涨知识!用逻辑规则进行机器学习
在准确率-召回率曲线上,同样的点是用不同的坐标轴绘制的。警告:左边的第一个红点(0%召回率,100%精度)对应于0条规则。左边的第二个点是第一个规则,等等。
Skope-rules使用树模型生成规则候选项。首先建立一些决策树,并将从根节点到内部节点或叶子节点的路径视为规则候选项。然后通过一些预定义的标准(如精确度和召回率)对这些候选规则进行过滤。只有那些精确度和召回率高于其阈值的才会被保留。最后,应用相似性过滤来选择具有足够多样性的规则。一般情况下,应用Skope-rules来学习每个根本原因的潜在规则。
项目地址:https://github.com/scikit-learn-contrib/skope-rules
- Skope-rules是一个建立在scikit-learn之上的Python机器学习模块,在3条款BSD许可下发布。
- Skope-rules旨在学习逻辑的、可解释的规则,用于 "界定 "目标类别,即高精度地检测该类别的实例。
- Skope-rules是决策树的可解释性和随机森林的建模能力之间的一种权衡。
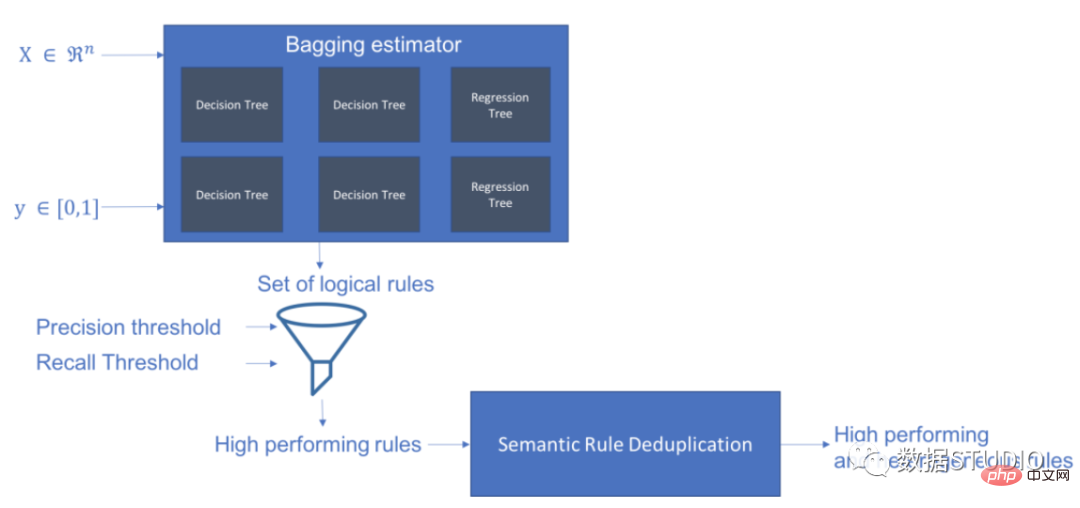
schema
安装
可以使用 pip 获取最新资源:
pip install skope-rules
快速开始
SkopeRules 可用于描述具有逻辑规则的类:
from sklearn.datasets import load_iris
from skrules import SkopeRules
dataset = load_iris()
feature_names = ['sepal_length', 'sepal_width', 'petal_length', 'petal_width']
clf = SkopeRules(max_depth_duplicatinotallow=2,
n_estimators=30,
precision_min=0.3,
recall_min=0.1,
feature_names=feature_names)
for idx, species in enumerate(dataset.target_names):
X, y = dataset.data, dataset.target
clf.fit(X, y == idx)
rules = clf.rules_[0:3]
print("Rules for iris", species)
for rule in rules:
print(rule)
print()
print(20*'=')
print()

注意:
如果出现如下错误:

