vue怎么判断元素是否在可视区域
三种方法:1、利用offsetTop和scrollTop获取元素的位置,判断是否小于等于viewPortHeight(视图端口距离)即可。2、利用getBoundingClientRect()判断,语法“元素对象.getBoundingClientRect()”。3、利用IntersectionObserver判断,只需要检查指定元素和可视区域是否重叠即可。

本教程操作环境:windows7系统、vue3版,DELL G3电脑。
可视区域是什么
可视区域即我们浏览网页的设备肉眼可见的区域,如下图
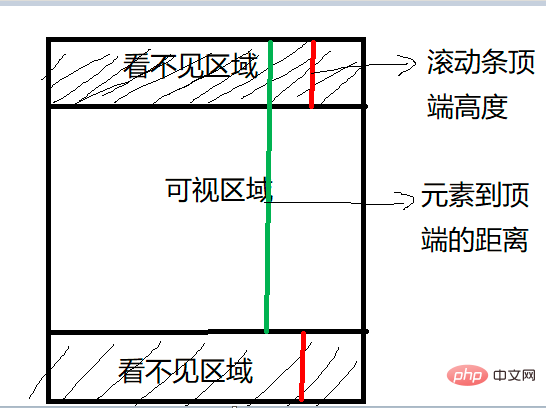
在日常开发中,我们经常需要判断目标元素是否在视窗之内或者和视窗的距离小于一个值(例如 100 px),从而实现一些常用的功能,例如:
- 图片的懒加载
- 列表的无限滚动
- 计算广告元素的曝光情况
- 可点击链接的预加载
判断元素是否在可视区域的三种方式
判断一个元素是否在可视区域,我们常用的有三种办法:
offsetTop、scrollTop
getBoundingClientRect
Intersection Observer
方法1、offsetTop、scrollTop
offsetTop,元素的上外边框至包含元素的上内边框之间的像素距离,其他offset属性如下图所示:
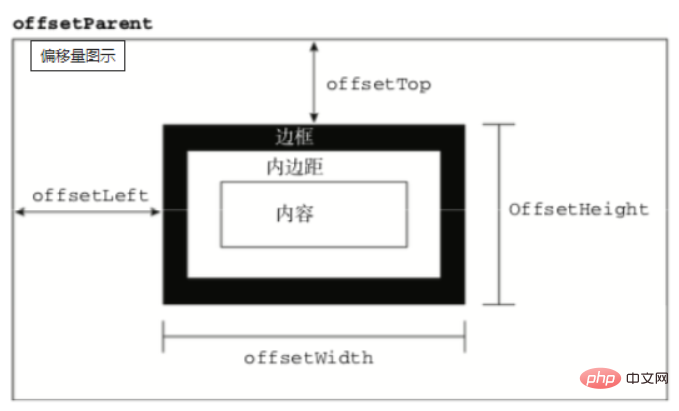
下面再来了解下clientWidth、clientHeight:
-
clientWidth:元素内容区宽度加上左右内边距宽度,即clientWidth = content + padding -
clientHeight:元素内容区高度加上上下内边距高度,即clientHeight = content + padding
这里可以看到client元素都不包括外边距
最后,关于scroll系列的属性如下:
scrollWidth和scrollHeight主要用于确定元素内容的实际大小scrollLeft和scrollTop属性既可以确定元素当前滚动的状态,也可以设置元素的滚动位置- 垂直滚动
scrollTop > 0 - 水平滚动
scrollLeft > 0
- 垂直滚动
将元素的
scrollLeft和scrollTop设置为 0,可以重置元素的滚动位置
注意
- 上述属性都是只读的,每次访问都要重新开始
下面再看看如何实现判断:
公式如下:
el.offsetTop - document.documentElement.scrollTop <= viewPortHeight
代码实现:
function isInViewPortOfOne (el) {
// viewPortHeight 兼容所有浏览器写法
const viewPortHeight = window.innerHeight || document.documentElement.clientHeight || document.body.clientHeight
const offsetTop = el.offsetTop
const scrollTop = document.documentElement.scrollTop
const top = offsetTop - scrollTop
return top <= viewPortHeight
}方法2:getBoundingClientRect
返回值是一个 DOMRect对象,拥有left, top, right, bottom, x, y, width, 和 height属性。【学习视频分享:vue视频教程、web前端视频】
const target = document.querySelector('.target');
const clientRect = target.getBoundingClientRect();
console.log(clientRect);
// {
// bottom: 556.21875,
// height: 393.59375,
// left: 333,
// right: 1017,
// top: 162.625,
// width: 684
// }属性对应的关系图如下所示:
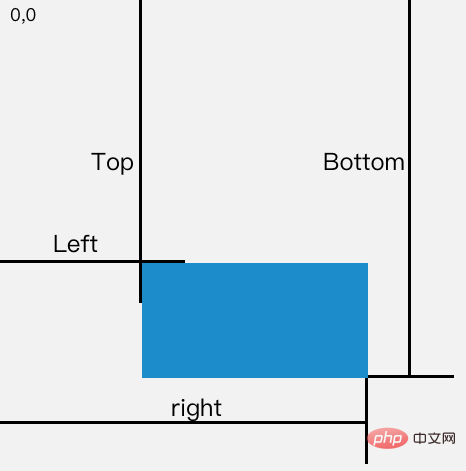
当页面发生滚动的时候,top与left属性值都会随之改变
如果一个元素在视窗之内的话,那么它一定满足下面四个条件:
- top 大于等于 0
- left 大于等于 0
- bottom 小于等于视窗高度
- right 小于等于视窗宽度
实现代码如下:
function isInViewPort(element) {
const viewWidth = window.innerWidth || document.documentElement.clientWidth;
const viewHeight = window.innerHeight || document.documentElement.clientHeight;
const {
top,
right,
bottom,
left,
} = element.getBoundingClientRect();
return (
top >= 0 &&
left >= 0 &&
right <= viewWidth &&
bottom <= viewHeight
);
}方法3:Intersection Observer
