十个 Python 小技巧,覆盖了90%的数据分析需求!
数据分析师日常工作会涉及各种任务,比如数据预处理、数据分析、机器学习模型创建、模型部署。
在本文中,我将分享10个 Python 操作,它们可覆盖90%的数据分析问题。有所收获点赞、收藏、关注。
1、阅读数据集
阅读数据是数据分析的组成部分,了解如何从不同的文件格式读取数据是数据分析师的第一步。下面是如何使用 pandas 读取包含 Covid-19 数据的 csv 文件的示例。
import pandas as pd
# reading the countries_data file along with the location within read_csv function.
countries_df = pd.read_csv('C:/Users/anmol/Desktop/Courses/Python for Data Science/Code/countries_data.csv')
# showing the first 5 rows of the dataframe
countries_df.head()
以下是 countries_df.head() 的输出,我们可以使用它查看数据框的前 5 行:
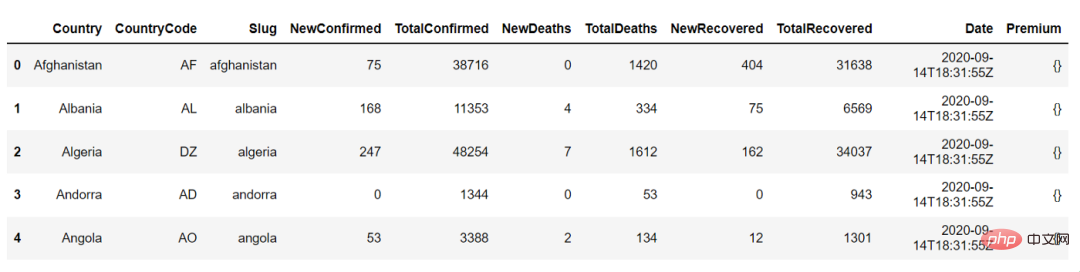
2、汇总统计
下一步就是通过查看数据汇总来了解数据,例如 NewConfirmed、TotalConfirmed 等数字列的计数、均值、标准偏差、分位数以及国家代码等分类列的频率、最高出现值
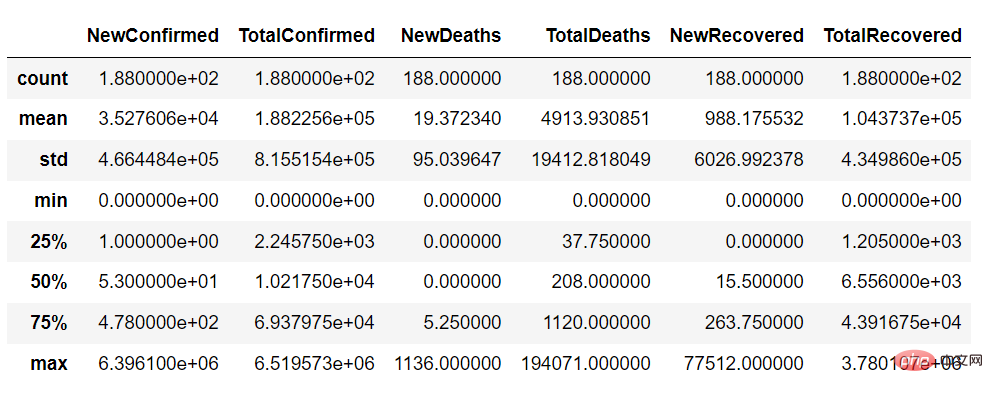
<span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">countries_df</span>.<span style="color: rgb(0, 92, 197); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">describe</span>()
使用 describe 函数,我们可以得到数据集连续变量的摘要,如下所示:
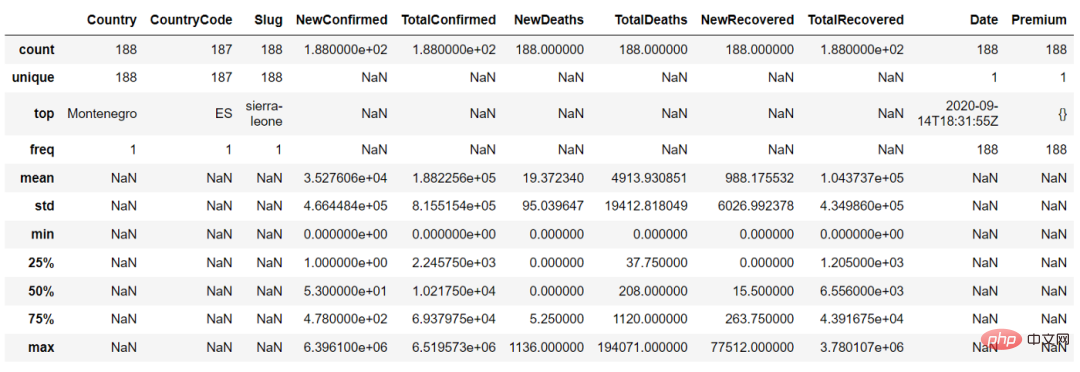
在 describe() 函数中,我们可以设置参数"include = 'all'"来获取连续变量和分类变量的摘要
countries_df.describe(include = 'all')
3、数据选择和过滤
分析其实不需要数据集的所有行和列,只需要选择感兴趣的列并根据问题过滤一些行。
例如,我们可以使用以下代码选择 Country 和 NewConfirmed 列:
countries_df[['Country','NewConfirmed']]
我们还可以将数据过滤Country,使用 loc,我们可以根据一些值过滤列,如下所示:
countries_df.loc[countries_df['Country'] == 'United States of America']

