Springboot集成Tile客户端之Set命令如何实现
set命令语法
SET key id [FIELD name value ...] [EX seconds] [NX|XX] (OBJECT geojson)|(POINT lat lon z)|(BOUNDS minlat minlon maxlat maxlon)|(HASH geohash)|(STRING value)
set命令就相当于redis中的hash命令的使用,也是一个key和id的组合,但是不同的是,Tile38的set命令还可以携带更多的其他属性,比如可以自定义FIELD字段,还可以设置EX有效期等等,那么我们需要给这个语法设计一套好用的java api,以便开发人员可以更好地使用Tile38。
语法分析
首先,根据上面提供的语法,我们可以分为三部分:
1.第一部分就是命令的启示关键字SET,我们把这个关键字单独作为一部分;
2.第二部分就是key id [FIELD name value ...] [EX seconds] [NX|XX],我们把这些都作为参数;
3.第三部分就是最后的目标数据对象:
(OBJECT geojson)|(POINT lat lon z)|(BOUNDS minlat minlon maxlat maxlon)|(HASH geohash)|(STRING value)
代码设计
1.我们把第一部分的命令关键字通过枚举的方式来管理:
enum Tile38Command implements ProtocolKeyword {
SET;
public final byte[] bytes;
static final String UNDERSCORE = "_";
static final String SPACE = " ";
Tile38Command() {
String name = StringUtils.replace(this.name(), UNDERSCORE, SPACE);
this.bytes = name.getBytes(StandardCharsets.US_ASCII);
}
@Override
public byte[] getBytes() {
return this.bytes;
}
}因为redis客户端工具在发送命令前需要对所有命令进行编码,所以要求所有的命令都必须实现ProtocolKeyword接口。如果命令的起始关键字是两个或多个单词,那么我们会使用下划线连接,转换成bytes的时候我们可以使用空格把下划线替换。
2.我们把命令的第二部分抽象成一个具体的class,通过相关的字段来进行描述:
public class SetOpts {
private String key;
private String id;
//字段值必须是双精度浮点型
private Map<String, Double> fields;
// 单位秒
private int ex;
// 创建方式:
// NX 不存在的时候创建
// XX 存在的时候更新
private NxXx nxXx;
private SetOpts(Builder builder) {
this.key = builder.key;
this.id = builder.id;
this.fields = builder.fields;
this.ex = builder.ex;
this.nxXx = builder.nxXx;
}
// 把所有的参数按顺序放到列表中
public List<String> commandLine() {
List<String> result = new LinkedList<>();
result.add(this.key);
result.add(this.id);
// 添加所有的FIELD
if (MapUtils.isNotEmpty(this.fields)) {
for (Map.Entry<String, Double> entry : this.fields.entrySet()) {
result.add("FIELD");
result.add(entry.getKey());
result.add(entry.getValue().toString());
}
}
// 添加`EX`
if (this.ex >= 0) {
result.add("EX");
result.add(String.valueOf(this.ex));
}
// 添加NX或XX
if (Objects.nonNull(this.nxXx)) {
result.add(this.nxXx.name());
}
// 返回结果
return result;
}
public enum NxXx {
NX,
XX
}
// 建造者模式
public static class Builder {
private String key;
private String id;
//字段值必须是双精度浮点型
private Map<String, Double> fields;
// 单位秒
private int ex = -1;
// 创建方式:
// NX 不存在的时候创建
// XX 存在的时候更新
private NxXx nxXx;
public Builder key(String key) {
this.key = key;
return this;
}
public Builder id(String id) {
this.id = id;
return this;
}
public Builder field(String field, double value) {
if (Objects.isNull(this.fields)) {
this.fields = new LinkedHashMap<>();
}
this.fields.put(field, value);
return this;
}
public Builder ex(int seconds) {
this.ex = seconds;
return this;
}
public Builder nxXx(NxXx nxXx) {
this.nxXx = nxXx;
return this;
}
public SetOpts build() throws AwesomeException {
if (StringUtils.isEmpty(this.key)) {
throw new AwesomeException(500, "key is empty");
}
if (StringUtils.isEmpty(this.id)) {
throw new AwesomeException(500, "id is empty");
}
// 创建SetOpts对象
return new SetOpts(this);
}
}
}我们上面通过建造者的设计模式,把所有的参数都转换成了SetOpts这个类当中,开发人员就可以通过SetOpts对象的构建来灵活地控制命令中的参数了。
3.我们需要把第三部分当中的不同数据对象转换成不同的类型:
POINT数据类型
Point关键的字段就是经纬度,除此之外,还有一个额外的字段z,用来存储额外的业务参数,可为空。
public class Point extends Element implements Serializable {
// 经度
private double lng;
// 维度
private double lat;
// 额外的数据
private double z;
public Point(double lng, double lat, double z) {
this.lat = lat;
this.lng = lng;
this.z = z;
}
