本文转载自微信公众号「尤而小屋」,作者尤而小屋 。转载本文请联系尤而小屋公众号。
大家好,我是Peter~
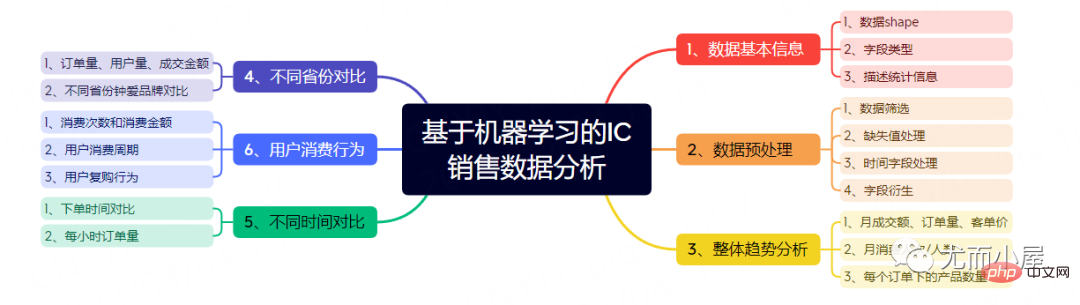
最近获取到了一份IC电子产品电商数据,后面会进行3个主题的数据分析与挖掘:
本文是第一个阶段,主要内容包含:
In [1]:
import pandas as pd import numpy as np import time import os from datetime import datetime import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import seaborn as sns %matplotlib inline #设置中文编码和负号的正常显示 plt.rcParams['font.sans-serif']=['SimHei'] plt.rcParams['axes.unicode_minus']=False import plotly_express as px import plotly.graph_objects as go import missingno as ms from sklearn.cluster import KMeans from sklearn.preprocessing import MinMaxScaler
df = pd.read_csv(
"ic_sale.csv",
encoding="utf-8",# 指定编码
cnotallow={"order_id":str,"product_id":str,"category_id":str,"user_id":str} # 指定字段类型
)
df.head()converters参数的作用:数据中的多个id字段全部是数字,在csv或者excel文件中被当做了数字(用科学计数法表示);本质上它们就是"字符串"信息,不具备任何大小含义。读取的时候需要特意指定类型。
读进来之后先查看数据的基本信息:
In [3]:
# 1、数据shape df.shape
Out[3]:
(564169, 11)
In [4]:
# 2、数据字段类型 df.dtypes
Out[4]:
event_timeobject order_idobject product_idobject category_id object category_code object brand object pricefloat64 user_id object ageint64 sex object local object dtype: object
In [5]:
描述统计信息是针对数值型的字段:
# 3、数据描述统计信息 df.describe()
Out[5]:
price | age | |
count | 564169.000000 | 564169.000000 |
mean | 208.269324 | 33.184388 |
std | 304.559875 | 10.122088 |
min | 0.000000 | 16.000000 |
25% | 23.130000 | 24.000000 |
50% | 87.940000 | 33.000000 |
75% | 277.750000 | 42.000000 |
max | 18328.680000 | 50.000000 |
In [6]:
# 4、总共多少个不同客户 df["user_id"].nunique()
Out[6]:
6908
In [7]:
# 5、总共多少个不同品牌 df["brand"].nunique()
Out[7]:
868
In [8]:
# 6、总共多少个订单 df["order_id"].nunique()
Out[8]:
234232
In [9]:
# 7、总共多少个产品 df["product_id"].nunique()
Out[9]:
