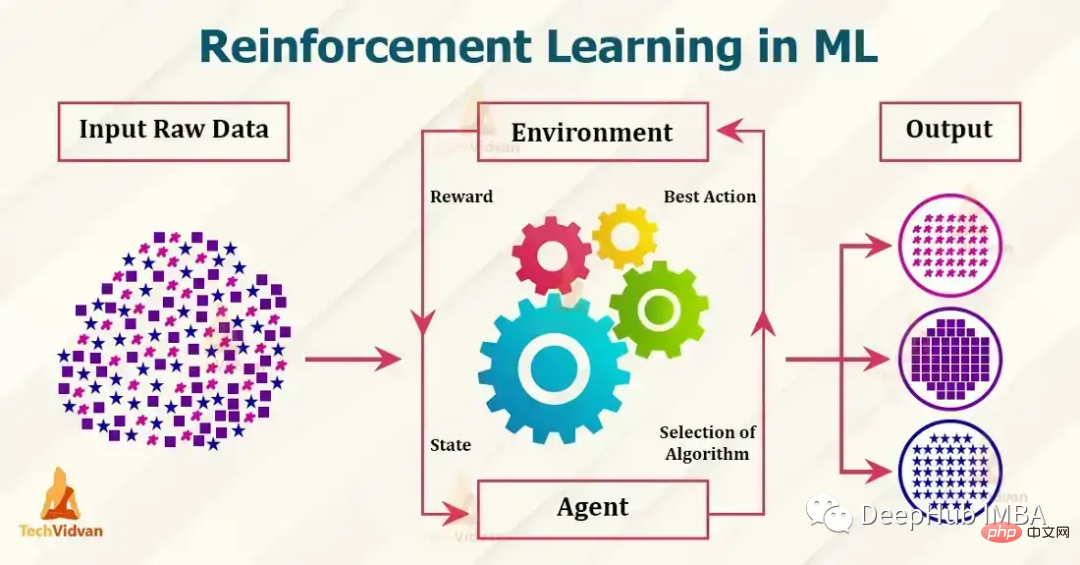
七个流行的强化学习算法及代码实现
目前流行的强化学习算法包括 Q-learning、SARSA、DDPG、A2C、PPO、DQN 和 TRPO。 这些算法已被用于在游戏、机器人和决策制定等各种应用中,并且这些流行的算法还在不断发展和改进,本文我们将对其做一个简单的介绍。
1、Q-learning
Q-learning:Q-learning 是一种无模型、非策略的强化学习算法。 它使用 Bellman 方程估计最佳动作值函数,该方程迭代地更新给定状态动作对的估计值。 Q-learning 以其简单性和处理大型连续状态空间的能力而闻名。
下面是一个使用 Python 实现 Q-learning 的简单示例:
import numpy as np # Define the Q-table and the learning rate Q = np.zeros((state_space_size, action_space_size)) alpha = 0.1 # Define the exploration rate and discount factor epsilon = 0.1 gamma = 0.99 for episode in range(num_episodes): current_state = initial_state while not done: # Choose an action using an epsilon-greedy policy if np.random.uniform(0, 1) < epsilon: action = np.random.randint(0, action_space_size) else: action = np.argmax(Q[current_state]) # Take the action and observe the next state and reward next_state, reward, done = take_action(current_state, action) # Update the Q-table using the Bellman equation Q[current_state, action] = Q[current_state, action] + alpha * (reward + gamma * np.max(Q[next_state]) - Q[current_state, action]) current_state = next_state
上面的示例中,state_space_size 和 action_space_size 分别是环境中的状态数和动作数。 num_episodes 是要为运行算法的轮次数。 initial_state 是环境的起始状态。 take_action(current_state, action) 是一个函数,它将当前状态和一个动作作为输入,并返回下一个状态、奖励和一个指示轮次是否完成的布尔值。
在 while 循环中,使用 epsilon-greedy 策略根据当前状态选择一个动作。 使用概率 epsilon选择一个随机动作,使用概率 1-epsilon选择对当前状态具有最高 Q 值的动作。
采取行动后,观察下一个状态和奖励,使用Bellman方程更新q。 并将当前状态更新为下一个状态。这只是 Q-learning 的一个简单示例,并未考虑 Q-table 的初始化和要解决的问题的具体细节。
2、SARSA
SARSA:SARSA 是一种无模型、基于策略的强化学习算法。 它也使用Bellman方程来估计动作价值函数,但它是基于下一个动作的期望值,而不是像 Q-learning 中的最优动作。 SARSA 以其处理随机动力学问题的能力而闻名。
import numpy as np # Define the Q-table and the learning rate Q = np.zeros((state_space_size, action_space_size)) alpha = 0.1 # Define the exploration rate and discount factor epsilon = 0.1 gamma = 0.99 for episode in range(num_episodes): current_state = initial_state action = epsilon_greedy_policy(epsilon, Q, current_state) while not done: # Take the action and observe the next state and reward next_state, reward, done = take_action(current_state, action) # Choose next action using epsilon-greedy policy next_action = epsilon_greedy_policy(epsilon, Q, next_state) # Update the Q-table using the Bellman equation Q[current_state, action] = Q[current_state, action] + alpha * (reward + gamma * Q[next_state, next_action] - Q[current_state, action]) current_state = next_state action = next_action
state_space_size和action_space_size分别是环境中的状态和操作的数量。num_episodes是您想要运行SARSA算法的轮次数。Initial_state是环境的初始状态。take_action(current_state, action)是一个将当前状态和作为操作输入的函数,并返回下一个状态、奖励和一个指示情节是否完成的布尔值。
在while循环中,使用在单独的函数epsilon_greedy_policy(epsilon, Q, current_state)中定义的epsilon-greedy策略来根据当前状态选择操作。使用概率 epsilon选择一个随机动作,使用概率 1-epsilon对当前状态具有最高 Q 值的动作。
上面与Q-learning相同,但是采取了一个行动后,在观察下一个状态和奖励时它然后使用贪心策略选择下一个行动。并使用Bellman方程更新q表。
3、DDPG
DDPG 是一种用于连续动作空间的无模型、非策略算法。 它是一种actor-critic算法,其中actor网络用于选择动作,而critic网络用于评估动作。 DDPG 对于机器人控制和其他连续控制任务特别有用。
