es6中find()怎么用
在es6中,find()用于通过回调函数查找数组中符合条件的第一个元素的值,语法“array.find(function(...),thisValue)”。find()会为数组中的每个元素都调用一次函数执行,当数组中的元素在测试条件时返回true时,find()返回符合条件的该元素,之后的值不会再调用执行函数;如果没有符合条件的元素返回undefined。
本教程操作环境:windows7系统、ECMAScript 6版、Dell G3电脑。
es6 find()的介绍
find() 方法返回通过测试(函数内判断)的数组的第一个元素的值。
find() 方法为数组中的每个元素都调用一次函数执行:
当数组中的元素在测试条件时返回 true 时, find() 返回符合条件的元素,之后的值不会再调用执行函数。
如果没有符合条件的元素返回 undefined
语法:
array.find(function(currentValue, index, arr),thisValue)
| 参数 | 描述 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| function(currentValue, index,arr) | 必需。数组每个元素需要执行的函数。
| ||||||
| thisValue | 可选。 传递给函数的值一般用 "this" 值。<🎜>如果这个参数为空, "undefined" 会传递给 "this" 值 |
返回值:返回符合测试条件的第一个数组元素值,如果没有符合条件的则返回 undefined。
注意:
find() 对于空数组,函数是不会执行的。
find() 并没有改变数组的原始值。
基本使用
Array.prototype.find
返回第一个满足条件的数组元素
const arr = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5];
const item = arr.find(function (item) {
return item > 3;
});
console.log(item);//4如果没有一个元素满足条件 返回undefined
const arr = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5];
const item = arr.find(function (item) {
return item > 5;
});
console.log(item); //undefined返回的元素和数组对应下标的元素是同一个引用
const arr = [
{
id: 1,
name: '张三',
},
{
id: 2,
name: '李四',
},
{
id: 3,
name: '王五',
},
];
const item = arr.find((item) => item.name === '李四');
console.log(item);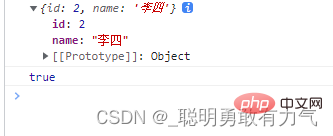
回调函数的返回值是boolean 第一个返回true的对应数组元素作为find的返回值
const arr = [
{
id: 1,
name: '张三',
},
{
id: 2,
name: '李四',
},
{
id: 3,
name: '王五',
},
];
const item = arr.find(function (item) {
return item.id > 1;
});
console.log(item);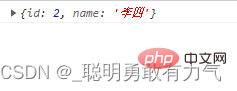
回调的参数
当前遍历的元素 当前遍历出的元素对应的下标 当前的数组
const arr = [
{
id: 1,
name: '张三',
},
{
id: 2,
name: '李四',
},
{
id: 3,
name: '王五',
},
];
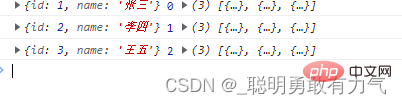
const item = arr.find(function (item, index, arr) {
console.log(item, index, arr);
});
find的第二个参数
更改回调函数内部的this指向
const arr = [
{
id: 1,
name: '张三',
},
{
id: 2,
name: '李四',
},
{
id: 3,
name: '王五',
},
];
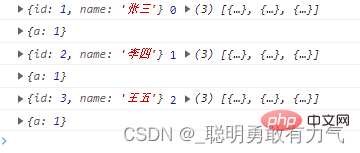
const item = arr.find(
function (item, index, arr) {
console.log(item, index, arr);
console.log(this);
},
{ a: 1 }
);
如果没有第二个参数
非严格模式下 this -> window
const arr = [
{
id: 1,
name: '张三',
},
{
id: 2,
name: '李四',
},
{
id: 3,