3756
从描述统计信息中发现price字段的最小值是0,应该是没有成交的数据;我们选择price大于0的信息:
In [10]:
df = df[df["price"] > 0]
In [11]:
df.isnull().sum()
Out[11]:
event_time0 order_id0 product_id0 category_id 0 category_code129344 brand 27215 price 0 user_id 0 age 0 sex 0 local 0 dtype: int64
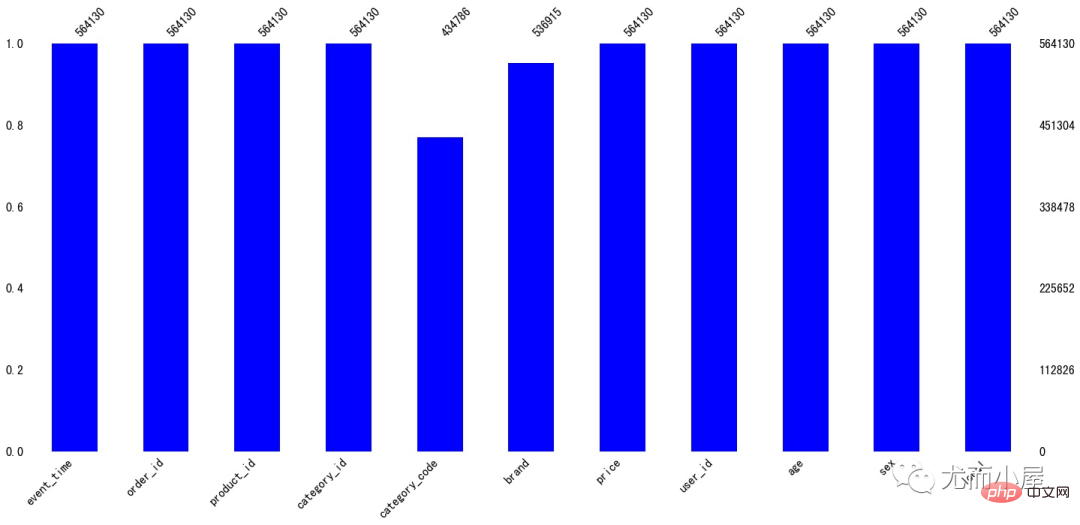
可以看到缺失值体现在字段:
In [12]:
ms.bar(df,color="blue")# 缺失值可视化 plt.show()
In [13]:
df.fillna("missing",inplace=True)In [14]:
df.isnull().sum()# 填充之后无缺失值
Out[14]:
event_time 0 order_id 0 product_id 0 category_id0 category_code0 brand0 price0 user_id0 age0 sex0 local0 dtype: int64
读进来的数据中时间字段是object类型,需要将其转成时间格式的类型
In [15]:
df["event_time"][:5] # 处理前
Out[15]:
02020-04-24 11:50:39 UTC 12020-04-24 11:50:39 UTC 22020-04-24 14:37:43 UTC 32020-04-24 14:37:43 UTC 42020-04-24 19:16:21 UTC Name: event_time, dtype: object
In [16]:
# 去掉最后的UTC df["event_time"] = df["event_time"].apply(lambda x: x[:19])
In [17]:
# 时间数据类型转化:字符类型---->指定时间格式 df['event_time'] = pd.to_datetime(df['event_time'], format="%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S")
In [18]:
# 提取多个时间相关字段 df['month']=df['event_time'].dt.month df['day'] = df['event_time'].dt.day df['dayofweek']=df['event_time'].dt.dayofweek df['hour']=df['event_time'].dt.hour
In [19]:
df["event_time"][:5] # 处理后
Out[19]:
0 2020-04-24 11:50:39 1 2020-04-24 11:50:39 2 2020-04-24 14:37:43 3 2020-04-24 14:37:43 4 2020-04-24 19:16:21 Name: event_time, dtype: datetime64[ns]
可以看到字段类型已经发生了变化
In [20]:
amount_by_month = df.groupby("month")["price"].sum().reset_index()
amount_by_monthOut[20]:
month | price | |
0 | 1 | 1953358.17 |
1 | 2 | 2267809.88 |
2 | 3 | 2897486.26 |
3 | 4 | 1704422.41 |
4 | 5 | 7768637.79 |
5 | 6 | 7691244.33 |
6 | 7 | 16354029.27 |
