如何使用Python和Matplotlib创建三维折线图
1.0简介
三维图像技术是现在国际最先进的计算机展示技术之一,任何普通电脑只需要安装一个插件,就可以在网络浏览器中呈现三维的产品,不但逼真,而且可以动态展示产品的组合过程,特别适合远程浏览。
立体图视觉上层次分明色彩鲜艳,具有很强的视觉冲击力,让观看的人驻景时间长,留下深刻的印象。立体图给人以真实、栩栩如生,人物呼之欲出,有身临其境的感觉,有很高的艺术欣赏价值。
2.0三维图画法与类型
首先要安装Matplotlib库可以使用pip:
pip install matplotlib
假设已经安装了matplotlib工具包。
利用matplotlib.figure.Figure创建一个图框:
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from mpl_toolkits.mplot3d import Axes3D fig = plt.figure() ax = fig.add_subplot(111, projection='3d')
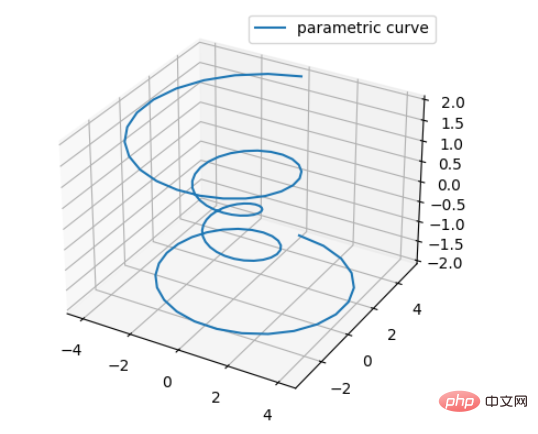
1、直线绘制(Line plots)
基本用法:ax.plot(x,y,z,label=' ')
代码如下:
import matplotlib as mpl from mpl_toolkits.mplot3d import Axes3D import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt mpl.rcParams['legend.fontsize'] = 10 fig = plt.figure() ax = fig.add_subplot(projection='3d') theta = np.linspace(-4 * np.pi, 4 * np.pi, 100) z = np.linspace(-2, 2, 100) r = z ** 2 + 1 x = r * np.sin(theta) y = r * np.cos(theta) ax.plot(x, y, z, label='parametric curve') ax.legend()
效果如下:
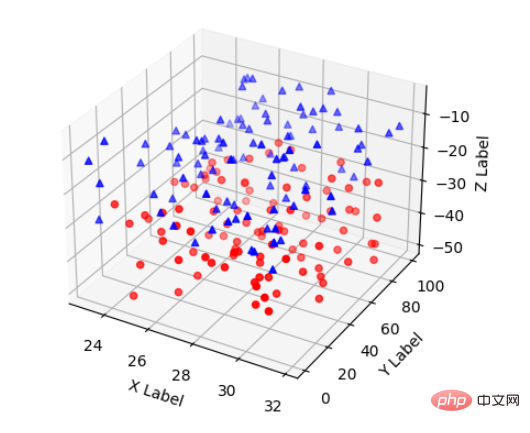
2、散点绘制(Scatter plots)
基本语法:
ax.scatter(xs, ys, zs, s=20, c=None, depthshade=True, *args, *kwargs)
代码大意为:
xs,ys,zs:输入数据;
s:scatter点的尺寸
c:颜色,如c = 'r’就是红色;
depthshase:透明化,True为透明,默认为True,False为不透明
*args等为扩展变量,如maker = ‘o’,则scatter结果为’o‘的形状
示例代码:
from mpl_toolkits.mplot3d import Axes3D
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
