怎么使用Spring Boot+gRPC构建微服务并部署
1. 为什么要用Istio?
目前,对于Java技术栈来说,构建微服务的最佳选择是Spring Boot而Spring Boot一般搭配目前落地案例很多的微服务框架Spring Cloud来使用。
Spring Cloud看似很完美,但是在实际上手开发后,很容易就会发现Spring Cloud存在以下比较严重的问题:
服务治理相关的逻辑存在于Spring Cloud Netflix等SDK中,与业务代码紧密耦合。
SDK对业务代码侵入太大,SDK发生升级且无法向下兼容时,业务代码必须做出改变以适配SDK的升级——即使业务逻辑并没有发生任何变化。
各种组件令人眼花缭乱,质量也参差不齐,学习成本太高,且组件之间代码很难完全复用,仅仅为了实现治理逻辑而学习SDK也并不是很好的选择。
绑定于Java技术栈,虽然可以接入其他语言但要手动实现服务治理相关的逻辑,不符合微服务“可以用多种语言进行开发”的原则。
Spring Cloud仅仅是一个开发框架,没有实现微服务所必须的服务调度、资源分配等功能,这些需求要借助Kubernetes等平台来完成。Spring Cloud and Kubernetes have overlapping functionality, and conflicting features create difficulties in smooth collaboration between the two.。
替代Spring Cloud的选择有没有呢?有!它就是Istio。
Istio将治理逻辑完全独立于业务代码之外,实现了一个独立的进程(Sidecar)。在部署时,Sidecar和业务代码共存于同一个Pod中,但业务代码完全无感知Sidecar的存在。这就实现了治理逻辑对业务代码的零侵入——实际上不仅是代码没有侵入,在运行时两者也没有任何的耦合。这使得不同的微服务完全可以使用不同语言、不同技术栈来开发,也不用担心服务治理问题,可以说这是一种很优雅的解决方案了。
所以,“为什么要使用Istio”这个问题也就迎刃而解了——因为Istio解决了传统微服务诸如业务逻辑与服务治理逻辑耦合、不能很好地实现跨语言等痛点,而且非常容易使用。学习如何使用Istio并不困难,只要掌握了Kubernetes。
1.1. 为什么要使用gRPC作为通信框架?
在微服务架构中,服务之间的通信是一个比较大的问题,一般采用RPC或者RESTful API来实现。
Spring Boot可以使用RestTemplate调用远程服务,但这种方式不直观,代码也比较复杂,进行跨语言通信也是个比较大的问题;而gRPC相比Dubbo等常见的Java RPC框架更加轻量,使用起来也很方便,代码可读性高,并且与Istio和Kubernetes可以很好地进行整合,在Protobuf和HTTP2的加持下性能也还不错,所以这次选择了gRPC来解决Spring Boot微服务间通信的问题。并且,虽然gRPC没有服务发现、负载均衡等能力,但是Istio在这方面就非常强大,两者形成了完美的互补关系。
由于考虑到各种grpc-spring-boot-starter可能会对Spring Boot与Istio的整合产生不可知的副作用,所以这一次我没有用任何的grpc-spring-boot-starter,而是直接手写了gRPC与Spring Boot的整合。如果您不想使用第三方框架来整合gRPC和Spring Boot,可以参考我的简单实现方法。
1.2. 编写业务代码
首先使用Spring Initializr建立父级项目spring-boot-istio,并引入gRPC的依赖。pom文件如下:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 https://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<modules>
<module>spring-boot-istio-api</module>
<module>spring-boot-istio-server</module>
<module>spring-boot-istio-client</module>
</modules>
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>2.2.6.RELEASE</version>
<relativePath/>
</parent>
<groupId>site.wendev</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-istio</artifactId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
<name>spring-boot-istio</name>
<description>Demo project for Spring Boot With Istio.</description>
<packaging>pom</packaging>
<properties>
<java.version>1.8</java.version>
</properties>
<dependencyManagement>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>io.grpc</groupId>
<artifactId>grpc-all</artifactId>
<version>1.28.1</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</dependencyManagement>
</project>然后建立公共依赖模块spring-boot-istio-api,pom文件如下,主要就是gRPC的一些依赖:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<parent>
<artifactId>spring-boot-istio</artifactId>
<groupId>site.wendev</groupId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
</parent>
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<artifactId>spring-boot-istio-api</artifactId>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>io.grpc</groupId>
<artifactId>grpc-all</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>javax.annotation</groupId>
<artifactId>javax.annotation-api</artifactId>
<version>1.3.2</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<extensions>
<extension>
<groupId>kr.motd.maven</groupId>
<artifactId>os-maven-plugin</artifactId>
<version>1.6.2</version>
</extension>
</extensions>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.xolstice.maven.plugins</groupId>
<artifactId>protobuf-maven-plugin</artifactId>
<version>0.6.1</version>
<configuration>
<protocArtifact>com.google.protobuf:protoc:3.11.3:exe:${os.detected.classifier}</protocArtifact>
<pluginId>grpc-java</pluginId>
<pluginArtifact>io.grpc:protoc-gen-grpc-java:1.28.1:exe:${os.detected.classifier}</pluginArtifact>