name: '王五',
},
];
const item = arr.find(function (item, index, arr) {
console.log(item, index, arr);
console.log(this);
});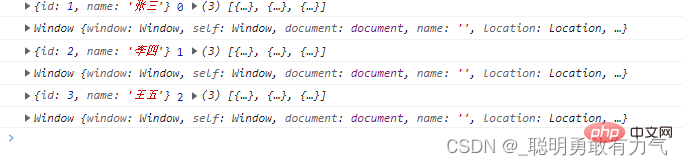
在严格模式下
不传入第二个参数 this为undefined 与严格模式规定相同
'use strict';
const arr = [
{
id: 1,
name: '张三',
},
{
id: 2,
name: '李四',
},
{
id: 3,
name: '王五',
},
];
const item = arr.find(function (item, index, arr) {
console.log(item, index, arr);
console.log(this);
});
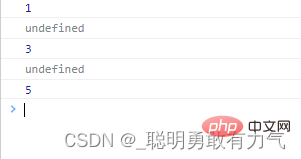
稀疏数组find
find会遍历稀疏数组的空隙 empty
具体遍历出的值 由undefined占位
const arr = Array(5);
arr[0] = 1;
arr[2] = 3;
arr[4] = 5;
const item = arr.find(function (item) {
console.log(item);
return false;
});
而ES5数组扩展方法forEach,map,filter,reduce,reduceRight,every,some 只会遍历有值的数组
find的遍历效率是低于ES5数组扩展方法的
find不会更改数组
虽然新增了元素 但是find会在第一次执行回调函数的时候 拿到这个数组最初的索引范围
const arr = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5];
const item = arr.find(function (item) {
arr.push(6);
console.log(item);
});
console.log(arr);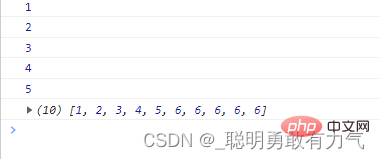
const arr = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5];
const item = arr.find(function (item) {
arr.splice(1, 1);
console.log(item);
});
console.log(arr);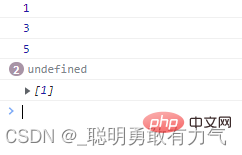
splice 删除对应项 该项位置不保留 在数据最后补上undefined
const arr = [1, 2, 3, , , , 7, 8, 9];
arr.find(function (item, index) {
if (index === 0) {
arr.splice(1, 1);
}
console.log(item);
});
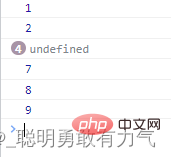
delete
删除该项的值 并填入undefined
const arr = [1, 2, 3, , , , 7, 8, 9];
arr.find(function (item, index) {
if (index === 0) {
delete arr[2];
}
console.log(item);
});
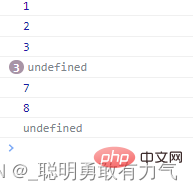
pop
删除该项的值 并填入undefined
const arr = [1, 2, 3, , , , 7, 8, 9];
arr.find(function (item, index) {
if (index === 0) {
arr.pop();
}
console.log(item);
});
创建myFind
Array.prototype.myFind = function (cb) {
if (this === null) {
throw new TypeError('"this" is null');
}
if (typeof cb !== 'function') {
throw new TypeError('Callback must be a function type');
}
var obj = Object(this),
len = obj.length >>> 0,
arg2 = arguments[1],
step = 0;
while (step < len) {
var value = obj[step];
if (cb.apply(arg2, [value, step, obj])) {
return value;
}
}
step++;
return undefined;
};【相关推荐:javascript视频教程、编程视频】
以上是es6中find()怎么用的详细内容。更多信息请关注PHP中文网其他相关文章!