解决方案:
关于 Python 导入错误 : cannot import name 'six' from 'sklearn.externals' ,云朵君在Stack Overflow上找到一个类似的问题:https://stackoverflow.com/questions/61867945/
解决方案如下
import six
import sys
sys.modules['sklearn.externals.six'] = six
import mlrose
亲测有效!
如果使用“score_top_rules”方法,SkopeRules 也可以用作预测器:
from sklearn.datasets import load_boston
from sklearn.metrics import precision_recall_curve
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
from skrules import SkopeRules
dataset = load_boston()
clf = SkopeRules(max_depth_duplicatinotallow=None,
n_estimators=30,
precision_min=0.2,
recall_min=0.01,
feature_names=dataset.feature_names)
X, y = dataset.data, dataset.target > 25
X_train, y_train = X[:len(y)//2], y[:len(y)//2]
X_test, y_test = X[len(y)//2:], y[len(y)//2:]
clf.fit(X_train, y_train)
y_score = clf.score_top_rules(X_test) # Get a risk score for each test example
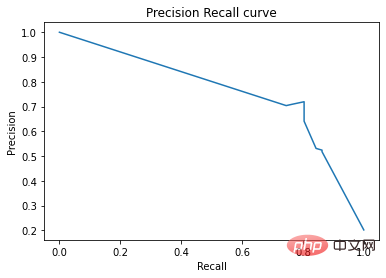
precision, recall, _ = precision_recall_curve(y_test, y_score)
plt.plot(recall, precision)
plt.xlabel('Recall')
plt.ylabel('Precision')
plt.title('Precision Recall curve')
plt.show()
实战案例
本案例展示了在著名的泰坦尼克号数据集上使用skope-rules。
skope-rules适用情况:
- 解决二分类问题
- 提取可解释的决策规则
本案例分为5个部分
- 导入相关库
- 数据准备
- 模型训练(使用ScopeRules().score_top_rules()方法)
- 解释 "生存规则"(使用SkopeRules().rules_属性)。
- 性能分析(使用SkopeRules.predict_top_rules()方法)。
导入相关库
# Import skope-rules
from skrules import SkopeRules
# Import librairies
import pandas as pd
from sklearn.ensemble import GradientBoostingClassifier, RandomForestClassifier
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeClassifier
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn.metrics import roc_curve, precision_recall_curve
from matplotlib import cm
import numpy as np
from sklearn.metrics import confusion_matrix
from IPython.display import display
# Import Titanic data
data = pd.read_csv('../data/titanic-train.csv')
数据准备
# 删除年龄缺失的行
data = data.query('Age == Age')
# 为变量Sex创建编码值
data['isFemale'] = (data['Sex'] == 'female') * 1
# 未变量Embarked创建编码值
data = pd.concat(
[data,
pd.get_dummies(data.loc[:,'Embarked'],
dummy_na=False,
prefix='Embarked',
prefix_sep='_')],
axis=1
)
# 删除没有使用的变量
data = data.drop(['Name', 'Ticket', 'Cabin',
'PassengerId', 'Sex', 'Embarked'],
axis = 1)
# 创建训练及测试集
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(
data.drop(['Survived'], axis=1),
data['Survived'],
test_size=0.25, random_state=42)
feature_names = X_train.columns
print('Column names are: ' + ' '.join(feature_names.tolist())+'.')
print('Shape of training set is: ' + str(X_train.shape) + '.')
Column names are: Pclass Age SibSp Parch Fare
isFemale Embarked_C Embarked_Q Embarked_S.
Shape of training set is: (535, 9).
模型训练
# 训练一个梯度提升分类器,用于基准测试
gradient_boost_clf = GradientBoostingClassifier(random_state=42, n_estimators=30, max_depth = 5)