public Point(double lng, double lat) {
this(lng, lat, Integer.MIN_VALUE);
}
@Override
public List<String> commandArgs() {
List<String> result = new LinkedList<>();
result.add("POINT");
result.add(String.valueOf(this.lng));
result.add(String.valueOf(this.lat));
if (this.z != Integer.MIN_VALUE) {
result.add(String.valueOf(this.z));
}
return result;
}
}BOUNDS数据类型
BOUNDS就是矩形,它的关键字段就是左下角和右上角两个点位,我们使用coordinate1和coordinate2来表示左下角和右上角;
@AllArgsConstructor
public class Bounds extends Element {
private double[] coordinate1;
private double[] coordinate2;
@Override
public List<String> commandArgs() {
List<String> result = new LinkedList<>();
result.add("BOUNDS");
result.add(String.valueOf(coordinate1[0]));
result.add(String.valueOf(coordinate1[1]));
result.add(String.valueOf(coordinate2[0]));
result.add(String.valueOf(coordinate2[1]));
return result;
}
}HASH和STRING数据类型
HASH和STRING其实就是一个单独的字符串,但是我们还是把它封装一下,以便开发人员使用;
@AllArgsConstructor
public class Geohash extends Element {
private String hash;
@Override
public List<String> commandArgs() {
List<String> result = new LinkedList<>();
result.add("HASH");
result.add(this.hash);
return result;
}
}
@AllArgsConstructor
public class RawString extends Element {
private String raw;
@Override
public List<String> commandArgs() {
List<String> result = new LinkedList<>();
result.add("STRING");
result.add(this.raw);
return result;
}
}OBJECT数据类型
OBJECT其实就是GeoJSON数据,这一类数据比较复杂一点,一共有六种类型,想了解的小伙伴可以看这里geojson.org/
Point, LineString, Polygon, MultiPoint, MultiLineString, MultiPolygon
为了开发人员能够更好的使用这六种类型,我们同样使用建造者模式来设计一下GeoJSON数据类型:
@Data
public class GeoJson {
public static class Builder {
public Point.Builder point() {
return new Point.Builder();
}
public MultiPoint.Builder multPoint() {
return new MultiPoint.Builder();
}
public LineString.Builder lineString() {
return new LineString.Builder();
}
public MultiLineString.Builder multiLineString() {
return new MultiLineString.Builder();
}
public Polygon.Builder polygon() {
return new Polygon.Builder();
}
public MultiPolygon.Builder multiPolygon() {
return new MultiPolygon.Builder();
}
}
}我们现在一个大类里面创建多个方法,每一个方法都把对应类型的建造者给创造出来,这样的话,就相当于这个类当中有创建六种对象的方式,每个建造者都只负责建造对应的那个对象。
下面分别是六个建造者的代码,每个对象都基于最基本的BaseGeoJson来构造,BaseGeoJson中把公共的字段type和额外的meta字段抽出来,各个类型不同的点在于坐标点的数量和层次不同,所以根据各自类型的特点,代码设计如下:
// Point类型
public static class Point extends BaseGeoJson {
// 坐标点
private double[] coordinates;
Point(Builder builder) {
super(builder);
this.type = GeoJsonType.Point;
this.coordinates = builder.coordinates;
}
@Override
protected Object coordinates() {
return this.coordinates;
}
public static class Builder extends BaseGeoJson.Builder {
private double[] coordinates;
public Builder coordinate(double lon, double lat) {
coordinates = new double[]{lat, lon};
return this;
}
public Point build() {
return new Point(this);
}
}
}
// MultiPoint类型
public static class MultiPoint extends BaseGeoJson {
private double[][] coordinates;
MultiPoint(Builder builder) {
super(builder);
this.type = GeoJsonType.MultiPoint;
this.coordinates = builder.convert2Array();
}
@Override
protected Object coordinates() {
return this.coordinates;
}
public static class Builder extends BaseGeoJson.Builder {
private List<Coordinate> coordinates;
public Builder coordinate(double lon, double lat) {
if (CollectionUtils.isEmpty(this.coordinates)) {
this.coordinates = new LinkedList<>();
}
this.coordinates.add(new Coordinate(lat, lon));