import numpy as np from keras.models import Model, Sequential from keras.layers import Dense, Input from keras.optimizers import Adam # Define the actor and critic models actor = Sequential() actor.add(Dense(32, input_dim=state_space_size, activation='relu')) actor.add(Dense(32, activation='relu')) actor.add(Dense(action_space_size, activation='tanh')) actor.compile(loss='mse', optimizer=Adam(lr=0.001)) critic = Sequential() critic.add(Dense(32, input_dim=state_space_size, activation='relu')) critic.add(Dense(32, activation='relu')) critic.add(Dense(1, activation='linear')) critic.compile(loss='mse', optimizer=Adam(lr=0.001)) # Define the replay buffer replay_buffer = [] # Define the exploration noise exploration_noise = OrnsteinUhlenbeckProcess(size=action_space_size, theta=0.15, mu=0, sigma=0.2) for episode in range(num_episodes): current_state = initial_state while not done: # Select an action using the actor model and add exploration noise action = actor.predict(current_state)[0] + exploration_noise.sample() action = np.clip(action, -1, 1) # Take the action and observe the next state and reward next_state, reward, done = take_action(current_state, action) # Add the experience to the replay buffer replay_buffer.append((current_state, action, reward, next_state, done)) # Sample a batch of experiences from the replay buffer batch = sample(replay_buffer, batch_size) # Update the critic model states = np.array([x[0] for x in batch]) actions = np.array([x[1] for x in batch]) rewards = np.array([x[2] for x in batch]) next_states = np.array([x[3] for x in batch]) target_q_values = rewards + gamma * critic.predict(next_states) critic.train_on_batch(states, target_q_values) # Update the actor model action_gradients = np.array(critic.get_gradients(states, actions)) actor.train_on_batch(states, action_gradients) current_state = next_state
在本例中,state_space_size和action_space_size分别是环境中的状态和操作的数量。num_episodes是轮次数。Initial_state是环境的初始状态。Take_action (current_state, action)是一个函数,它接受当前状态和操作作为输入,并返回下一个操作。
4、A2C
A2C(Advantage Actor-Critic)是一种有策略的actor-critic算法,它使用Advantage函数来更新策略。 该算法实现简单,可以处理离散和连续的动作空间。
import numpy as np from keras.models import Model, Sequential from keras.layers import Dense, Input from keras.optimizers import Adam from keras.utils import to_categorical # Define the actor and critic models state_input = Input(shape=(state_space_size,)) actor = Dense(32, activation='relu')(state_input) actor = Dense(32, activation='relu')(actor) actor = Dense(action_space_size, activation='softmax')(actor) actor_model = Model(inputs=state_input, outputs=actor) actor_model.compile(loss='categorical_crossentropy', optimizer=Adam(lr=0.001)) state_input = Input(shape=(state_space_size,)) critic = Dense(32, activation='relu')(state_input) critic = Dense(32, activation='relu')(critic) critic = Dense(1, activation='linear')(critic) critic_model = Model(inputs=state_input, outputs=critic) critic_model.compile(loss='mse', optimizer=Adam(lr=0.001)) for episode in range(num_episodes): current_state = initial_state done = False while not done: # Select an action using the actor model and add exploration noise action_probs = actor_model.predict(np.array([current_state]))[0] action = np.random.choice(range(action_space_size), p=action_probs) # Take the action and observe the next state and reward next_state, reward, done = take_action(current_state, action) # Calculate the advantage target_value = critic_model.predict(np.array([next_state]))[0][0] advantage = reward + gamma * target_value - critic_model.predict(np.array([current_state]))[0][0] # Update the actor model action_one_hot = to_categorical(action, action_space_size) actor_model.train_on_batch(np.array([current_state]), advantage * action_one_hot) # Update the critic model critic_model.train_on_batch(np.array([current_state]), reward + gamma * target_value) current_state = next_state