<protocExecutable>/Users/jiangwen/tools/protoc-3.11.3/bin/protoc</protocExecutable>
</configuration>
<executions>
<execution>
<goals>
<goal>compile</goal>
<goal>compile-custom</goal>
</goals>
</execution>
</executions>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
</project>建立src/main/proto文件夹,在此文件夹下建立hello.proto,定义服务间的接口如下:
syntax = "proto3";
option java_package = "site.wendev.spring.boot.istio.api";
option java_outer_classname = "HelloWorldService";
package helloworld;
service HelloWorld {
rpc SayHello (HelloRequest)
returns (HelloResponse) {}
}
message HelloRequest {
string name = 1;
}
message HelloResponse {
string message = 1;
}很简单,就是发送一个name返回一个带name的message。
然后生成服务端和客户端的代码,并且放到java文件夹下。这部分内容可以参考gRPC的官方文档。
一旦API模块可用,即可开发服务提供者(服务器)和服务消费者(客户端)。这里我们重点看一下如何整合gRPC和Spring Boot。
1) 服务端
业务代码非常简单:
/**
* 服务端业务逻辑实现
*
* @author 江文
* @date 2020/4/12 2:49 下午
*/
@Slf4j
@Component
public class HelloServiceImpl extends HelloWorldGrpc.HelloWorldImplBase {
@Override
public void sayHello(HelloWorldService.HelloRequest request,
StreamObserver<HelloWorldService.HelloResponse> responseObserver) {
// 根据请求对象建立响应对象,返回响应信息
HelloWorldService.HelloResponse response = HelloWorldService.HelloResponse
.newBuilder()
.setMessage(String.format("Hello, %s. This message comes from gRPC.", request.getName()))
.build();
responseObserver.onNext(response);
responseObserver.onCompleted();
log.info("Client Message Received:[{}]", request.getName());
}
}除了业务代码之外,我们还需要在应用启动时同时启动 gRPC Server。首先写一下Server端的启动、关闭等逻辑:
/**
* gRPC Server的配置——启动、关闭等
* 需要使用<code>@Component</code>注解注册为一个Spring Bean
*
* @author 江文
* @date 2020/4/12 2:56 下午
*/
@Slf4j
@Componentpublic class GrpcServerConfiguration {
@Autowired
HelloServiceImpl service;
/** 注入配置文件中的端口信息 */
@Value("${grpc.server-port}")
private int port;
private Server server;
public void start() throws IOException {
// 构建服务端
log.info("Starting gRPC on port {}.", port);
server = ServerBuilder.forPort(port).addService(service).build().start();
log.info("gRPC server started, listening on {}.", port);
// 添加服务端关闭的逻辑
Runtime.getRuntime().addShutdownHook(new Thread(() -> {
log.info("Shutting down gRPC server.");
GrpcServerConfiguration.this.stop();
log.info("gRPC server shut down successfully.");
}));
}
private void stop() {
if (server != null) {
// 关闭服务端
server.shutdown();
}
}
public void block() throws InterruptedException {
if (server != null) {
// 服务端启动后直到应用关闭都处于阻塞状态,方便接收请求
server.awaitTermination();
}
}
}定义好gRPC的启动、停止等逻辑后,就可以使用CommandLineRunner把它加入到Spring Boot的启动中去了:
/**
* 加入gRPC Server的启动、停止等逻辑到Spring Boot的生命周期中
*
* @author 江文
* @date 2020/4/12 3:10 下午
*/
@Component
public class GrpcCommandLineRunner implements CommandLineRunner {
@Autowired
GrpcServerConfiguration configuration;
@Override
public void run(String... args) throws Exception {
configuration.start();
configuration.block();
}
}我们将gRPC的逻辑注册成Spring Bean是因为需要获取到它的实例并进行相应的操作。
这样,在启动Spring Boot时,由于CommandLineRunner的存在,gRPC服务端也就可以一同启动了。
2) 客户端
业务代码同样非常简单:
/**
* 客户端业务逻辑实现
*
* @author 江文
* @date 2020/4/12 3:26 下午
*/
@RestController
@Slf4j
public class HelloController {
@Autowired
GrpcClientConfiguration configuration;
@GetMapping("/hello")
public String hello(@RequestParam(name = "name", defaultValue = "JiangWen", required = false) String name) {
// 构建一个请求 HelloWorldService.HelloRequest request = HelloWorldService.HelloRequest
.newBuilder()
.setName(name)
.build(); // 使用stub发送请求至服务端
HelloWorldService.HelloResponse response = configuration.getStub().sayHello(request);
log.info("Server response received: [{}]", response.getMessage());
return response.getMessage();
}
}在启动客户端时,我们需要打开gRPC的客户端,并获取到channel和stub以进行RPC通信,来看看gRPC客户端的实现逻辑:
/**
* gRPC Client的配置——启动、建立channel、获取stub、关闭等
* 需要注册为Spring Bean
*
* @author 江文