7 | 8 | 27982605.44 |
8 | 9 | 17152310.57 |
9 | 10 | 19765680.76 |
10 | 11 | 11961511.52 |
In [21]:
fig = px.scatter(amount_by_month,x="month",y="price",size="price",color="price") fig.update_layout(height=500, width=1000, title_text="每月成交金额") fig.show()
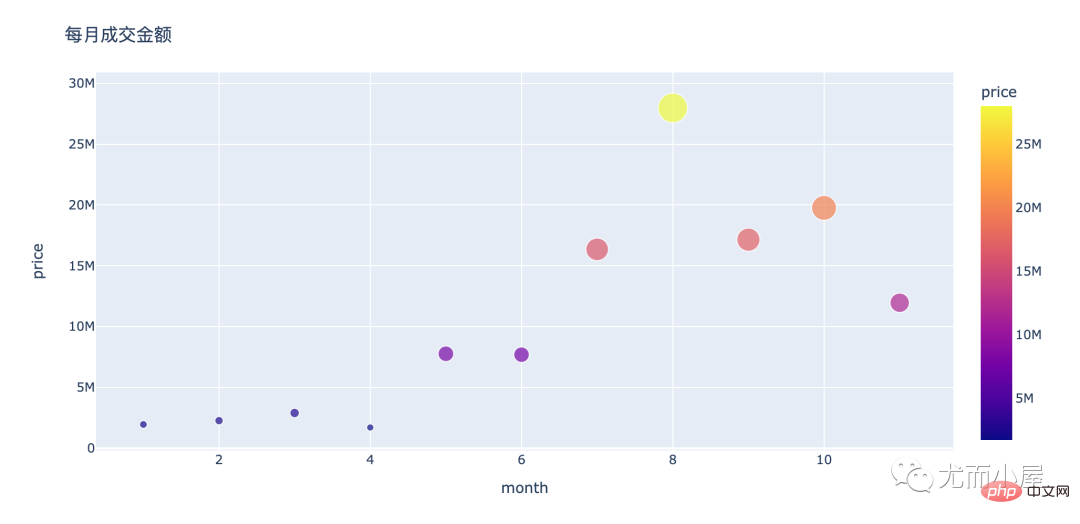
可以看到:
In [22]:
order_by_month = df.groupby("month")["order_id"].nunique().reset_index()
order_by_monthOut[22]:
month | order_id | |
0 | 1 | 10353 |
1 | 2 | 11461 |
2 | 3 | 12080 |
3 | 4 | 9001 |
4 | 5 | 30460 |
5 | 6 | 28978 |
6 | 7 | 57659 |
7 | 8 | 73897 |
8 | 9 | 345 |
9 | 10 | 14 |
10 | 11 | 6 |
In [23]:
fig = px.line(order_by_month,x="month",y="order_id") fig.update_layout(height=500, width=1000, title_text="每月成交订单量") fig.show()
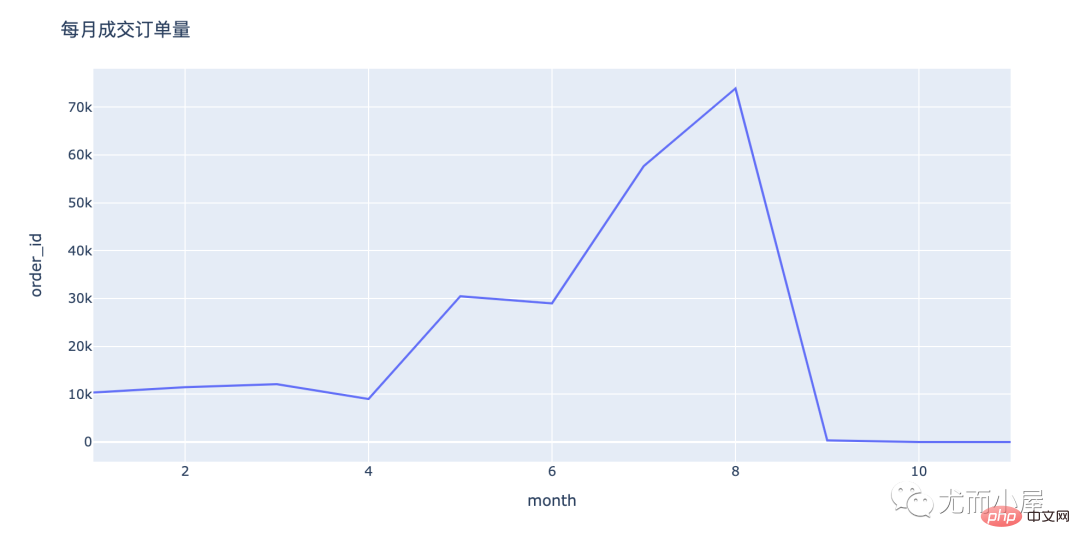
关于订单量:
In [24]:
# nunique:对每个user_id进行去重:消费人数
# count:统计user_id 的次数;消费人次(存在一人多次购买)
people_by_month = df.groupby("month")["user_id"].agg(["nunique","count"]).reset_index()
people_by_monthOut[24]:
month | nunique | count | |
0 | 1 | 1388 | 15575 |
1 | 2 | 1508 | 17990 |
2 | 3 | 1597 | 18687 |
3 | 4 | 1525 | 11867 |
4 | 5 | 3168 | 40332 |
5 | 6 | 3966 | 41355 |
6 | 7 | 5159 | 76415 |
7 | 8 | 6213 | 100006 |
8 | 9 | 5497 | 70496 |
9 | 10 | 4597 | 104075 |
10 | 11 | 3134 | 67332 |
In [25]:
fig = px.line(people_by_month,x="month",y="nunique") fig.update_layout(height=500, width=1000, title_text="每月成交人数") fig.show()
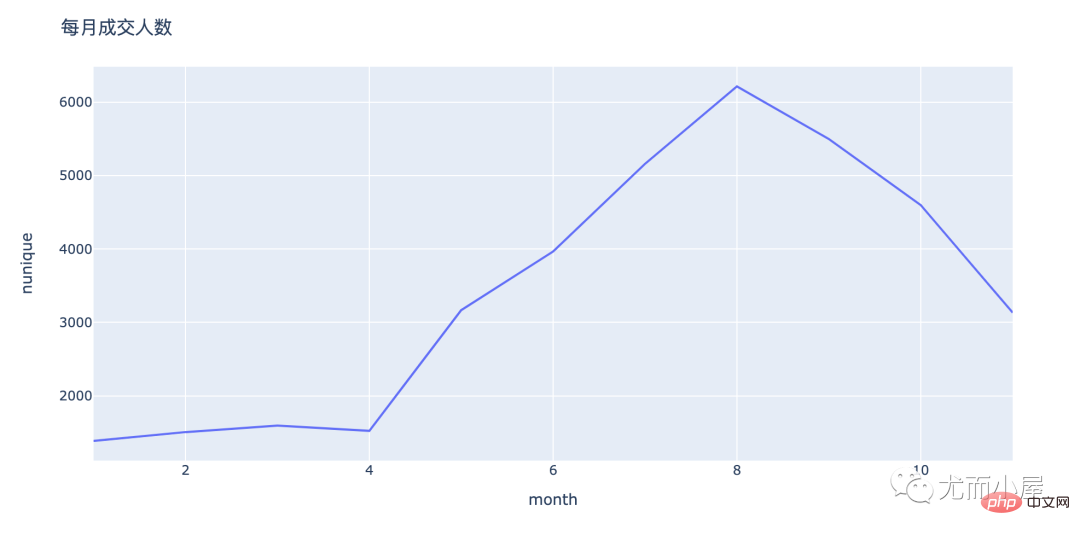
fig = px.line(people_by_month,x="month",y="count") fig.update_layout(height=500, width=1000, title_text="每月成交人次") fig.show()
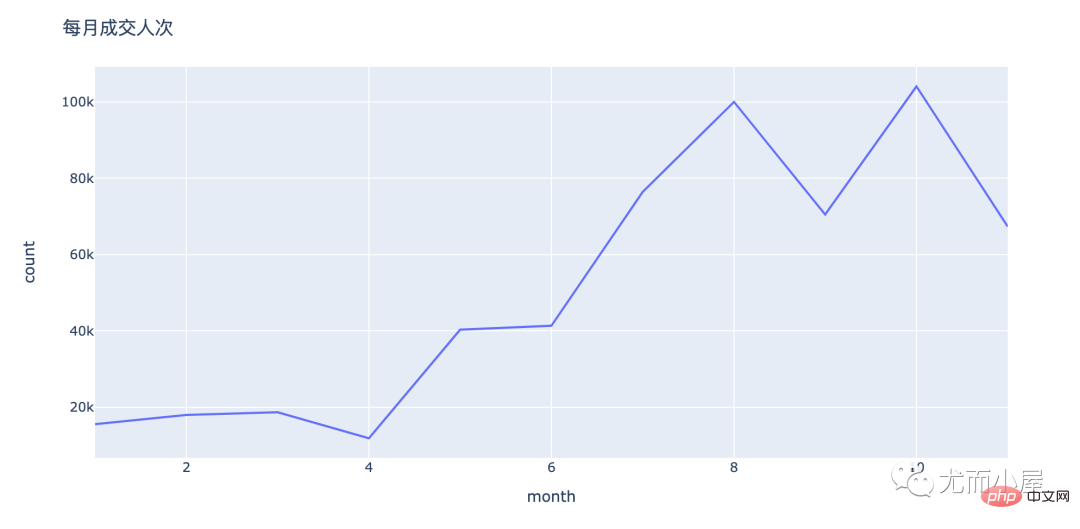
In [27]:
amount_by_month# 每月成交金额
Out[27]:
month | price | |
0 | 1 | 1953358.17 |
1 | 2 | 2267809.88 |
2 | 3 | 2897486.26 |