def randrange(n, vmin, vmax):
'''
Helper function to make an array of random numbers having shape (n, )
with each number distributed Uniform(vmin, vmax).
'''
return (vmax - vmin)*np.random.rand(n) + vmin
fig = plt.figure()
ax = fig.add_subplot(111, projection='3d')
n = 100
# For each set of style and range settings, plot n random points in the box
# defined by x in [23, 32], y in [0, 100], z in [zlow, zhigh].
for c, m, zlow, zhigh in [('r', 'o', -50, -25), ('b', '^', -30, -5)]:
xs = randrange(n, 23, 32)
ys = randrange(n, 0, 100)
zs = randrange(n, zlow, zhigh)
ax.scatter(xs, ys, zs, c=c, marker=m)
ax.set_xlabel('X Label')
ax.set_ylabel('Y Label')
ax.set_zlabel('Z Label')
plt.show()效果:
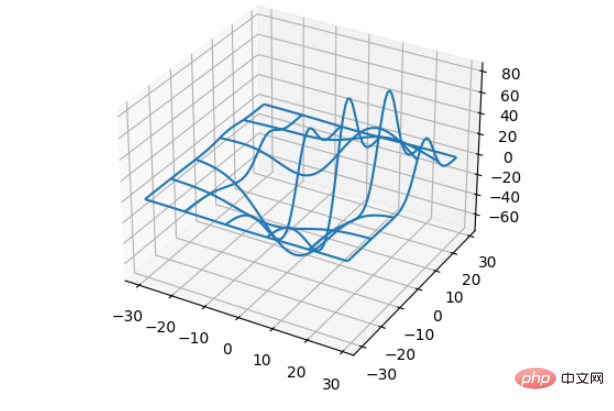
3、线框图(Wireframe plots)
基本用法:ax.plot_wireframe(X, Y, Z, *args, **kwargs)
X,Y,Z:输入数据
rstride:行步长
cstride:列步长
rcount:行数上限
ccount:列数上限
示例代码:
from mpl_toolkits.mplot3d import axes3d import matplotlib.pyplot as plt fig = plt.figure() ax = fig.add_subplot(100, projection='3d') # Grab some test data. X, Y, Z = axes3d.get_test_data(0.12) # Plot a basic wireframe. ax.plot_wireframe(X, Y, Z, rstride=10, cstride=10) plt.show()
4、三角表面图(Tri-Surface plots)
基本用法:ax.plot_trisurf(*args, **kwargs)
ax.plot_trisurf(*args, **kwargs)
X,Y,Z:数据
其他参数类似surface-plot