return this;
}
protected double[][] convert2Array() {
int length = this.coordinates.size();
double[][] result = new double[length][];
for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) {
result[i] = this.coordinates.get(i).convertToArray();
}
return result;
}
@Override
public MultiPoint build() {
return new MultiPoint(this);
}
}
}
// LineString类型
public static class LineString extends MultiPoint {
private double[][] coordinates;
LineString(Builder builder) {
super(builder);
this.type = GeoJsonType.LineString;
}
public static class Builder extends MultiPoint.Builder {
@Override
public LineString build() {
return new LineString(this);
}
}
}
// MultiLineString类型
public static class MultiLineString extends BaseGeoJson {
private double[][][] coordinates;
MultiLineString(Builder builder) {
super(builder);
this.type = GeoJsonType.MultiLineString;
this.coordinates = builder.convertToArray();
}
@Override
protected Object coordinates() {
return this.coordinates;
}
public static class Builder extends BaseGeoJson.Builder {
private List<Line> lines = new LinkedList<>();
public Line line() {
return new Line(this);
}
void addLine(Line line) {
lines.add(line);
}
double[][][] convertToArray() {
int length = this.lines.size();
double[][][] result = new double[length][][];
for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) {
Line line = this.lines.get(i);
result[i] = line.convert2Array();
}
return result;
}
@Override
public BaseGeoJson build() {
return new MultiLineString(this);
}
}
static class Line {
private List<Coordinate> coordinates;
private Builder builder;
Line(Builder builder) {
this.builder = builder;
this.builder.addLine(this);
}
private double[][] convert2Array() {
int length = this.coordinates.size();
double[][] result = new double[length][];
for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) {
result[i] = this.coordinates.get(i).convertToArray();
}
return result;
}
public Line coordinate(double lon, double lat) {
if (CollectionUtils.isEmpty(this.coordinates)) {
this.coordinates = new LinkedList<>();
}
this.coordinates.add(new Coordinate(lat, lon));
return this;
}
public Line nextLine() {
return new Line(this.builder);
}
public Builder end() {
return this.builder;
}
}
}
// Polygon类型
public static class Polygon extends MultiPoint {
private double[][][] coordinates;
Polygon(Builder builder) {
super(builder);
this.type = GeoJsonType.Polygon;
this.coordinates = new double[][][]{builder.convert2Array()};
}
public static class Builder extends MultiPoint.Builder {
@Override
public Polygon build() {
return new Polygon(this);
}
}
}
// MultiPolygon类型
public static class MultiPolygon extends BaseGeoJson {
private double[][][][] coordinates;
MultiPolygon(Builder builder) {
super(builder);
this.type = GeoJsonType.MultiPolygon;
this.coordinates = new double[][][][]{builder.convert2Array()};
}
@Override
protected Object coordinates() {
return this.coordinates;
}
public static class Builder extends BaseGeoJson.Builder {
private List<Polygon> polygons = new LinkedList<>();
@Override
public BaseGeoJson build() {
return new MultiPolygon(this);
}
void addPolygon(Polygon polygon) {
polygons.add(polygon);
}
private double[][][] convert2Array() {
int length = this.polygons.size();
double[][][] result = new double[length][][];
for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) {
result[i] = this.polygons.get(i).convert2Array();
}
return result;