3 | 4 | 1704422.41 |
4 | 5 | 7768637.79 |
5 | 6 | 7691244.33 |
6 | 7 | 16354029.27 |
7 | 8 | 27982605.44 |
8 | 9 | 17152310.57 |
9 | 10 | 19765680.76 |
10 | 11 | 11961511.52 |
In [28]:
order_by_month# 每月订单数
Out[28]:
month | order_id | |
0 | 1 | 10353 |
1 | 2 | 11461 |
2 | 3 | 12080 |
3 | 4 | 9001 |
4 | 5 | 30460 |
5 | 6 | 28978 |
6 | 7 | 57659 |
7 | 8 | 73897 |
8 | 9 | 345 |
9 | 10 | 14 |
10 | 11 | 6 |
In [29]:
amount_by_userid = pd.merge(amount_by_month,order_by_month) amount_by_userid
Out[29]:
month | price | order_id | |
0 | 1 | 1953358.17 | 10353 |
1 | 2 | 2267809.88 | 11461 |
2 | 3 | 2897486.26 | 12080 |
3 | 4 | 1704422.41 | 9001 |
4 | 5 | 7768637.79 | 30460 |
5 | 6 | 7691244.33 | 28978 |
6 | 7 | 16354029.27 | 57659 |
7 | 8 | 27982605.44 | 73897 |
8 | 9 | 17152310.57 | 345 |
9 | 10 | 19765680.76 | 14 |
10 | 11 | 11961511.52 | 6 |
In [30]:
amount_by_userid["average"] = amount_by_userid["price"] / amount_by_userid["order_id"] amount_by_userid
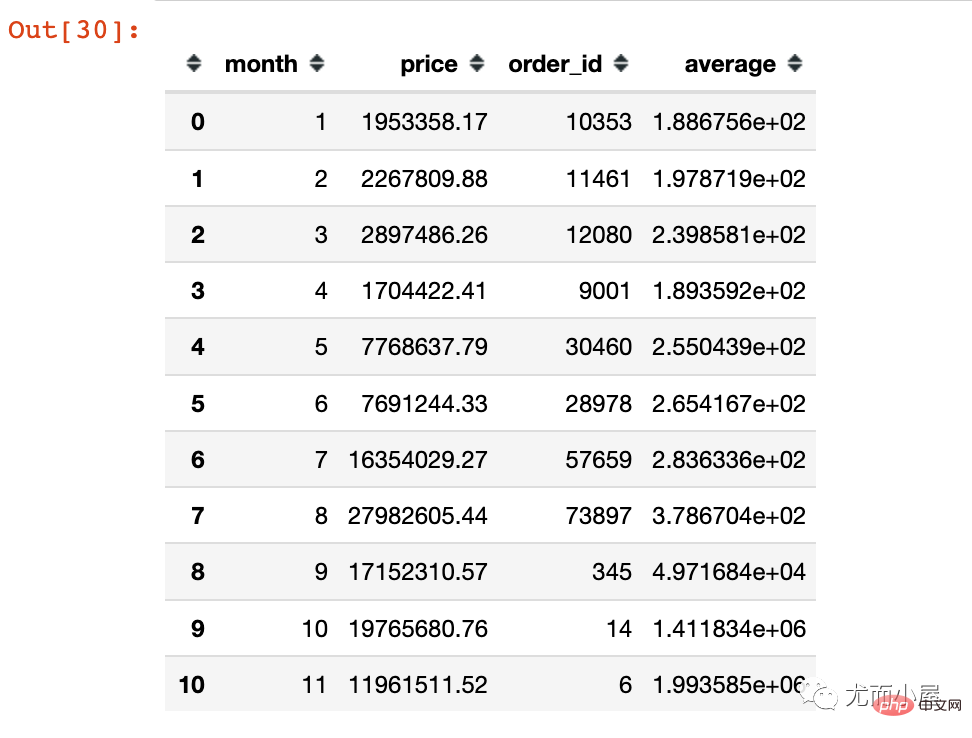
fig = px.line(amount_by_userid,x="month",y="average") fig.update_layout(height=500, width=1000, title_text="每月客单价") fig.show()
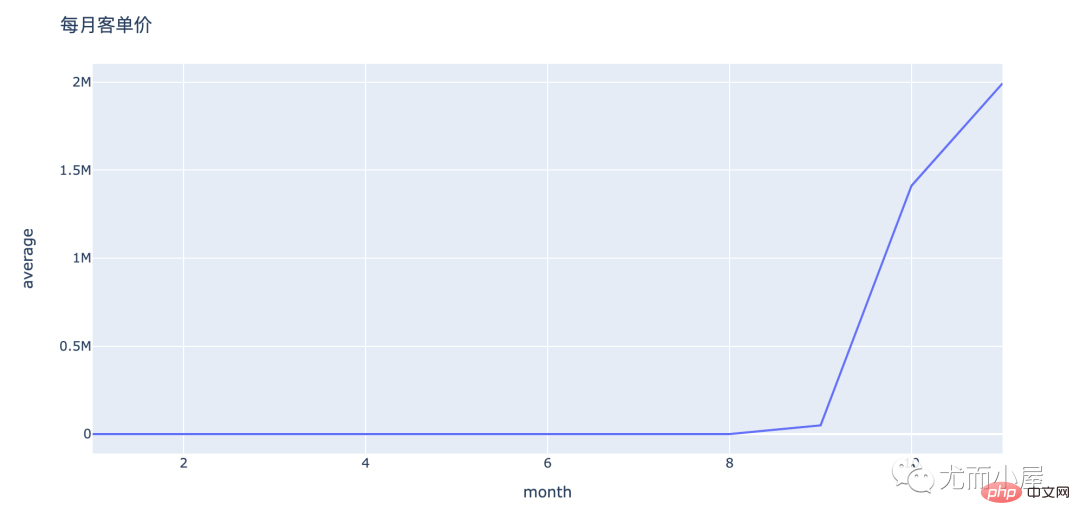
从上面的折线图可以看出来:
In [32]:
product_by_order = df.groupby("order_id")["product_id"].count().reset_index().sort_values("product_id",ascending=False)
product_by_order.head(10)Out[32]:
order_id | product_id | |
234208 | 2388440981134640000 | 15021 |
234210 | 2388440981134660000 | 14891 |
234211 | 2388440981134670000 | 14845 |
234212 | 2388440981134680000 | 14765 |
234202 | 2388440981134580000 | 14587 |
234205 | 2388440981134610000 | 14571 |
234207 | 2388440981134630000 | 14443 |
234204 | 2388440981134600000 | 14416 |
234206 | 2388440981134620000 | 14414 |