gradient_boost_clf.fit(X_train, y_train)
# 训练一个随机森林分类器,用于基准测试
random_forest_clf = RandomForestClassifier(random_state=42, n_estimators=30, max_depth = 5)
random_forest_clf.fit(X_train, y_train)
# 训练一个决策树分类器,用于基准测试
decision_tree_clf = DecisionTreeClassifier(random_state=42, max_depth = 5)
decision_tree_clf.fit(X_train, y_train)
# 训练一个 skope-rules-boosting 分类器
skope_rules_clf = SkopeRules(feature_names=feature_names, random_state=42, n_estimators=30,
recall_min=0.05, precision_min=0.9,
max_samples=0.7,
max_depth_duplicatinotallow= 4, max_depth = 5)
skope_rules_clf.fit(X_train, y_train)
# 计算预测分数
gradient_boost_scoring = gradient_boost_clf.predict_proba(X_test)[:, 1]
random_forest_scoring = random_forest_clf.predict_proba(X_test)[:, 1]
decision_tree_scoring = decision_tree_clf.predict_proba(X_test)[:, 1]
skope_rules_scoring = skope_rules_clf.score_top_rules(X_test)
"生存规则" 的提取
# 获得创建的生存规则的数量
print("用SkopeRules建立了" + str(len(skope_rules_clf.rules_)) + "条规则n")
# 打印这些规则
rules_explanations = [
"3岁以下和37岁以下,在头等舱或二等舱的女性。"
"3岁以上乘坐头等舱或二等舱,支付超过26欧元的女性。"
"坐一等舱或二等舱,支付超过29欧元的女性。"
"年龄在39岁以上,在头等舱或二等舱的女性。"
]
print('其中表现最好的4条 "泰坦尼克号生存规则" 如下所示:/n')
for i_rule, rule in enumerate(skope_rules_clf.rules_[:4])
print(rule[0])
print('->'+rules_explanations[i_rule]+ 'n')
用SkopeRules建立了9条规则。
其中表现最好的4条 "泰坦尼克号生存规则" 如下所示:
Age <= 37.0 and Age > 2.5
and Pclass <= 2.5 and isFemale > 0.5
-> 3岁以下和37岁以下,在头等舱或二等舱的女性。
Age > 2.5 and Fare > 26.125
and Pclass <= 2.5 and isFemale > 0.5
-> 3岁以上乘坐头等舱或二等舱,支付超过26欧元的女性。
Fare > 29.356250762939453
and Pclass <= 2.5 and isFemale > 0.5
-> 坐一等舱或二等舱,支付超过29欧元的女性。
Age > 38.5 and Pclass <= 2.5
and isFemale > 0.5
-> 年龄在39岁以上,在头等舱或二等舱的女性。
def compute_y_pred_from_query(X, rule):
score = np.zeros(X.shape[0])
X = X.reset_index(drop=True)
score[list(X.query(rule).index)] = 1
return(score)
def compute_performances_from_y_pred(y_true, y_pred, index_name='default_index'):
df = pd.DataFrame(data=
{
'precision':[sum(y_true * y_pred)/sum(y_pred)],
'recall':[sum(y_true * y_pred)/sum(y_true)]
},
index=[index_name],
columns=['precision', 'recall']
)
return(df)
def compute_train_test_query_performances(X_train, y_train, X_test, y_test, rule):
y_train_pred = compute_y_pred_from_query(X_train, rule)
y_test_pred = compute_y_pred_from_query(X_test, rule)
performances = None
performances = pd.concat([
performances,
compute_performances_from_y_pred(y_train, y_train_pred, 'train_set')],
axis=0)
performances = pd.concat([
performances,
compute_performances_from_y_pred(y_test, y_test_pred, 'test_set')],
axis=0)
return(performances)
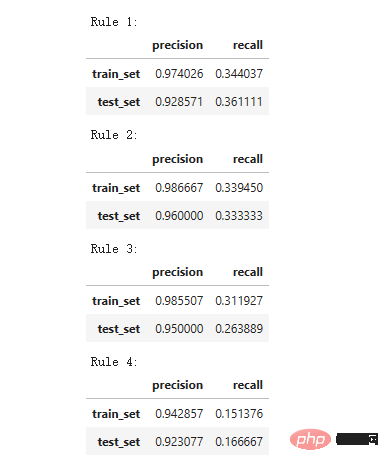
print('Precision = 0.96 表示规则确定的96%的人是幸存者。')
print('Recall = 0.12 表示规则识别的幸存者占幸存者总数的12%n')