* @date 2020/4/12 3:27 下午
*/
@Slf4j
@Component
public class GrpcClientConfiguration {
/** gRPC Server的地址 */
@Value("${server-host}")
private String host;
/** gRPC Server的端口 */
@Value("${server-port}")
private int port;
private ManagedChannel channel;
private HelloWorldGrpc.HelloWorldBlockingStub stub;
public void start() {
// 开启channel
channel = ManagedChannelBuilder.forAddress(host, port).usePlaintext().build();
// 通过channel获取到服务端的stub
stub = HelloWorldGrpc.newBlockingStub(channel);
log.info("gRPC client started, server address: {}:{}", host, port);
}
public void shutdown() throws InterruptedException {
// 调用shutdown方法后等待1秒关闭channel
channel.shutdown().awaitTermination(1, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
log.info("gRPC client shut down successfully.");
}
public HelloWorldGrpc.HelloWorldBlockingStub getStub() {
return this.stub;
}
}比服务端要简单一些。
最后,仍然需要一个CommandLineRunner把这些启动逻辑加入到Spring Boot的启动过程中:
/**
* 加入gRPC Client的启动、停止等逻辑到Spring Boot生命周期中
*
* @author 江文
* @date 2020/4/12 3:36 下午
*/
@Component
@Slf4j
public class GrpcClientCommandLineRunner implements CommandLineRunner {
@Autowired
GrpcClientConfiguration configuration;
@Override
public void run(String... args) {
// 开启gRPC客户端
configuration.start();
// 添加客户端关闭的逻辑
Runtime.getRuntime().addShutdownHook(new Thread(() -> {
try {
configuration.shutdown();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}));
}
}1.3、 编写Dockerfile
业务代码跑通之后,就可以制作Docker镜像,准备部署到Istio中去了。
在开始编写Dockerfile之前,先改动一下客户端的配置文件:
server:
port: 19090
spring:
application:
name: spring-boot-istio-clientserver-host: ${server-host}server-port: ${server-port}接下来编写Dockerfile:
1) 服务端:
FROM openjdk:8u121-jdk RUN /bin/cp /usr/share/zoneinfo/Asia/Shanghai /etc/localtime \ && echo 'Asia/Shanghai' >/etc/timezone ADD /target/spring-boot-istio-server-0.0.1-SNAPSHOT.jar /ENV SERVER_PORT="18080" ENTRYPOINT java -jar /spring-boot-istio-server-0.0.1-SNAPSHOT.jar
主要是规定服务端应用的端口为18080,并且在容器启动时让服务端也一起启动。
2) 客户端:
FROM openjdk:8u121-jdk RUN /bin/cp /usr/share/zoneinfo/Asia/Shanghai /etc/localtime \ && echo 'Asia/Shanghai' >/etc/timezoneADD /target/spring-boot-istio-client-0.0.1-SNAPSHOT.jar /ENV GRPC_SERVER_HOST="spring-boot-istio-server"ENV GRPC_SERVER_PORT="18888"ENTRYPOINT java -jar /spring-boot-istio-client-0.0.1-SNAPSHOT.jar \ --server-host=$GRPC_SERVER_HOST \ --server-port=$GRPC_SERVER_PORT
可以看到这里添加了启动参数,配合前面的配置,当这个镜像部署到Kubernetes集群时,就可以在Kubernetes的配合之下通过服务名找到服务端了。
同时,服务端和客户端的pom文件中添加:
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
<configuration>
<executable>true</executable>
</configuration>
</plugin>
<plugin>
<groupId>com.spotify</groupId>
<artifactId>dockerfile-maven-plugin</artifactId>
<version>1.4.13</version>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>javax.activation</groupId>
<artifactId>activation</artifactId>
<version>1.1</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<executions>
<execution>
<id>default</id>
<goals>
<goal>build</goal>
<goal>push</goal>
</goals>
</execution>
</executions>
<configuration>
<repository>wendev-docker.pkg.coding.net/develop/docker/${project.artifactId}</repository>
<tag>${project.version}</tag>
<buildArgs>
<JAR_FILE>${project.build.finalName}.jar</JAR_FILE>
</buildArgs>
</configuration>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>这样执行mvn clean package时就可以同时把docker镜像构建出来了。
2. 编写部署文件
有了镜像之后,就可以写部署文件了:
1) 服务端:
apiVersion: v1
kind:
Servicemetadata:
name: spring-boot-istio-server
spec:
type: ClusterIP
ports:
- name: http
port: 18080
targetPort: 18080
- name: grpc
port: 18888
targetPort: 18888
selector:
app: spring-boot-istio-server
---apiVersion: apps/v1
kind:
Deploymentmetadata:
name: spring-boot-istio-server
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
app: spring-boot-istio-server