Intersection Observer 即重叠观察者,从这个命名就可以看出它用于判断两个元素是否重叠,因为不用进行事件的监听,性能方面相比getBoundingClientRect会好很多
使用步骤主要分为两步:创建观察者和传入被观察者
创建观察者
const options = {
// 表示重叠面积占被观察者的比例,从 0 - 1 取值,
// 1 表示完全被包含
threshold: 1.0,
root:document.querySelector('#scrollArea') // 必须是目标元素的父级元素
};
const callback = (entries, observer) => { ....}
const observer = new IntersectionObserver(callback, options);通过new IntersectionObserver创建了观察者 observer,传入的参数 callback 在重叠比例超过 threshold 时会被执行`
关于callback回调函数常用属性如下:
// 上段代码中被省略的 callback
const callback = function(entries, observer) {
entries.forEach(entry => {
entry.time; // 触发的时间
entry.rootBounds; // 根元素的位置矩形,这种情况下为视窗位置
entry.boundingClientRect; // 被观察者的位置举行
entry.intersectionRect; // 重叠区域的位置矩形
entry.intersectionRatio; // 重叠区域占被观察者面积的比例(被观察者不是矩形时也按照矩形计算)
entry.target; // 被观察者
});
};通过 observer.observe(target) 这一行代码即可简单的注册被观察者
const target = document.querySelector('.target'); observer.observe(target);
案例分析
实现:创建了一个十万个节点的长列表,当节点滚入到视窗中时,背景就会从红色变为黄色
Html结构如下:
<div class="container"></div>
css样式如下:
.container {
display: flex;
flex-wrap: wrap;
}
.target {
margin: 5px;
width: 20px;
height: 20px;
background: red;
}往container插入1000个元素
const $container = $(".container");
// 插入 100000 个 <div class="target"></div>
function createTargets() {
const htmlString = new Array(100000)
.fill('<div class="target"></div>')
.join("");
$container.html(htmlString);
}这里,首先使用getBoundingClientRect方法进行判断元素是否在可视区域
function isInViewPort(element) {
const viewWidth = window.innerWidth || document.documentElement.clientWidth;
const viewHeight =
window.innerHeight || document.documentElement.clientHeight;
const { top, right, bottom, left } = element.getBoundingClientRect();
return top >= 0 && left >= 0 && right <= viewWidth && bottom <= viewHeight;
}然后开始监听scroll事件,判断页面上哪些元素在可视区域中,如果在可视区域中则将背景颜色设置为yellow
$(window).on("scroll", () => {
console.log("scroll !");
$targets.each((index, element) => {
if (isInViewPort(element)) {
$(element).css("background-color", "yellow");
}
});
});通过上述方式,可以看到可视区域颜色会变成黄色了,但是可以明显看到有卡顿的现象,原因在于我们绑定了scroll事件,scroll事件伴随了大量的计算,会造成资源方面的浪费
下面通过Intersection Observer的形式同样实现相同的功能
首先创建一个观察者
const observer = new IntersectionObserver(getYellow, { threshold: 1.0 });getYellow回调函数实现对背景颜色改变,如下:
function getYellow(entries, observer) {
entries.forEach(entry => {
$(entry.target).css("background-color", "yellow");
});
}最后传入观察者,即.target元素
$targets.each((index, element) => {
observer.observe(element);
});以上是vue怎么判断元素是否在可视区域的详细内容。更多信息请关注PHP中文网其他相关文章!