在这个例子中,actor模型是一个神经网络,它有2个隐藏层,每个隐藏层有32个神经元,具有relu激活函数,输出层具有softmax激活函数。critic模型也是一个神经网络,它有2个隐含层,每层32个神经元,具有relu激活函数,输出层具有线性激活函数。
使用分类交叉熵损失函数训练actor模型,使用均方误差损失函数训练critic模型。动作是根据actor模型预测选择的,并添加了用于探索的噪声。
5、PPO
PPO(Proximal Policy Optimization)是一种策略算法,它使用信任域优化的方法来更新策略。 它在具有高维观察和连续动作空间的环境中特别有用。 PPO 以其稳定性和高样品效率而著称。
import numpy as np from keras.models import Model, Sequential from keras.layers import Dense, Input from keras.optimizers import Adam # Define the policy model state_input = Input(shape=(state_space_size,)) policy = Dense(32, activation='relu')(state_input) policy = Dense(32, activation='relu')(policy) policy = Dense(action_space_size, activation='softmax')(policy) policy_model = Model(inputs=state_input, outputs=policy) # Define the value model value_model = Model(inputs=state_input, outputs=Dense(1, activation='linear')(policy)) # Define the optimizer optimizer = Adam(lr=0.001) for episode in range(num_episodes): current_state = initial_state while not done: # Select an action using the policy model action_probs = policy_model.predict(np.array([current_state]))[0] action = np.random.choice(range(action_space_size), p=action_probs) # Take the action and observe the next state and reward next_state, reward, done = take_action(current_state, action) # Calculate the advantage target_value = value_model.predict(np.array([next_state]))[0][0] advantage = reward + gamma * target_value - value_model.predict(np.array([current_state]))[0][0] # Calculate the old and new policy probabilities old_policy_prob = action_probs[action] new_policy_prob = policy_model.predict(np.array([next_state]))[0][action] # Calculate the ratio and the surrogate loss ratio = new_policy_prob / old_policy_prob surrogate_loss = np.minimum(ratio * advantage, np.clip(ratio, 1 - epsilon, 1 + epsilon) * advantage) # Update the policy and value models policy_model.trainable_weights = value_model.trainable_weights policy_model.compile(optimizer=optimizer, loss=-surrogate_loss) policy_model.train_on_batch(np.array([current_state]), np.array([action_one_hot])) value_model.train_on_batch(np.array([current_state]), reward + gamma * target_value) current_state = next_state
6、DQN
DQN(深度 Q 网络)是一种无模型、非策略算法,它使用神经网络来逼近 Q 函数。 DQN 特别适用于 Atari 游戏和其他类似问题,其中状态空间是高维的,并使用神经网络近似 Q 函数。
import numpy as np from keras.models import Sequential from keras.layers import Dense, Input from keras.optimizers import Adam from collections import deque # Define the Q-network model model = Sequential() model.add(Dense(32, input_dim=state_space_size, activation='relu')) model.add(Dense(32, activation='relu')) model.add(Dense(action_space_size, activation='linear')) model.compile(loss='mse', optimizer=Adam(lr=0.001)) # Define the replay buffer replay_buffer = deque(maxlen=replay_buffer_size) for episode in range(num_episodes): current_state = initial_state while not done: # Select an action using an epsilon-greedy policy if np.random.rand() < epsilon: action = np.random.randint(0, action_space_size) else: action = np.argmax(model.predict(np.array([current_state]))[0]) # Take