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: spring-boot-istio-server
spec:
containers:
- name: spring-boot-istio-server
image: wendev-docker.pkg.coding.net/develop/docker/spring-boot-istio-server:0.0.1-SNAPSHOT
imagePullPolicy: Always
tty: true
ports:
- name: http
protocol: TCP
containerPort: 18080
- name: grpc
protocol: TCP
containerPort: 18888主要是暴露服务端的端口:18080和gRPC Server的端口18888,以便可以从Pod外部访问服务端。
2) 客户端:
apiVersion: v1
kind:
Servicemetadata:
name:
spring-boot-istio-client
spec:
type: ClusterIP
ports:
- name: http
port: 19090
targetPort: 19090
selector:
app: spring-boot-istio-client
---apiVersion: apps/v1
kind:
Deploymentmetadata:
name: spring-boot-istio-client
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
app: spring-boot-istio-client
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: spring-boot-istio-client
spec:
containers:
- name: spring-boot-istio-client
image: wendev-docker.pkg.coding.net/develop/docker/spring-boot-istio-client:0.0.1-SNAPSHOT
imagePullPolicy: Always
tty: true
ports:
- name: http
protocol: TCP
containerPort: 19090主要是暴露客户端的端口19090,以便访问客户端并调用服务端。
如果想先试试把它们部署到k8s可不可以正常访问,可以这样配置Ingress:
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1beta1
kind:
Ingressmetadata:
name: nginx-web
annotations:
kubernetes.io/ingress.class: "nginx"
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/use-reges: "true"
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/proxy-connect-timeout: "600"
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/proxy-send-timeout: "600"
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/proxy-read-timeout: "600"
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/proxy-body-size: "10m"
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/rewrite-target: /
spec:
rules:
- host: dev.wendev.site
http:
paths:
- path: /
backend:
serviceName: spring-boot-istio-client
servicePort: 19090Istio的网关配置文件与k8s不大一样:
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1alpha3
kind:
Gatewaymetadata:
name: spring-boot-istio-gateway
spec:
selector:
istio: ingressgateway
servers:
- port:
number: 80
name: http
protocol: HTTP
hosts:
- "*"
---apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1alpha3
kind: Virtual
Servicemetadata:
name: spring-boot-istio
spec:
hosts:
- "*"
gateways:
- spring-boot-istio-gateway
http:
- match:
- uri:
exact: /hello
route:
- destination:
host: spring-boot-istio-client
port:
number: 19090主要就是暴露/hello这个路径,并且指定对应的服务和端口。
3. 部署应用到Istio
首先搭建k8s集群并且安装istio。我使用的k8s版本是1.16.0,Istio版本是最新的1.6.0-alpha.1,使用istioctl命令安装Istio。建议跑通官方的bookinfo示例之后再来部署本项目。
注:以下命令都是在开启了自动注入Sidecar的前提下运行的
我是在虚拟机中运行的k8s,所以istio-ingressgateway没有外部ip:
$ kubectl get svc istio-ingressgateway -n istio-system
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S)
AGEistio-ingressgateway NodePort 10.97.158.232 <none> 15020:30388/TCP,80:31690/TCP,443:31493/TCP,15029:32182/TCP,15030:31724/TCP,15031:30887/TCP,15032:30369/TCP,31400:31122/TCP,15443:31545/TCP 26h所以,需要设置IP和端口,以NodePort的方式访问gateway:
export INGRESS_PORT=$(kubectl -n istio-system get service istio-ingressgateway -o jsonpath='{.spec.ports[?(@.name=="http2")].nodePort}')
export SECURE_INGRESS_PORT=$(kubectl -n istio-system get service istio-ingressgateway -o jsonpath='{.spec.ports[?(@.name=="https")].nodePort}')
export INGRESS_HOST=127.0.0.1export GATEWAY_URL=$INGRESS_HOST:$INGRESS_PORT这样就可以了。
接下来部署服务:
$ kubectl apply -f spring-boot-istio-server.yml $ kubectl apply -f spring-boot-istio-client.yml $ kubectl apply -f istio-gateway.yml
必须要等到两个pod全部变为Running而且Ready变为2/2才算部署完成。
接下来就可以通过
curl -s http://${GATEWAY_URL}/hello访问到服务了。如果成功返回了Hello, JiangWen. This message comes from gRPC.的结果,没有出错则说明部署完成。
以上是怎么使用Spring Boot+gRPC构建微服务并部署的详细内容。更多信息请关注PHP中文网其他相关文章!