234203 | 2388440981134590000 | 14194 |
In [33]:
fig = px.bar(product_by_order[:20], x="order_id", y="product_id", text="product_id" ) fig.show()
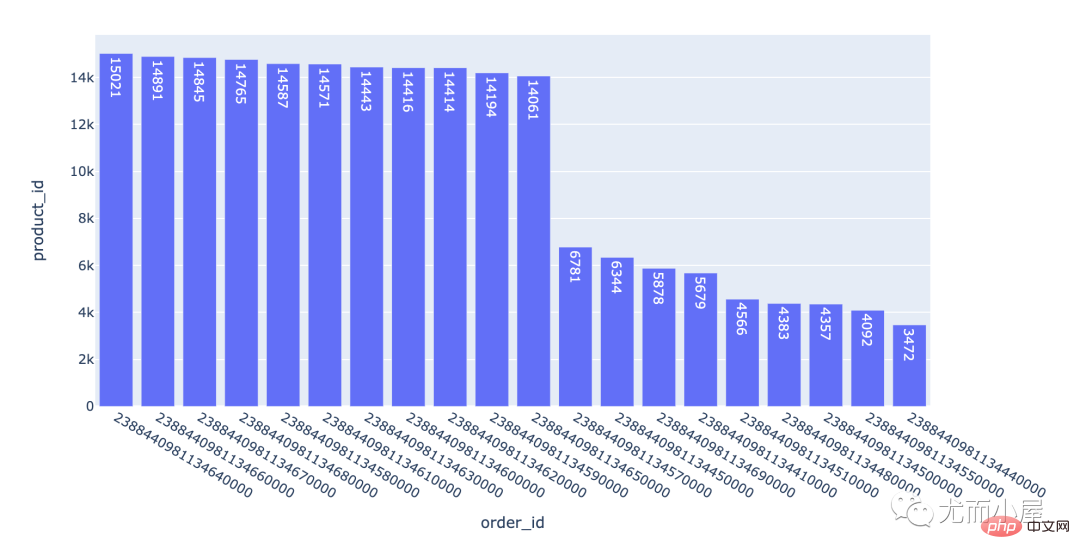
一个订单下包含的产品数量是不同;上万的订单可能是小型的ic元器件产品。
不同省份下的订单量、用户量和成交金额对比
In [34]:
local = df.groupby("local").agg({"order_id":"nunique","user_id":"nunique","price":sum}).reset_index()
local.head()Out[34]:
local | order_id | user_id | price | |
0 | 上海 | 39354 | 5680 | 19837942.20 |
1 | 北京 | 38118 | 5702 | 19137748.75 |
2 | 四川 | 13396 | 3589 | 6770891.28 |
3 | 天津 | 13058 | 3497 | 6433736.85 |
4 | 广东 | 51471 | 6085 | 26013770.86 |
In [35]:
df1 = local.sort_values("order_id",ascending=True)# 订单量升序
df1Out[35]:
local | order_id | user_id | price | |
6 | 浙江 | 12790 | 3485 | 6522657.59 |
8 | 湖北 | 12810 | 3488 | 5993820.57 |
3 | 天津 | 13058 | 3497 | 6433736.85 |
10 | 重庆 | 13058 | 3496 | 6479488.14 |
7 | 海南 | 13076 | 3587 | 6968674.41 |
2 | 四川 | 13396 | 3589 | 6770891.28 |
5 | 江苏 | 13575 | 3598 | 6357286.87 |
9 | 湖南 | 13879 | 3481 | 6983078.88 |
1 | 北京 | 38118 | 5702 | 19137748.75 |
0 | 上海 | 39354 | 5680 | 19837942.20 |
4 | 广东 | 51471 | 6085 | 26013770.86 |
In [36]:
fig = px.pie(df1, names="local",labels="local",values="price") fig.update_traces( textpositinotallow="inside", textinfo="percent+label" ) fig.show()
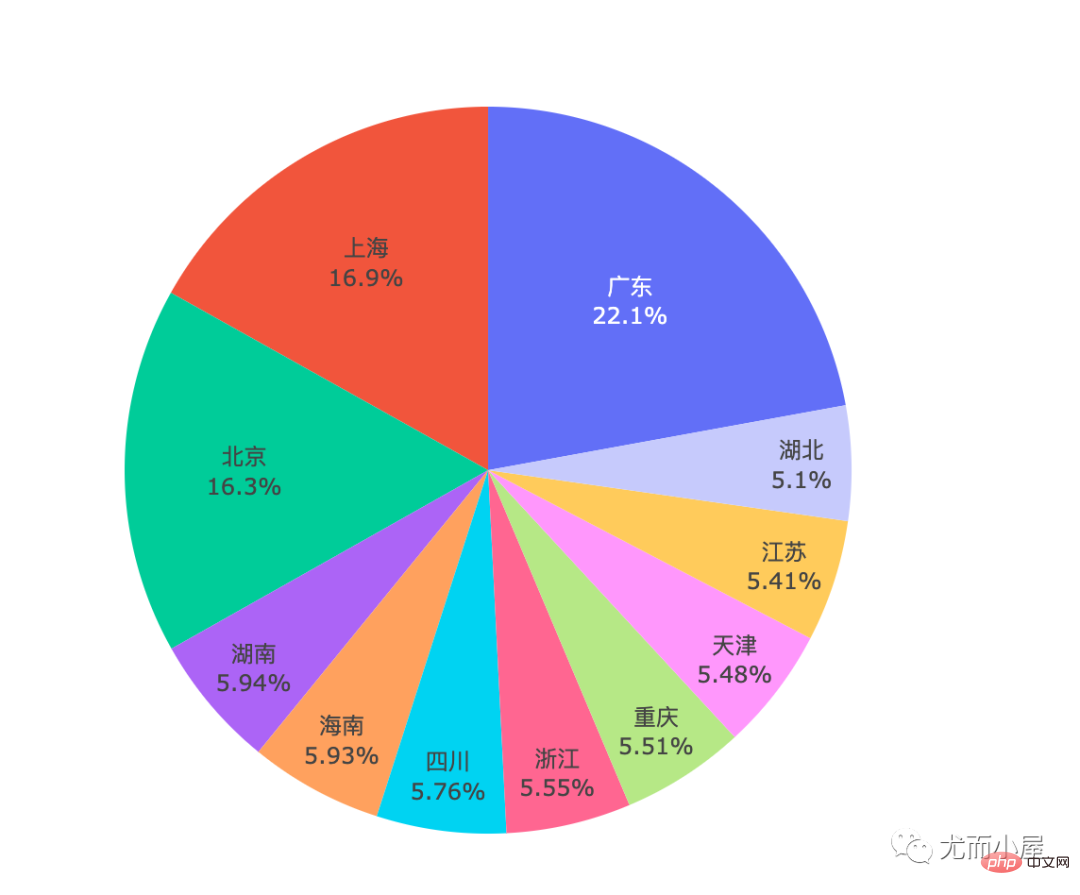
无疑:广东省No.1
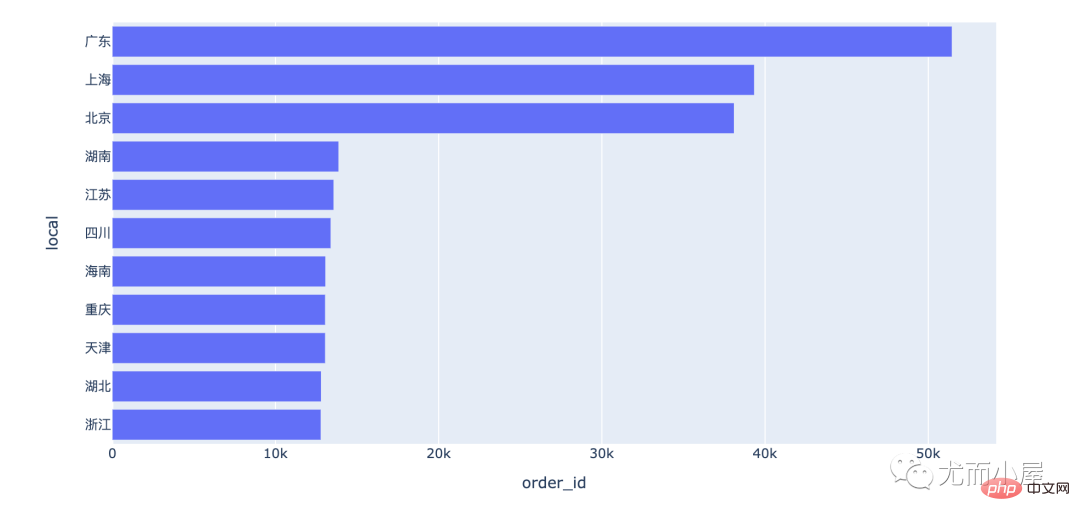
每个省份的订单量对比:
fig = px.bar(df1,x="order_id",y="local",orientatinotallow="h") fig.show()
# 整体的可视化效果 fig = px.scatter_3d(local, x="order_id", y="user_id", z="price", color="order_id", hover_name="local" ) fig.show()
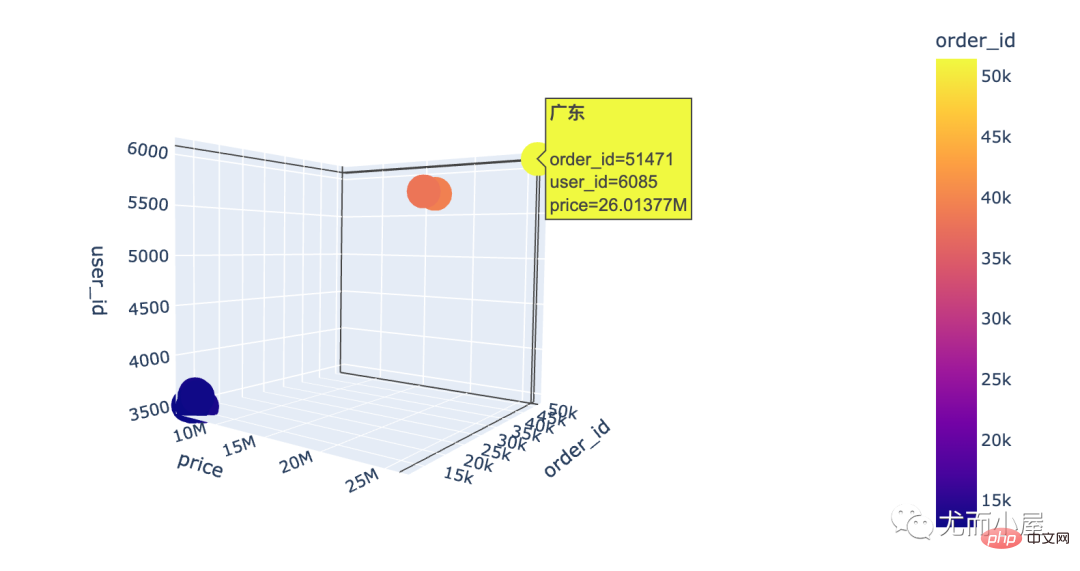
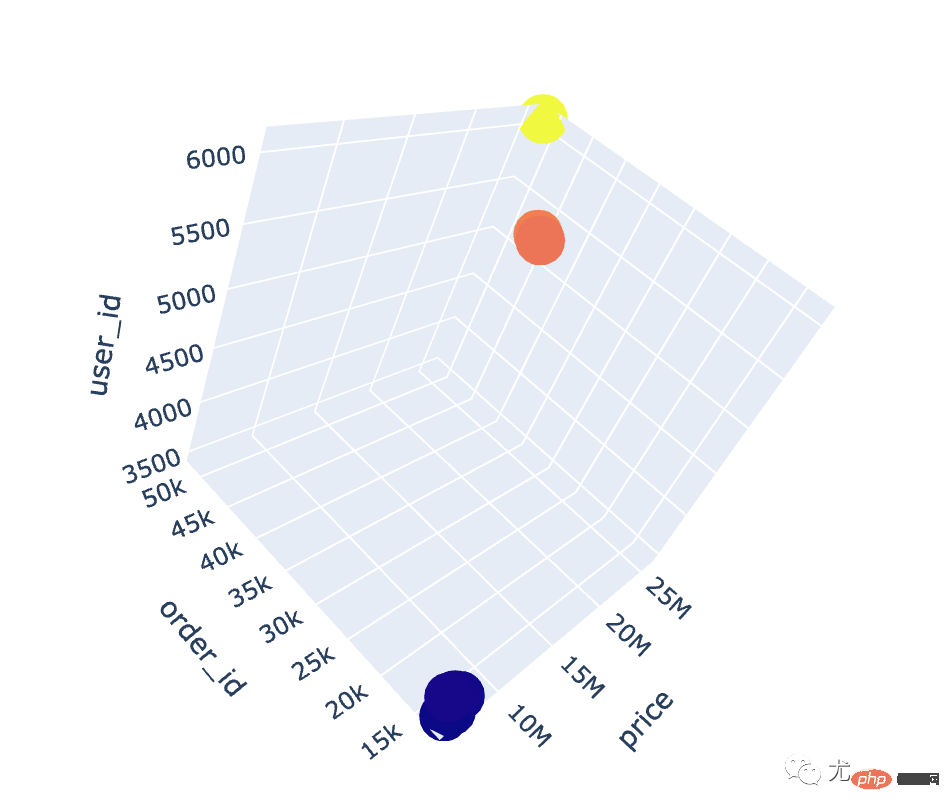
通过3D散点图我们发现:广东省真的是一骑绝尘!