for i in range(4):
print('Rule '+str(i+1)+':')
display(compute_train_test_query_performances(X_train, y_train,
X_test, y_test,
skope_rules_clf.rules_[i][0])
)
Precision = 0.96 表示规则确定的96%的人是幸存者。
Recall = 0.12 表示规则识别的幸存者占幸存者总数的12%。
模型性能检测
def plot_titanic_scores(y_true, scores_with_line=[], scores_with_points=[],
labels_with_line=['Gradient Boosting', 'Random Forest', 'Decision Tree'],
labels_with_points=['skope-rules']):
gradient = np.linspace(0, 1, 10)
color_list = [ cm.tab10(x) for x in gradient ]
fig, axes = plt.subplots(1, 2, figsize=(12, 5),
sharex=True, sharey=True)
ax = axes[0]
n_line = 0
for i_score, score in enumerate(scores_with_line):
n_line = n_line + 1
fpr, tpr, _ = roc_curve(y_true, score)
ax.plot(fpr, tpr, linestyle='-.', c=color_list[i_score], lw=1, label=labels_with_line[i_score])
for i_score, score in enumerate(scores_with_points):
fpr, tpr, _ = roc_curve(y_true, score)
ax.scatter(fpr[:-1], tpr[:-1], c=color_list[n_line + i_score], s=10, label=labels_with_points[i_score])
ax.set_title("ROC", fnotallow=20)
ax.set_xlabel('False Positive Rate', fnotallow=18)
ax.set_ylabel('True Positive Rate (Recall)', fnotallow=18)
ax.legend(loc='lower center', fnotallow=8)
ax = axes[1]
n_line = 0
for i_score, score in enumerate(scores_with_line):
n_line = n_line + 1
precision, recall, _ = precision_recall_curve(y_true, score)
ax.step(recall, precision, linestyle='-.', c=color_list[i_score], lw=1, where='post', label=labels_with_line[i_score])
for i_score, score in enumerate(scores_with_points):
precision, recall, _ = precision_recall_curve(y_true, score)
ax.scatter(recall, precision, c=color_list[n_line + i_score], s=10, label=labels_with_points[i_score])
ax.set_title("Precision-Recall", fnotallow=20)
ax.set_xlabel('Recall (True Positive Rate)', fnotallow=18)
ax.set_ylabel('Precision', fnotallow=18)
ax.legend(loc='lower center', fnotallow=8)
plt.show()
plot_titanic_scores(y_test,
scores_with_line=[gradient_boost_scoring, random_forest_scoring, decision_tree_scoring],
scores_with_points=[skope_rules_scoring]
)
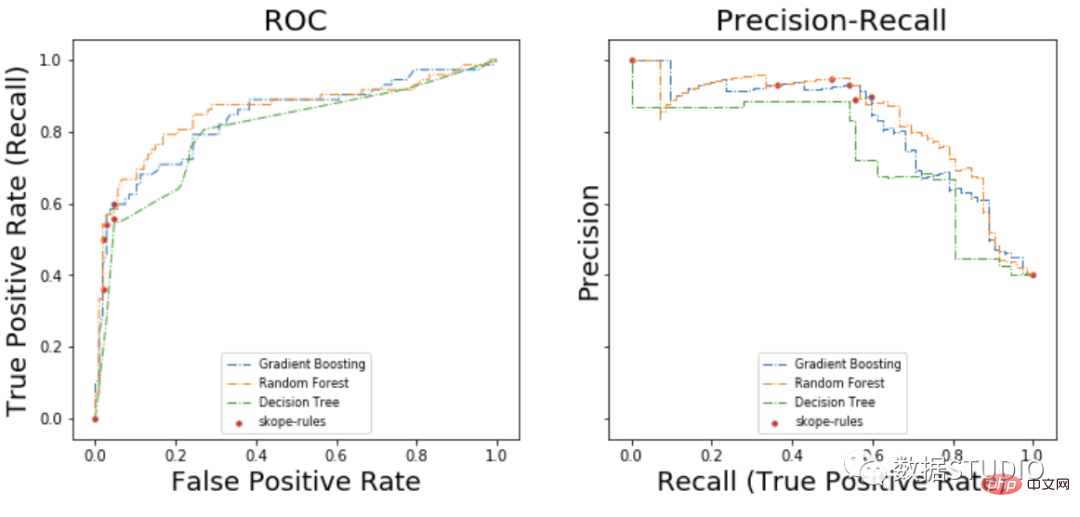
在ROC曲线上,每个红点对应于激活的规则(来自skope-rules)的数量。例如,最低点是1个规则(最好的)的结果点。第二低点是2条规则结果点,等等。
在准确率-召回率曲线上,同样的点是用不同的坐标轴绘制的。警告:左边的第一个红点(0%召回率,100%精度)对应于0条规则。左边的第二个点是第一个规则,等等。
从这个例子可以得出一些结论。
- skope-rules的表现比决策树好。
- skope-rules的性能与随机森林/梯度提升相似(在这个例子中)。
- 使用4个规则可以获得很好的性能(61%的召回率,94%的精确度)(在这个例子中)。
n_rule_chosen = 4
y_pred = skope_rules_clf.predict_top_rules(X_test, n_rule_chosen)
print('The performances reached with '+str(n_rule_chosen)+' discovered rules are the following:')
compute_performances_from_y_pred(y_test, y_pred, 'test_set')
predict_top_rules(new_data, n_r)方法用来计算对new_data的预测,其中有前n_r条skope-rules规则。
以上是涨知识!用逻辑规则进行机器学习的详细内容。更多信息请关注PHP中文网其他相关文章!