the action and observe the next state and reward next_state, reward, done = take_action(current_state, action) # Add the experience to the replay buffer replay_buffer.append((current_state, action, reward, next_state, done)) # Sample a batch of experiences from the replay buffer batch = random.sample(replay_buffer, batch_size) # Prepare the inputs and targets for the Q-network inputs = np.array([x[0] for x in batch]) targets = model.predict(inputs) for i, (state, action, reward, next_state, done) in enumerate(batch): if done: targets[i, action] = reward else: targets[i, action] = reward + gamma * np.max(model.predict(np.array([next_state]))[0]) # Update the Q-network model.train_on_batch(inputs, targets) current_state = next_state
上面的代码,Q-network有2个隐藏层,每个隐藏层有32个神经元,使用relu激活函数。该网络使用均方误差损失函数和Adam优化器进行训练。
7、TRPO
TRPO (Trust Region Policy Optimization)是一种无模型的策略算法,它使用信任域优化方法来更新策略。 它在具有高维观察和连续动作空间的环境中特别有用。
TRPO 是一个复杂的算法,需要多个步骤和组件来实现。TRPO不是用几行代码就能实现的简单算法。
所以我们这里使用实现了TRPO的现有库,例如OpenAI Baselines,它提供了包括TRPO在内的各种预先实现的强化学习算法,。
要在OpenAI Baselines中使用TRPO,我们需要安装:
pip install baselines
然后可以使用baselines库中的trpo_mpi模块在你的环境中训练TRPO代理,这里有一个简单的例子:
import gym
from baselines.common.vec_env.dummy_vec_env import DummyVecEnv
from baselines.trpo_mpi import trpo_mpi
#Initialize the environment
env = gym.make("CartPole-v1")
env = DummyVecEnv([lambda: env])
# Define the policy network
policy_fn = mlp_policy
#Train the TRPO model
model = trpo_mpi.learn(env, policy_fn, max_iters=1000)我们使用Gym库初始化环境。然后定义策略网络,并调用TRPO模块中的learn()函数来训练模型。
还有许多其他库也提供了TRPO的实现,例如TensorFlow、PyTorch和RLLib。下面时一个使用TF 2.0实现的样例
import tensorflow as tf
import gym
# Define the policy network
class PolicyNetwork(tf.keras.Model):
def __init__(self):
super(PolicyNetwork, self).__init__()
self.dense1 = tf.keras.layers.Dense(16, activation='relu')
self.dense2 = tf.keras.layers.Dense(16, activation='relu')
self.dense3 = tf.keras.layers.Dense(1, activation='sigmoid')
def call(self, inputs):
x = self.dense1(inputs)
x = self.dense2(x)
x = self.dense3(x)
return x
# Initialize the environment
env = gym.make("CartPole-v1")
# Initialize the policy network
policy_network = PolicyNetwork()
# Define the optimizer
optimizer = tf.optimizers.Adam()
# Define the loss function
loss_fn = tf.losses.BinaryCrossentropy()
# Set the maximum number of iterations
max_iters = 1000
# Start the training loop
for i in range(max_iters):
# Sample an action from the policy network
action = tf.squeeze(tf.random.categorical(policy_network(observation), 1))
# Take a step in the environment
observation, reward, done, _ = env.step(action)
with tf.GradientTape() as tape:
# Compute the loss
loss = loss_fn(reward, policy_network(observation))
# Compute the gradients
grads = tape.gradient(loss, policy_network.trainable_variables)
# Perform the update step
optimizer.apply_gradients(zip(grads, policy_network.trainable_variables))
if done:
# Reset the environment
observation = env.reset()在这个例子中,我们首先使用TensorFlow的Keras API定义一个策略网络。然后使用Gym库和策略网络初始化环境。然后定义用于训练策略网络的优化器和损失函数。
在训练循环中,从策略网络中采样一个动作,在环境中前进一步,然后使用TensorFlow的GradientTape计算损失和梯度。然后我们使用优化器执行更新步骤。
这是一个简单的例子,只展示了如何在TensorFlow 2.0中实现TRPO。TRPO是一个非常复杂的算法,这个例子没有涵盖所有的细节,但它是试验TRPO的一个很好的起点。
总结
以上就是我们总结的7个常用的强化学习算法,这些算法并不相互排斥,通常与其他技术(如值函数逼近、基于模型的方法和集成方法)结合使用,可以获得更好的结果。
以上是七个流行的强化学习算法及代码实现的详细内容。更多信息请关注PHP中文网其他相关文章!