In [39]:
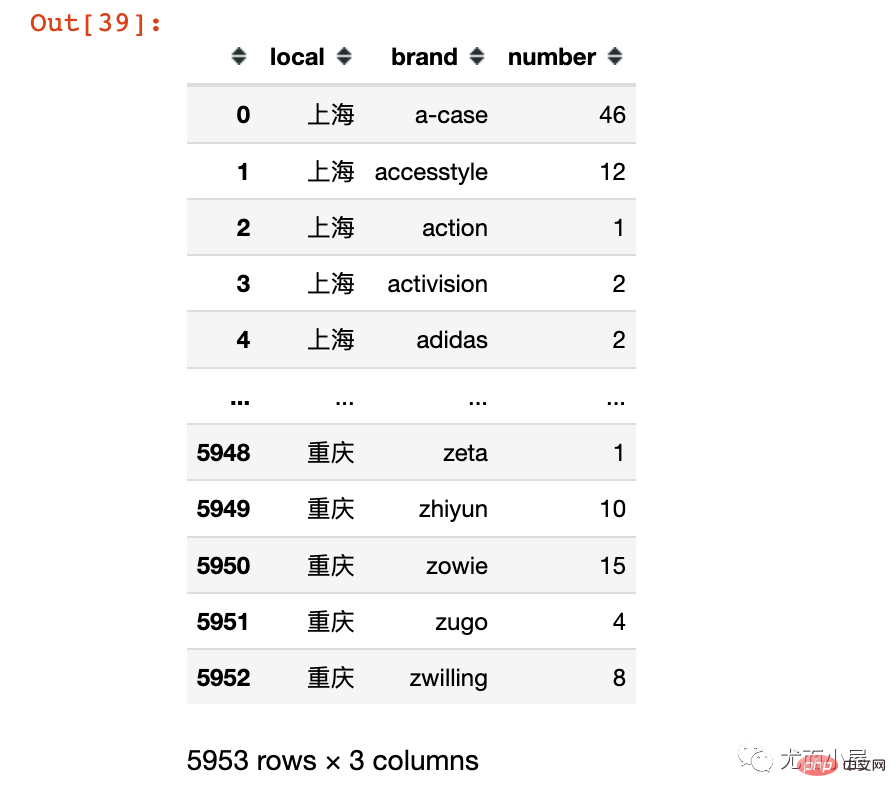
local_brand = df.groupby(["local","brand"]).size().to_frame().reset_index() local_brand.columns = ["local","brand","number"]# 修改字段名 local_brand
# 根据local和number进行排序
local_brand.sort_values(["local","number"],ascending=[True,False],inplace=True,ignore_index=True)
local_brand = local_brand[local_brand["brand"] != "missing"]
# 每个local下面最受欢迎的前3个品牌
local_brand = local_brand.groupby("local").head(3)
local_brand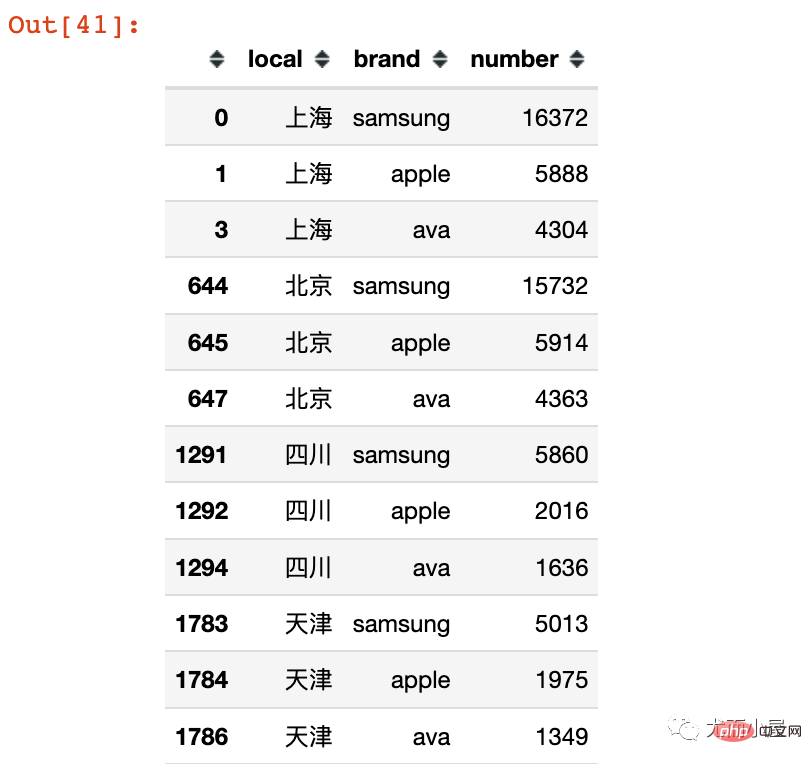
fig = px.bar(local_brand, x="brand", y="number", color="number", facet_col="local") fig.update_layout(height=500,width=1000) fig.show()
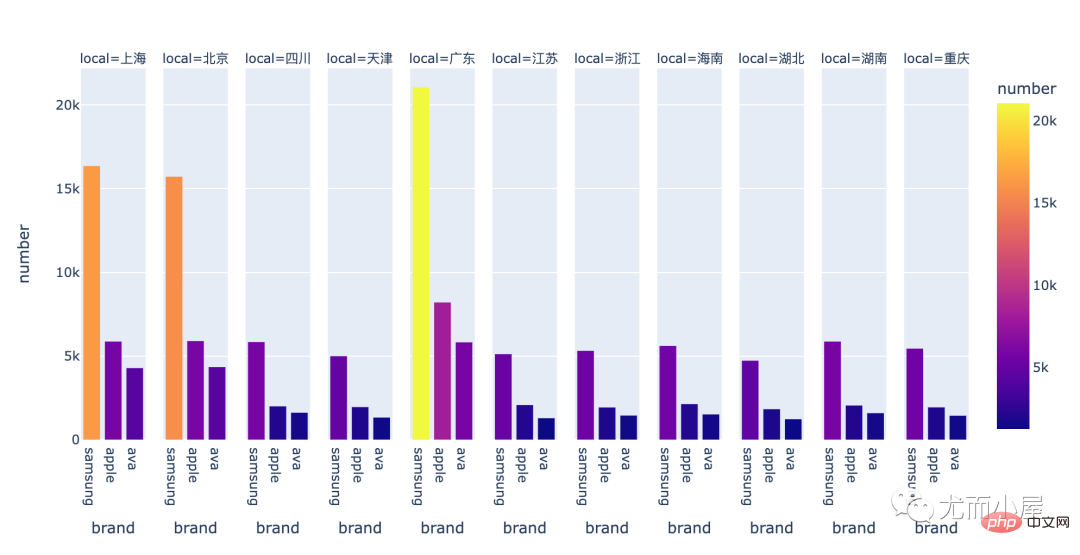
看来大家都很喜欢: samsung 、apple、ava
In [43]:
df.columns
Out[43]:
Index(['event_time', 'order_id', 'product_id', 'category_id', 'category_code', 'brand', 'price', 'user_id', 'age', 'sex', 'local', 'month', 'day', 'dayofweek', 'hour'], dtype='object')
In [44]:
df2 = df.groupby("dayofweek")["order_id"].nunique().reset_index()
df2Out[44]:
dayofweek | order_id | |
0 | 0 | 35690 |
1 | 1 | 34256 |
2 | 2 | 31249 |
3 | 3 | 31555 |
4 | 4 | 33010 |
5 | 5 | 34772 |