热AI工具

Undresser.AI Undress
人工智能驱动的应用程序,用于创建逼真的裸体照片

AI Clothes Remover
用于从照片中去除衣服的在线人工智能工具。

Undress AI Tool
免费脱衣服图片

Clothoff.io
AI脱衣机

AI Hentai Generator
免费生成ai无尽的。

热门文章

热工具

记事本++7.3.1
好用且免费的代码编辑器

SublimeText3汉化版
中文版,非常好用

禅工作室 13.0.1
功能强大的PHP集成开发环境

Dreamweaver CS6
视觉化网页开发工具

SublimeText3 Mac版
神级代码编辑软件(SublimeText3)

热门话题
 OpenOOD更新v1.5:全面、精确的分布外检测代码库及测试平台,支持在线排行榜、一键测试
Jul 03, 2023 pm 04:41 PM
OpenOOD更新v1.5:全面、精确的分布外检测代码库及测试平台,支持在线排行榜、一键测试
Jul 03, 2023 pm 04:41 PM
分布外(OOD)检测对于开放世界智能系统的可靠运行至关重要,但目前面向对象的检测方法存在「评估不一致」(evaluationinconsistencies)的问题。之前的工作OpenOODv1统一了OOD检测的评估,但在可扩展性和可用性方面仍然存在限制。最近开发团队再次提出OpenOODv1.5,相比上一版本,新的OOD检测方法评估在确保准确、标准化和用户友好等方面得到显著提升。图片Paper:https://arxiv.org/abs/2306.09301OpenOODCodebase:htt
 涨知识!用逻辑规则进行机器学习
Apr 01, 2023 pm 10:07 PM
涨知识!用逻辑规则进行机器学习
Apr 01, 2023 pm 10:07 PM
在准确率-召回率曲线上,同样的点是用不同的坐标轴绘制的。警告:左边的第一个红点(0%召回率,100%精度)对应于0条规则。左边的第二个点是第一个规则,等等。 Skope-rules使用树模型生成规则候选项。首先建立一些决策树,并将从根节点到内部节点或叶子节点的路径视为规则候选项。然后通过一些预定义的标准(如精确度和召回率)对这些候选规则进行过滤。只有那些精确度和召回率高于其阈值的才会被保留。最后,应用相似性过滤来选择具有足够多样性的规则。一般情况下,应用Skope-rules来学习每个根本原因的
 如何在Java中找到运行时提供的参数数量?
Sep 23, 2023 pm 01:13 PM
如何在Java中找到运行时提供的参数数量?
Sep 23, 2023 pm 01:13 PM
在Java中,在运行时传递参数的一种方法是使用命令行或终端。在检索命令行参数的这些值时,我们可能需要查找用户在运行时提供的参数数量,这可以借助length属性来实现。本文旨在借助示例程序解释传递和获取用户提供的参数数量的过程。获取用户在运行时提供的参数数量在查找命令行参数的数量之前,我们的第一步是创建一个允许用户在运行时传递参数的程序。字符串[]参数在编写Java程序时,我们经常遇到main()方法。当JVM调用此方法时,Java应用程序开始执行。它与一个名为String[]args的参数一起使
 Linux命令:查看telnet进程数量的方法
Mar 01, 2024 am 11:39 AM
Linux命令:查看telnet进程数量的方法
Mar 01, 2024 am 11:39 AM