4、聚合
计数、总和、均值等数据聚合,是数据分析最常执行的任务之一。
我们可以使用聚合找到各国的 NewConfimed 病例总数。使用 groupby 和 agg 函数执行聚合。
countries_df.groupby(['Country']).agg({'NewConfirmed':'sum'})5、Join
使用 Join 操作将 2 个数据集组合成一个数据集。
例如:一个数据集可能包含不同国家/地区的 Covid-19 病例数,另一个数据集可能包含不同国家/地区的纬度和经度信息。
现在我们需要结合这两个信息,那么我们可以执行如下所示的连接操作
countries_lat_lon = pd.read_excel('C:/Users/anmol/Desktop/Courses/Python for Data Science/Code/countries_lat_lon.xlsx')
# joining the 2 dataframe : countries_df and countries_lat_lon
# syntax : pd.merge(left_df, right_df, on = 'on_column', how = 'type_of_join')
joined_df = pd.merge(countries_df, countries_lat_lon, on = 'CountryCode', how = 'inner')
joined_df6、内建函数
了解数学内建函数,如 min()、max()、mean()、sum() 等,对于执行不同的分析非常有帮助。
我们可以通过调用它们直接在数据帧上应用这些函数,这些函数可以在列上或在聚合函数中独立使用,如下所示:
# finding sum of NewConfirmed cases of all the countries
countries_df['NewConfirmed'].sum()
# Output : 6,631,899
# finding the sum of NewConfirmed cases across different countries
countries_df.groupby(['Country']).agg({'NewConfirmed':'sum'})
# Output
#NewConfirmed
#Country
#Afghanistan75
#Albania 168
#Algeria 247
#Andorra0
#Angola537、用户自定义函数
我们自己编写的函数是用户自定义函数。我们可以在需要时通过调用该函数来执行这些函数中的代码。例如,我们可以创建一个函数来添加 2 个数字,如下所示:
# User defined function is created using 'def' keyword, followed by function definition - 'addition()' # and 2 arguments num1 and num2 def addition(num1, num2): return num1+num2 # calling the function using function name and providing the arguments print(addition(1,2)) #output : 3
8、Pivot
Pivot 是将一列行内的唯一值转换为多个新列,这是很棒的数据处理技术。
在 Covid-19 数据集上使用 pivot_table() 函数,我们可以将国家名称转换为单独的新列:
# using pivot_table to convert values within the Country column into individual columns and # filling the values corresponding to these columns with numeric variable - NewConfimed pivot_df = pd.pivot_table(countries_df,columns = 'Country', values = 'NewConfirmed') pivot_df
9、遍历数据框
很多时候需要遍历数据框的索引和行,我们可以使用 iterrows 函数遍历数据框:
# iterating over the index and row of a dataframe using iterrows() function
for index, row in countries_df.iterrows():
print('Index is ' + str(index))
print('Country is '+ str(row['Country']))
# Output :
# Index is 0
# Country is Afghanistan
# Index is 1
# Country is Albania
# .......10、字符串操作
很多时候我们处理数据集中的字符串列,在这种情况下,了解一些基本的字符串操作很重要。
例如如何将字符串转换为大写、小写以及如何找到字符串的长度。
# country column to upper case countries_df['Country_upper'] = countries_df['Country'].str.upper() # country column to lower case countries_df['CountryCode_lower']=countries_df['CountryCode'].str.lower() # finding length of characters in the country column countries_df['len'] = countries_df['Country'].str.len() countries_df.head()
以上是十个 Python 小技巧,覆盖了90%的数据分析需求!的详细内容。更多信息请关注PHP中文网其他相关文章!