from mpl_toolkits.mplot3d import Axes3D import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import numpy as np n_radii = 8 n_angles = 36 radii = np.linspace(0.125, 1.0, n_radii) angles = np.linspace(0, 2*np.pi, n_angles, endpoint=False) angles = np.repeat(angles[..., np.newaxis], n_radii, axis=1) # points in the (x, y) plane. x = np.append(0, (radii*np.cos(angles)).flatten()) y = np.append(0, (radii*np.sin(angles)).flatten()) z = np.sin(-x*y) fig = plt.figure() ax = fig.add_subplot(projection='3d') ax.plot_trisurf(x, y, z, linewidth=0.2, antialiased=True) plt.show()
运行效果图:
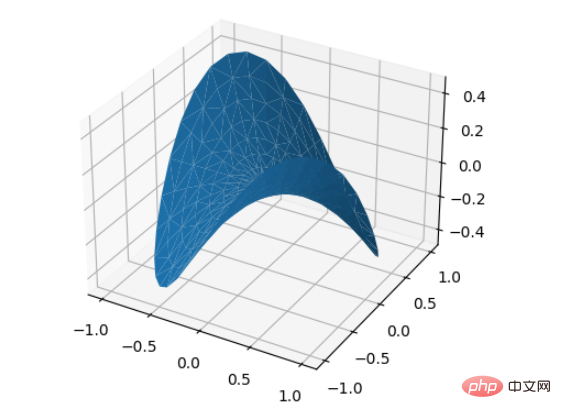
5.随机散点图
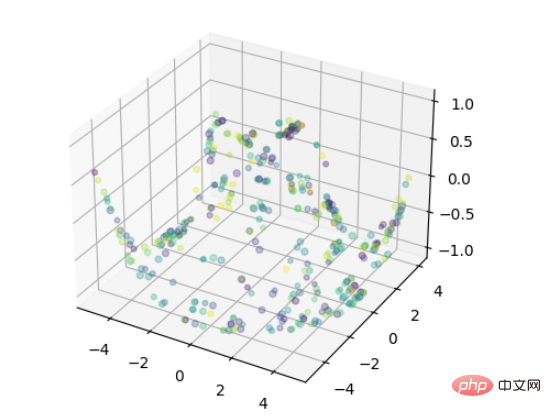
利用scatter生成随机散点图。
函数定义:
#函数定义
matplotlib.pyplot.scatter(x, y,
s=None, #散点的大小 array scalar
c=None, #颜色序列 array、sequency
marker=None, #点的样式
cmap=None, #colormap 颜色样式
norm=None, #归一化 归一化的颜色camp
vmin=None, vmax=None, #对应上面的归一化范围
alpha=None, #透明度
linewidths=None, #线宽
verts=None, #
edgecolors=None, #边缘颜色
data=None,
**kwargs
)
示例代码:
import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt #定义坐标轴 fig4 = plt.figure() ax4 = plt.axes(projection='3d') #生成三维数据 xx = np.random.random(20)*10-5 #取100个随机数,范围在5~5之间 yy = np.random.random(20)*10-5 X, Y = np.meshgrid(xx, yy) Z = np.sin(np.sqrt(X**2+Y**2)) #作图 ax4.scatter(X,Y,Z,alpha=0.3,c=np.random.random(400),s=np.random.randint(10,20,size=(20, 20))) #生成散点.利用c控制颜色序列,s控制大小 plt.show()
效果:
以上是如何使用Python和Matplotlib创建三维折线图的详细内容。更多信息请关注PHP中文网其他相关文章!

