的forEach方法并不直接支持这种方式。本文将解释原因,并探讨在Stream处理系统中实现提前终止的替代方法。 延伸阅读: Java Stream API改进 理解Stream forEach forEach方法是一个终端操作,它对Stream中的每个元素执行一个操作。它的设计意图是处
 PHP:网络开发的关键语言
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:08 AM
PHP:网络开发的关键语言
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:08 AM
PHP是一种广泛应用于服务器端的脚本语言,特别适合web开发。1.PHP可以嵌入HTML,处理HTTP请求和响应,支持多种数据库。2.PHP用于生成动态网页内容,处理表单数据,访问数据库等,具有强大的社区支持和开源资源。3.PHP是解释型语言,执行过程包括词法分析、语法分析、编译和执行。4.PHP可以与MySQL结合用于用户注册系统等高级应用。5.调试PHP时,可使用error_reporting()和var_dump()等函数。6.优化PHP代码可通过缓存机制、优化数据库查询和使用内置函数。7
 PHP与Python:了解差异
Apr 11, 2025 am 12:15 AM
PHP与Python:了解差异
Apr 11, 2025 am 12:15 AM
PHP和Python各有优势,选择应基于项目需求。1.PHP适合web开发,语法简单,执行效率高。2.Python适用于数据科学和机器学习,语法简洁,库丰富。
 Java程序查找胶囊的体积
Feb 07, 2025 am 11:37 AM
Java程序查找胶囊的体积
Feb 07, 2025 am 11:37 AM
胶囊是一种三维几何图形,由一个圆柱体和两端各一个半球体组成。胶囊的体积可以通过将圆柱体的体积和两端半球体的体积相加来计算。本教程将讨论如何使用不同的方法在Java中计算给定胶囊的体积。 胶囊体积公式 胶囊体积的公式如下: 胶囊体积 = 圆柱体体积 两个半球体体积 其中, r: 半球体的半径。 h: 圆柱体的高度(不包括半球体)。 例子 1 输入 半径 = 5 单位 高度 = 10 单位 输出 体积 = 1570.8 立方单位 解释 使用公式计算体积: 体积 = π × r2 × h (4
 PHP与其他语言:比较
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:19 AM
PHP与其他语言:比较
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:19 AM
PHP适合web开发,特别是在快速开发和处理动态内容方面表现出色,但不擅长数据科学和企业级应用。与Python相比,PHP在web开发中更具优势,但在数据科学领域不如Python;与Java相比,PHP在企业级应用中表现较差,但在web开发中更灵活;与JavaScript相比,PHP在后端开发中更简洁,但在前端开发中不如JavaScript。
 PHP与Python:核心功能
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:16 AM
PHP与Python:核心功能
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:16 AM
PHP和Python各有优势,适合不同场景。1.PHP适用于web开发,提供内置web服务器和丰富函数库。2.Python适合数据科学和机器学习,语法简洁且有强大标准库。选择时应根据项目需求决定。