}
}
static class Polygon {
private List<Coordinate> coordinates;
private Builder builder;
Polygon(Builder builder) {
this.builder = builder;
this.builder.addPolygon(this);
}
private double[][] convert2Array() {
int length = this.coordinates.size();
double[][] result = new double[length][];
for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) {
result[i] = this.coordinates.get(i).convertToArray();
}
return result;
}
public Polygon coordinate(double lon, double lat) {
if (CollectionUtils.isEmpty(this.coordinates)) {
this.coordinates = new LinkedList<>();
}
this.coordinates.add(new Coordinate(lat, lon));
return this;
}
public Polygon nextLine() {
return new Polygon(this.builder);
}
public Builder end() {
return this.builder;
}
}
}
// 基类BaseGeoJson
public abstract static class BaseGeoJson extends Element {
// 公共字段type
protected GeoJsonType type;
// 公共字段metadata
private Map<String, String> metadata;
BaseGeoJson(Builder builder) {
this.metadata = builder.metadata;
}
protected abstract Object coordinates();
// 转换成命令参数
@Override
public List<String> commandArgs() {
List<String> result = new LinkedList<>();
result.add("OBJECT");
result.add(toJson());
return result;
}
// 提供统一的转json方法
protected String toJson() {
Map<String, Object> map = new LinkedHashMap<>();
map.put("type", this.type);
map.put("coordinates", coordinates());
if (!CollectionUtils.isEmpty(this.metadata)) {
for (Map.Entry<String, String> entry : this.metadata.entrySet()) {
map.put(entry.getKey(), entry.getValue());
}
}
return JsonUtil.obj2String(map);
}
abstract static class Builder {
private Map<String, String> metadata;
public Builder meta(String key, String value) {
if (MapUtils.isEmpty(this.metadata)) {
this.metadata = new LinkedHashMap<>();
}
this.metadata.put(key, value);
return this;
}
public abstract BaseGeoJson build();
}
static class Coordinate {
private double lat;
private double lon;
Coordinate(double lat, double lon) {
this.lat = lat;
this.lon = lon;
}
public double[] convertToArray() {
return new double[]{this.lat, this.lon};
}
}
// GeoJSON所有的数据类型
enum GeoJsonType {
Point,
LineString,
Polygon,
MultiPoint,
MultiLineString,
MultiPolygon
}
}最后,再补充一个基类Element:
public abstract class Element implements Serializable {
public abstract List<String> commandArgs();
}如何使用
我们针对所有的数据类型全部转换成具体的代码设计,下面我们看看如何使用:
private String setElement(SetOpts setOpts, Element element) {
List<String> args1 = setOpts.commandLine();
List<String> commandArgs = element.commandArgs();
return execute(Tile38Command.SET, args1, commandArgs);
}
/**
* 设置点位
*
* @param setOpts
* @param point
* @return
*/
public String setPoint(SetOpts setOpts, Point point) {
return setElement(setOpts, point);
}
/**
* 设置对象
*
* @param setOpts
* @param geoJson
* @return
*/
public String setObject(SetOpts setOpts, GeoJson.BaseGeoJson geoJson) {
return setElement(setOpts, geoJson);
}
/**
* 设置矩形边界
*
* @param setOpts
* @param bounds
* @return
*/
public String setBounds(SetOpts setOpts, Bounds bounds) {
return setElement(setOpts, bounds);
}
/**
* 设置geohash
*
* @param setOpts
* @param geohash
* @return
*/
public String setGeohash(SetOpts setOpts, Geohash geohash) {
return setElement(setOpts, geohash);
}
/**
* 设置String
*
* @param setOpts
* @param string
* @return
*/
public String setString(SetOpts setOpts, RawString string) {
return setElement(setOpts, string);
}以上是Springboot集成Tile客户端之Set命令如何实现的详细内容。更多信息请关注PHP中文网其他相关文章!