热AI工具

Undresser.AI Undress
人工智能驱动的应用程序,用于创建逼真的裸体照片

AI Clothes Remover
用于从照片中去除衣服的在线人工智能工具。

Undress AI Tool
免费脱衣服图片

Clothoff.io
AI脱衣机

AI Hentai Generator
免费生成ai无尽的。

热门文章

热工具

记事本++7.3.1
好用且免费的代码编辑器

SublimeText3汉化版
中文版,非常好用

禅工作室 13.0.1
功能强大的PHP集成开发环境

Dreamweaver CS6
视觉化网页开发工具

SublimeText3 Mac版
神级代码编辑软件(SublimeText3)

热门话题
 PS羽化如何控制过渡的柔和度?
Apr 06, 2025 pm 07:33 PM
PS羽化如何控制过渡的柔和度?
Apr 06, 2025 pm 07:33 PM
羽化控制的关键在于理解其渐变本质。PS本身不提供直接控制渐变曲线的选项,但你可以通过多次羽化、配合蒙版、精细选区,灵活调整半径和渐变柔和度,实现自然过渡效果。
 mysql安装后怎么使用
Apr 08, 2025 am 11:48 AM
mysql安装后怎么使用
Apr 08, 2025 am 11:48 AM
文章介绍了MySQL数据库的上手操作。首先,需安装MySQL客户端,如MySQLWorkbench或命令行客户端。1.使用mysql-uroot-p命令连接服务器,并使用root账户密码登录;2.使用CREATEDATABASE创建数据库,USE选择数据库;3.使用CREATETABLE创建表,定义字段及数据类型;4.使用INSERTINTO插入数据,SELECT查询数据,UPDATE更新数据,DELETE删除数据。熟练掌握这些步骤,并学习处理常见问题和优化数据库性能,才能高效使用MySQL。
 mysql 是否要付费
Apr 08, 2025 pm 05:36 PM
mysql 是否要付费
Apr 08, 2025 pm 05:36 PM
MySQL 有免费的社区版和收费的企业版。社区版可免费使用和修改,但支持有限,适合稳定性要求不高、技术能力强的应用。企业版提供全面商业支持,适合需要稳定可靠、高性能数据库且愿意为支持买单的应用。选择版本时考虑的因素包括应用关键性、预算和技术技能。没有完美的选项,只有最合适的方案,需根据具体情况谨慎选择。
 PS羽化怎么设置?
Apr 06, 2025 pm 07:36 PM
PS羽化怎么设置?
Apr 06, 2025 pm 07:36 PM
PS羽化是一种图像边缘模糊效果,通过在边缘区域对像素加权平均实现。设置羽化半径可以控制模糊程度,数值越大越模糊。灵活调整半径可根据图像和需求优化效果,如处理人物照片时使用较小半径保持细节,处理艺术作品时使用较大半径营造朦胧感。但需注意,半径过大易丢失边缘细节,过小则效果不明显。羽化效果受图像分辨率影响,且需要根据图像理解和效果把握进行调整。
 PS羽化对图像质量有什么影响?
Apr 06, 2025 pm 07:21 PM
PS羽化对图像质量有什么影响?
Apr 06, 2025 pm 07:21 PM
PS羽化会导致图像细节丢失、色彩饱和度降低和噪点增加。为了减少影响,建议使用较小的羽化半径,复制图层后再羽化,以及仔细对比羽化前后图像质量。此外,羽化并不适用于所有情况,有时蒙版等工具更适合处理图像边缘。
 mysql安装后怎么优化数据库性能
Apr 08, 2025 am 11:36 AM
mysql安装后怎么优化数据库性能
Apr 08, 2025 am 11:36 AM
MySQL性能优化需从安装配置、索引及查询优化、监控与调优三个方面入手。1.安装后需根据服务器配置调整my.cnf文件,例如innodb_buffer_pool_size参数,并关闭query_cache_size;2.创建合适的索引,避免索引过多,并优化查询语句,例如使用EXPLAIN命令分析执行计划;3.利用MySQL自带监控工具(SHOWPROCESSLIST,SHOWSTATUS)监控数据库运行状况,定期备份和整理数据库。通过这些步骤,持续优化,才能提升MySQL数据库性能。
 如何针对高负载应用程序优化 MySQL 性能?
Apr 08, 2025 pm 06:03 PM
如何针对高负载应用程序优化 MySQL 性能?
Apr 08, 2025 pm 06:03 PM
MySQL数据库性能优化指南在资源密集型应用中,MySQL数据库扮演着至关重要的角色,负责管理海量事务。然而,随着应用规模的扩大,数据库性能瓶颈往往成为制约因素。本文将探讨一系列行之有效的MySQL性能优化策略,确保您的应用在高负载下依然保持高效响应。我们将结合实际案例,深入讲解索引、查询优化、数据库设计以及缓存等关键技术。1.数据库架构设计优化合理的数据库架构是MySQL性能优化的基石。以下是一些核心原则:选择合适的数据类型选择最小的、符合需求的数据类型,既能节省存储空间,又能提升数据处理速度
 mysql安装错误解决方法
Apr 08, 2025 am 10:48 AM
mysql安装错误解决方法
Apr 08, 2025 am 10:48 AM
MySQL安装失败常见原因及解决方法:1.用户名或密码错误,或MySQL服务未启动,需检查用户名密码并启动服务;2.端口冲突,需更改MySQL监听端口或关闭占用3306端口的程序;3.依赖库缺失,需使用系统包管理器安装必要依赖库;4.权限不足,需使用sudo或管理员权限运行安装程序;5.配置文件错误,需检查my.cnf配置文件,确保配置正确。稳扎稳打,仔细排查,才能顺利安装MySQL。