6 | 6 | 33922 |
In [45]:
plt.figure(figsize=(12,7))
df2["order_id"].plot.bar()
plt.xticks(range(7),['周一','周二','周三','周四','周五','周六','周日'],rotatinotallow=0)
plt.xlabel('星期')
plt.ylabel('订单量')
plt.title('订单数随星期变化')
plt.show()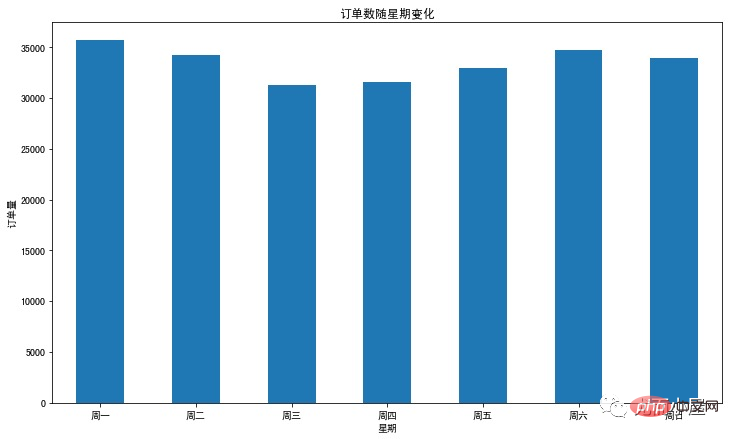
In [46]:
df3 = df.groupby("hour")["order_id"].nunique().reset_index()
df3.head(10)Out[46]:
hour | order_id | |
0 | 0 | 2865 |
1 | 1 | 2711 |
2 | 2 | 3981 |
3 | 3 | 6968 |
4 | 4 | 12176 |
5 | 5 | 16411 |
6 | 6 | 18667 |
7 | 7 | 20034 |
8 | 8 | 20261 |
9 | 9 | 20507 |
In [47]:
plt.figure(figsize=(14,8))
df3["order_id"].plot()
plt.xlabel('小时')
plt.ylabel('订单数量')
plt.title('订单随小时数变化')
plt.grid()
plt.show()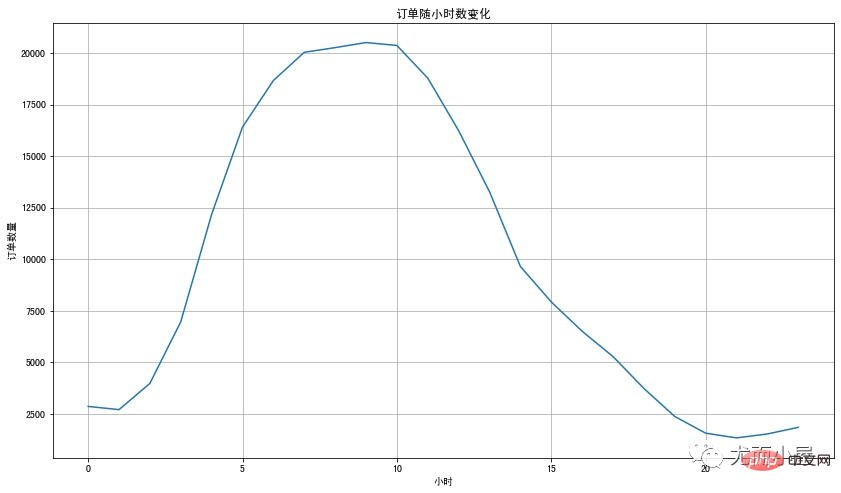
用户都喜欢在上午8、9、10点下单;可能是刚开始上班工作,大家更积极
In [48]:
df4 = df.groupby("user_id").agg({"order_id":"nunique", "price":sum})
fig = px.scatter(df4,
x="order_id",
y="price",
color="price",
size="price")
fig.show()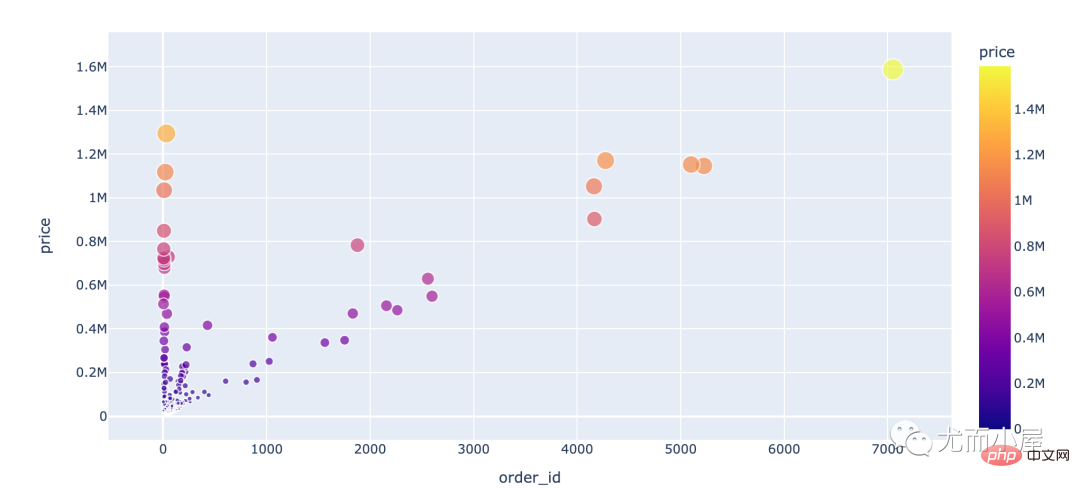
In [50]:
# 用户消费周期
# shift函数:移动一个单位
purchase_time=df.groupby('user_id').apply(lambda x: x['event_time'] - x['event_time'].shift()).dt.days
purchase_timeOut[50]:
user_id 151591562543995000096014NaN 1515915625440030000374760 NaN 48492735.0 1515915625440050000463812 NaN 473430 1.0 ... 1515915625514880000564132 0.0 564143 0.0 564164 0.0 1515915625514890000564158 NaN 564165 0.0 Name: event_time, Length: 564130, dtype: float64
In [51]:
purchase_time[purchase_time>0].describe()
Out[51]:
count120629.000000 mean 35.494500 std 663.803583 min 1.000000 25% 2.000000 50% 4.000000 75%12.000000 max 18466.000000 Name: event_time, dtype: float64
说明:
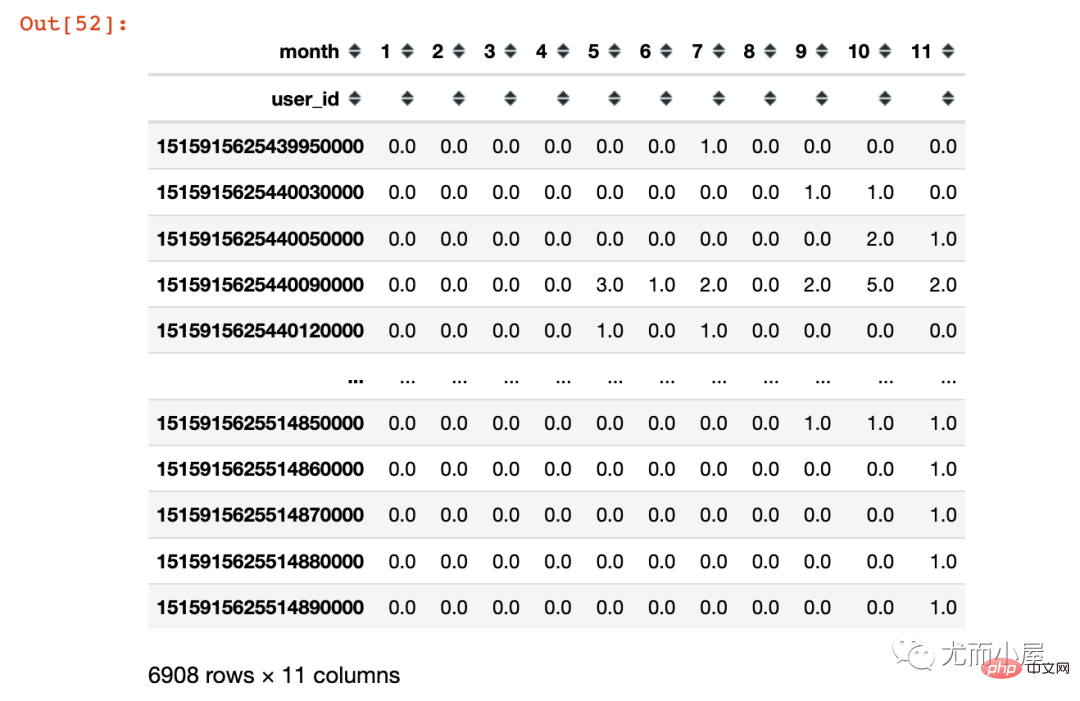
In [52]:
pivoted_counts = df.pivot_table(index='user_id', columns='month', values='order_id', aggfunc='nunique').fillna(0) pivoted_counts
Out[52]:
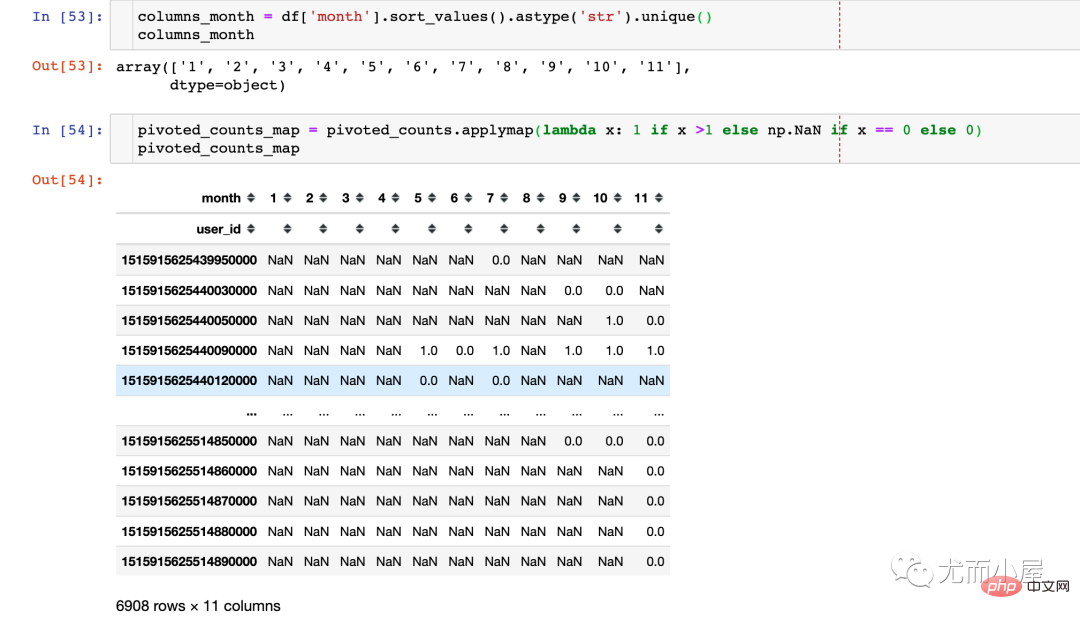
pivoted_counts_map.sum() / pivoted_counts_map.count() # 结果 month 1 0.406340 2 0.439655 3 0.474640 4 0.700328 5 0.829861 6 0.792990 7 0.891452 8 0.920328 9 0.781153 100.609963 110.419592 dtype: float64
(pivoted_counts_map.sum()/pivoted_counts_map.count()).plot(figsize=(12,6))
plt.xticks(range(11),columns_month)
plt.title('复购率')
plt.show()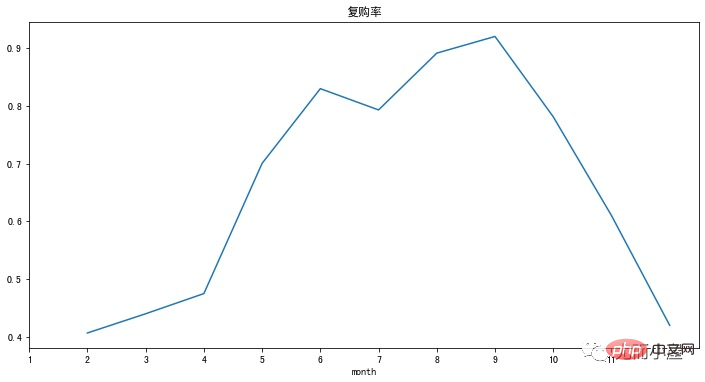
以上是基于机器学习的电商数据挖掘 | 数据探索篇的详细内容。更多信息请关注PHP中文网其他相关文章!