热AI工具

Undresser.AI Undress
人工智能驱动的应用程序,用于创建逼真的裸体照片

AI Clothes Remover
用于从照片中去除衣服的在线人工智能工具。

Undress AI Tool
免费脱衣服图片

Clothoff.io
AI脱衣机

AI Hentai Generator
免费生成ai无尽的。

热门文章

热工具

记事本++7.3.1
好用且免费的代码编辑器

SublimeText3汉化版
中文版,非常好用

禅工作室 13.0.1
功能强大的PHP集成开发环境

Dreamweaver CS6
视觉化网页开发工具

SublimeText3 Mac版
神级代码编辑软件(SublimeText3)

热门话题
 如何使用WebSocket和JavaScript实现在线语音识别系统
Dec 17, 2023 pm 02:54 PM
如何使用WebSocket和JavaScript实现在线语音识别系统
Dec 17, 2023 pm 02:54 PM
如何使用WebSocket和JavaScript实现在线语音识别系统引言:随着科技的不断发展,语音识别技术已经成为了人工智能领域的重要组成部分。而基于WebSocket和JavaScript实现的在线语音识别系统,具备了低延迟、实时性和跨平台的特点,成为了一种被广泛应用的解决方案。本文将介绍如何使用WebSocket和JavaScript来实现在线语音识别系
 WebSocket与JavaScript:实现实时监控系统的关键技术
Dec 17, 2023 pm 05:30 PM
WebSocket与JavaScript:实现实时监控系统的关键技术
Dec 17, 2023 pm 05:30 PM
WebSocket与JavaScript:实现实时监控系统的关键技术引言:随着互联网技术的快速发展,实时监控系统在各个领域中得到了广泛的应用。而实现实时监控的关键技术之一就是WebSocket与JavaScript的结合使用。本文将介绍WebSocket与JavaScript在实时监控系统中的应用,并给出代码示例,详细解释其实现原理。一、WebSocket技
 如何利用JavaScript和WebSocket实现实时在线点餐系统
Dec 17, 2023 pm 12:09 PM
如何利用JavaScript和WebSocket实现实时在线点餐系统
Dec 17, 2023 pm 12:09 PM
如何利用JavaScript和WebSocket实现实时在线点餐系统介绍:随着互联网的普及和技术的进步,越来越多的餐厅开始提供在线点餐服务。为了实现实时在线点餐系统,我们可以利用JavaScript和WebSocket技术。WebSocket是一种基于TCP协议的全双工通信协议,可以实现客户端与服务器的实时双向通信。在实时在线点餐系统中,当用户选择菜品并下单
 如何使用WebSocket和JavaScript实现在线预约系统
Dec 17, 2023 am 09:39 AM
如何使用WebSocket和JavaScript实现在线预约系统
Dec 17, 2023 am 09:39 AM
如何使用WebSocket和JavaScript实现在线预约系统在当今数字化的时代,越来越多的业务和服务都需要提供在线预约功能。而实现一个高效、实时的在线预约系统是至关重要的。本文将介绍如何使用WebSocket和JavaScript来实现一个在线预约系统,并提供具体的代码示例。一、什么是WebSocketWebSocket是一种在单个TCP连接上进行全双工
 JavaScript和WebSocket:打造高效的实时天气预报系统
Dec 17, 2023 pm 05:13 PM
JavaScript和WebSocket:打造高效的实时天气预报系统
Dec 17, 2023 pm 05:13 PM
JavaScript和WebSocket:打造高效的实时天气预报系统引言:如今,天气预报的准确性对于日常生活以及决策制定具有重要意义。随着技术的发展,我们可以通过实时获取天气数据来提供更准确可靠的天气预报。在本文中,我们将学习如何使用JavaScript和WebSocket技术,来构建一个高效的实时天气预报系统。本文将通过具体的代码示例来展示实现的过程。We
 简易JavaScript教程:获取HTTP状态码的方法
Jan 05, 2024 pm 06:08 PM
简易JavaScript教程:获取HTTP状态码的方法
Jan 05, 2024 pm 06:08 PM
JavaScript教程:如何获取HTTP状态码,需要具体代码示例前言:在Web开发中,经常会涉及到与服务器进行数据交互的场景。在与服务器进行通信时,我们经常需要获取返回的HTTP状态码来判断操作是否成功,根据不同的状态码来进行相应的处理。本篇文章将教你如何使用JavaScript获取HTTP状态码,并提供一些实用的代码示例。使用XMLHttpRequest
 javascript中如何使用insertBefore
Nov 24, 2023 am 11:56 AM
javascript中如何使用insertBefore
Nov 24, 2023 am 11:56 AM
用法:在JavaScript中,insertBefore()方法用于在DOM树中插入一个新的节点。这个方法需要两个参数:要插入的新节点和参考节点(即新节点将要被插入的位置的节点)。
 如何在JavaScript中获取HTTP状态码的简单方法
Jan 05, 2024 pm 01:37 PM
如何在JavaScript中获取HTTP状态码的简单方法
Jan 05, 2024 pm 01:37 PM
JavaScript中的HTTP状态码获取方法简介:在进行前端开发中,我们常常需要处理与后端接口的交互,而HTTP状态码就是其中非常重要的一部分。了解和获取HTTP状态码有助于我们更好地处理接口返回的数据。本文将介绍使用JavaScript获取HTTP状态码的方法,并提供具体代码示例。一、什么是HTTP状态码HTTP状态码是指当浏览器向服务器发起请求时,服务