热AI工具

Undresser.AI Undress
人工智能驱动的应用程序,用于创建逼真的裸体照片

AI Clothes Remover
用于从照片中去除衣服的在线人工智能工具。

Undress AI Tool
免费脱衣服图片

Clothoff.io
AI脱衣机

AI Hentai Generator
免费生成ai无尽的。

热门文章

热工具

记事本++7.3.1
好用且免费的代码编辑器

SublimeText3汉化版
中文版,非常好用

禅工作室 13.0.1
功能强大的PHP集成开发环境

Dreamweaver CS6
视觉化网页开发工具

SublimeText3 Mac版
神级代码编辑软件(SublimeText3)
 Springboot怎么集成Jasypt实现配置文件加密
Jun 01, 2023 am 08:55 AM
Springboot怎么集成Jasypt实现配置文件加密
Jun 01, 2023 am 08:55 AM
Jasypt介绍Jasypt是一个java库,它允许开发员以最少的努力为他/她的项目添加基本的加密功能,并且不需要对加密工作原理有深入的了解用于单向和双向加密的高安全性、基于标准的加密技术。加密密码,文本,数字,二进制文件...适合集成到基于Spring的应用程序中,开放API,用于任何JCE提供程序...添加如下依赖:com.github.ulisesbocchiojasypt-spring-boot-starter2.1.1Jasypt好处保护我们的系统安全,即使代码泄露,也可以保证数据源的
 怎么在SpringBoot中使用Redis实现分布式锁
Jun 03, 2023 am 08:16 AM
怎么在SpringBoot中使用Redis实现分布式锁
Jun 03, 2023 am 08:16 AM
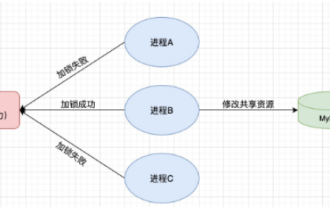
一、Redis实现分布式锁原理为什么需要分布式锁在聊分布式锁之前,有必要先解释一下,为什么需要分布式锁。与分布式锁相对就的是单机锁,我们在写多线程程序时,避免同时操作一个共享变量产生数据问题,通常会使用一把锁来互斥以保证共享变量的正确性,其使用范围是在同一个进程中。如果换做是多个进程,需要同时操作一个共享资源,如何互斥呢?现在的业务应用通常是微服务架构,这也意味着一个应用会部署多个进程,多个进程如果需要修改MySQL中的同一行记录,为了避免操作乱序导致脏数据,此时就需要引入分布式锁了。想要实现分
 springboot读取文件打成jar包后访问不到怎么解决
Jun 03, 2023 pm 04:38 PM
springboot读取文件打成jar包后访问不到怎么解决
Jun 03, 2023 pm 04:38 PM
springboot读取文件,打成jar包后访问不到最新开发出现一种情况,springboot打成jar包后读取不到文件,原因是打包之后,文件的虚拟路径是无效的,只能通过流去读取。文件在resources下publicvoidtest(){Listnames=newArrayList();InputStreamReaderread=null;try{ClassPathResourceresource=newClassPathResource("name.txt");Input
 SpringBoot与SpringMVC的比较及差别分析
Dec 29, 2023 am 11:02 AM
SpringBoot与SpringMVC的比较及差别分析
Dec 29, 2023 am 11:02 AM