热AI工具

Undresser.AI Undress
人工智能驱动的应用程序,用于创建逼真的裸体照片

AI Clothes Remover
用于从照片中去除衣服的在线人工智能工具。

Undress AI Tool
免费脱衣服图片

Clothoff.io
AI脱衣机

AI Hentai Generator
免费生成ai无尽的。

热门文章

热工具

记事本++7.3.1
好用且免费的代码编辑器

SublimeText3汉化版
中文版,非常好用

禅工作室 13.0.1
功能强大的PHP集成开发环境

Dreamweaver CS6
视觉化网页开发工具

SublimeText3 Mac版
神级代码编辑软件(SublimeText3)

热门话题
 Springboot怎么集成Jasypt实现配置文件加密
Jun 01, 2023 am 08:55 AM
Springboot怎么集成Jasypt实现配置文件加密
Jun 01, 2023 am 08:55 AM
Jasypt介绍Jasypt是一个java库,它允许开发员以最少的努力为他/她的项目添加基本的加密功能,并且不需要对加密工作原理有深入的了解用于单向和双向加密的高安全性、基于标准的加密技术。加密密码,文本,数字,二进制文件...适合集成到基于Spring的应用程序中,开放API,用于任何JCE提供程序...添加如下依赖:com.github.ulisesbocchiojasypt-spring-boot-starter2.1.1Jasypt好处保护我们的系统安全,即使代码泄露,也可以保证数据源的
 详解MyBatis动态SQL标签中的Set标签功能
Feb 26, 2024 pm 07:48 PM
详解MyBatis动态SQL标签中的Set标签功能
Feb 26, 2024 pm 07:48 PM
MyBatis动态SQL标签解读:Set标签用法详解MyBatis是一个优秀的持久层框架,它提供了丰富的动态SQL标签,可以灵活地构建数据库操作语句。其中,Set标签是用于生成UPDATE语句中SET子句的标签,在更新操作中非常常用。本文将详细解读MyBatis中Set标签的用法,以及通过具体的代码示例来演示其功能。什么是Set标签Set标签用于MyBati
 SpringBoot怎么集成Redisson实现延迟队列
May 30, 2023 pm 02:40 PM
SpringBoot怎么集成Redisson实现延迟队列
May 30, 2023 pm 02:40 PM
使用场景1、下单成功,30分钟未支付。支付超时,自动取消订单2、订单签收,签收后7天未进行评价。订单超时未评价,系统默认好评3、下单成功,商家5分钟未接单,订单取消4、配送超时,推送短信提醒……对于延时比较长的场景、实时性不高的场景,我们可以采用任务调度的方式定时轮询处理。如:xxl-job今天我们采
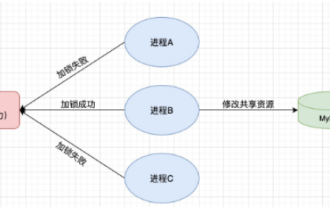 怎么在SpringBoot中使用Redis实现分布式锁
Jun 03, 2023 am 08:16 AM
怎么在SpringBoot中使用Redis实现分布式锁
Jun 03, 2023 am 08:16 AM
一、Redis实现分布式锁原理为什么需要分布式锁在聊分布式锁之前,有必要先解释一下,为什么需要分布式锁。与分布式锁相对就的是单机锁,我们在写多线程程序时,避免同时操作一个共享变量产生数据问题,通常会使用一把锁来互斥以保证共享变量的正确性,其使用范围是在同一个进程中。如果换做是多个进程,需要同时操作一个共享资源,如何互斥呢?现在的业务应用通常是微服务架构,这也意味着一个应用会部署多个进程,多个进程如果需要修改MySQL中的同一行记录,为了避免操作乱序导致脏数据,此时就需要引入分布式锁了。想要实现分
 springboot读取文件打成jar包后访问不到怎么解决
Jun 03, 2023 pm 04:38 PM
springboot读取文件打成jar包后访问不到怎么解决
Jun 03, 2023 pm 04:38 PM
springboot读取文件,打成jar包后访问不到最新开发出现一种情况,springboot打成jar包后读取不到文件,原因是打包之后,文件的虚拟路径是无效的,只能通过流去读取。文件在resources下publicvoidtest(){Listnames=newArrayList();InputStreamReaderread=null;try{ClassPathResourceresource=newClassPathResource("name.txt");Input
 Springboot+Mybatis-plus不使用SQL语句进行多表添加怎么实现
Jun 02, 2023 am 11:07 AM
Springboot+Mybatis-plus不使用SQL语句进行多表添加怎么实现
Jun 02, 2023 am 11:07 AM
在Springboot+Mybatis-plus不使用SQL语句进行多表添加操作我所遇到的问题准备工作在测试环境下模拟思维分解一下:创建出一个带有参数的BrandDTO对象模拟对后台传递参数我所遇到的问题我们都知道,在我们使用Mybatis-plus中进行多表操作是极其困难的,如果你不使用Mybatis-plus-join这一类的工具,你只能去配置对应的Mapper.xml文件,配置又臭又长的ResultMap,然后再去写对应的sql语句,这种方法虽然看上去很麻烦,但具有很高的灵活性,可以让我们
 SpringBoot与SpringMVC的比较及差别分析
Dec 29, 2023 am 11:02 AM
SpringBoot与SpringMVC的比较及差别分析
Dec 29, 2023 am 11:02 AM
SpringBoot和SpringMVC都是Java开发中常用的框架,但它们之间有一些明显的差异。本文将探究这两个框架的特点和用途,并对它们的差异进行比较。首先,我们来了解一下SpringBoot。SpringBoot是由Pivotal团队开发的,它旨在简化基于Spring框架的应用程序的创建和部署。它提供了一种快速、轻量级的方式来构建独立的、可执行
 SpringBoot怎么自定义Redis实现缓存序列化
Jun 03, 2023 am 11:32 AM
SpringBoot怎么自定义Redis实现缓存序列化
Jun 03, 2023 am 11:32 AM
1、自定义RedisTemplate1.1、RedisAPI默认序列化机制基于API的Redis缓存实现是使用RedisTemplate模板进行数据缓存操作的,这里打开RedisTemplate类,查看该类的源码信息publicclassRedisTemplateextendsRedisAccessorimplementsRedisOperations,BeanClassLoaderAware{//声明了key、value的各种序列化方式,初始值为空@NullableprivateRedisSe