Linux命令是系统管理员日常工作中必不可少的工具之一,它们可以帮助我们完成各种系统管理任务。在运维工作中,有时候需要查看系统中某个进程的数量以便及时发现问题和进行调优。本文将介绍如何使用Linux命令查看telnet进程的数量,让我们一起来学习吧。在Linux系统中,我们可以使用ps命令结合grep命令来查看telnet进程的数量。首先,我们需要打开终端,
 使用C++编写代码,找到具有相同最小值和最大值的子数组的数量
Aug 25, 2023 pm 11:33 PM
使用C++编写代码,找到具有相同最小值和最大值的子数组的数量
Aug 25, 2023 pm 11:33 PM
在本文中,我们将使用C++解决寻找最大值和最小值相同的子数组数量的问题。以下是该问题的示例−Input:array={2,3,6,6,2,4,4,4}Output:12Explanation:{2},{3},{6},{6},{2},{4},{4},{4},{6,6},{4,4},{4,4}and{4,4,4}arethesubarrayswhichcanbeformedwithmaximumandminimumelementsame.Input:array={3,3,1,5,
 使用C++找到遍历N叉树的方式的数量
Sep 04, 2023 pm 05:01 PM
使用C++找到遍历N叉树的方式的数量
Sep 04, 2023 pm 05:01 PM
给定一个N叉树,我们的任务是找到遍历这棵树的总方式数,例如−对于上面的树,我们的输出将是192。对于这个问题,我们需要一些组合学的知识。现在在这个问题中,我们只需要检查每条路径的所有可能组合,这将给我们答案。找到解决方案的方法在这个方法中,我们只需要执行一次层次遍历,检查每个节点有多少个子节点,然后将其阶乘乘以答案。示例上述方法的C++代码#include<bits/stdc++.h>usingnamespacestd;structNode{//s
 二叉树中等腰三角形的数量
Sep 05, 2023 am 09:41 AM
二叉树中等腰三角形的数量
Sep 05, 2023 am 09:41 AM
二叉树是一种数据结构,其中每个节点最多可以有两个子节点。这些孩子分别称为左孩子和右孩子。假设我们得到了一个父数组表示,您必须使用它来创建一棵二叉树。二叉树可能有几个等腰三角形。我们必须找到该二叉树中可能的等腰三角形的总数。在本文中,我们将探讨几种在C++中解决这个问题的技术。理解问题给你一个父数组。您必须以二叉树的形式表示它,以便数组索引形成树节点的值,而数组中的值给出该特定索引的父节点。请注意,-1始终是根父节点。下面给出的是一个数组及其二叉树表示。Parentarray=[0,-1,3,1,
 使用C++编写代码,找到具有奇数和的子数组的数量
Sep 21, 2023 am 08:45 AM
使用C++编写代码,找到具有奇数和的子数组的数量
Sep 21, 2023 am 08:45 AM
子数组是数组的连续部分。例如,我们考虑一个数组[5,6,7,8],那么有十个非空子数组,如(5),(6),(7),(8),(5,6),(6,7)、(7,8)、(5,6,7)、(6,7,8)和(5,6,7,8)。在本指南中,我们将解释在C++中查找所有可能的信息来查找具有奇数和的子数组的数量。为了找到奇数和的子数组的数量,我们可以使用不同的方法,所以这里是一个简单的例子-Input:array={9,8,7,6,5}Output:9Explanation:Sumofsubarray-{9}=9{7