热AI工具

Undresser.AI Undress
人工智能驱动的应用程序,用于创建逼真的裸体照片

AI Clothes Remover
用于从照片中去除衣服的在线人工智能工具。

Undress AI Tool
免费脱衣服图片

Clothoff.io
AI脱衣机

Video Face Swap
使用我们完全免费的人工智能换脸工具轻松在任何视频中换脸!

热门文章

热工具

记事本++7.3.1
好用且免费的代码编辑器

SublimeText3汉化版
中文版,非常好用

禅工作室 13.0.1
功能强大的PHP集成开发环境

Dreamweaver CS6
视觉化网页开发工具

SublimeText3 Mac版
神级代码编辑软件(SublimeText3)

热门话题
 7654
7654
 15
15
 1393
1393
 52
52
 91
91
 11
11
 73
73
 19
19
 37
37
 110
110
 vue.js vs.反应:特定于项目的考虑因素
Apr 09, 2025 am 12:01 AM
vue.js vs.反应:特定于项目的考虑因素
Apr 09, 2025 am 12:01 AM
Vue.js适合中小型项目和快速迭代,React适用于大型复杂应用。1)Vue.js易于上手,适用于团队经验不足或项目规模较小的情况。2)React的生态系统更丰富,适合有高性能需求和复杂功能需求的项目。
 vue中怎么用bootstrap
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:33 PM
vue中怎么用bootstrap
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:33 PM
在 Vue.js 中使用 Bootstrap 分为五个步骤:安装 Bootstrap。在 main.js 中导入 Bootstrap。直接在模板中使用 Bootstrap 组件。可选:自定义样式。可选:使用插件。
 vue怎么给按钮添加函数
Apr 08, 2025 am 08:51 AM
vue怎么给按钮添加函数
Apr 08, 2025 am 08:51 AM
可以通过以下步骤为 Vue 按钮添加函数:将 HTML 模板中的按钮绑定到一个方法。在 Vue 实例中定义该方法并编写函数逻辑。
 vue中的watch怎么用
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:36 PM
vue中的watch怎么用
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:36 PM
Vue.js 中的 watch 选项允许开发者监听特定数据的变化。当数据发生变化时,watch 会触发一个回调函数,用于执行更新视图或其他任务。其配置选项包括 immediate,用于指定是否立即执行回调,以及 deep,用于指定是否递归监听对象或数组的更改。
 vue多页面开发是啥意思
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:57 PM
vue多页面开发是啥意思
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:57 PM
Vue 多页面开发是一种使用 Vue.js 框架构建应用程序的方法,其中应用程序被划分为独立的页面:代码维护性:将应用程序拆分为多个页面可以使代码更易于管理和维护。模块化:每个页面都可以作为独立的模块,便于重用和替换。路由简单:页面之间的导航可以通过简单的路由配置来管理。SEO 优化:每个页面都有自己的 URL,这有助于搜索引擎优化。
 vue返回上一页的方法
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:30 PM
vue返回上一页的方法
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:30 PM
Vue.js 返回上一页有四种方法:$router.go(-1)$router.back()使用 <router-link to="/"> 组件window.history.back(),方法选择取决于场景。
 vue遍历怎么用
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:48 PM
vue遍历怎么用
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:48 PM
Vue.js 遍历数组和对象有三种常见方法:v-for 指令用于遍历每个元素并渲染模板;v-bind 指令可与 v-for 一起使用,为每个元素动态设置属性值;.map 方法可将数组元素转换为新数组。
 vue怎么a标签跳转
Apr 08, 2025 am 09:24 AM
vue怎么a标签跳转
Apr 08, 2025 am 09:24 AM
实现 Vue 中 a 标签跳转的方法包括:HTML 模板中使用 a 标签指定 href 属性。使用 Vue 路由的 router-link 组件。使用 JavaScript 的 this.$router.push() 方法。可通过 query 参数传递参数,并在 router 选项中配置路由以进行动态跳转。