热AI工具

Undresser.AI Undress
人工智能驱动的应用程序,用于创建逼真的裸体照片

AI Clothes Remover
用于从照片中去除衣服的在线人工智能工具。

Undress AI Tool
免费脱衣服图片

Clothoff.io
AI脱衣机

AI Hentai Generator
免费生成ai无尽的。

热门文章

热工具

记事本++7.3.1
好用且免费的代码编辑器

SublimeText3汉化版
中文版,非常好用

禅工作室 13.0.1
功能强大的PHP集成开发环境

Dreamweaver CS6
视觉化网页开发工具

SublimeText3 Mac版
神级代码编辑软件(SublimeText3)

热门话题
 H5页面制作是否需要持续维护
Apr 05, 2025 pm 11:27 PM
H5页面制作是否需要持续维护
Apr 05, 2025 pm 11:27 PM
H5页面需要持续维护,这是因为代码漏洞、浏览器兼容性、性能优化、安全更新和用户体验提升等因素。有效维护的方法包括建立完善的测试体系、使用版本控制工具、定期监控页面性能、收集用户反馈和制定维护计划。
 PS一直显示正在载入是什么原因?
Apr 06, 2025 pm 06:39 PM
PS一直显示正在载入是什么原因?
Apr 06, 2025 pm 06:39 PM
PS“正在载入”问题是由资源访问或处理问题引起的:硬盘读取速度慢或有坏道:使用CrystalDiskInfo检查硬盘健康状况并更换有问题的硬盘。内存不足:升级内存以满足PS对高分辨率图片和复杂图层处理的需求。显卡驱动程序过时或损坏:更新驱动程序以优化PS和显卡之间的通信。文件路径过长或文件名有特殊字符:使用简短的路径和避免使用特殊字符。PS自身问题:重新安装或修复PS安装程序。
 如何获取58同城工作页面上的实时申请和浏览人数数据?
Apr 05, 2025 am 08:06 AM
如何获取58同城工作页面上的实时申请和浏览人数数据?
Apr 05, 2025 am 08:06 AM
如何在爬虫时获取58同城工作页面的动态数据?在使用爬虫工具爬取58同城的某个工作页面时,可能会遇到这样�...
 JavaScript代码换行:如何优雅地处理长字符串和对象属性访问?
Apr 05, 2025 am 08:03 AM
JavaScript代码换行:如何优雅地处理长字符串和对象属性访问?
Apr 05, 2025 am 08:03 AM
JavaScript代码换行技巧详解在编写JavaScript代码时,我们经常会遇到一行代码过长的情况,这不仅影响代码的可读�...
 PS启动时一直显示正在载入如何解决?
Apr 06, 2025 pm 06:36 PM
PS启动时一直显示正在载入如何解决?
Apr 06, 2025 pm 06:36 PM
PS启动时卡在“正在载入”可能是由于各种原因造成的:禁用损坏或冲突的插件。删除或重命名损坏的配置文件。关闭不必要的程序或升级内存,避免内存不足。升级到固态硬盘,加快硬盘读取速度。重装PS修复损坏的系统文件或安装包问题。查看错误日志分析启动过程中的错误信息。
 【Rust自学】简介
Apr 04, 2025 am 08:03 AM
【Rust自学】简介
Apr 04, 2025 am 08:03 AM
1.0.1前言这个项目(包括代码和注释)是在我自学Rust的过程中记录的。可能有不准确或表述不清的地方,还请大家谅解。如果您从中受益,那就更好了。1.0.2为什么使用RustRust可靠且高效。Rust可以取代C和C,性能相似但安全性更高,并且不需要像C和C那样频繁重新编译来检查错误。主要优点包括:内存安全(防止空指针取消引用、悬空指针和数据争用)。线程安全(确保多线程代码在执行前是安全的)。避免未定义的行为(例如,数组越界、未初始化的变量或访问已释放的内存)。Rust提供现代语言功能(例如泛型
 如何加快PS的载入速度?
Apr 06, 2025 pm 06:27 PM
如何加快PS的载入速度?
Apr 06, 2025 pm 06:27 PM
解决 Photoshop 启动慢的问题需要多管齐下,包括:升级硬件(内存、固态硬盘、CPU);卸载过时或不兼容的插件;定期清理系统垃圾和过多的后台程序;谨慎关闭无关紧要的程序;启动时避免打开大量文件。
 PS载入慢与电脑配置有关吗?
Apr 06, 2025 pm 06:24 PM
PS载入慢与电脑配置有关吗?
Apr 06, 2025 pm 06:24 PM
PS载入慢的原因在于硬件(CPU、内存、硬盘、显卡)和软件(系统、后台程序)的综合影响。解决方法包括:升级硬件(尤其是更换固态硬盘),优化软件(清理系统垃圾、更新驱动、检查PS设置),处理PS文件。定期维护电脑也有助于提升PS运行速度。