热AI工具

Undresser.AI Undress
人工智能驱动的应用程序,用于创建逼真的裸体照片

AI Clothes Remover
用于从照片中去除衣服的在线人工智能工具。

Undress AI Tool
免费脱衣服图片

Clothoff.io
AI脱衣机

AI Hentai Generator
免费生成ai无尽的。

热门文章

热工具

记事本++7.3.1
好用且免费的代码编辑器

SublimeText3汉化版
中文版,非常好用

禅工作室 13.0.1
功能强大的PHP集成开发环境

Dreamweaver CS6
视觉化网页开发工具

SublimeText3 Mac版
神级代码编辑软件(SublimeText3)

热门话题
 字节跳动剪映推出 SVIP 超级会员:连续包年 499 元,提供多种 AI 功能
Jun 28, 2024 am 03:51 AM
字节跳动剪映推出 SVIP 超级会员:连续包年 499 元,提供多种 AI 功能
Jun 28, 2024 am 03:51 AM
本站6月27日消息,剪映是由字节跳动旗下脸萌科技开发的一款视频剪辑软件,依托于抖音平台且基本面向该平台用户制作短视频内容,并兼容iOS、安卓、Windows、MacOS等操作系统。剪映官方宣布会员体系升级,推出全新SVIP,包含多种AI黑科技,例如智能翻译、智能划重点、智能包装、数字人合成等。价格方面,剪映SVIP月费79元,年费599元(本站注:折合每月49.9元),连续包月则为59元每月,连续包年为499元每年(折合每月41.6元)。此外,剪映官方还表示,为提升用户体验,向已订阅了原版VIP
 使用Rag和Sem-Rag提供上下文增强AI编码助手
Jun 10, 2024 am 11:08 AM
使用Rag和Sem-Rag提供上下文增强AI编码助手
Jun 10, 2024 am 11:08 AM
通过将检索增强生成和语义记忆纳入AI编码助手,提升开发人员的生产力、效率和准确性。译自EnhancingAICodingAssistantswithContextUsingRAGandSEM-RAG,作者JanakiramMSV。虽然基本AI编程助手自然有帮助,但由于依赖对软件语言和编写软件最常见模式的总体理解,因此常常无法提供最相关和正确的代码建议。这些编码助手生成的代码适合解决他们负责解决的问题,但通常不符合各个团队的编码标准、惯例和风格。这通常会导致需要修改或完善其建议,以便将代码接受到应
 微调真的能让LLM学到新东西吗:引入新知识可能让模型产生更多的幻觉
Jun 11, 2024 pm 03:57 PM
微调真的能让LLM学到新东西吗:引入新知识可能让模型产生更多的幻觉
Jun 11, 2024 pm 03:57 PM
大型语言模型(LLM)是在巨大的文本数据库上训练的,在那里它们获得了大量的实际知识。这些知识嵌入到它们的参数中,然后可以在需要时使用。这些模型的知识在训练结束时被“具体化”。在预训练结束时,模型实际上停止学习。对模型进行对齐或进行指令调优,让模型学习如何充分利用这些知识,以及如何更自然地响应用户的问题。但是有时模型知识是不够的,尽管模型可以通过RAG访问外部内容,但通过微调使用模型适应新的领域被认为是有益的。这种微调是使用人工标注者或其他llm创建的输入进行的,模型会遇到额外的实际知识并将其整合
 七个很酷的GenAI & LLM技术性面试问题
Jun 07, 2024 am 10:06 AM
七个很酷的GenAI & LLM技术性面试问题
Jun 07, 2024 am 10:06 AM