SpringBoot和SpringMVC都是Java开发中常用的框架,但它们之间有一些明显的差异。本文将探究这两个框架的特点和用途,并对它们的差异进行比较。首先,我们来了解一下SpringBoot。SpringBoot是由Pivotal团队开发的,它旨在简化基于Spring框架的应用程序的创建和部署。它提供了一种快速、轻量级的方式来构建独立的、可执行
 如何在 Golang 中使用 gRPC 实现文件上传?
Jun 03, 2024 pm 04:54 PM
如何在 Golang 中使用 gRPC 实现文件上传?
Jun 03, 2024 pm 04:54 PM
如何使用gRPC实现文件上传?创建配套服务定义,包括请求和响应消息。在客户端,打开要上传的文件并将其分成块,然后通过gRPC流流式传输发送到服务端。在服务端,接收文件块并将其存储到文件中。服务端在文件上传完成后发送响应,指示上传是否成功。
 SpringBoot怎么自定义Redis实现缓存序列化
Jun 03, 2023 am 11:32 AM
SpringBoot怎么自定义Redis实现缓存序列化
Jun 03, 2023 am 11:32 AM
1、自定义RedisTemplate1.1、RedisAPI默认序列化机制基于API的Redis缓存实现是使用RedisTemplate模板进行数据缓存操作的,这里打开RedisTemplate类,查看该类的源码信息publicclassRedisTemplateextendsRedisAccessorimplementsRedisOperations,BeanClassLoaderAware{//声明了key、value的各种序列化方式,初始值为空@NullableprivateRedisSe
 Springboot+Mybatis-plus不使用SQL语句进行多表添加怎么实现
Jun 02, 2023 am 11:07 AM
Springboot+Mybatis-plus不使用SQL语句进行多表添加怎么实现
Jun 02, 2023 am 11:07 AM
在Springboot+Mybatis-plus不使用SQL语句进行多表添加操作我所遇到的问题准备工作在测试环境下模拟思维分解一下:创建出一个带有参数的BrandDTO对象模拟对后台传递参数我所遇到的问题我们都知道,在我们使用Mybatis-plus中进行多表操作是极其困难的,如果你不使用Mybatis-plus-join这一类的工具,你只能去配置对应的Mapper.xml文件,配置又臭又长的ResultMap,然后再去写对应的sql语句,这种方法虽然看上去很麻烦,但具有很高的灵活性,可以让我们
 springboot怎么获取application.yml里值
Jun 03, 2023 pm 06:43 PM
springboot怎么获取application.yml里值
Jun 03, 2023 pm 06:43 PM
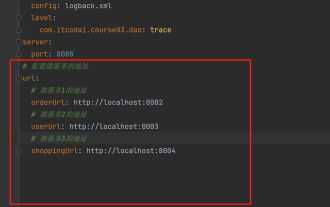
在项目中,很多时候需要用到一些配置信息,这些信息在测试环境和生产环境下可能会有不同的配置,后面根据实际业务情况有可能还需要再做修改。我们不能将这些配置在代码中写死,最好是写到配置文件中,比如可以把这些信息写到application.yml文件中。那么,怎么在代码里获取或者使用这个地址呢?有2个方法。方法一:我们可以通过@Value注解的${key}即可获取配置文件(application.yml)中和key对应的value值,这个方法适用于微服务比较少的情形方法二:在实际项目中,遇到业务繁琐,逻