想了解更多AIGC的内容,请访问:51CTOAI.x社区https://www.51cto.com/aigc/译者|晶颜审校|重楼不同于互联网上随处可见的传统问题库,这些问题需要跳出常规思维。大语言模型(LLM)在数据科学、生成式人工智能(GenAI)和人工智能领域越来越重要。这些复杂的算法提升了人类的技能,并在诸多行业中推动了效率和创新性的提升,成为企业保持竞争力的关键。LLM的应用范围非常广泛,它可以用于自然语言处理、文本生成、语音识别和推荐系统等领域。通过学习大量的数据,LLM能够生成文本
 为大模型提供全新科学复杂问答基准与测评体系,UNSW、阿贡、芝加哥大学等多家机构联合推出SciQAG框架
Jul 25, 2024 am 06:42 AM
为大模型提供全新科学复杂问答基准与测评体系,UNSW、阿贡、芝加哥大学等多家机构联合推出SciQAG框架
Jul 25, 2024 am 06:42 AM
编辑|ScienceAI问答(QA)数据集在推动自然语言处理(NLP)研究发挥着至关重要的作用。高质量QA数据集不仅可以用于微调模型,也可以有效评估大语言模型(LLM)的能力,尤其是针对科学知识的理解和推理能力。尽管当前已有许多科学QA数据集,涵盖了医学、化学、生物等领域,但这些数据集仍存在一些不足。其一,数据形式较为单一,大多数为多项选择题(multiple-choicequestions),它们易于进行评估,但限制了模型的答案选择范围,无法充分测试模型的科学问题解答能力。相比之下,开放式问答
 你所不知道的机器学习五大学派
Jun 05, 2024 pm 08:51 PM
你所不知道的机器学习五大学派
Jun 05, 2024 pm 08:51 PM
机器学习是人工智能的重要分支,它赋予计算机从数据中学习的能力,并能够在无需明确编程的情况下改进自身能力。机器学习在各个领域都有着广泛的应用,从图像识别和自然语言处理到推荐系统和欺诈检测,它正在改变我们的生活方式。机器学习领域存在着多种不同的方法和理论,其中最具影响力的五种方法被称为“机器学习五大派”。这五大派分别为符号派、联结派、进化派、贝叶斯派和类推学派。1.符号学派符号学(Symbolism),又称为符号主义,强调利用符号进行逻辑推理和表达知识。该学派认为学习是一种逆向演绎的过程,通过已有的
 SOTA性能,厦大多模态蛋白质-配体亲和力预测AI方法,首次结合分子表面信息
Jul 17, 2024 pm 06:37 PM
SOTA性能,厦大多模态蛋白质-配体亲和力预测AI方法,首次结合分子表面信息
Jul 17, 2024 pm 06:37 PM
编辑|KX在药物研发领域,准确有效地预测蛋白质与配体的结合亲和力对于药物筛选和优化至关重要。然而,目前的研究没有考虑到分子表面信息在蛋白质-配体相互作用中的重要作用。基于此,来自厦门大学的研究人员提出了一种新颖的多模态特征提取(MFE)框架,该框架首次结合了蛋白质表面、3D结构和序列的信息,并使用交叉注意机制进行不同模态之间的特征对齐。实验结果表明,该方法在预测蛋白质-配体结合亲和力方面取得了最先进的性能。此外,消融研究证明了该框架内蛋白质表面信息和多模态特征对齐的有效性和必要性。相关研究以「S
 布局 AI 等市场,格芯收购泰戈尔科技氮化镓技术和相关团队
Jul 15, 2024 pm 12:21 PM
布局 AI 等市场,格芯收购泰戈尔科技氮化镓技术和相关团队
Jul 15, 2024 pm 12:21 PM
本站7月5日消息,格芯(GlobalFoundries)于今年7月1日发布新闻稿,宣布收购泰戈尔科技(TagoreTechnology)的功率氮化镓(GaN)技术及知识产权组合,希望在汽车、物联网和人工智能数据中心应用领域探索更高的效率和更好的性能。随着生成式人工智能(GenerativeAI)等技术在数字世界的不断发展,氮化镓(GaN)已成为可持续高效电源管理(尤其是在数据中心)的关键解决方案。本站援引官方公告内容,在本次收购过程中,泰戈尔科技公司工程师团队将加入格芯,进一步开发氮化镓技术。G






